问题
给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次
说明:
所有数字(包括目标数)都是正整数
解集不能包含重复的组合
示例 1:
输入: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8
所求解集为:
[
[1, 7],
[1, 2, 5],
[2, 6],
[1, 1, 6]
]
示例 2:
输入: candidates = [2,5,2,1,2], target = 5
所求解集为:
[
[1,2,2],
[5]
]
思路
这道题目和leetcode-39:求组合总和如下区别:
- 本题
candidates中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次 - 本题数组
candidates的元素是有重复的,而之前是无重复元素的数组candidates
最后本题要求解集不能包含重复的组合
本题的难点在于:集合(数组candidates)有重复元素,但还不能有重复的组合
我们需要在搜索的过程中就去掉重复组合
所谓去重,其实就是使用过的元素不能重复选取
都知道组合问题可以抽象为树形结构,那么“使用过”在这个树形结构上是有两个维度的,一个维度是同一树枝上使用过,一个维度是同一树层上使用过。没有理解这两个层面上的“使用过” 是造成大家没有彻底理解去重的根本原因
那么问题来了,我们是要同一树层上使用过,还是同一树枝上使用过呢?
回看一下题目,元素在同一个组合内是可以重复的,怎么重复都没事,但两个组合不能相同
所以我们要去重的是同一树层上的“使用过”,同一树枝上的都是一个组合里的元素,不用去重
为了理解去重我们来举一个例子,candidates = [1, 1, 2], target = 3,(方便起见candidates已经排序了)
选择过程树形结构如图所示: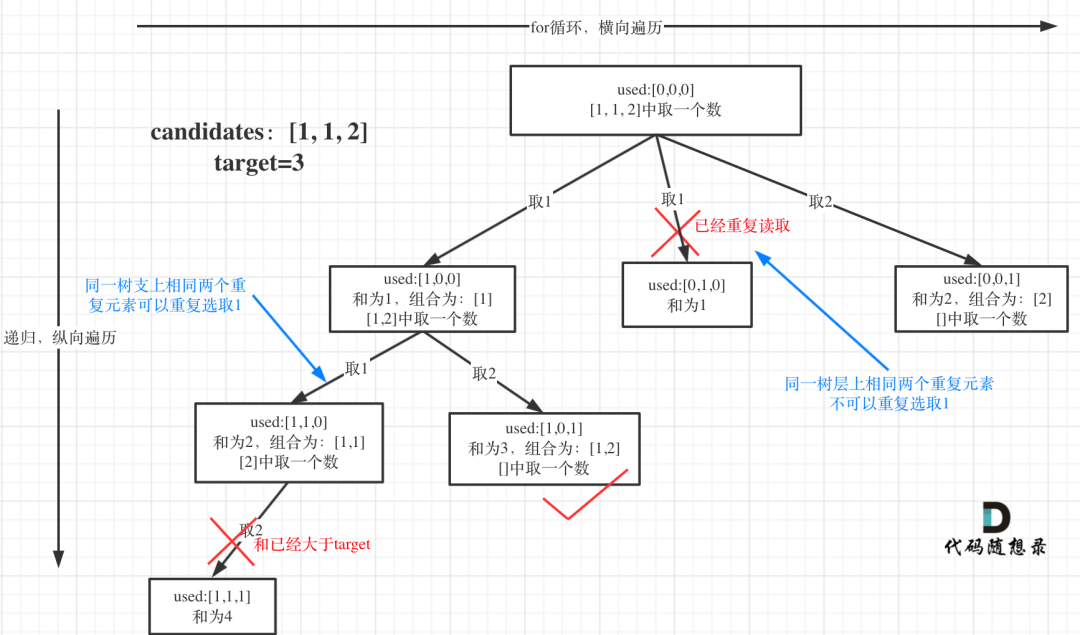
可以看到图中,每个节点相对于leetcode-39:求组合总和多加了used数组
回溯三部曲
递归函数参数
- 此题还需要加一个
bool型数组used,用来记录同一树枝上的元素是否使用过List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); // 存放组合集合List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<Integer>(); // 符合条件的组合public void backtracking(int[] candidates, int target, int sum, int startIndex, boolean[] used)
- 此题还需要加一个
递归终止条件
if (sum > target) { // 这个条件其实可以省略return;}if (sum == target) {result.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(path));return;}
单层搜索的逻辑
- 这里最需要注意的地方就是去重
- 前面我们提到:要去重的是“同一树层上的使用过”,如何判断同一树层上元素(相同的元素)是否使用过了呢
- 这里最需要注意的地方就是去重
如果**candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]** 并且 **used[i - 1] == false**,就说明:前一个树枝,使用了**candidates[i - 1]**,也就是说同一树层使用过**candidates[i - 1]**
此时for循环里就应该做continue的操作
这块比较抽象,如图: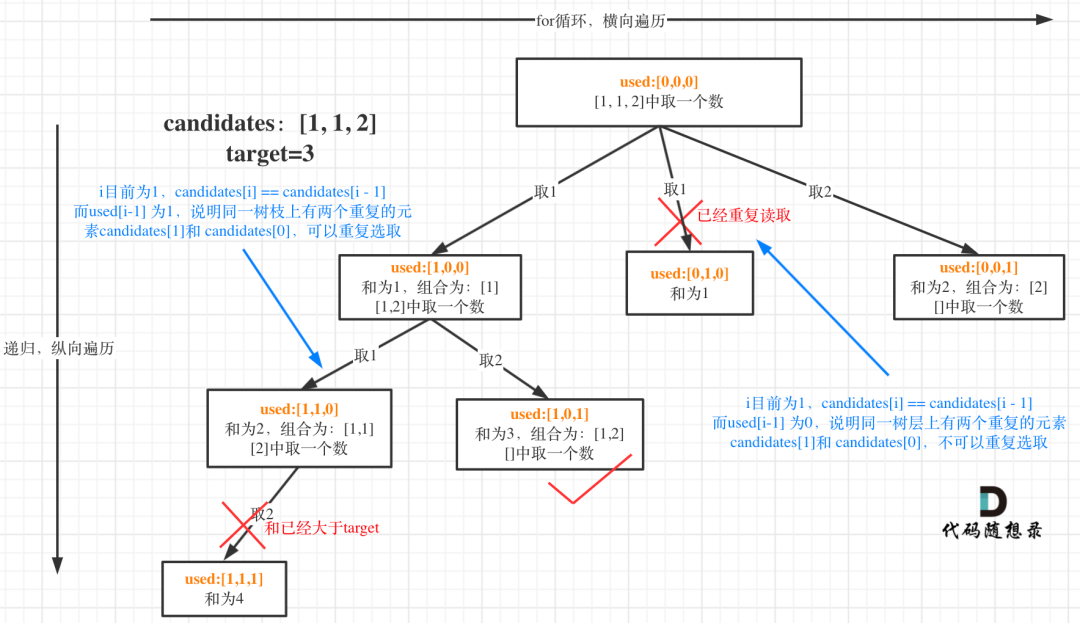
我在图中将used的变化用橘黄色标注上,可以看出在candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]相同的情况下:
