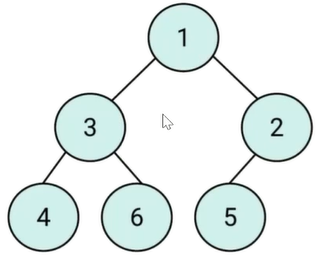
简介
- 堆是一种特殊的完全二叉树
- 完全二叉树:每层节点都完全填满,在最后一层如果不是满的,则只缺少右边的若干节点
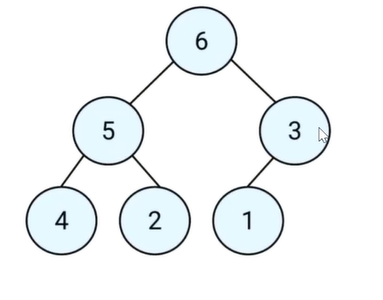
- 满二叉树:特殊的完全二叉树。每一层都是满的
最大堆:所有节点都大于等于其子节点
最小堆:所有节点都小于等于其子节点
- JS中的堆:数组来表示堆
- 树去广度优先遍历
- 左侧子节点的位置是
2 * index(父节点位置) + 1 - 右侧子节点的位置是
2 * index(父节点位置) + 2 - 父节点的位置是
[index(自己的位置) - 1] / 2,向下取整 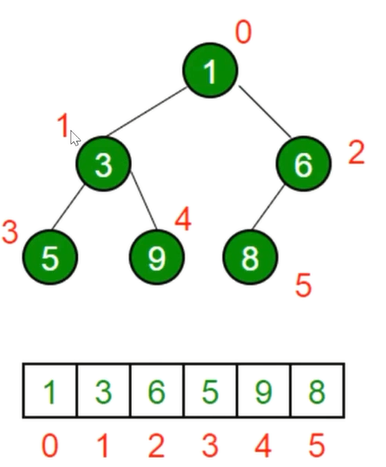
- 堆的应用
- 堆能高效、快速地找出最大值,最小值
- 时间复杂度为 O(1)
- 找出第K个最大(小)元素
- 堆能高效、快速地找出最大值,最小值
如何创建一个大(小)顶堆
常用的方式有两种:
- 插入式创建:每次插入一个节点,实现一个大顶堆(或小顶堆)
原地创建:又称堆化,给定一组节点,实现一个大顶堆(或小顶堆)
插入式建堆
最小堆类的实现
实现步骤
- 在类里,声明一个数组,用来装元素
- 插入
- 将值插入堆的底部,即数组的尾部
- 然后上移:将这个值和它的父节点进行交换,直到父节点小于等于这个插入的值
- 大小为K的堆中,插入元素的时间复杂度为
O(logk)
- 删除堆顶
- 用数组尾部元素替换堆顶(直接删除堆顶会破坏堆结构)
- 然后下移:将新堆顶和它子节点进行交换,直到子节点大于等于这个新堆顶
- 大小为k的堆中,删除元素的时间复杂度为
O(logk)
- 获取堆顶
- 返回数组头部
- 获取堆大小
- 返回数组长度 ```javascript class miniHeap { constructor() { this.heap = []; }
// 获取父节点的位置 getParentIndex(i) { return (i - 1) >> 1; } // 获取左侧子节点 getLeftIndex(i) { return i * 2 + 1; }
// 获取右侧子节点 getRightIndex(i) { return i * 2 + 2; }
swap(i1, i2) { const tmp = this.heap[i1]; this.heap[i1] = this.heap[i2]; this.heap[i2] = tmp; }
// 将节点上移,直到父节点小于等于这个节点 shiftUp(index) { if (index === 0) return; const parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index); if (this.heap[parentIndex] > this.heap[index]) {
this.swap(parentIndex, index);this.shiftUp(parentIndex);
} }
// 将节点进行下移,直到父节点小于等于这个节点 shiftDown(index) { const leftIndex = this.getLeftIndex(index); const rightIndex = this.getRightIndex(index); if (this.heap[leftIndex] < this.heap[index]) {
this.swap(leftIndex, index);this.shiftDown(leftIndex);
} if (this.heap[rightIndex] < this.heap[index]) {
this.swap(rightIndex, index);this.shiftDown(rightIndex);
} }
pop() { this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop(); this.shiftDown(0); }
insert(value) { this.heap.push(value); this.shiftUp(this.heap.length - 1); } peek() { return this.heap[0]; }
size() { return this.heap.length; } }
const h = new miniHeap();
h.insert(3); h.insert(2); h.insert(1); h.pop();
