路径总和问题(包含递归什么时候不需要返回参数的说明)
路径总和
题目描述
力扣链接🔗

代码分析
可以使用深度优先遍历的方式(本题前中后序都可以,无所谓,因为中节点也没有处理逻辑)来遍历二叉树。
- 确定递归函数的参数和返回类型
参数:需要二叉树的根节点,还需要一个计数器,这个计数器用来计算二叉树的一条边之和是否正好是目标和,计数器为int型。再来看返回值,递归函数什么时候需要返回值?什么时候不需要返回值?这里总结如下三点:- 如果需要搜索整棵二叉树且不用处理递归返回值,递归函数就不要返回值。(这种情况下一题)
- 如果需要搜索整棵二叉树且需要处理递归返回值,递归函数就需要返回值。 (这种情况在二叉树的最近公共祖先中)
- 如果要搜索其中一条符合条件的路径,那么递归一定需要返回值,因为遇到符合条件的路径了就要及时返回。(本题的情况)其实还有一种就是后序遍历需要根据左右递归的返回值推出中间节点的状态,这种需要有返回值,例如完全二叉树的节点个数(opens new window),110.平衡二叉树
 图中可以看出,遍历的路线,并不要遍历整棵树,所以递归函数需要返回值,可以用bool类型表示。
图中可以看出,遍历的路线,并不要遍历整棵树,所以递归函数需要返回值,可以用bool类型表示。
- 确定终止条件
使用计数器,可以每次相加再来判断总和是否等于条件,但此方法有点麻烦,而可以使用计数器,每次减其值,在最后叶子节点判断是否为0即可。 - 确定单层递归的逻辑
因为终止条件是判断叶子节点,所以递归的过程中就不要让空节点进入递归了。递归函数是有返回值的,如果递归函数返回true,说明找到了合适的路径,应该立刻返回。
class Solution {public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if (root == null) {return false;}// 赋值给计数器int count = targetSum - root.val;return traversal(root, count);}public boolean traversal(TreeNode root, int count) {if (root.left == null && root.right == null && count == 0) return true; // 当为叶子节点,且计数器为0,那么存在此路径if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return false; // 当为叶子节点,计数器不为0,不存在if (root.left != null) {count -= root.left.val; // 减去节点值,递归,处理节点if(traversal(root.left, count)) return true; // 递归函数是有返回值的,如果递归函数返回true,说明找到了合适的路径,应该立刻返回。count += root.left.val; // 回溯}if (root.right != null) {count -= root.right.val; // 减去节点值,递归,处理节点if(traversal(root.right, count)) return true; // 递归函数是有返回值的,如果递归函数返回true,说明找到了合适的路径,应该立刻返回。count += root.right.val; // 回溯}return false;}}
路径总和ii
题目描述
力扣链接🔗

代码分析
由于要遍历整个树,找到所有路径,所以递归函数不要返回值!

