第四节:细胞聚类分析
在本节教程中,我们将基于批次矫正后的整合数据集进行细胞聚类分析,我们使用PCA线性降维的结果分别执行k-最近邻图聚类,层次聚类和k-均值聚类。
加载所需的R包和数据集
if (!require(clustree)) {install.packages("clustree", dependencies = FALSE)}## Loading required package: clustree## Loading required package: ggraphsuppressPackageStartupMessages({library(Seurat)library(cowplot)library(ggplot2)library(pheatmap)library(rafalib)library(clustree)})alldata <- readRDS("data/results/covid_qc_dr_int.rds")
执行k-最近邻图聚类
在执行图聚类的过程中主要包括以下3个步骤:
- Build a kNN graph from the data
- Prune spurious connections from kNN graph (optional step). This is a SNN graph.
- Find groups of cells that maximizes the connections within the group compared other groups.
构建kNN/SNN图
执行图聚类的第一步是构建一个kNN图,我们使用PCA降维的前_N个_PC用于计算。
我们可以使用Seurat包中的FindNeighbors函数计算构建KNN和SNN图。
# check that CCA is still the active assayalldata@active.assay## [1] "CCA"# 使用FindNeighbors函数构建SNN图alldata <- FindNeighbors(alldata, dims = 1:30, k.param = 60, prune.SNN = 1/15)## Computing nearest neighbor graph## Computing SNN# check the names for graphs in the object.names(alldata@graphs)## [1] "CCA_nn" "CCA_snn"
我们可以看一下kNN图,它是一个连接矩阵,其中不同细胞之间的每个连接都表示为1个s,这称之为未加权图(Seurat中的默认值)。但是,某些细胞之间的连接可能比其他细胞的更重要,在这种情况下,图的尺度会从0到最大距离。通常,距离越小,两点越接近,它们之间的连接也越牢固,这称之为加权图。加权图和未加权图均适用于图聚类,但是对于大型数据集(>100k细胞),使用非加权图在聚类上的速度会更快。
pheatmap(alldata@graphs$CCA_nn[1:200, 1:200],
col = c("white", "black"), border_color = "grey90",
legend = F, cluster_rows = F, cluster_cols = F, fontsize = 2)
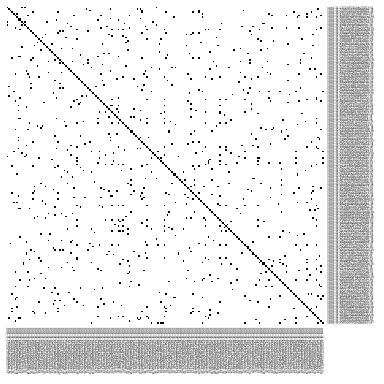
基于SNN图进行细胞聚类
在构建好SNN图后,我们可以基于其执行图聚类。选用不同的分辨率(resolution)进行细胞聚类,分辨率越大,聚类出来的细胞簇数越多。
在Seurat中,我们使用FindClusters函数进行细胞聚类,默认情况下(algorithm = 1),该函数将使用“ Louvain”算法进行基于图的聚类。要使用leiden算法,我们需要将其设置为algorithm = 4。
# Clustering with louvain (algorithm 1)
for (res in c(0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2)) {
alldata <- FindClusters(alldata, graph.name = "CCA_snn", resolution = res, algorithm = 1)
