基于版本 react@15.7.0
本质上,看this.setState是否命中batchingStrategy.isBatchingUpdates——组件正在更新。
如果batchingStrategy.isBatchingUpdates = true,则批量合并且更新 this.setState,看起来像异步,实际上不是异步,因为只执行了一次。
如果batchingStrategy.isBatchingUpdates = false,则this.setState是同步的。
设计 isBatchingUpdates 的初衷
我们从一段代码来理解一下。
正如下面的代码,当点击 Child 组件的按钮时,将触发子组件的更新。
由于事件的冒泡机制,父组件也将更新,这将导致子组件再一次的更新。
子组件第一次更新完全是浪费的。所以 React 设计成 setState 不立即触发重新渲染,而是先执行完所有的 事件回调 ,然后用一次重新渲染完成所有更新。
function Parent() {let [count, setCount] = useState(0);return (<div onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>Parent clicked {count} times<Child /></div>);}function Child() {let [count, setCount] = useState(0);return (<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>Child clicked {count} times</button>);}
示例
import React, { Component } from 'react'class App extends Component {state = {count: 0}componentDidMount() {// 执行完,count = 2this.btn.onclick = () => {this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });}}asyncClick = () => {// 由于执行完,count = 1,看起来 this.state 像是异步执行的。// 但过一会之后,count 还是等于 1,这并不符合异步的逻辑啊this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });}syncClick = () => {// 执行完,count = 2setTimeout(() => {this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });}, 0)this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });}render() {return (<div><button onClick={this.asyncClick}>异步: 合成事件</button><button onClick={this.syncClick}>同步</button><button ref={(ref) => { this.btn = ref }}>原生事件</button><p>{this.state.count}</p></div>)}}export default App
从源码来看
setState 是挂载在 React.Component 类原型上的方法,它会将待处理的 state 存入 enqueueSetState 队列
// React/ReactBaseClasses.js/*** @param {object|function} partialState 用于更新当前 state 的 新的部分 state* @param {?function} callback 当 state 更新完成后,执行的回调函数**/ReactComponent.prototype.setState = function (partialState, callback) {!(typeof partialState === 'object' || typeof partialState === 'function' || partialState == null) ? process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' ? invariant(false, 'setState(...): takes an object of state variables to update or a function which returns an object of state variables.') : _prodInvariant('85') : void 0;this.updater.enqueueSetState(this, partialState);if (callback) {this.updater.enqueueCallback(this, callback, 'setState');}};
// react-dom/ReactUpdateQueue.jsfunction getInternalInstanceReadyForUpdate(publicInstance, callerName) {// ReactInstanceMap 是一个映射:组件示例 与 组件示例在 react 内部的特性之间的映射。这不必细究// ReactInstanceMap:Store a reference from the instance back to the internal representationvar internalInstance = ReactInstanceMap.get(publicInstance);if (!internalInstance) {if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {var ctor = publicInstance.constructor;// Only warn when we have a callerName. Otherwise we should be silent.// We're probably calling from enqueueCallback. We don't want to warn// there because we already warned for the corresponding lifecycle method.process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' ? warning(!callerName, '%s(...): Can only update a mounted or mounting component. ' + 'This usually means you called %s() on an unmounted component. ' + 'This is a no-op. Please check the code for the %s component.', callerName, callerName, ctor && (ctor.displayName || ctor.name) || 'ReactClass') : void 0;}return null;}if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' ? warning(ReactCurrentOwner.current == null, '%s(...): Cannot update during an existing state transition (such as ' + "within `render` or another component's constructor). Render methods " + 'should be a pure function of props and state; constructor ' + 'side-effects are an anti-pattern, but can be moved to ' + '`componentWillMount`.', callerName) : void 0;}return internalInstance;}/*** ReactUpdateQueue allows for state updates to be scheduled into a later* reconciliation step.*/const ReactUpdateQueue = {/*** @param {ReactClass} publicInstance 需要重新渲染的组件实例.* @param {object} partialState 待更新的部分 state* @internal*/enqueueSetState: function (publicInstance, partialState) {if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {ReactInstrumentation.debugTool.onSetState();process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' ? warning(partialState != null, 'setState(...): You passed an undefined or null state object; ' + 'instead, use forceUpdate().') : void 0;}var internalInstance = getInternalInstanceReadyForUpdate(publicInstance, 'setState');if (!internalInstance) {return;}// 看下面这几行就好,var queue = internalInstance._pendingStateQueue || (internalInstance._pendingStateQueue = []);queue.push(partialState);enqueueUpdate(internalInstance);},}
// react-dom/ReactUpdates.js/*** Mark a component as needing a rerender, adding an optional callback to a* list of functions which will be executed once the rerender occurs.*/function enqueueUpdate(component) {ensureInjected();// 命中 isbatchingUpdates,this.setState 批量合并,然后再更新组件if (!batchingStrategy.isBatchingUpdates) {batchingStrategy.batchedUpdates(enqueueUpdate, component);return;}dirtyComponents.push(component);if (component._updateBatchNumber == null) {component._updateBatchNumber = updateBatchNumber + 1;}}
// react-dom/ReactDefaultBatchingStrategy.js// react 默认的 batchingStrategy,这个就是上面代码 batchingStrategy 默认值var ReactDefaultBatchingStrategy = {isBatchingUpdates: false, // 批量更新的标志,true 则批量更新 setState/*** Call the provided function in a context within which calls to `setState`* and friends are batched such that components aren't updated unnecessarily.*/batchedUpdates: function (callback, a, b, c, d, e) {var alreadyBatchingUpdates = ReactDefaultBatchingStrategy.isBatchingUpdates;ReactDefaultBatchingStrategy.isBatchingUpdates = true;// The code is written this way to avoid extra allocationsif (alreadyBatchingUpdates) {return callback(a, b, c, d, e);} else {return transaction.perform(callback, null, a, b, c, d, e);}}};
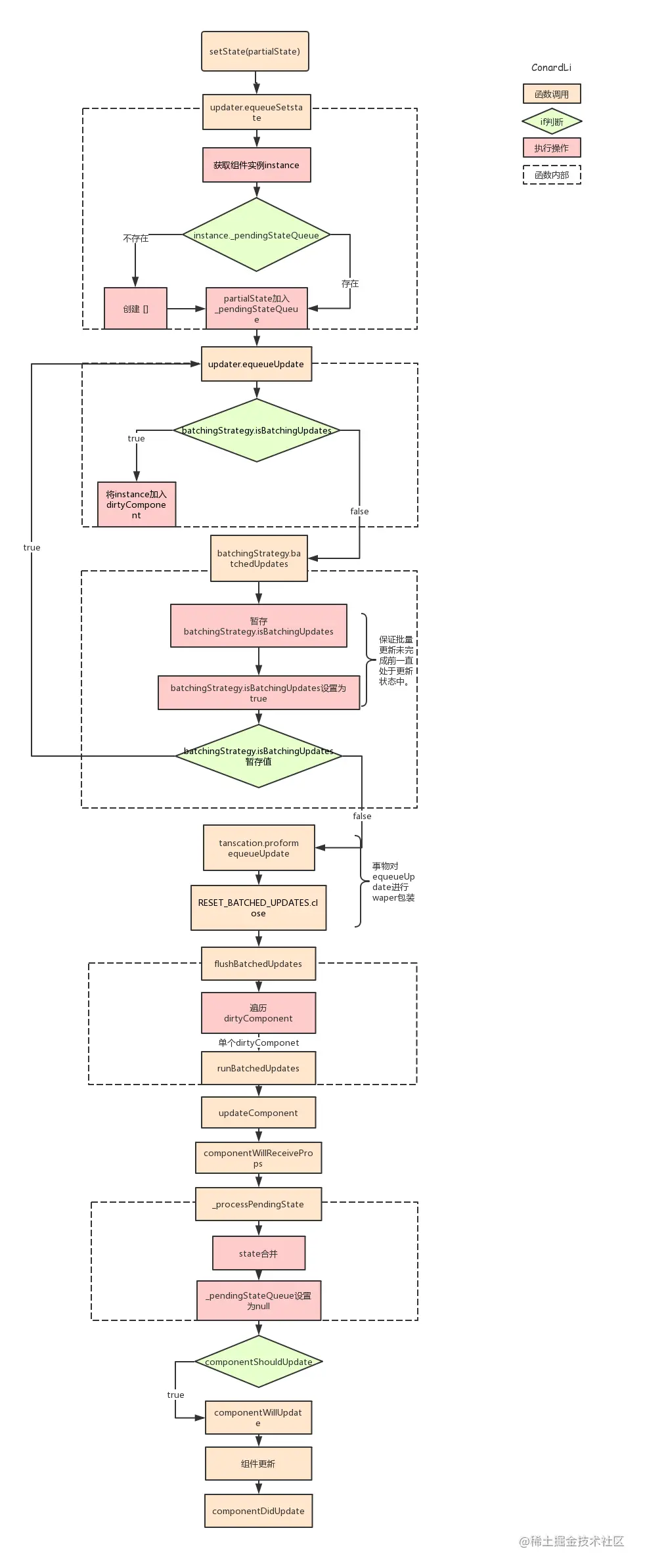
流程图
什么情况命中 isBatchingUpdates
命中
合成事件中的 this.setState
import React, { Component } from 'react'class App extends Component {state = {count: 0}asyncClick = () => {// 由于执行完,count = 1,看起来 this.state 像是异步执行的。// 但过一会之后,count 还是等于 1,这并不符合异步的逻辑啊this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });}render() {return (<div><button onClick={this.asyncClick}>异步: 合成事件</button><p>{this.state.count}</p></div>)}}export default App
生命周期中的 this.setState
import React, { Component } from 'react'class App extends Component {state = {count: 0}componentDidMount() {this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });}render() {return (<div><p>{this.state.count}</p></div>)}}export default App
不命中
原生事件中的 this.setState
import React, { Component } from 'react'class App extends Component {state = {count: 0}componentDidMount() {this.btn.onclick = () => {this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });}}render() {return (<div><button ref={(ref) => { this.btn = ref }}>同步:原生事件</button><p>{this.state.count}</p></div>)}}export default App
定时器中的 this.setState
import React, { Component } from 'react'class App extends Component {state = {count: 0}syncClick = () => {// 执行完,count = 2setTimeout(() => {this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });}, 0)this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });}render() {return (<div><button onClick={this.syncClick}>同步</button><p>{this.state.count}</p></div>)}}export default App