问题
设计链表的实现。您可以选择使用单链表或双链表。单链表中的节点应该具有两个属性:val和 next。val是当前节点的值,next是指向下一个节点的指针/引用。如果要使用双向链表,则还需要一个属性 prev以指示链表中的上一个节点。假设链表中的所有节点都是 0-index 的。
在链表类中实现这些功能:
- get(index):获取链表中第 index 个节点的值。如果索引无效,则返回-1
- addAtHead(val):在链表的第一个元素之前添加一个值为 val 的节点。插入后,新节点将成为链表的第一个节点
- addAtTail(val):将值为 val 的节点追加到链表的最后一个元素
- addAtIndex(index,val):在链表中的第 index 个节点之前添加值为 val 的节点。如果 index 等于链表的长度,则该节点将附加到链表的末尾。如果 index 大于链表长度,则不会插入节点。如果index小于0,则在头部插入节点
- deleteAtIndex(index):如果索引 index 有效,则删除链表中的第 index 个节点
示例:
MyLinkedList linkedList = new MyLinkedList();linkedList.addAtHead(1);linkedList.addAtTail(3);linkedList.addAtIndex(1,2); //链表变为1-> 2-> 3linkedList.get(1); //返回2linkedList.deleteAtIndex(1); //现在链表是1-> 3linkedList.get(1); //返回3