used[i - 1] == true,说明同一树支candidates[i - 1]使用过used[i - 1] == false,说明同一树层candidates[i - 1]使用过for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length && sum + candidates[i] <= target; i++) {if (i > 0 && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false) {continue;}sum += candidates[i];path.add(candidates[i]);used[i] = true;backtracking(candidates, target, sum, i + 1, used);used[i] = false;sum -= candidates[i];path.remove(path.size() - 1);}
class Solution {List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); // 存放组合集合List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<Integer>(); // 符合条件的组合public void backtracking(int[] candidates, int target, int sum, int startIndex, boolean[] used){if (sum == target) {result.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(path));//Java默认传引用,将path变量中的元素放入result中,需要重新new一个return;}for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length && sum + candidates[i] <= target; i++) {if (i > 0 && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false) {continue;}sum += candidates[i];path.add(candidates[i]);used[i] = true;backtracking(candidates, target, sum, i + 1, used);used[i] = false;sum -= candidates[i];path.remove(path.size() - 1);}}public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {boolean[] used = new boolean[candidates.length];// 首先把给candidates排序,让其相同的元素都挨在一起。Arrays.sort(candidates);backtracking(candidates, target, 0, 0, used);return result;}}
官解
```java import java.util.ArrayDeque; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Deque; import java.util.List;
public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {int len = candidates.length;List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();if (len == 0) {return res;}// 关键步骤Arrays.sort(candidates);Deque<Integer> path = new ArrayDeque<>(len);dfs(candidates, len, 0, target, path, res);return res;}/*** @param candidates 候选数组* @param len 冗余变量* @param begin 从候选数组的 begin 位置开始搜索* @param target 表示剩余,这个值一开始等于 