}
# each time you run clustering, the data is stored in meta data columns:
# seurat_clusters - lastest results only CCA_snn_res.XX - for each different
# resolution you test.
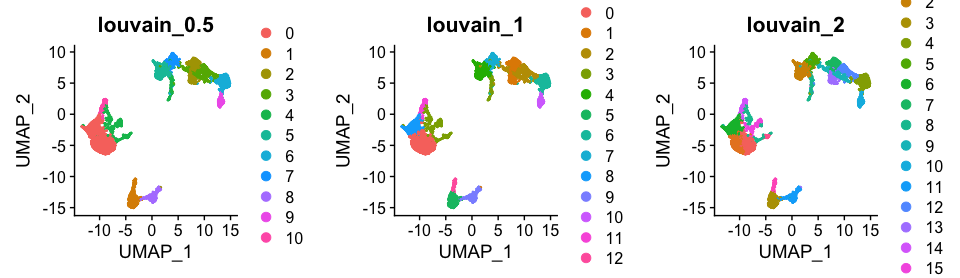
plot_grid(ncol = 3, DimPlot(alldata, reduction = "umap", group.by = "CCA_snn_res.0.5") + ggtitle("louvain_0.5"),
DimPlot(alldata, reduction = "umap", group.by = "CCA_snn_res.1") + ggtitle("louvain_1"),
DimPlot(alldata, reduction = "umap", group.by = "CCA_snn_res.2") + ggtitle("louvain_2"))
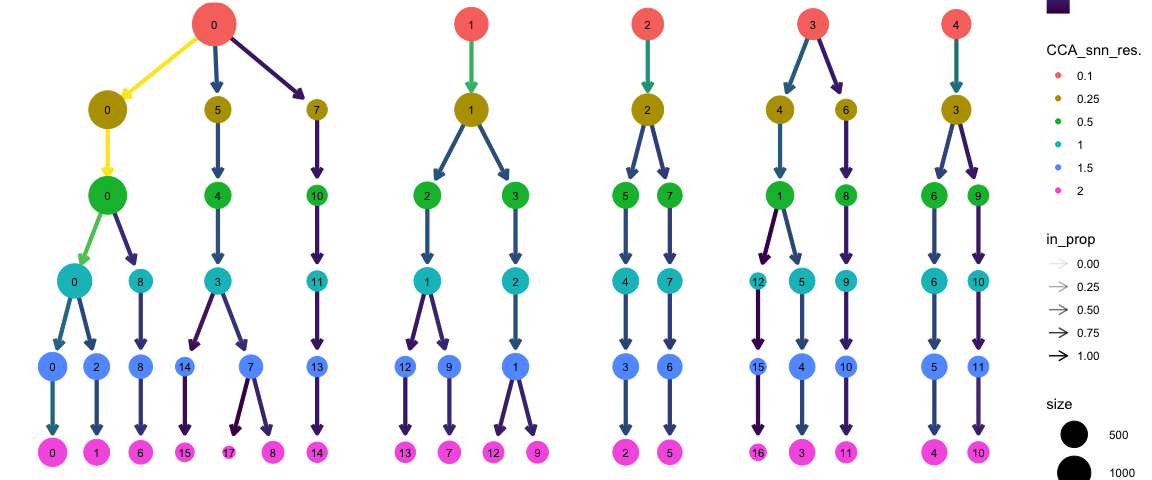
现在,我们可以使用clustree包来可视化不同分辨率下细胞在聚类群之间的分配。
# install.packages('clustree')
suppressPackageStartupMessages(library(clustree))
clustree(alldata@meta.data, prefix = "CCA_snn_res.")
K均值聚类
K-means是一种常用的聚类算法,已在许多应用领域中使用。在R中,可以通过kmeans函数进行调用。通常,它应用于表达数据的降维表示(由于低维距离的可解释性,因此通常用于PCA)。
我们需要预先设定聚类群的数量。由于聚类的结果取决于群集中心的初始化,因此通常建议使用多个启动配置(通过nstart参数)运行K-means。
for (k in c(5, 7, 10, 12, 15, 17, 20)) {
alldata@meta.data[, paste0("kmeans_", k)] <- kmeans(x = alldata@reductions[["pca"]]@cell.embeddings, centers = k, nstart = 100)$cluster
}
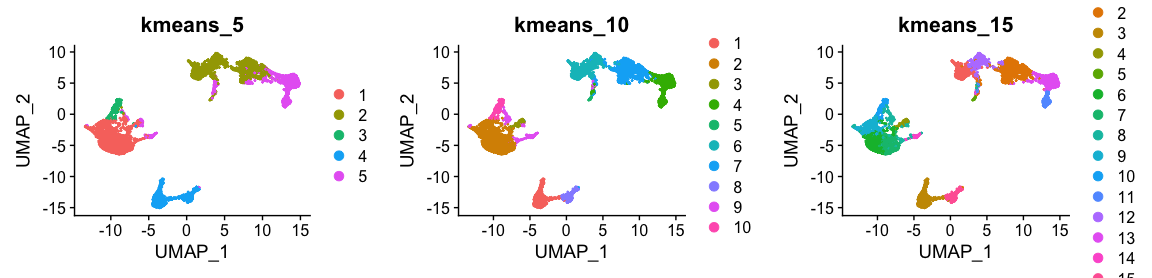
plot_grid(ncol = 3, DimPlot(alldata, reduction = "umap", group.by = "kmeans_5") + ggtitle("kmeans_5"),
DimPlot(alldata, reduction = "umap", group.by = "kmeans_10") + ggtitle("kmeans_10"),
DimPlot(alldata, reduction = "umap", group.by = "kmeans_15") + ggtitle("kmeans_15"))
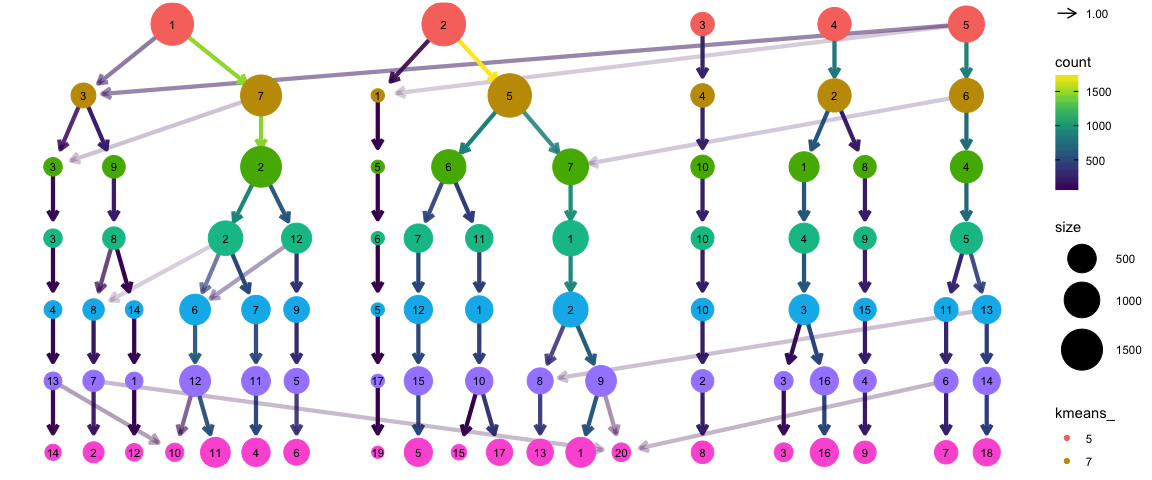
使用clustree函数查看不同聚类群的结果
clustree(alldata@meta.data, prefix = "kmeans_")
层次聚类
定义细胞之间的距离
基本的Rstats包中包含一个dist函数,可以用于计算所有成对样本之间的距离。由于我们要计算样本之间的距离,而不是基因之间的距离,因此我们需要先对表达数据进行转置,然后再将其应用于dist函数中。dist函数中可用的距离计算方法有:“euclidean”, “maximum”, “manhattan”, “canberra”, “binary” or “minkowski”.
d <- dist(alldata@reductions[["pca"]]@cell.embeddings, method = "euclidean")
