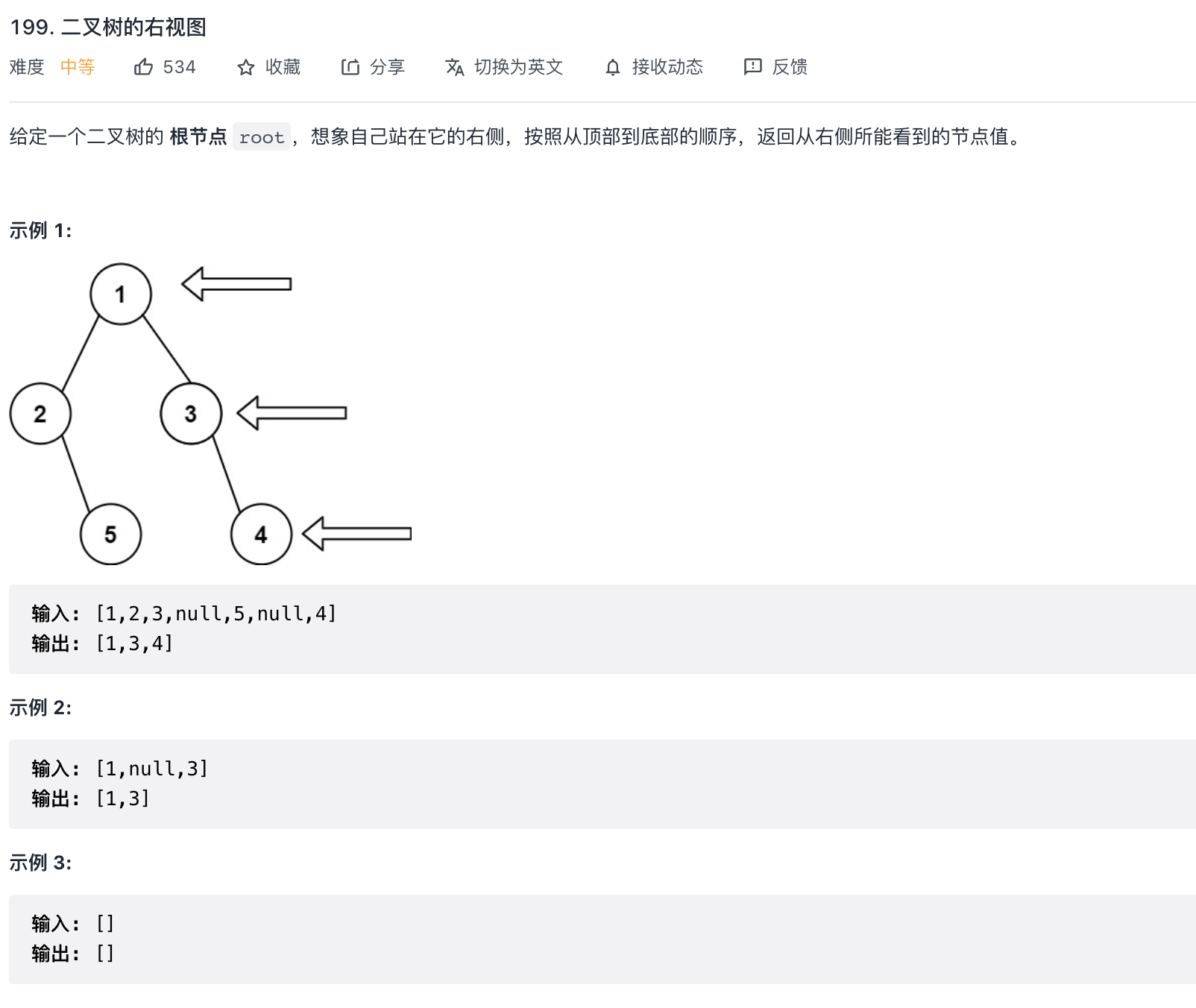
题目
解题思路
深度优先
对树进行深度优先搜索,在搜索过程中,总是先访问右子树。那么对于每一层来说,在这层见到的第一个结点一定是最右边的结点。这样一来,可以存储在每个深度访问的第一个结点,一旦知道了树的层数,就可以得到最终的结果数组。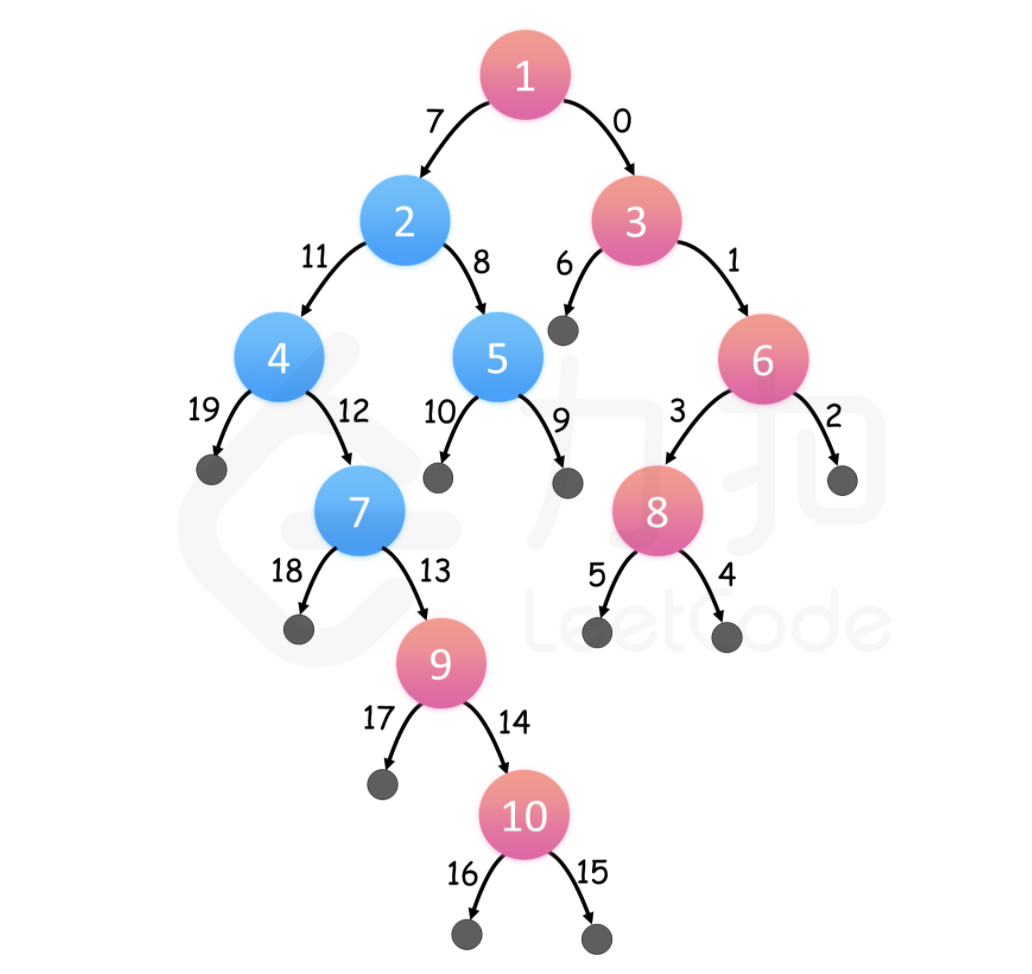
广度优先
可以对二叉树进行层次遍历,那么对于每层来说,最右边的结点一定是最后被遍历到的。二叉树的层次遍历可以用广度优先搜索实现。
执行广度优先搜索,左结点排在右结点之前,这样,对每一层都从左到右访问。
因此,只保留每个深度最后访问的结点,就可以在遍历完整棵树后得到每个深度最右的结点。
代码
1、DFS
class Solution {public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {Map<Integer, Integer> rightmostValueAtDepth = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();int max_depth = -1;Stack<TreeNode> nodeStack = new Stack<TreeNode>();Stack<Integer> depthStack = new Stack<Integer>();nodeStack.push(root);depthStack.push(0);while (!nodeStack.isEmpty()) {TreeNode node = nodeStack.pop();int depth = depthStack.pop();if (node != null) {// 维护二叉树的最大深度max_depth = Math.max(max_depth, depth);// 如果不存在对应深度的节点我们才插入if (!rightmostValueAtDepth.containsKey(depth)) {rightmostValueAtDepth.put(depth, node.val);}nodeStack.push(node.left);nodeStack.push(node.right);depthStack.push(depth + 1);depthStack.push(depth + 1);}}List<Integer> rightView = new ArrayList<Integer>();for (int depth = 0; depth <= max_depth; depth++) {rightView.add(rightmostValueAtDepth.get(depth));}return rightView;}}
2、BFS
class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
Map<Integer, Integer> rightmostValueAtDepth = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
int max_depth = -1;
Stack<TreeNode> nodeStack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
Stack<Integer> depthStack = new Stack<Integer>();
nodeStack.push(root);
depthStack.push(0);
while (!nodeStack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = nodeStack.pop();
int depth = depthStack.pop();
if (node != null) {
// 维护二叉树的最大深度
max_depth = Math.max(max_depth, depth);
// 如果不存在对应深度的节点我们才插入
if (!rightmostValueAtDepth.containsKey(depth)) {
rightmostValueAtDepth.put(depth, node.val);
}
nodeStack.push(node.left);
nodeStack.push(node.right);
depthStack.push(depth + 1);
depthStack.push(depth + 1);
}
}
List<Integer> rightView = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int depth = 0; depth <= max_depth; depth++) {
rightView.add(rightmostValueAtDepth.get(depth));
}
return rightView;
}
}