SpringCloud Alibaba 实战 - 前京东金融架构师 - 拉勾教育
在前面的章节,我们分别讲解了 Spring Cloud Alibaba 中主要的组成部分,其中包括:注册中心与配置管理组件 Nacos、Ribbon 客户端负载均衡、OpenFeign 与 Dubbo 通信组件、Sentinel 服务限流与熔断保护组件、Sleuth+Zipkin 与 Skywalking 实现分布式追踪、Seata 分布式事务组件以及 RocketMQ 消息异步通信中间件,这些组件各司其职为微服务架构提供了有效的支撑。
从本章开始,我们综合运用这些组件,再结合我多年来分布式开发的经验,为你分享一些成熟的组合搭配与案例,让你在分布式开发这条路上少走些弯路。
本讲咱们进入第一个话题:利用 Seata 与 Nacos 构建分布式事务架构。在第 16 讲我们介绍了 Seata 的使用原理及解决方案,但并未涉及落地的开发技巧。今天我们补上这一块内容,我将手把手带你搭建可用的 Seata 分布式事务架构。
本讲涉及的内容较多,按搭建顺序将分为以下几个阶段:
- 部署 Nacos 注册中心与配置中心;
- 部署 TC 组件 Seata-Server;
- 开发 RM 资源管理器;
- 开发 TM 事务管理器;
- 验证分布式事务。
下面我们一步步实现前面的 “商城销售积分” 应用案例。
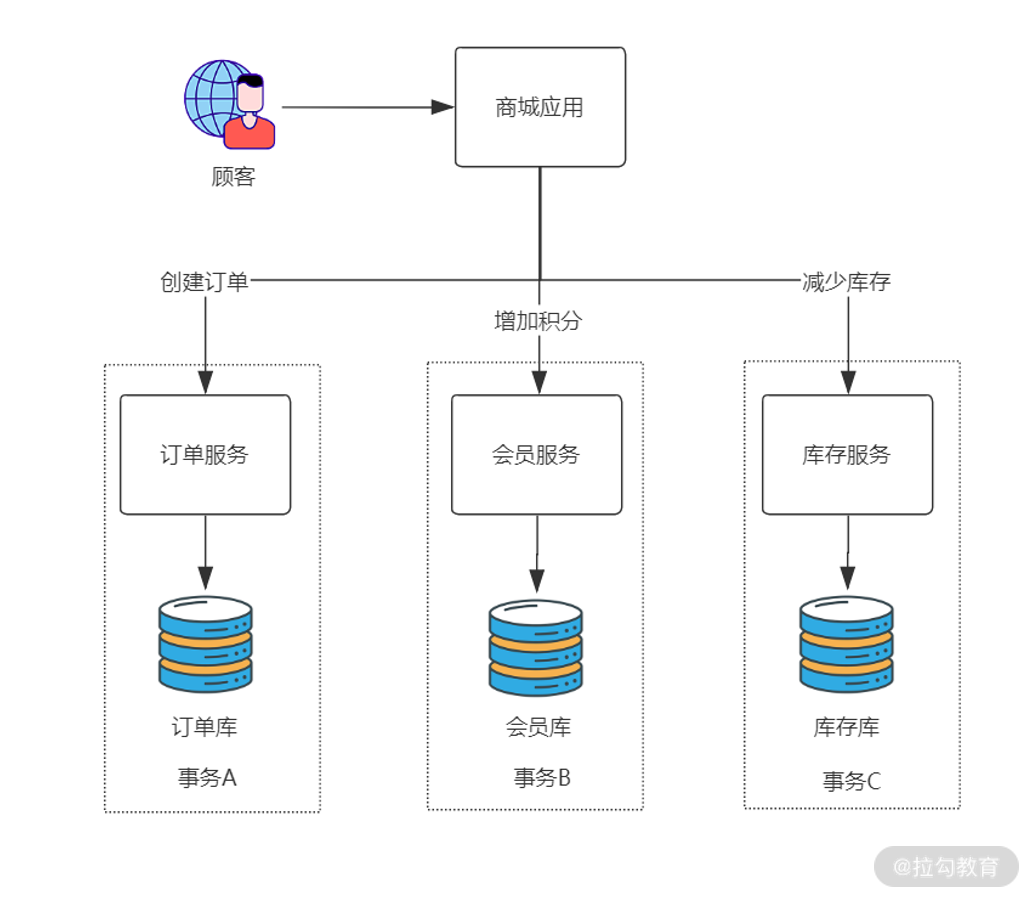
案例示意图
首先咱们来看整体架构图:
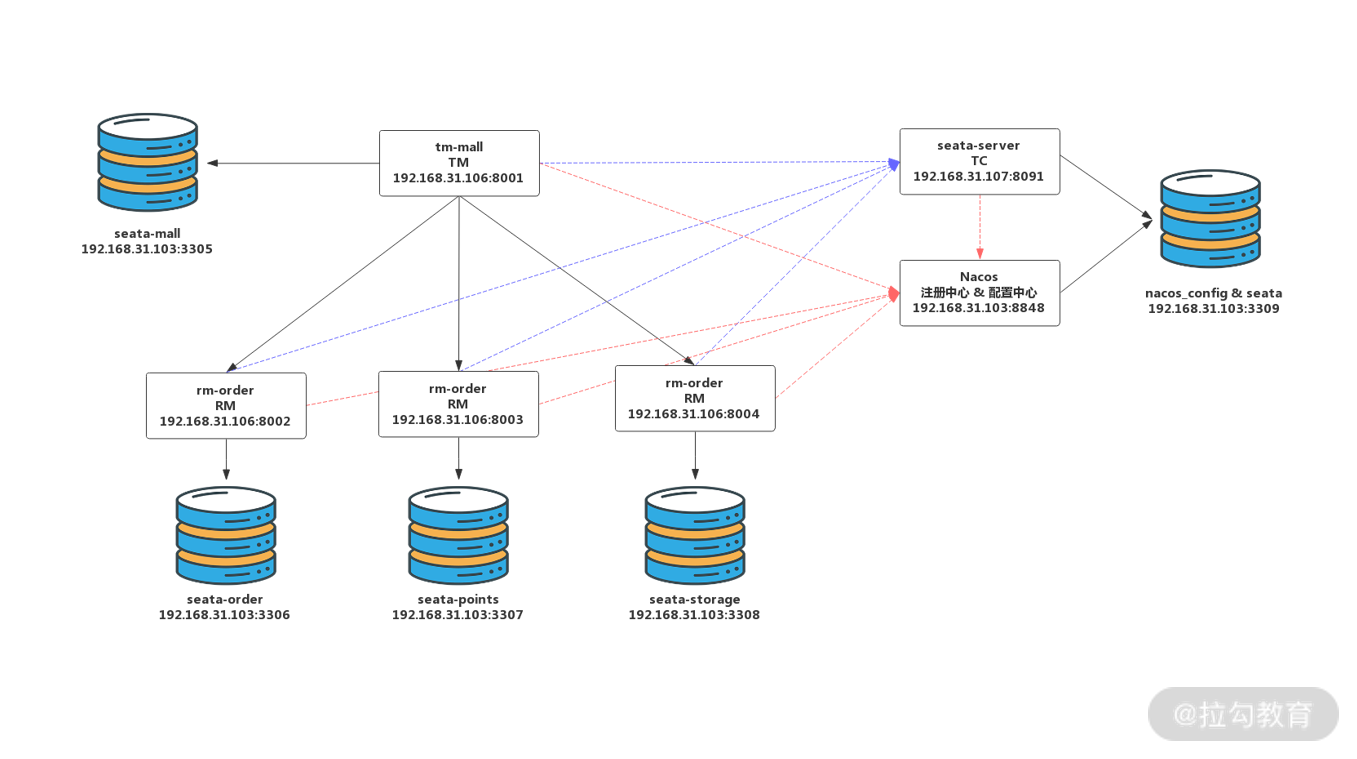
基于 Seata 的分布式事务架构
我在 192.168.31.103 虚拟机构建了 5 个 MySQL 5.7 数据库实例,通过设置不同端口来模拟 5 台数据库服务器,它们的用途是:
- 3309 端口数据库存储 Nacos 配置信息以及 Seata-Server 的分布式事务数据;
- 3305 端口数据库存储 TM 端商城数据;
- 3306 端口数据库存储 RM 端订单服务数据;
- 3307 端口数据库存储 RM 端会员积分数据;
- 3308 端口数据库存储 RM 端库存数据。
应用方面包含 6 个节点:
- 192.168.31.103:8848 节点是 Nacos 注册中心与配置中心服务器,提供微服务架构核心支撑;
- 192.168.31.107:8091 节点是 Seata-Server,也就是 TC 组件,用于协调全局事务的开启、提交与回滚;
- 192.168.31.106:8001 节点是 TM,也就是商城应用,TM 用于定义事务边界与事务的范围;
- 192.168.31.106:8002/8003/8004 则是具体的 RM 实例,分别对应订单、积分与库存服务。
其中所有 TM、RM、TC 实例在启动时都要向 Nacos 进行注册登记,以保证服务可以被发现。同时 TC(Seata-Server) 自身的配置信息也要托管在 Nacos 配置中心中,不再单独存储。所有 TM、RM 在启动时也要额外在 TC 中进行注册,以保证全局事务的完整性。
下面咱们开始第一个阶段:部署 Nacos 注册中心与配置中心。
部署 Nacos 注册中心与配置中心
部署 Nacos 注册中心与配置中心与前面课程内容并无二致,咱们快速完成即可。
第一步,下载 Nacos,上传到 192.168.31.103 节点解压缩。
tar -xvf nacos-server-1.4.0.tar.gz
第二步,配置 conf/application.properties,增加数据库配置。
### Count of DB:db.num=1### Connect URL of DB:db.url.0=jdbc:mysql://192.168.31.103:3309/nacos_config?characterEncoding=utf8&connectTimeout=1000&socketTimeout=3000&autoReconnect=true&useUnicode=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTCdb.user=rootdb.password=root
第三步,创建 3309 端口的 nacos_config 数据库,执行 conf/nacos-mysql.sql,完成 Nacos 注册中心表创建。
第四步,创建 conf/cluster.conf 集群配置文件,配置一个单节点集群。
#it is ip#example192.168.31.10:8848
第五步,运行 startup 脚本,启动 Nacos。
sh /usr/local/nacos/bin/startup.sh
至此,阶段一:Nacos 注册中心与配置中心部署完成,因为这些内容前面都讲过,所以不再赘述。
下面咱们开始阶段二:部署 TC 组件 Seata-Server。
从部署 TC 组件 Seata-Server 开始就是全新的内容,我将更细致地为你介绍每一步操作过程。
部署 TC 组件 Seata-Server
第一步,下载 Seata-Server。
在 192.168.31.107 设备上安装好 JDK 1.8,之后访问 Seata 的 GitHub,下载最新的 1.4.0 压缩包。
https://github.com/seata/seata/releases/download/v1.4.0/seata-server-1.4.0.tar.gz
解压后将 seata-server-1.4 上传到 192.168.31.107 节点的 /usr/local 目录下。
Seata-Server 目录结构
第二步,编辑 conf/registry.conf 文件,这个配置文件说明 Seata-Server 接入哪种注册中心与配置中心,官方提供的默认模板存在大量冗余配置,这里我提供接入 Nacos 最精简的配置内容以方便学习。下面是 Seata-Server 接入注册中心的配置信息。