可以看到,dist函数不能实现correlation的方法。但是,我们可以创建自己的距离并将其转换为距离对象。我们首先可以使用cor函数计算样本之间的相关性。如您所知,相关性的范围是从-1到1的,其中1表示两个样本最接近,-1表示两个样本最远,0介于两者之间。但是,这在定义距离时会产生问题,因为距离0表示两个样本最接近,距离1表示两个样本最远,而距离-1没有意义。因此,我们需要将相关性转换为正尺度(又称adjacency):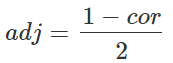
将相关性转换为0-1比例后,我们可以简单地使用as.dist函数将其转换为距离对象。
# Compute sample correlations
# 计算细胞之间的相关性
sample_cor <- cor(Matrix::t(alldata@reductions[["pca"]]@cell.embeddings))
# Transform the scale from correlations
sample_cor <- (1 - sample_cor)/2
# Convert it to a distance object
d2 <- as.dist(sample_cor)
基于细胞之间的距离进行层次聚类
在计算出所有样本之间的距离之后,我们可以对其进行层次聚类。我们将使用hclust函数实现该功能,在该函数中,我们可以简单地使用上面创建的距离对象来运行它。可用的方法有:“ward.D”, “ward.D2”, “single”, “complete”, “average”, “mcquitty”, “median” or “centroid”。
# euclidean
h_euclidean <- hclust(d, method = "ward.D2")
# correlation
h_correlation <- hclust(d2, method = "ward.D2")
创建好分层聚类树后,下一步就是定义哪些样本属于特定簇。我们可以使用cutree函数根据特定k值切割聚类树,以定义聚类群。我们还可以定义簇的数量或确定高度。
#euclidean distance
alldata$hc_euclidean_5 <- cutree(h_euclidean,k = 5)
alldata$hc_euclidean_10 <- cutree(h_euclidean,k = 10)
alldata$hc_euclidean_15 <- cutree(h_euclidean,k = 15)
#correlation distance
alldata$hc_corelation_5 <- cutree(h_correlation,k = 5)
alldata$hc_corelation_10 <- cutree(h_correlation,k = 10)
alldata$hc_corelation_15 <- cutree(h_correlation,k = 15)
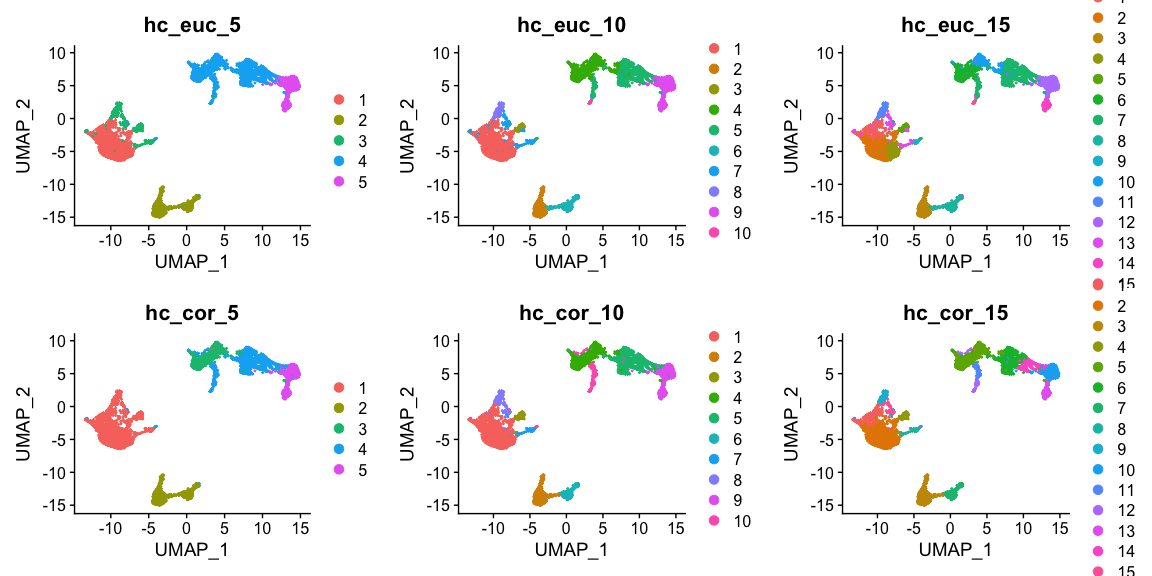
plot_grid(ncol = 3,
DimPlot(alldata, reduction = "umap", group.by = "hc_euclidean_5")+ggtitle("hc_euc_5"),
DimPlot(alldata, reduction = "umap", group.by = "hc_euclidean_10")+ggtitle("hc_euc_10"),
DimPlot(alldata, reduction = "umap", group.by = "hc_euclidean_15")+ggtitle("hc_euc_15"),
DimPlot(alldata, reduction = "umap", group.by = "hc_corelation_5")+ggtitle("hc_cor_5"),
DimPlot(alldata, reduction = "umap", group.by = "hc_corelation_10")+ggtitle("hc_cor_10"),
DimPlot(alldata, reduction = "umap", group.by = "hc_corelation_15")+ggtitle("hc_cor_15")
)
保存细胞聚类的结果
saveRDS(alldata, "data/results/covid_qc_dr_int_cl.rds")