<a name="TFstA"></a>### 最大堆类的实现```javascriptclass MaxHeap {constructor() {this.heap = []}getParentIndex(index) {return index >> 1}swap(i, j) {const tmp = this.heap[i]this.heap[i] = this.heap[j];this.heap[j] = tmp;}shiftUp(index) {if (index === 0) return;const { heap } = this;const parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index);if (heap[parentIndex] < heap[index]) {this.swap(parentIndex, index);this.shiftUp(parentIndex);}}insert(value) {this.heap.push(value);this.shiftUp(this.heap.length - 1)}peek() {return this.heap[0];}size() {return this.heap.length;}}
原地建堆
原地建堆的方法有两种:
- 自下而上式堆化 :将节点与其父节点比较,如果节点大于父节点(大顶堆)或节点小于父节点(小顶堆),则节点与父节点调整位置
- 自上往下式堆化 :将节点与其左右子节点比较,如果存在左右子节点大于该节点(大顶堆)或小于该节点(小顶堆),则将子节点的最大值(大顶堆)或最小值(小顶堆)与之交换
自下而上的堆化
```javascript const array = [3, 44, 38, 5, 47, 15, 36, 26, 1, 27, 46, 4, 19, 50, 48];
// 自下而上的建堆 const buildHeap = (arr, heapSize = 1) => { arr.unshift(null); // 在数组的第一个补个空元素,方便建堆 while (heapSize < arr.length - 1) { heapSize++; heapify(arr, heapSize) } arr.shift(); // 把空元素去除 }
// 堆化,比较元素与父元素的大小,依次往上排 const heapify = (arr, i) => { // 由于补了空元素,使得 Math.floor(i / 2) 就是第 i 项的父元素的位置 while (Math.floor(i / 2) > 0 && arr[i] < arr[Math.floor(i / 2)]) { swap(arr, i, Math.floor(i / 2)); i = Math.floor(i / 2) } }
const swap = (arr, i, j) => { const tmp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = tmp }
buildHeap(array)
console.log(array); // [1, 3, 4, 5, 27, 15, 36, 44, 26, 47, 46, 38, 19, 50, 48]
<a name="LVRz2"></a>### 自上而下的堆化```javascriptconst array = [3, 44, 38, 5, 47, 15, 36, 26, 1, 27, 46, 4, 19, 50, 48];// 自上而下的建最大堆const buildMaxHeap = (arr) => {const len = arr.length;// 找到元素的父元素for (let i = Math.floor(len / 2); i >= 0; i--) {heapify(arr, i);}}// 堆化:const heapify = (arr, i) => {const len = arr.length;let left = 2 * i + 1; // 左子节点let right = 2 * i + 2; // 右子节点let largest = i; // 父元素if (left < len && arr[left] > arr[largest]) {largest = left;}if (right < len && arr[right] > arr[largest]) {largest = right;}if (largest !== i) {swap(arr, i, largest);heapify(arr, largest);}}// 交换元素const swap = (arr, i, j) => {const tmp = arr[i];arr[i] = arr[j];arr[j] = tmp;}buildMaxHeap(array);console.log(array); // [50, 47, 48, 26, 46, 19, 38, 5, 1, 27, 44, 4,15, 36, 3]