registry {# Seata-Server支持以下几种注册中心,这里改为nacos,默认是file文件形式不介入任何注册中心。# file 、nacos 、eureka、redis、zk、consul、etcd3、sofatype = "nacos"# 负载均衡采用随机策略loadBalance = "RandomLoadBalance"loadBalanceVirtualNodes = 10# nacos注册中心接入配置nacos {# 应用名称application = "seata-server"#IP地址与端口serverAddr = "192.168.31.10:8848"# 分配应用组,采用默认值SEATA_GROUP即可group = "SEATA_GROUP"namespace = ""# 集群名称,采用默认值default即可cluster = "default"# Nacos接入用户名密码username = "nacos"password = "nacos"}}#Seata-Server接入配置中心config {# Seata-Server支持以下配置中心产品,这里设置为nacos,默认是file即文件形式保存配置内容。# file、nacos 、apollo、zk、consul、etcd3type = "nacos"# 设置Nacos的通信地址nacos {serverAddr = "192.168.31.10:8848"namespace = ""group = "SEATA_GROUP"username = "nacos"password = "nacos"}}
上面的配置文件你可以直接复制到自己工程中修改下 IP 端口即可。
第三步,在 Nacos 配置中心中初始化 Seata 配置。
Seata 官方也为我们提供了初始化配置脚本,请按我的步骤操作。
首先访问下面的地址查看 Seata 在 Nacos 中需要的设置项。
https://github.com/seata/seata/blob/1.4.0/script/config-center/config.txt
Seata-Server 配置项
将 GitHub 页面中 80 行文本内容复制后,在 /usr/local/seata-server-1.4.0 目录下创建 config.txt 文件,将 80 行文本粘贴其中。
config.txt 文件路径
在内容粘贴到 config.txt 后,有两个地方需要修改:
- 34 行 store.mode=file 改为 store.mode=db 代表采用数据库存储 Seata-Server 的全局事务数据
- 44~46 行配置 Seata-Server 的全局事务数据库,数据库 URL 指向 107 节点 3309 端口。这个全局事务数据库是 Seata 维护分布式事务的关键所在,后面咱们马上就要创建这个数据库。
store.db.url=jdbc:mysql:store.db.user=rootstore.db.password=root
config.txt 保存后,还需要访问下面地址下载 nacos-config.sh 运行脚本。
https://github.com/seata/seata/blob/1.4.0/script/config-center/nacos/nacos-config.sh
nacos-config.sh
这个脚本用来读取前面的 config.txt 并将配置项载入 Nacos 配置中心。将页面中 101 行文本复制,然后在 /usr/local/seata-server-1.4.0 目录下创建 script 子目录,在 scirpt 子目录下创建 nacos-config.sh 文件,并将 101 行文本保存其中。
nacos-config.sh 文件路径
保存后执行下面命令运行导入脚本。
sh nacos-config.sh -h 192.168.31.10
这条命令有两个参数,h 选项指向 Nacos 的 IP,执行后你会看到如下日志。
...Set metrics.registryType=compact successfullySet metrics.exporterList=prometheus successfullySet metrics.exporterPrometheusPort=9898 successfully=========================================================================Complete initialization parameters, total-count:80 , failure-count:0=========================================================================Init nacos config finished, please start seata-server.
80 个配置选项导入成功后,我们便可在 Nacos 的配置中心页面看到它们,访问 Nacos 后台http://192.168.31.10:8848/nacos
你会看到大量 SEATA_GROUP 分组的配置,这些配置信息在 Seata-Server 启动时都会自动读取。
Seata-Server 配置信息
第四步,创建并初始化 Seata-Server 全局事务数据库。
访问下面网址
https://github.com/seata/seata/blob/1.4.0/script/server/db/mysql.sql,下载 SQL 脚本。在 3309 端口 MySQL 创建新的数据库 seata,执行 SQL 脚本创建全局事务表。
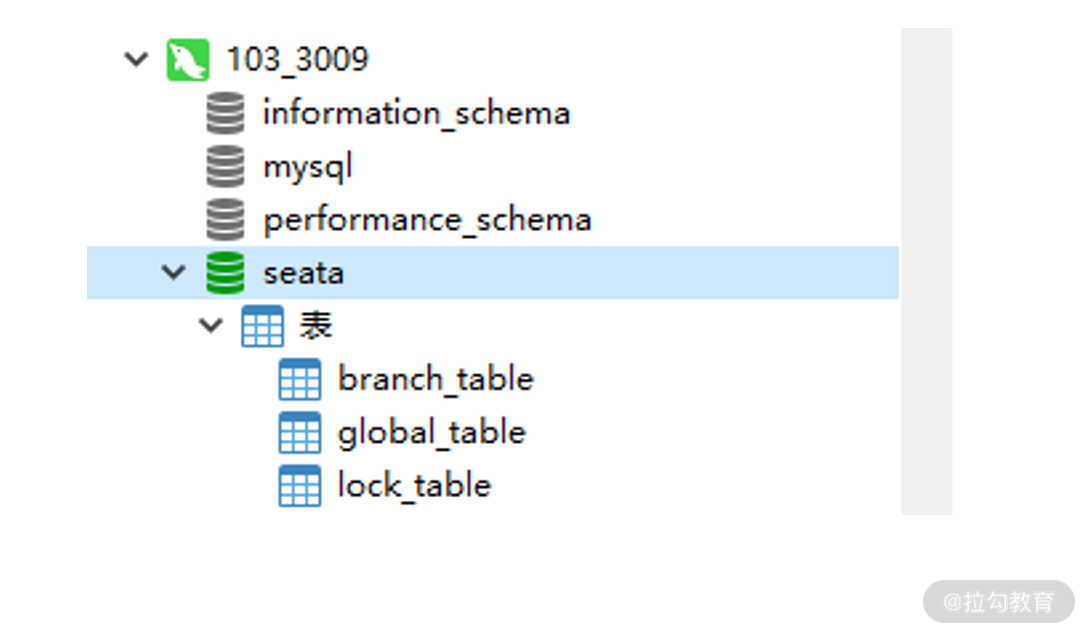
Seata 全局事务数据库
脚本执行后会创建 3 张表,我们了解下即可。
- global_table 保存全局事务数据;
- branch_table 保存分支事务数据;
- lock_table 保存锁定资源数据。
第五步,启动 seata-server。
seata-server 启动只需要执行 bin/seata-server.sh。
启动后,看到下面 Server started 代表启动成功。
10:52:38.254 INFO --- [ main] com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource : {dataSource-1} inited10:52:38.501 INFO --- [ main] i.s.core.rpc.netty.NettyServerBootstrap : Server started, listen port: 8091