sessionInfo()
## R version 4.0.3 (2020-10-10)
## Platform: x86_64-apple-darwin13.4.0 (64-bit)
## Running under: macOS Catalina 10.15.5
##
## Matrix products: default
## BLAS/LAPACK: /Users/paulo.czarnewski/.conda/envs/scRNAseq2021/lib/libopenblasp-r0.3.12.dylib
##
## locale:
## [1] en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/C/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8
##
## attached base packages:
## [1] parallel stats4 grid stats graphics grDevices utils
## [8] datasets methods base
##
## other attached packages:
## [1] rafalib_1.0.0 pheatmap_1.0.12
## [3] clustree_0.4.3 ggraph_2.0.4
## [5] reticulate_1.18 harmony_1.0
## [7] Rcpp_1.0.6 scran_1.18.0
## [9] SingleCellExperiment_1.12.0 SummarizedExperiment_1.20.0
## [11] Biobase_2.50.0 GenomicRanges_1.42.0
## [13] GenomeInfoDb_1.26.0 IRanges_2.24.0
## [15] S4Vectors_0.28.0 BiocGenerics_0.36.0
## [17] MatrixGenerics_1.2.0 matrixStats_0.57.0
## [19] ggplot2_3.3.3 cowplot_1.1.1
## [21] KernSmooth_2.23-18 fields_11.6
## [23] spam_2.6-0 dotCall64_1.0-0
## [25] DoubletFinder_2.0.3 Matrix_1.3-2
## [27] Seurat_3.2.3 RJSONIO_1.3-1.4
## [29] optparse_1.6.6
##
## loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
## [1] tidyselect_1.1.0 htmlwidgets_1.5.3
## [3] BiocParallel_1.24.0 Rtsne_0.15
## [5] munsell_0.5.0 codetools_0.2-18
## [7] ica_1.0-2 statmod_1.4.35
## [9] future_1.21.0 miniUI_0.1.1.1
## [11] withr_2.4.0 colorspace_2.0-0
## [13] knitr_1.30 ROCR_1.0-11
## [15] tensor_1.5 listenv_0.8.0
## [17] labeling_0.4.2 GenomeInfoDbData_1.2.4
## [19] polyclip_1.10-0 bit64_4.0.5
## [21] farver_2.0.3 parallelly_1.23.0
## [23] vctrs_0.3.6 generics_0.1.0
## [25] xfun_0.20 R6_2.5.0
## [27] graphlayouts_0.7.1 rsvd_1.0.3
## [29] locfit_1.5-9.4 hdf5r_1.3.3
## [31] bitops_1.0-6 spatstat.utils_1.20-2
## [33] DelayedArray_0.16.0 assertthat_0.2.1
## [35] promises_1.1.1 scales_1.1.1
## [37] gtable_0.3.0 