要素
链表是一个包含零个或多个元素的数据结构。每个元素都包含一个值和到另一个元素的链接。根据链接数的不同,可以分为单链表,双链表和多重链表
单链表是最简单的一种,它提供了在常数时间内的addAtHead操作和在线性时间内的addAtTail的操作。双链表是最常用的一种,因为它提供了在常数时间内的 addAtHead 和 addAtTail 操作,并且优化的插入和删除
双链表在 Java 中的实现为 LinkedList,在 Python 中为 list。这些结构都比较常用,有两个要点:
- 哨兵节点:
- 哨兵节点在树和链表中被广泛用作伪头、伪尾等,通常不保存任何数据
- 我们将使用伪头来简化我们简化插入和删除。在接下来的两种方法中应用此方法
- 双链表的双向搜索:我们可以从头部或尾部进行搜索
单链表
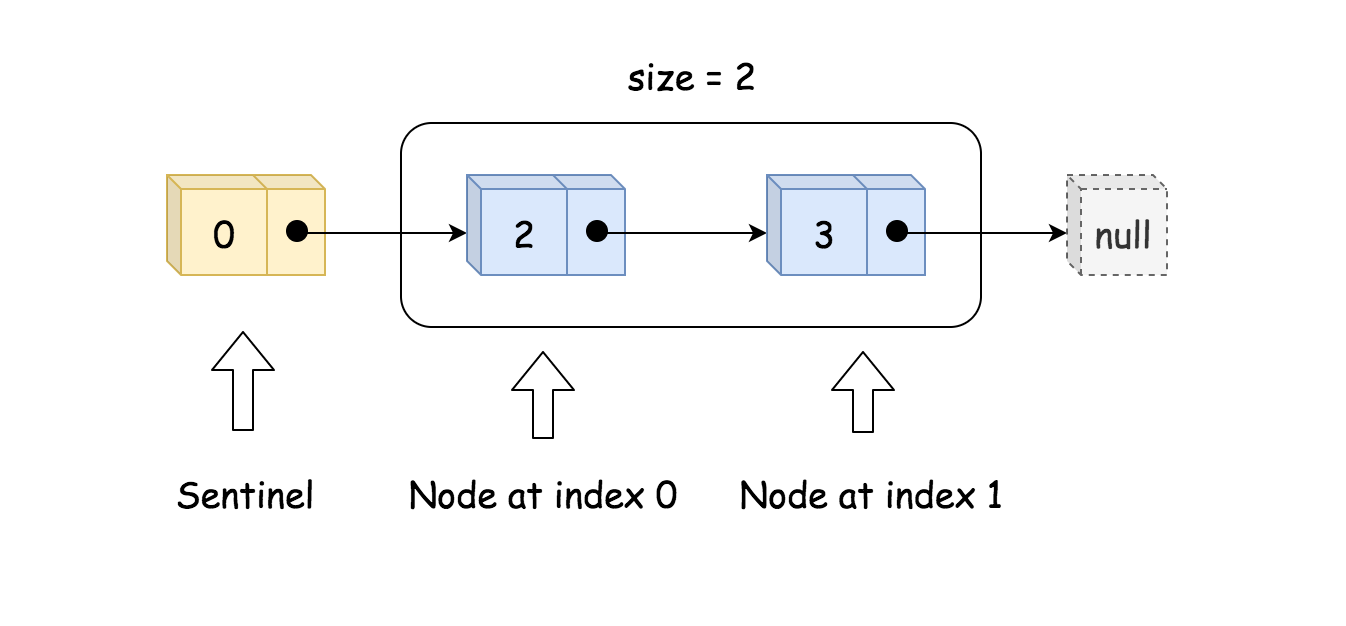
class MyLinkedList {int size;ListNode head; // sentinel node as pseudo-headpublic MyLinkedList() {size = 0;head = new ListNode(0);}}
哨兵节点被用作伪头始终存在,这样结构中永远不为空,它将至少包含一个伪头
MyLinkedList 中所有节点均包含:值 + 链接到下一个元素的指针
public class ListNode {int val;ListNode next;ListNode(int x) { val = x; }}