这里有个细节,如果启动过程中提示数据库无法访问,说明 IP、端口配置有问题,可以通过 Nacos 配置中心设置 store.db.url 选项,而不是重新导入 config.txt。
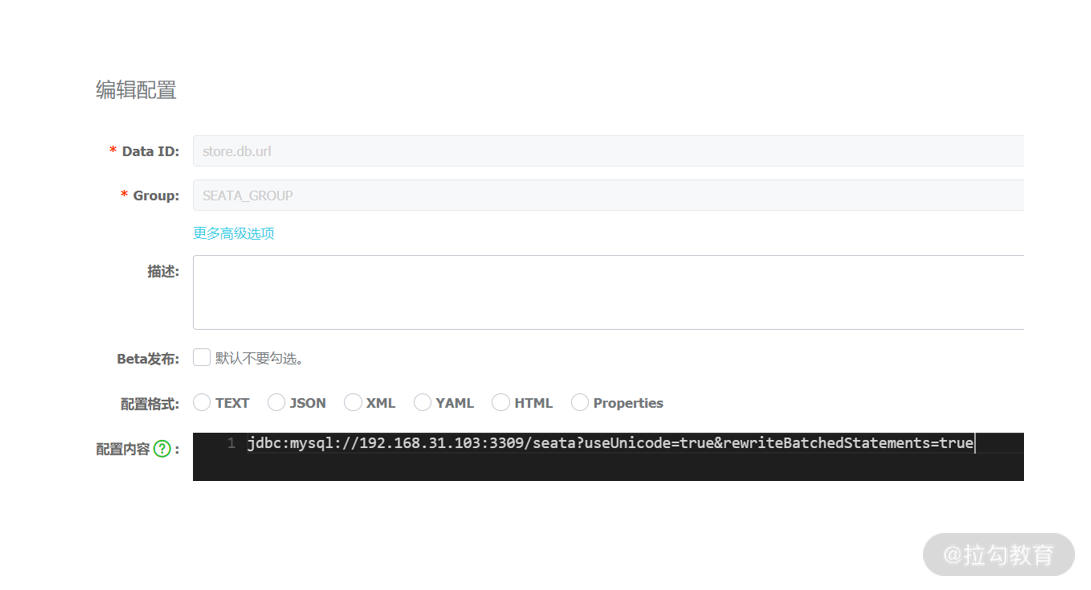
修改 Seata 连接字符串
到这里,阶段二:部署 TC 组件 Seata-Server 已经完成。后面的事情就是基于 TC 组件 Seata-Server 实现分布式事务。
开发 RM 资源管理器
在 Seata 中 RM 资源管理器代表处理具体业务的模块,例如:订单服务创建订单、会员服务增加积分、库存服务减少库存都是 RM 资源管理器,下面我们来开发订单服务、会员服务与库存服务。
订单服务 rm-order
这里开发框架采用 Spring Boot + JPA(Hibernate)+ Druid 实现。
第一步,创建 seata-order 数据库与 undo_log 表。
在 103 节点的 3306 数据库上,创建 seata-order 数据库,执行下面的 SQL 初始化数据库。
SET NAMES utf8mb4;SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `order`;CREATE TABLE `order` (`order_id` int(255) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '订单编号',`goods_id` int(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '商品编号',`member_id` int(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '会员编号',`quantity` int(255) NOT NULL COMMENT '购买数量',`points` int(255) NOT NULL COMMENT '增加会员积分',PRIMARY KEY (`order_id`) USING BTREE) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 51 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `undo_log`;CREATE TABLE `undo_log` (`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`branch_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL,`xid` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL,`context` varchar(128) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL,`rollback_info` longblob NOT NULL,`log_status` int(11) NOT NULL,`log_created` datetime(0) NOT NULL,`log_modified` datetime(0) NOT NULL,`ext` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE,UNIQUE INDEX `ux_undo_log`(`xid`, `branch_id`) USING BTREE) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 5 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
数据库包含两张表,一张是订单业务表 order,字段含义已在脚本中注释。而另一张 undo_log 回滚日志表。undo_log 是 Seata 强制要求在每个 RM 端数据库创建的表,用于存储反向 SQL 的元数据。undo_log 表的脚本可以从 Seata GitHub 官方获取,然后在自己的业务库中执行。
https://github.com/seata/seata/blob/1.4.0/script/client/at/db/mysql.sql
到这里 RM 数据库创建完毕。
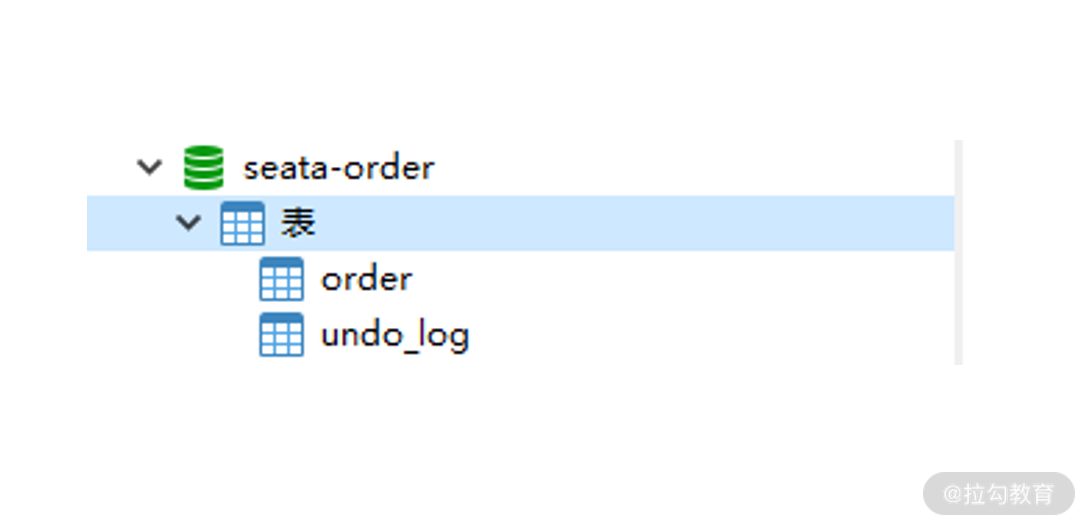
seata-order 数据库
第二步,利用 Spring Initializr 向导创建 rm-order 工程,确保 pom.xml 引入以下依赖。
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-seata</artifactId><exclusions><exclusion><groupId>io.seata</groupId><artifactId>seata-all</artifactId></exclusion><exclusion><groupId>io.seata</groupId><artifactId>seata-spring-boot-starter</artifactId></exclusion></exclusions></dependency><dependency><groupId>io.seata</groupId><artifactId>seata-all</artifactId><version>1.4.0</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>io.seata</groupId><artifactId>seata-spring-boot-starter</artifactId><version>1.4.0</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>mysql</groupId><artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId><scope>runtime</scope></dependency>
