题目描述
解题思路
详解🔗
和合并2个有序列表思路一致。只不过是合并k个。
合并2个有序链表:
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode a, ListNode b) {if (a == null || b == null) {return a != null ? a : b;}ListNode head = new ListNode(0);ListNode tail = head, aPtr = a, bPtr = b;while (aPtr != null && bPtr != null) {if (aPtr.val < bPtr.val) {tail.next = aPtr;aPtr = aPtr.next;} else {tail.next = bPtr;bPtr = bPtr.next;}tail = tail.next;}tail.next = (aPtr != null ? aPtr : bPtr);return head.next;}
顺序合并
每次遍历就合并一个链表,一次合并。
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {if (lists == null && lists.length == 0) return null;if (lists.length == 1) return lists[0];ListNode head = lists[0];ListNode cur = head;for (int i = 1; i < lists.length; i++) {ListNode node = lists[i];ListNode newHead = new ListNode(0);ListNode newCur = newHead;while (cur != null && node != null) {if (cur.val < node.val) {newCur.next = cur;cur = cur.next;newCur = newCur.next;}else {newCur.next = node;node = node.next;newCur = newCur.next;}}newCur.next = cur == null ? node : cur;cur = newHead.next;}return cur;}
官解:
我们可以想到一种最朴素的方法:用一个变量 ans 来维护以及合并的链表,第 i 次循环把第 i 个链表和 ans 合并,答案保存到 ans 中。
class Solution {public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {ListNode ans = null;for (int i = 0; i < lists.length; ++i) {ans = mergeTwoLists(ans, lists[i]);}return ans;}public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode a, ListNode b) {if (a == null || b == null) {return a != null ? a : b;}ListNode head = new ListNode(0);ListNode tail = head, aPtr = a, bPtr = b;while (aPtr != null && bPtr != null) {if (aPtr.val < bPtr.val) {tail.next = aPtr;aPtr = aPtr.next;} else {tail.next = bPtr;bPtr = bPtr.next;}tail = tail.next;}tail.next = (aPtr != null ? aPtr : bPtr);return head.next;}}
分治合并

我们可以一次合并一次的合并,递归到最后2个链表进行合并,合并成了k/2,然和在合并最后两个,合并成了k/2;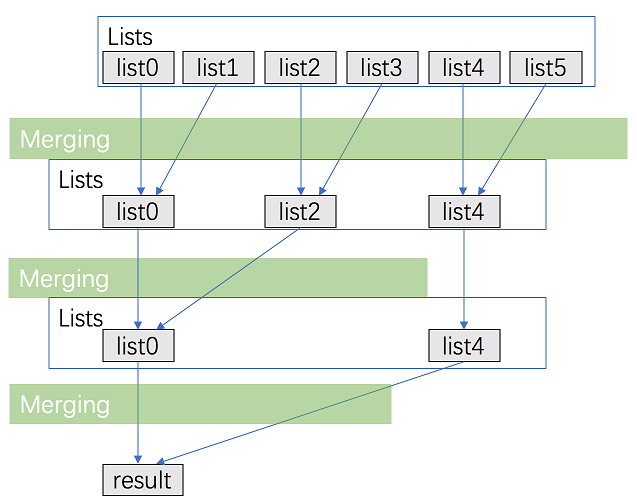
主要体现分而治之的是这句代码:return mergeTwoLists(merge(lists, l, mid), merge(lists, mid + 1, r));
mergeTwoLists函数是合并2个链表,两个链表继续递归,最终停止递归后返回合并的链表,在2个链表进行合并。
// 分治// 分治public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {return merge(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);}public ListNode merge(ListNode[] lists, int l, int r) {if (l == r) return lists[l];if (l > r) return null;// 分儿治之int mid = (l + r) >> 1;// 左闭右开return mergeTwoLists(merge(lists, l, mid), merge(lists, mid + 1, r));}public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode A, ListNode B) {if (A == null || B == null) return A == null ? B : A;ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);ListNode cur = dummy, a = A, b = B;while (a != null && b != null) {if (a.val < b.val) {cur.next = a;a = a.next;} else {cur.next = b;b = b.next;}cur = cur.next;}cur.next = a == null ? b : a;return dummy.next;}
使用优先队列合并
可以使用一个优先队列记录每个节点的的头元素,注意优先队列需要小的在前面,因为合并成升序,出队便是最小的。注意记录的知识头节点,所以头节点加入节点之后,next不为空时还需要入队列。
// 优先级队列public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {PriorityQueue<ListNode> queue = new PriorityQueue<ListNode>((a, b) -> a.val - b.val);ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);ListNode cur = dummy;// 将每个链表都节点按照从小到大放入队列for (ListNode node : lists) {if (node != null) {queue.offer(node);}}while (!queue.isEmpty()) {ListNode node = queue.poll();cur.next = node;cur = cur.next;// 如果node节点不为空,继续入队if (node.next != null) {queue.offer(node.next);}}return dummy.next;}