addAtIndex
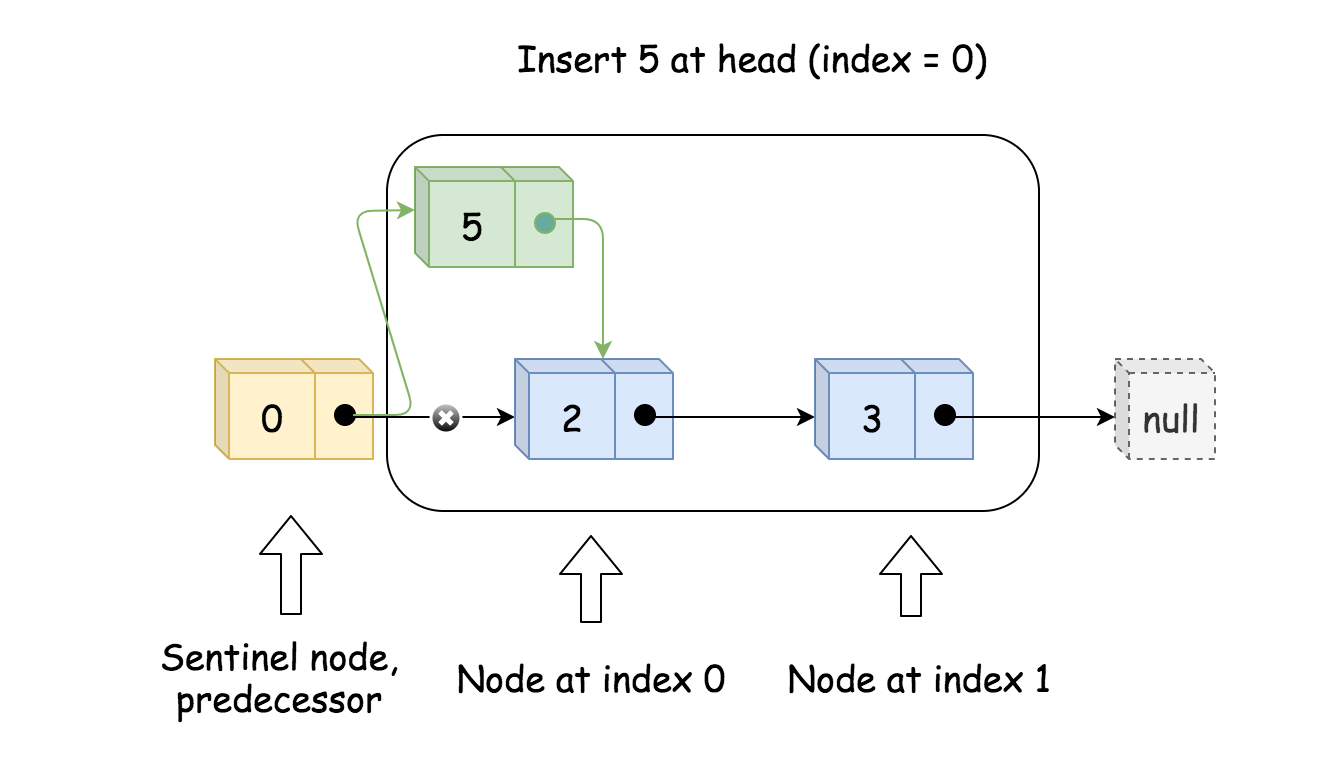
因为伪头的关系 addAtHead和 addAtTail可以使用 addAtIndex来完成
这个想法很简单:
- 找到要插入位置节点的前驱节点。如果要在头部插入,则它的前驱节点就是伪头。如果要在尾部插入节点,则前驱节点就是尾节点
通过改变 next 来插入节点
toAdd.next = pred.next; pred.next = toAdd;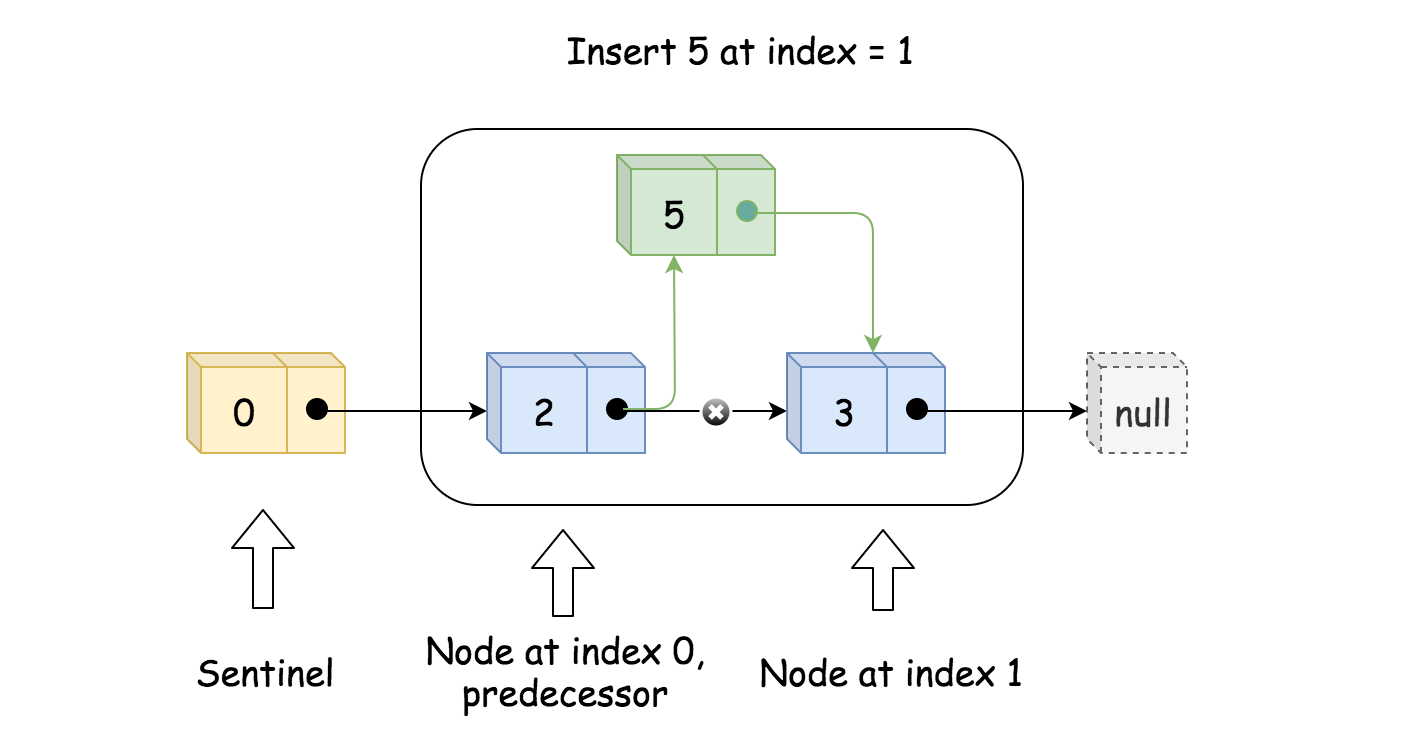
deleteAtIndex**找到要删除节点的前驱节点
- 通过改变
next来删除节点// delete pred.next pred.next = pred.next.next;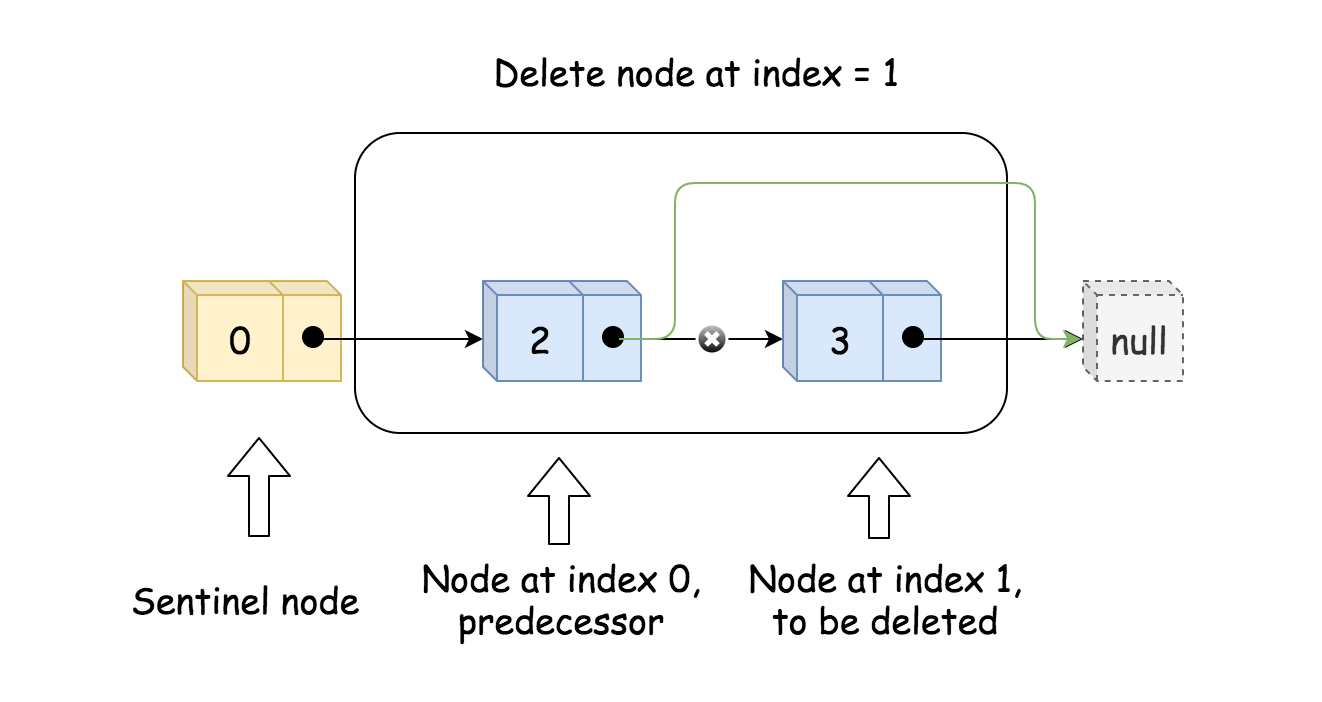
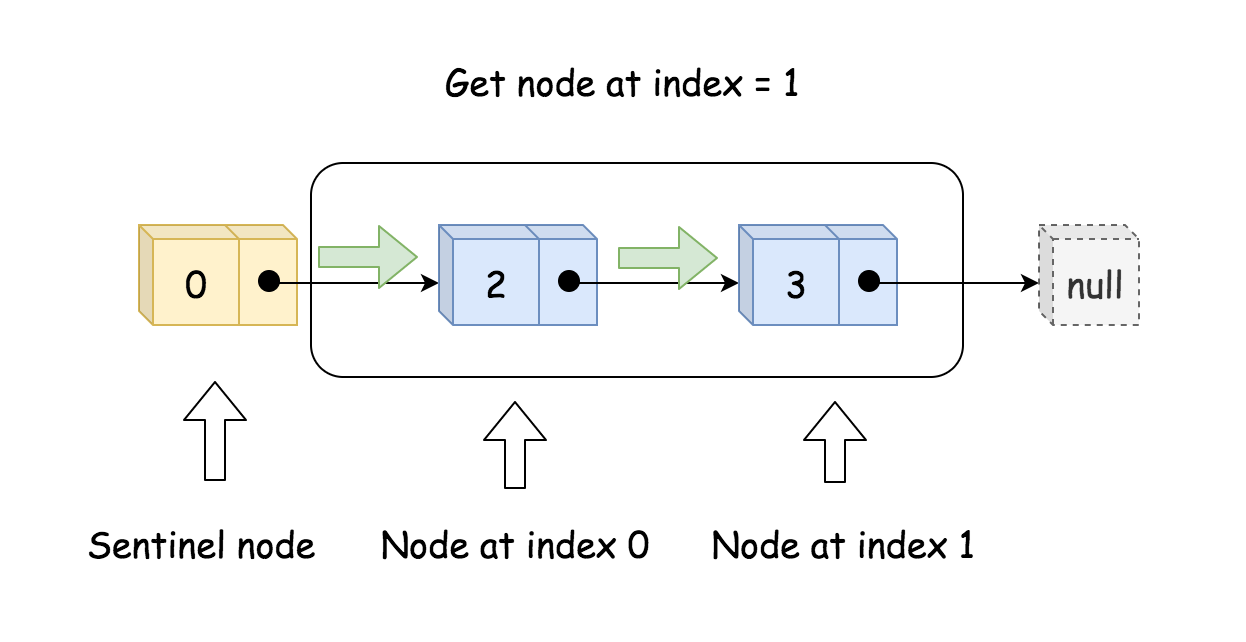
get
从伪头节点开始,向前走 index+1 步
```java public class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode(int x) { val = x; } }// index steps needed // to move from sentinel node to wanted index for(int i = 0; i < index + 1; ++i) curr = curr.next; return curr.val;
class MyLinkedList { int size; ListNode head; // sentinel node as pseudo-head public MyLinkedList() { size = 0; head = new ListNode(0); }
/* Get the value of the index-th node in the linked list. If the index is invalid, return -1. / public int get(int index) { // if index is invalid if (index < 0 || index >= size) return -1;
ListNode curr = head;
// index steps needed
// to move from sentinel node to wanted index
for(int i = 0; i < index + 1; ++i) curr = curr.next;
return curr.val;
}
/* Add a node of value val before the first element of the linked list. After the insertion, the new node will be the first node of the linked list. / public void addAtHead(int val) { addAtIndex(0, val); }
/* Append a node of value val to the last element of the linked list. / public void addAtTail(int val) { addAtIndex(size, val); }
/* Add a node of value val before the index-th node in the linked list. If index equals to the length of linked list, the node will be appended to the end of linked list. If index is greater than the length, the node will not be inserted. / public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) { // If index is greater than the length, // the node will not be inserted. if (index > size) return;
// [so weird] If index is negative,
// the node will be inserted at the head of the list.