这份依赖有个注意事项,默认 starter-alibaba-seata 依赖内置的是旧版 1.3.0 的 Seata 客户端,因此要排除,在后面引入最新的 1.4.0,保证客户端与 Seate-Server 版本一致。
第三步,配置 application.yml。
application.yml 额外配置了事务分组与 Nacos 的信息,我已在配置文件中进行了注释说明。
seata:enabled: truetx-service-group: my_test_tx_groupenable-auto-data-source-proxy: trueservice:vgroup-mapping:my_test_tx_group: defaultgrouplist:default: 192.168.31.107:8091enable-degrade: falsedisable-global-transaction: falseconfig:type: nacosnacos:namespace:serverAddr: 192.168.31.10:8848group: SEATA_GROUPusername: nacospassword: nacoscluster: defaultregistry:type: nacosnacos:application: seata-serverserver-addr: 192.168.31.10:8848group : SEATA_GROUPnamespace:username: nacospassword: nacoscluster: defaultspring:application:name: rm-orderdatasource:driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driverurl: jdbc:mysql://192.168.31.103:3306/seata-orderusername: rootpassword: rootcloud:nacos:discovery:username: nacospassword: nacosserver-addr: 192.168.31.10:8848jpa:show-sql: trueserver:port: 8002logging:level:io:seata: debug
第四步,像单机应用一样开发数据库 CRUD,代码很简单,我已给出注释。
Order 实体类,让属性与字段进行映射。
@Entity@Table(name = "`order`")public class Order {@Id@Column(name = "order_id")private Integer id;private Integer memberId;@Column(name = "goods_id")private Integer goodsId;private Integer points;private Integer quantity;public Order() {}public Order(Integer id, Integer memberId, Integer goodsId, Integer points, Integer quantity) {this.id = id;this.memberId = memberId;this.points = points;this.goodsId = goodsId;this.quantity = quantity;}}
OrderRepository 接口用于声明 CRUD 操作。
public interface OrderRepository extends JpaRepository<Order,Integer> {}
OrderService 的 createOrder 方法实现创建订单的业务逻辑,注意在 createOrder 方法上必须增加 @Transactional 注解,Seata 客户端对这个注解进行扩展支持了分布式事务。
@Servicepublic class OrderService {@Resourceprivate OrderRepository orderRepository;@Transactionalpublic Order createOrder(Integer orderId,Integer memberId,Integer goodsId,Integer points,Integer quantity){return orderRepository.save(new Order(orderId, memberId,goodsId,points,quantity));}}
OrderController 的 createOrder 方法用于对外暴露 RESTful API,等待被 TM 调用。
@RestControllerpublic class OrderController {@Resourceprivate OrderService orderService;@GetMapping("/create_order")public String createOrder(Integer orderId,Integer memberId,Integer goodsId,Integer points,Integer quantity) throws JsonProcessingException {Map result = new HashMap<>();Order order = orderService.createOrder(orderId,memberId,goodsId,points,quantity);result.put("code", "0");result.put("message", "create order success");return new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(result);}}