class Solution {List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if (root == null) {return res;}traversal(root, path, targetSum - root.val);return res;}public void traversal(TreeNode root, List<Integer> path, int count) {path.add(root.val); // 将值加入路径if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { // 路径和满足,加入结果if (count == 0) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); // 注意赋值}return;}if (root.left != null) {count -= root.left.val;traversal(root.left, path, count);count += root.left.val; // 回溯path.remove(path.size() - 1);}if (root.right != null) {count -= root.right.val;traversal(root.right, path, count);count += root.right.val; // 回溯path.remove(path.size() - 1);}return;}}
搜索一条边和一棵树的写法
搜索一条边的写法:
if (递归函数(root->left)) return ;if (递归函数(root->right)) return ;
例如🔗
搜索整个树写法:
left = 递归函数(root->left);right = 递归函数(root->right);left与right的逻辑处理;
注意如果需要left和right做逻辑处理,那就需要搜索整棵树
例如🔗
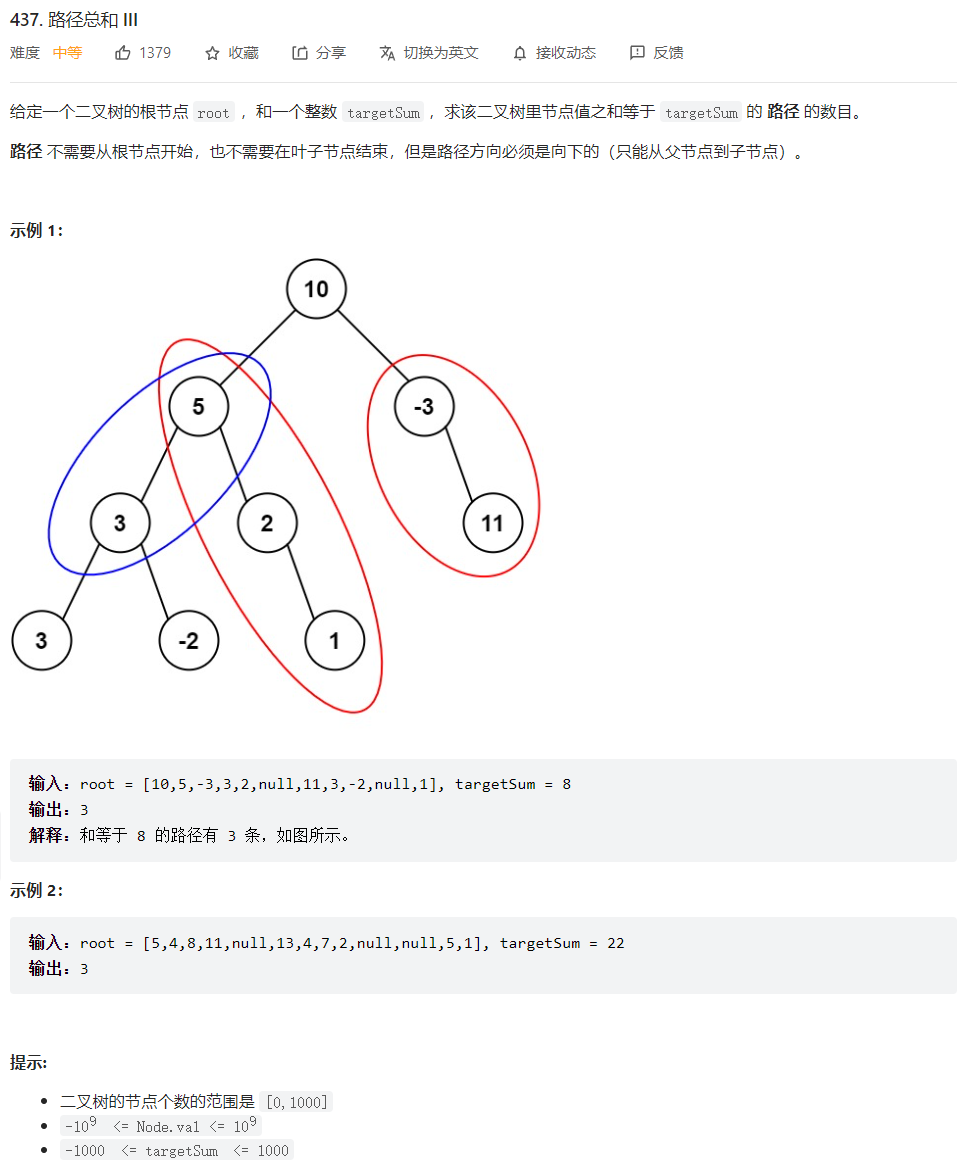
437. 路径总和 III
题目描述
解题思路
枚举
本题每个节点求路径问题也就是上面2题求路径问题,但是此题每个节点都需要求路径,所以我们每一枚举所有的节点的路径。
如何枚举每个节点,在🔗中写法一致。
// 时间复杂度O(n * n),空间复杂度O(n)public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if (root == null) return 0;int res = 0;res += pathSum(root, targetSum);res += pathSum(root.left, targetSum);res += pathSum(root.right, targetSum);return res;}public int traversal(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if (root == null) return 0;int pathCount = 0;// 判断本身if (root.val == targetSum) pathCount++;if (targetSum == 0) pathCount++;pathCount += traversal(root.left, targetSum - root.val);pathCount += traversal(root.right, targetSum - root.val);return pathCount;}
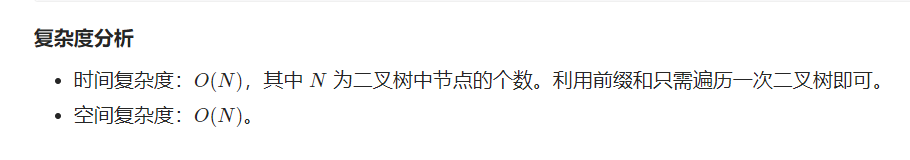
前缀和
官解:https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum-iii/solution/lu-jing-zong-he-iii-by-leetcode-solution-z9td/
此题会使用枚举的方法会存在重复的计算,所以我们可以使用map来记录前缀和出现的次数。
前缀和意思就是:在这个节点之前,经过的路径的所有前缀总和(要能到达此节点)。那么此时我们要求哪条路径的节点相差target,此时我们使用sum来记录这条路径,包括当前节点的路径总和,此时就可以在所有前缀和中寻找等于sum - target的前缀和。得到的就是共有几条相差target的路径。
注意:0也要放入前缀和中,如果当前节点刚好等于target时,也满足一条路径。
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {Map<Long, Integer> preMap = new HashMap<>();// 0的前缀和有一个,当节点本身等于target时也算preMap.put(0L, 1);int res = dfs(root, preMap, 0, targetSum);return res;}public int dfs(TreeNode root, Map<Long, Integer> preMap, long sum, int targetSum) {if (root == null) return 0;sum += root.val;int pathCount = preMap.getOrDefault(sum - targetSum, 0);// 加入前缀和preMap.put(sum, preMap.getOrDefault(sum, 0) + 1);pathCount += dfs(root.left, preMap, sum, targetSum);pathCount += dfs(root.right, preMap, sum, targetSum);// 回溯preMap.put(sum, preMap.getOrDefault(sum, 0) - 1);return pathCount;}