if (index < 0) index = 0;
++size;
// find predecessor of the node to be added
ListNode pred = head;
for(int i = 0; i < index; ++i) pred = pred.next;
// node to be added
ListNode toAdd = new ListNode(val);
// insertion itself
toAdd.next = pred.next;
pred.next = toAdd;
}
/* Delete the index-th node in the linked list, if the index is valid. / public void deleteAtIndex(int index) { // if the index is invalid, do nothing if (index < 0 || index >= size) return;
size--;
// find predecessor of the node to be deleted
ListNode pred = head;
for(int i = 0; i < index; ++i){
pred = pred.next;}
// delete pred.next
pred.next = pred.next.next;
} }
时间复杂度:
- `addAtHead`: 
- `addAtInder`,`get`,`deleteAtIndex`: ,其中  指的是元素的索引
- `addAtTail`:,其中  指的是链表的元素个数
- 空间复杂度:所有的操作都是 
<a name="L8z2G"></a>
## 双链表
双链表比单链表快得多,测试用例花费的时间比单链表快了两倍。但是它更加复杂,它包含了 size,记录链表元素个数,和伪头伪尾<br />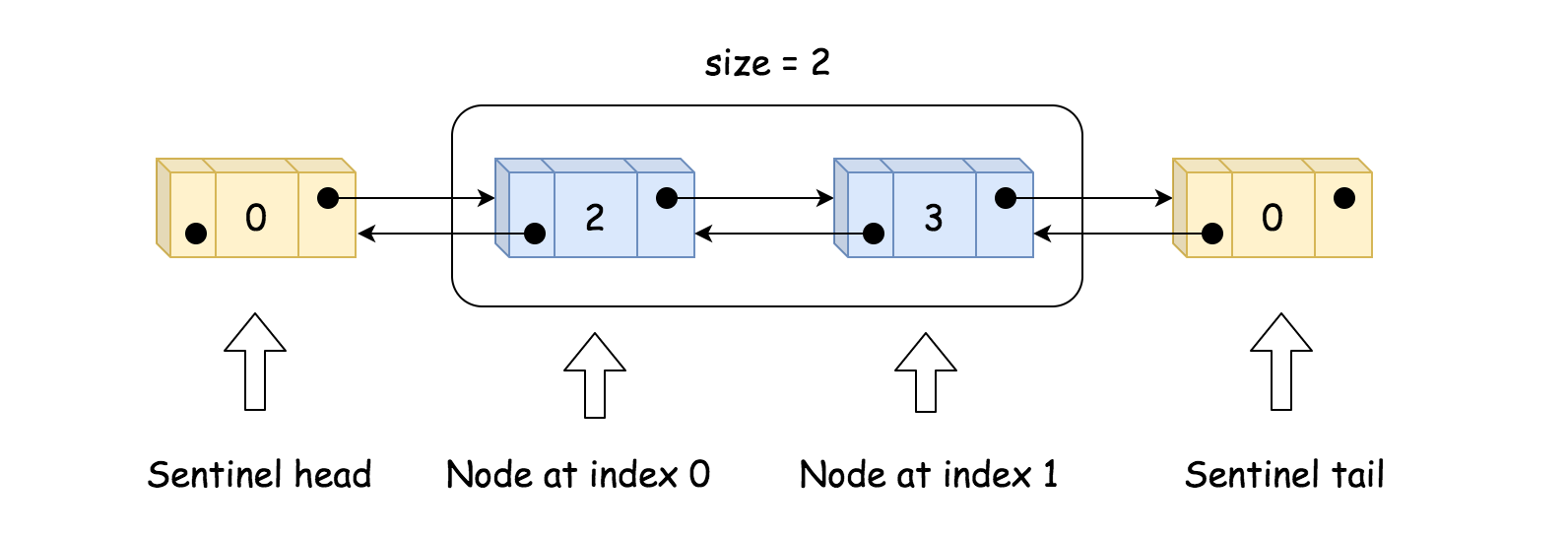
```java
class MyLinkedList {
int size;
// sentinel nodes as pseudo-head and pseudo-tail
ListNode head, tail;
public MyLinkedList() {
size = 0;
head = new ListNode(0);
tail = new ListNode(0);
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
}
伪头和伪尾总是存在,MyLinkedList 中所有节点都包含:值 + 指向前一个节点的指针 + 指向后一个节点的指针
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode prev;
ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
addAtIndex,addAtHead和 addAtTail:
- 找到要插入节点的前驱节点和后继节点。如果要在头部插入节点,则它的前驱结点是伪头。如果要在尾部插入节点,则它的后继节点是伪尾
通过改变前驱结点和后继节点的链接关系添加元素
toAdd.prev = pred toAdd.next = succ pred.next = toAdd succ.prev = toAdd deleteAtIndex:
deleteAtIndex:找到要删除节点的前驱结点和后继节点
通过改变前驱结点和后继节点的链接关系删除元素
pred.next = succ succ.prev = pred
get通过比较 index 和 size - index 的大小判断从头开始较快还是从尾巴开始较快
- 从较快的方向开始
// choose the fastest way: to move from the head // or to move from the tail ListNode curr = head; if (index + 1 < size - index) for(int i = 0; i < index + 1; ++i) curr = curr.next; else { curr = tail; for(int i = 0; i < size - index; ++i) curr = curr.prev; } ```java
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode prev;
ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
```java
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode prev;
ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
class MyLinkedList { int size; // sentinel nodes as pseudo-head and pseudo-tail ListNode head, tail; public MyLinkedList() { size = 0; head = new ListNode(0); tail = new ListNode(0); head.next = tail; tail.prev = head; }
/* Get the value of the index-th node in the linked list. If the index is invalid, return -1. / public int get(int index) { // if index is invalid if (index < 0 || index >= size) return -1;