第五步,最重要的一步,要让 Seata 客户端在处理事务时自动生成反向 SQL,必须额外配置 DataSourceProxy 数据源代理类,DataSourceProxy 是 Seata 提供的 DataSource 代理类,在分布式事务执行过程中,用于自动生成 undo_log 回滚数据,以及自动完成 RM 端分布式事务的提交或回滚操作。
在 Spring Boot 中利用 Java Config 方式对 DataSourceProxy 进行配置。
package com.lagou.rmorder.datasource;import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;import io.seata.rm.datasource.DataSourceProxy;import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;@Configurationpublic class DataSourceProxyConfig {@Bean@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")public DruidDataSource druidDataSource() {return new DruidDataSource();}@Primary@Beanpublic DataSourceProxy dataSource(DruidDataSource druidDataSource) {return new DataSourceProxy(druidDataSource);}}
最后,启动 rm-order,在浏览器地址栏访问 create_order 接口,看到 create order success,在数据库中也出现对应记录。
http://192.168.31.106:8002/create_order?orderId=6&memberId=1&goodsId=2&points=20&quantity=200
{code: "0",message: "create order success"}
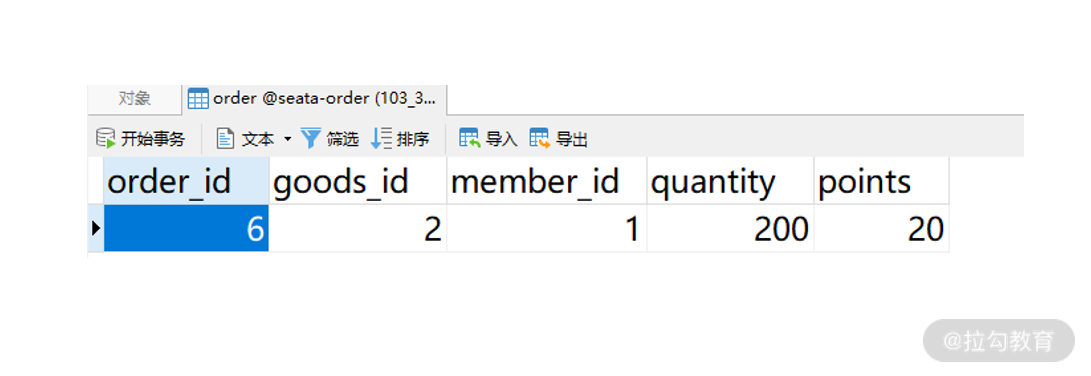
订单数据
以上是 rm-order 订单服务的开发过程,除了配置 Seata 选项与创建 DataSourceProxy 外,其他的开发要素与单机应用几乎是一样的,这使得新人也可以很快上手。
下面咱们如法炮制开发 rm-points 积分服务与 rm-storage 库存服务。
积分服务 rm-points
因为积分服务的开发过程与订单服务几乎是一致的,我们只需给出关键代码。
第一步,在 3307 端口数据库创建 seata-points 数据库,包含 points 会员积分表与 undo_log 表。
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `points`;CREATE TABLE `points` (`member_id` int(255) NOT NULL COMMENT '会员编号',`points` int(255) NOT NULL COMMENT '积分数量',PRIMARY KEY (`member_id`) USING BTREE) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;INSERT INTO `points` VALUES (1, 100);INSERT INTO `points` VALUES (2, 100);INSERT INTO `points` VALUES (3, 100);INSERT INTO `points` VALUES (4, 100);DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `undo_log`;CREATE TABLE `undo_log` (`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`branch_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL,`xid` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL,`context` varchar(128) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL,`rollback_info` longblob NOT NULL,`log_status` int(11) NOT NULL,`log_created` datetime(0) NOT NULL,`log_modified` datetime(0) NOT NULL,`ext` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE,UNIQUE INDEX `ux_undo_log`(`xid`, `branch_id`) USING BTREE) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 5 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
第二步,创建 rm-points 积分服务,pom.xml 与 rm-order 依赖完全相同。
第三步,配置 application.yml,只有应用名、端口与数据库 URL 不同,其他与 rm-order 完全相同,这里就不再赘述。
seata:...spring:application:name: rm-pointsdatasource:driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driverurl: jdbc:mysql://192.168.31.103:3307/seata-pointsusername: rootpassword: root...server:port: 8003...