target,基于题目中说明的"所有数字(包括目标数)都是正整数"这个条件* @param path 从根结点到叶子结点的路径* @param res*/private void dfs(int[] candidates, int len, int begin, int target, Deque<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> res) {if (target == 0) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}for (int i = begin; i < len; i++) {// 大剪枝:减去 candidates[i] 小于 0,减去后面的 candidates[i + 1]、// candidates[i + 2] 肯定也小于 0,因此用 breakif (target - candidates[i] < 0) {break;}// 小剪枝:同一层相同数值的结点,从第 2 个开始,候选数更少,结果一定发生重复,// 因此跳过,用 continueif (i > begin && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]) {continue;}path.addLast(candidates[i]);// 调试语句 ①// System.out.println("递归之前 => " + path + ",剩余 = " +// (target - candidates[i]));// 因为元素不可以重复使用,这里递归传递下去的是 i + 1 而不是 idfs(candidates, len, i + 1, target - candidates[i], path, res);path.removeLast();// 调试语句 ②// System.out.println("递归之后 => " + path + ",剩余 = " +// (target - candidates[i]));}}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] candidates = new int[]{10, 1, 2, 7, 6, 1, 5};int target = 8;Solution solution = new Solution();List<List<Integer>> res = solution.combinationSum2(candidates, target);System.out.println("输出 => " + res);}
}
递归之前 => [1],剩余 = 7 递归之前 => [1, 1],剩余 = 6 递归之前 => [1, 1, 2],剩余 = 4 递归之后 => [1, 1],剩余 = 4 递归之前 => [1, 1, 5],剩余 = 1 递归之后 => [1, 1],剩余 = 1 递归之前 => [1, 1, 6],剩余 = 0 递归之后 => [1, 1],剩余 = 0 递归之后 => [1],剩余 = 6 递归之前 => [1, 2],剩余 = 5 递归之前 => [1, 2, 5],剩余 = 0 递归之后 => [1, 2],剩余 = 0 递归之后 => [1],剩余 = 5 递归之前 => [1, 5],剩余 = 2 递归之后 => [1],剩余 = 2 递归之前 => [1, 6],剩余 = 1 递归之后 => [1],剩余 = 1 递归之前 => [1, 7],剩余 = 0 递归之后 => [1],剩余 = 0 递归之后 => [],剩余 = 7 递归之前 => [2],剩余 = 6 递归之前 => [2, 5],剩余 = 1 递归之后 => [2],剩余 = 1 递归之前 => [2, 6],剩余 = 0 递归之后 => [2],剩余 = 0 递归之后 => [],剩余 = 6 递归之前 => [5],剩余 = 3 递归之后 => [],剩余 = 3 递归之前 => [6],剩余 = 2 递归之后 => [],剩余 = 2 递归之前 => [7],剩余 = 1 递归之后 => [],剩余 = 1 输出 => [[1, 1, 6], [1, 2, 5], [1, 7], [2, 6]] ```