beachmat_2.6.0
## [39] globals_0.14.0 goftest_1.2-2
## [41] tidygraph_1.2.0 rlang_0.4.10
## [43] splines_4.0.3 lazyeval_0.2.2
## [45] checkmate_2.0.0 yaml_2.2.1
## [47] reshape2_1.4.4 abind_1.4-5
## [49] backports_1.2.1 httpuv_1.5.5
## [51] tools_4.0.3 ellipsis_0.3.1
## [53] RColorBrewer_1.1-2 ggridges_0.5.3
## [55] plyr_1.8.6 sparseMatrixStats_1.2.0
## [57] zlibbioc_1.36.0 purrr_0.3.4
## [59] RCurl_1.98-1.2 rpart_4.1-15
## [61] deldir_0.2-9 pbapply_1.4-3
## [63] viridis_0.5.1 zoo_1.8-8
## [65] ggrepel_0.9.1 cluster_2.1.0
## [67] magrittr_2.0.1 data.table_1.13.6
## [69] RSpectra_0.16-0 scattermore_0.7
## [71] lmtest_0.9-38 RANN_2.6.1
## [73] fitdistrplus_1.1-3 patchwork_1.1.1
## [75] mime_0.9 evaluate_0.14
## [77] xtable_1.8-4 gridExtra_2.3
## [79] compiler_4.0.3 tibble_3.0.5
## [81] maps_3.3.0 crayon_1.3.4
## [83] htmltools_0.5.1 mgcv_1.8-33
## [85] venn_1.9 later_1.1.0.1
## [87] tidyr_1.1.2 DBI_1.1.1
## [89] tweenr_1.0.1 formatR_1.7
## [91] MASS_7.3-53 getopt_1.20.3
## [93] igraph_1.2.6 pkgconfig_2.0.3
## [95] plotly_4.9.3 scuttle_1.0.0
## [97] admisc_0.11 dqrng_0.2.1
## [99] XVector_0.30.0 stringr_1.4.0
## [101] digest_0.6.27 sctransform_0.3.2
## [103] RcppAnnoy_0.0.18 spatstat.data_1.7-0
## [105] rmarkdown_2.6 leiden_0.3.6
## [107] uwot_0.1.10 edgeR_3.32.0
## [109] DelayedMatrixStats_1.12.0 curl_4.3
## [111] shiny_1.5.0 lifecycle_0.2.0
## [113] nlme_3.1-151 jsonlite_1.7.2
## [115] BiocNeighbors_1.8.0 viridisLite_0.3.0
## [117] limma_3.46.0 pillar_1.4.7
## [119] lattice_0.20-41 fastmap_1.0.1
## [121] httr_1.4.2 survival_3.2-7
## [123] glue_1.4.2 remotes_2.2.0
## [125] spatstat_1.64-1 png_0.1-7
## [127] bluster_1.0.0 bit_4.0.4
## [129] ggforce_0.3.2 stringi_1.5.3
## [131] BiocSingular_1.6.0 dplyr_1.0.3
## [133] irlba_2.3.3 future.apply_1.7.0
参考来源:https://nbisweden.github.io/workshop-scRNAseq/labs/compiled/seurat/seurat_04_clustering.html