第四步:实现新增积分代码,基础的实体类与 Repository 不做赘述,我们关注 PointsService 与 PointsController。
PointsService.addPoints 方法实现会员积分增加业务,同样需要 @Transactional 注解。
@Servicepublic class PointsService {@Resourceprivate PointsRepository orderRepository;@Transactionalpublic Points addPoints(Integer memberId,Integer points){Points entity = orderRepository.findById(memberId).get();entity.setPoints( entity.getPoints() + points);return orderRepository.save(new Points(memberId,entity.getPoints()));}}
PointsController 对外暴露 add_points 接口调用 service 类实现业务。
@RestControllerpublic class PointsController {@Resourceprivate PointsService pointsService;@GetMapping("/add_points")public String addPoints(Integer memberId,Integer points) throws JsonProcessingException {Map result = new HashMap<>();Points entity = pointsService.addPoints(memberId, points);result.put("code", "0");result.put("message", "add points success");return new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(result);}}
第五步,最后不要忘记设置 DataSourceProxyConfig,代码与 rm-order 完全相同。
代码书写完毕,启动应用访问地址http://192.168.31.106:8003/add_points?memberId=1&points=20
可以得到 “add points success” 结果。
{code: "0",message: "add points success"}
库存服务 rm-storage
RM 库存服务也是遵循相同套路开发。
第一步,创建数据库 seata-storage,执行建表脚本,包含库存表 storage 与回滚表 undo_log。
SET NAMES utf8mb4;SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `storage`;CREATE TABLE `storage` (`goods_id` int(255) NOT NULL,`quantity` int(255) NOT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`goods_id`) USING BTREE) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;INSERT INTO `storage` VALUES (1, 100);INSERT INTO `storage` VALUES (2, 98);INSERT INTO `storage` VALUES (3, 100);INSERT INTO `storage` VALUES (4, 100);DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `undo_log`;CREATE TABLE `undo_log` (`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`branch_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL,`xid` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL,`context` varchar(128) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL,`rollback_info` longblob NOT NULL,`log_status` int(11) NOT NULL,`log_created` datetime(0) NOT NULL,`log_modified` datetime(0) NOT NULL,`ext` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE,UNIQUE INDEX `ux_undo_log`(`xid`, `branch_id`) USING BTREE) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 2 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
第二步,创建 rm-storage 库存服务,pom.xml 与 rm-order 依赖完全相同。
第三步,配置 application.yml,只有应用名、端口与数据库 URL 不同,其他与 rm-order 完全相同。
seata:...spring:application:name: rm-storagedatasource:driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driverurl: jdbc:mysql://192.168.31.103:3308/seata-storageusername: rootpassword: root...server:port: 8004...