// choose the fastest way: to move from the head
// or to move from the tail
ListNode curr = head;
if (index + 1 < size - index)
for(int i = 0; i < index + 1; ++i) curr = curr.next;
else {
curr = tail;
for(int i = 0; i < size - index; ++i) curr = curr.prev;
}
return curr.val;
}
/* Add a node of value val before the first element of the linked list. After the insertion, the new node will be the first node of the linked list. / public void addAtHead(int val) { ListNode pred = head, succ = head.next;
++size;
ListNode toAdd = new ListNode(val);
toAdd.prev = pred;
toAdd.next = succ;
pred.next = toAdd;
succ.prev = toAdd;
}
/* Append a node of value val to the last element of the linked list. / public void addAtTail(int val) { ListNode succ = tail, pred = tail.prev;
++size;
ListNode toAdd = new ListNode(val);
toAdd.prev = pred;
toAdd.next = succ;
pred.next = toAdd;
succ.prev = toAdd;
}
/* Add a node of value val before the index-th node in the linked list. If index equals to the length of linked list, the node will be appended to the end of linked list. If index is greater than the length, the node will not be inserted. / public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) { // If index is greater than the length, // the node will not be inserted. if (index > size) return;
// [so weird] If index is negative,
// the node will be inserted at the head of the list.
if (index < 0) index = 0;
// find predecessor and successor of the node to be added
ListNode pred, succ;
if (index < size - index) {
pred = head;
for(int i = 0; i < index; ++i) pred = pred.next;
succ = pred.next;
}
else {
succ = tail;
for (int i = 0; i < size - index; ++i) succ = succ.prev;
pred = succ.prev;
}
// insertion itself
++size;
ListNode toAdd = new ListNode(val);
toAdd.prev = pred;
toAdd.next = succ;
pred.next = toAdd;
succ.prev = toAdd;
}
/* Delete the index-th node in the linked list, if the index is valid. / public void deleteAtIndex(int index) { // if the index is invalid, do nothing if (index < 0 || index >= size) return;
// find predecessor and successor of the node to be deleted
ListNode pred, succ;
if (index < size - index) {
pred = head;
for(int i = 0; i < index; ++i) pred = pred.next;
succ = pred.next.next;
}
else {
succ = tail;
for (int i = 0; i < size - index - 1; ++i) succ = succ.prev;
pred = succ.prev.prev;
}
// delete pred.next
--size;
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
} } ``` 时间复杂度:
addAtHead,addAtTail:get,addAtIndex,delete:,其中 k 指的是元素的索引
空间复杂度:

