一句话概括:由于 hooks 的存储结构是链表结构。 每次重新渲染组件,会调用上一次 hooks 链表的初始值,赋值给新创建的 hooks 链表, 如果在循环、条件、嵌套函数中使用 hooks,会导致赋值错误。
注意:hooks 链表存储顺序,不等同于 hooks 的调用的时机顺序
链表存储在源码中的体现
每次调用 hooks 都会生成 hook 对象,其结构如下
export type Hook = {|memoizedState: any,baseState: any,baseQueue: Update<any, any> | null,queue: UpdateQueue<any, any> | null,next: Hook | null,|};
着重关注memoizedState和next属性,不同hooks的hook对象的memoizedState保存着不同对象。
useState:hook.memoizedState = state;useEffect:hook.memoizedState = effectuseMemo:hook.memoizedState = [nextValue, nextDeps];useCallback:hook.memoizedState = [callback, nextDeps];useRef:hook.memoizedState = ref;
一般我们会在函数组件中多次使用hooks,这会产生多个hook对象。
组件挂载时
这些对象通过next属性连接形成链表,连接是在挂载时形成的,主要函数是 mountWorkInProgressHook。
function mountWorkInProgressHook() {const hook = {memoizedState: null,baseState: null,baseQueue: null,queue: null,next: null,};if (workInProgressHook === null) {// This is the first hook in the list// 设置一个链表头currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = hook;} else {// Append to the end of the list// 将其他 hook 连接到 nextworkInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = hook;}return workInProgressHook;}
挂载时,hooks 都会调用该函数生成 hook 对象并连接。
- 如果
workInProgressHook === null,说明是hook链中的第一个,将其赋值给currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState并更新workInProgressHook,这说明函数组件的Fiber的memoizedState保存着第一个hook的引用。 当
workInProgressHook !== null,则将新生成的hook赋值给上个hook的next属性并更新workInProgressHook组件更新时
更新时,
hooks都会调用 updateWorkInProgressHook 函数生成新的hook 对象并连接形成hook 链以供下次更新时使用。function updateWorkInProgressHook(): Hook {let nextCurrentHook: null | Hook;if (currentHook === null) { // currentHook === null 说明当前是hook链的第一个// current 为上次更新的组件对应的Fiberconst current = currentlyRenderingFiber.alternate;if (current !== null) {// current.memoizedState保存着hook链的第一个hooknextCurrentHook = current.memoizedState;} else {nextCurrentHook = null;}} else {// 取出 currentHook.next,即上次更新中hook链的下一个hooknextCurrentHook = currentHook.next;}// 此时nextCurrentHook代表着本hooks在上次更新中的hook对象let nextWorkInProgressHook: null | Hook;if (workInProgressHook === null) { //workInProgressHook === null 说明当前是hook链的第一个nextWorkInProgressHook = currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState;} else {nextWorkInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next;}// 此时nextWorkInProgressHook绝大多数时候为null,因为 renderWithHooks 函数在执行函数组件前会将// currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState置为null,workInProgressHook.next也为nullif (nextWorkInProgressHook !== null) { // 忽略这条分支// There's already a work-in-progress. Reuse it.workInProgressHook = nextWorkInProgressHook;nextWorkInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next;currentHook = nextCurrentHook;} else {// 绝大多数时候会进入此分支// currentHook即上次更新中相应顺序的hook对象currentHook = nextCurrentHook;// 复用上次更新的hook对象的属性,生成新的hook对象const newHook: Hook = {memoizedState: currentHook.memoizedState,baseState: currentHook.baseState,baseQueue: currentHook.baseQueue,queue: currentHook.queue,next: null,};//形成新的 hook 链,和挂载时一样if (workInProgressHook === null) {// This is the first hook in the list.currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = newHook;} else {// Append to the end of the list.workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = newHook;}}return workInProgressHook;}
画图理解
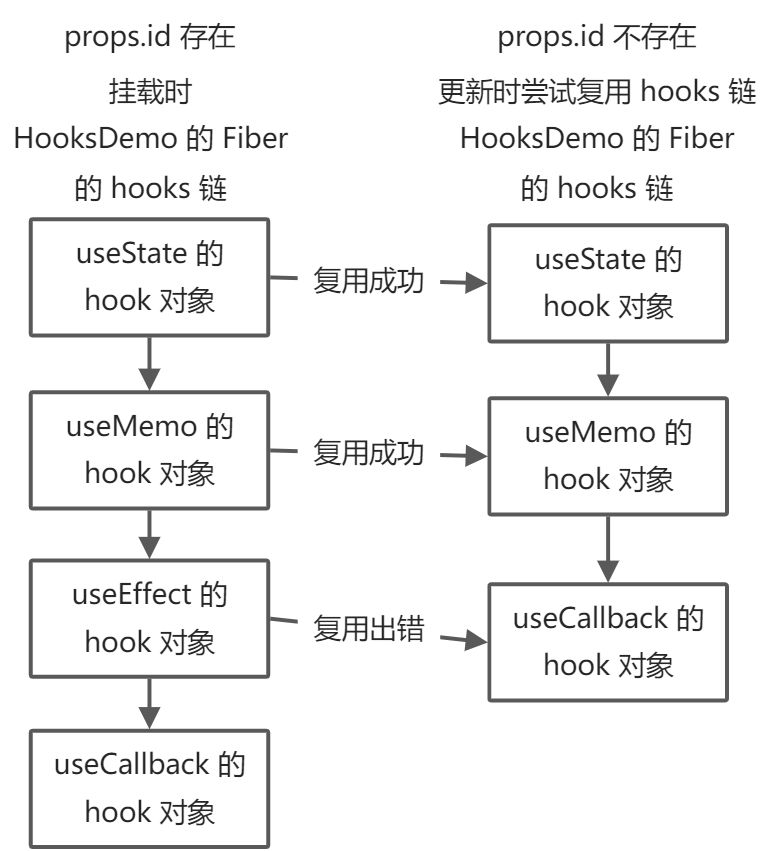
假如有这样一个不规范的组件。
挂载时props.id存在,但更新时props.id不存在 ```jsx import { useState, useMemo, useEffect, useCallback } from ‘react’
const HooksDemo = (props) => { const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const memoObj = useMemo(() => { return { name: ‘konsoue’ } }, [])
// useEffect 被嵌套了 if (props.id) { useEffect(() => { console.log(‘useEffect’); }, []) }
const handler = useCallback(() => console.log(‘useCallback’), [])
return (
export default HooksDemo
```