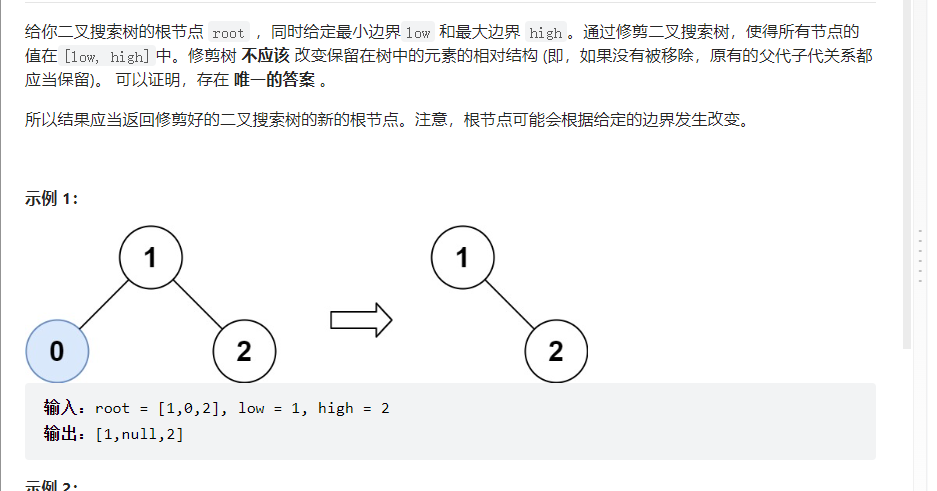
题目描述
解题思路
递归法
- 确定递归函数的参数以及返回值
这里我们为什么需要返回值呢?
因为是要遍历整棵树,做修改,其实不需要返回值也可以,我们也可以完成修剪(其实就是从二叉树中移除节点)的操作。
但是有返回值,更方便,可以通过递归函数的返回值来移除节点。
- 确定终止条件
修剪的操作并不是在终止条件上进行的,所以就是遇到空节点返回就可以了。
- 确定单层递归的逻辑
如果该节点的值大于high,那么右子树都是大于该节点的值,所以都不满足,应该递归左孩子,进 行剪切,同理小于low递归右孩子。递归之后返回递归的值,返回给上一层。
如果该节点的在low,high区间中,那么继续递归左右孩子,并返回给上一层。
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {if (root == null) {return null;}// 如果大于high,说明root右边的都大于high,所以返回左边满足的,但是左边不一定全部满足,所以继续递归剪枝if (root.val > high) {TreeNode left = trimBST(root.left, low, high);return left;}// 同理if (root.val < low) {TreeNode right = trimBST(root.right, low, high);return right;}// 如果此节点妈祖[low,high]区间,左右孩子不一定满足,递归左右孩子,并接住返回值root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, high);root.right = trimBST(root.right, low, high);return root;}
迭代法
// 迭代法public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {if (root == null) return null;// 使根节点移动到[low,high]区间中while (root != null && (root.val < low || root.val > high)) {if (root.val < low) root = root.right;else root = root.left;}// 此时处理根节点的左节点,使其在[low,high]区间中TreeNode cur = root;while (cur != null) {// 注意使用while,左节点的右节点也不满足while (cur.left != null && cur.left.val < low) {cur.left = cur.left.right;}// 此时左节点的右节点满足,但是左节点的右节点的左节点不一定满足// 所以移动到下一个节点继续判断cur = cur.left;}// 处理右节点cur = root;while (cur != null) {while (cur.right != null && cur.right.val > high) {cur.right = cur.right.left;}cur = cur.right;}return root;}