第四步,创建 StorageService 与 StorageController,实现减少库存业务。
StorageService.reduceStorage 方法实现商品库存减少,如果库存不足则抛出 IllegalStateException 异常。
@Servicepublic class StorageService {@Resourceprivate StorageRepository storageRepository;@Transactionalpublic Storage reduceStorage(Integer goodsId, Integer quantity){Storage storage = storageRepository.findById(goodsId).get();if(storage.getQuantity() < quantity){throw new IllegalStateException(goodsId + "商品库存不足");}storage.setQuantity(storage.getQuantity() - quantity);return storageRepository.save(storage);}}
StorageController 对外暴露 reduce_storage 接口,实现减少库存业务。
@RestControllerpublic class StorageController {@Resourceprivate StorageService storageService;@GetMapping("/reduce_storage")public String reduceStorage(Integer goodsId,Integer quantity) throws JsonProcessingException {Map result = new HashMap<>();Storage storage = storageService.reduceStorage(goodsId, quantity);result.put("code", "0");result.put("message", "reduce storage success");return new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(result);}}
第五步,DataSourceProxyConfig 代码与 rm-order 完全相同不再赘述。
启动应用,访问地址
http://localhost:8004/reduce_storage?goodsId=2&quantity=10
得到结果 ”reduce storage success”。
{code: "0",message: "reduce storage success"}
到这里我们将订单、积分、库存三个 RM 示例都已开发完毕,这些服务都是独立运行,并没有形成整体,最后咱们还要开发商城应用 tm-mall,tm-mall 作为 TM 将服务串行调用,并形成分布式事务整体。
开发 TM 事务管理器
商城应用 tm-mall
第一步,3305 端口创建 seata-mall 数据库,因为真实的商城应用本身也需要往本地库写入数据,TM 本身也是一个 RM,因此在商城库中也要创建 undo_log 表。
tm-mall 数据库
第二步,创建 tm-mall 应用,框架同样采用 SpringBoot + JPA + druid,除了依赖 Seata 外,还需要额外引入 OpenFeign 实现微服务的远程调用。
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-seata</artifactId><exclusions><exclusion><groupId>io.seata</groupId><artifactId>seata-all</artifactId></exclusion><exclusion><groupId>io.seata</groupId><artifactId>seata-spring-boot-starter</artifactId></exclusion></exclusions></dependency><dependency><groupId>io.seata</groupId><artifactId>seata-all</artifactId><version>1.4.0</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>io.seata</groupId><artifactId>seata-spring-boot-starter</artifactId><version>1.4.0</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>mysql</groupId><artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId><scope>runtime</scope></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId><version>${spring-cloud-alibaba.version}</version></dependency>
第三步,配置 application.yml,只有应用名、端口与数据库 URL 不同,其他与 rm-order 完全相同。
seata:...spring:application:name: tm-malldatasource:driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driverurl: jdbc:mysql://192.168.31.103:3305/seata-mallusername: rootpassword: root...server:port: 8001...
