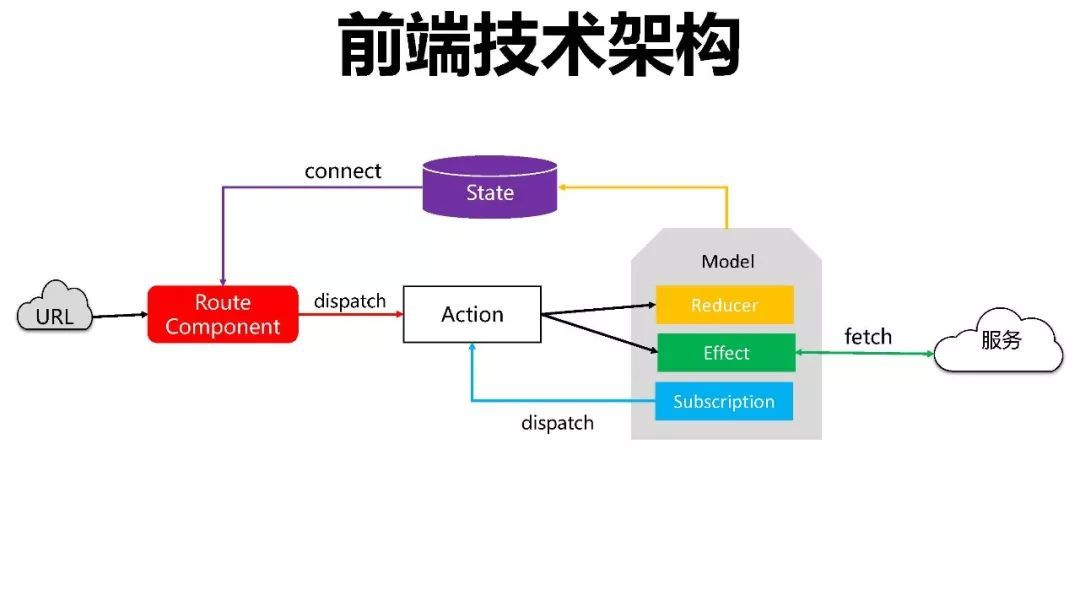
当有一个请求过来后,会通过Component或Route来展示界面。同时也会接收用户的点击事件,每一个点击事件都会由dispath来触发一个Action,这之后会产生两种结果。
一种是直接通过reducers函数改变状态state,使与前台关联的model发生变化,由此来改变前台页面。另一种是调用后台的服务,通过fetch进行后端服务的访问,后台服务返回的数据会由effects函数处理,处理后会交给reducers函数去改变状态state,进而触发前端的组件刷新和渲染。
最后还有一个subscriptions函数是进行前端拦截的,当拦截到一个URL请求之后仍然是触发一个Action,然后又会导致上面的两种变更
router
- 约定式路由, 会自动识别 pages 下的文件是否为路由文件
- dva 插件会自动识别 models 下的文件是否为 dva model
models
- call() 请求
- put 发送到 reducers里面的 type
models 接管 state的数据操作
export default {namespace: 'card',state: {list: []},// 同步的方法reducers: {getList(state, action) {return {...state,list: action.payload}}},// 异步的方法*effects: {*asyncList(action, effect) {const {payload} = actionconst { put, call } = effectconst res = yield call(API.list, payload)const action = {type: 'getList',payload: res.data}yield put(action)},*getListAsync({payload}, {call, put}) {const res = yield call('/api/list', payload)yield put({type: 'getList',payload: res.data})}}}
事件触发 dispatch(action)
onChange = () => {const action = {type: 'card/asyncList',payload: 100}this.props.dispatch(action)}