第四步,在应用入口增加 @EnableFeignClients 注解,开启 OpenFeign 远程调用功能。
@SpringBootApplication@EnableFeignClientspublic class TmMallApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(TmMallApplication.class, args);}}
第五步,开发三个 RM 的 OpenFeign 客户端。
OrderFeignClient 是 rm-order 服务的 OpenFeign 客户端。
@FeignClient("rm-order")public interface OrderFeignClient {@GetMapping("/create_order")public String createOrder(@RequestParam("orderId") Integer orderId,@RequestParam("memberId") Integer memberId,@RequestParam("goodsId") Integer goodsId,@RequestParam("points") Integer points,@RequestParam("quantity") Integer quantity);}
PointsFeignClient 是 rm-points 服务的 OpenFeign 客户端。
@FeignClient("rm-points")public interface PointsFeignClient {@GetMapping("/add_points")public String addPoints(@RequestParam("memberId") Integer memberId, @RequestParam("points") Integer points);}
StorageFeignClient 是 rm-storage 服务的 OpenFeign 客户端。
@FeignClient("rm-storage")public interface StorageFeignClient {@GetMapping("/reduce_storage")public String reduceStorage(@RequestParam("goodsId") Integer goodsId, @RequestParam("quantity") Integer quantity);}
第六步,开发 MallService,定义全局事务范围。这里最重要的是 @GlobalTransactional 注解,该注解是全局事务注解,当进入 MallService.sale 方法时通知 TC 开启全局事务,sale 方法执行成功自动通知 TC 进行全局提交;sale 方法抛出异常时自动通知 TC 进行全局回滚。
@Servicepublic class MallService {@ResourceOrderFeignClient orderFeignClient;@ResourcePointsFeignClient pointsFeignClient;@ResourceStorageFeignClient storageFeignClient;@GlobalTransactional(name = "seata-group-tx-mall", rollbackFor = {Exception.class})public String sale(Integer orderId,Integer memberId,Integer goodsId,Integer points,Integer quantity) {String orderResult = orderFeignClient.createOrder(orderId,memberId,goodsId,points,quantity);String pointsResult = pointsFeignClient.addPoints(memberId, points);String storageResult = storageFeignClient.reduceStorage(goodsId, quantity);return orderResult + " / " + pointsResult + " / " + storageResult;}}
第七步,开发 MallController 对外暴露 sale 接口提供调用。
@RestControllerpublic class MallController {@Resourceprivate MallService mallService;@GetMapping("/sale")public String sale(Integer orderId,Integer memberId,Integer goodsId,Integer points,Integer quantity){return mallService.sale(orderId,memberId,goodsId,points,quantity);}}
第八步,最后不要忘记配置 DataSourceProxyConfig,这是所有 TM 与 RM 都要设置的。
@Configurationpublic class DataSourceProxyConfig {@Bean@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")public DruidDataSource druidDataSource() {return new DruidDataSource();}@Primary@Beanpublic DataSourceProxy dataSource(DruidDataSource druidDataSource) {return new DataSourceProxy(druidDataSource);}}
到这里所有 TM 与 RM 都已开发完毕,下面咱们来验证分布式事务的执行效果。
验证分布式事务
将 Nacos、TC、TM、3 个 RM 都启动,之后访问 tm-mall 的 sale 接口。
http://localhost:8001/sale?orderId=6&memberId=1&goodsId=2&points=20&quantity=20
{"code":"0","message":"create order success"}/ {"code":"0","message":"add points success"}/ {"code":"0","message":"reduce storage success"}
从结果中可以看到三个服务调用都已成功,我们从控制台看一下具体过程。
从日志中可以发现 TM 端负责开启全局事务,执行成功后通知 TC 全局事务提交。
## TM端日志# 启动全局事务i.seata.tm.api.DefaultGlobalTransaction : Begin new global transaction [192.168.31.107:8091:100622589646344192]...# 全局事务已提交i.seata.tm.api.DefaultGlobalTransaction : [192.168.31.107:8091:100622589646344192] commit status: Committed
而 RM 端则负责两件事,成功提交本地的分支事务与删除 undo_log 回滚日志。
## RM日志# 分支事务已提交i.s.c.r.p.c.RmBranchCommitProcessor : branch commit result:xid=192.168.31.107:8091:100622589646344192,branchId=100622590170632192,branchStatus=PhaseTwo_Committed,result code =Success,getMsg =null# 清空undo_log表i.s.r.d.undo.mysql.MySQLUndoLogManager : batch delete undo log size 1
分析了提交过程,下面咱们再进行异常验证,将 quantity 设置为 200,这必将超出库存报错,看能否全局回滚。
http://localhost:8001/sale?orderId=6&memberId=1&goodsId=2&points=20&quantity=200
运行后程序报异常。
java.lang.IllegalStateException: 商品库存不足。
观察发现 TM 向 TC 发起全局回滚通知。
i.seata.tm.api.DefaultGlobalTransaction : Begin new global transaction [192.168.31.107:8091:100626590567763968]i.s.c.rpc.netty.AbstractNettyRemoting : io.seata.core.rpc.netty.TmNettyRemotingClient@2e81af7d msgId:1726, body:globalStatus=Rollbacked,ResultCode=Success,Msg=null
TC 向 RM 下达分支事务回滚通知,RM 收到通知做两件事:第一,根据 undo_log 表生成的反向 SQL,将之前写入的数据撤销;第二,删除 undo_log 数据。这两步操作保证了 RM 端数据能撤销回之前的状态。
i.s.r.d.undo.AbstractUndoLogManager : Flushing UNDO LOG: {"@class":"io.seata.rm.datasource.undo.BranchUndoLog","xid":"192.168.31.107:8091:100626590567763968","branchId":100626590894919681...io.seata.rm.AbstractRMHandler : Branch Rollbacking: 192.168.31.107:8091:100626590567763968 100626590894919681 jdbc:mysql:i.s.r.d.undo.AbstractUndoLogManager : xid 192.168.31.107:8091:100626590567763968 branch 100626590894919681, undo_log deleted with GlobalFinished
到这里搭建 Seata 分布式事务架构的内容全部完成,最后咱们来做一下总结。
小结与预告
本讲是一套 Spring Cloud Alibaba 微服务架构的综合运用,我们从零开始一步步搭建了一套分布式事务的基础架构,也开发了实际的案例,通过程序运行结果让我们也理解了 Seata 的执行过程。这套框架的难点在于如何将 Seata-Server 与 Nacos 配置中心整合起来,因 Seata-Server 迭代很快,文档严重滞后,在搭建过程中又遇到了很多 BUG,没办法只能通过分析源码一点点排查,在这个过程中自己也对 Seata 有了更深刻的理解,希望你也能按我的操作过程完成分布式事务架构的搭建。
在这我给你留一道动手题:当前架构 Nacos 与 Seata-Server 都是单点的,不具备高可用特性,请你搭建对应的高可用集群。
下一讲,咱们将学习在微服务架构下如何设计多级缓存来提高应用性能。

