在本教程中,我们将学习使用Signac包对多样本的scATAC-seq数据进行整合分析。这里,我们对来自10x Genomics和sci-ATAC-seq技术测序的成年小鼠大脑的多个单细胞ATAC-seq数据集进行了整合分析。
其中,10x Genomics平台产生的原始数据可从官网下载:
- The Raw data
- The Metadata
- The fragments file
- The fragments file index
sci-ATAC-seq技术产生的数据集由Cusanovich和Hill等人生成。原始数据可从作者的网站下载:
我们将演示使用Seurat v3中的数据整合方法(dataset integration and label transfer)对多个scATAC-seq数据集进行整合分析,以及使用harmony包进行数据整合。
安装并加载所需的R包
if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE))install.packages("BiocManager")BiocManager::install("rtracklayer")library(devtools)install_github("immunogenomics/harmony")library(Signac)library(Seurat)library(patchwork)set.seed(1234)
加载数据集并构建Seurat对象
# this object was created following the mouse brain vignette# 加载10x Genomics的小鼠大脑的scATAC-seq数据tenx <- readRDS(file = "/home/dongwei/scATAC-seq/brain/10x/adult_mouse_brain.rds")tenx$tech <- '10x'tenx$celltype <- Idents(tenx)# 加载sci-ATAC-seq的小鼠大脑数据sci.metadata <- read.table(file = "/home/dongwei/scATAC-seq/brain/sci/cell_metadata.txt",header = TRUE,row.names = 1,sep = "\t")# subset to include only the brain datasci.metadata <- sci.metadata[sci.metadata$tissue == 'PreFrontalCortex', ]sci.counts <- readRDS(file = "/home/dongwei/scATAC-seq/brain/sci/atac_matrix.binary.qc_filtered.rds")sci.counts <- sci.counts[, rownames(x = sci.metadata)]
数据预处理
在上述两个数据集中,sci-ATAC-seq数据是比对到小鼠mm9参考基因组的,而10x的数据是比对到小鼠mm10参考基因组的,因此这两个数据集中peaks的基因组坐标信息是不同的。我们可以使用rtracklayer包将mm9参考基因组的坐标信息转换到mm10中,并使用mm10的坐标更换sci-ATAC-seq数据中peaks的坐标,其中liftover转换的chain文件可以从UCSC官网进行下载。
# 将peaks坐标信息转换成GRanges格式sci_peaks_mm9 <- StringToGRanges(regions = rownames(sci.counts), sep = c("_", "_"))# 导入mm9ToMm10.over.chain文件mm9_mm10 <- rtracklayer::import.chain("/home/dongwei/data/liftover/mm9ToMm10.over.chain")# 使用rtracklayer包中的liftOver函数转换坐标信息sci_peaks_mm10 <- rtracklayer::liftOver(x = sci_peaks_mm9, chain = mm9_mm10)names(sci_peaks_mm10) <- rownames(sci.counts)# discard any peaks that were mapped to >1 region in mm10correspondence <- S4Vectors::elementNROWS(sci_peaks_mm10)sci_peaks_mm10 <- sci_peaks_mm10[correspondence == 1]sci_peaks_mm10 <- unlist(sci_peaks_mm10)sci.counts <- sci.counts[names(sci_peaks_mm10), ]# rename peaks with mm10 coordinatesrownames(sci.counts) <- GRangesToString(grange = sci_peaks_mm10)# create Seurat object and perform some basic QC filtering# 构建Seurat对象sci <- CreateSeuratObject(counts = sci.counts,meta.data = sci.metadata,assay = 'peaks',project = 'sci')# 数据过滤sci.ds <- sci[, sci$nFeature_peaks > 2000 & sci$nCount_peaks > 5000 & !(sci$cell_label %in% c("Collisions", "Unknown"))]sci$tech <- 'sciATAC'# 使用RunTFIDF函数进行数据归一化sci <- RunTFIDF(sci)# 使用FindTopFeatures函数提取高变异的peakssci <- FindTopFeatures(sci, min.cutoff = 50)# 使用RunSVD函数进行线性降维sci <- RunSVD(sci, n = 30, reduction.name = 'lsi', reduction.key = 'LSI_')# 使用RunUMAP函数进行非线性降维sci <- RunUMAP(sci, reduction = 'lsi', dims = 2:30)
现在,我们构建好了两个scATAC-seq对象,并且它们都含有基于相同的mm10参考基因组坐标系统得到的peaks信息。但是,由于这两个实验都单独进行了peak calling,因此这两个数据集中得到的peaks坐标不太可能完全重叠。为了在我们要整合的数据集中具有共同的特征,我们可以基于10x Genomics数据集对sci-ATAC-seq中peaks的reads进行计数,并使用这些计数创建一个新的assay。
# find peaks that intersect in both datasets# 使用GetIntersectingFeatures函数提取两个数据集中重叠的peak区域intersecting.regions <- GetIntersectingFeatures(object.1 = sci,object.2 = tenx,sep.1 = c("-", "-"),sep.2 = c(":", "-"))# choose a subset of intersecting peakspeaks.use <- sample(intersecting.regions[[1]], size = 10000, replace = FALSE)# count fragments per cell overlapping the set of peaks in the 10x data# 使用FeatureMatrix函数对peaks中的reads进行计数sci_peaks_tenx <- FeatureMatrix(fragments = GetFragments(object = tenx, assay = 'peaks'),features = StringToGRanges(peaks.use),cells = colnames(tenx))# create a new assay and add it to the 10x dataset# 使用CreateAssayObject函数新建一个assay对象tenx[['sciPeaks']] <- CreateAssayObject(counts = sci_peaks_tenx, min.cells = 1)# 数据归一化tenx <- RunTFIDF(object = tenx, assay = 'sciPeaks')
多样本scATAC-seq数据集的整合
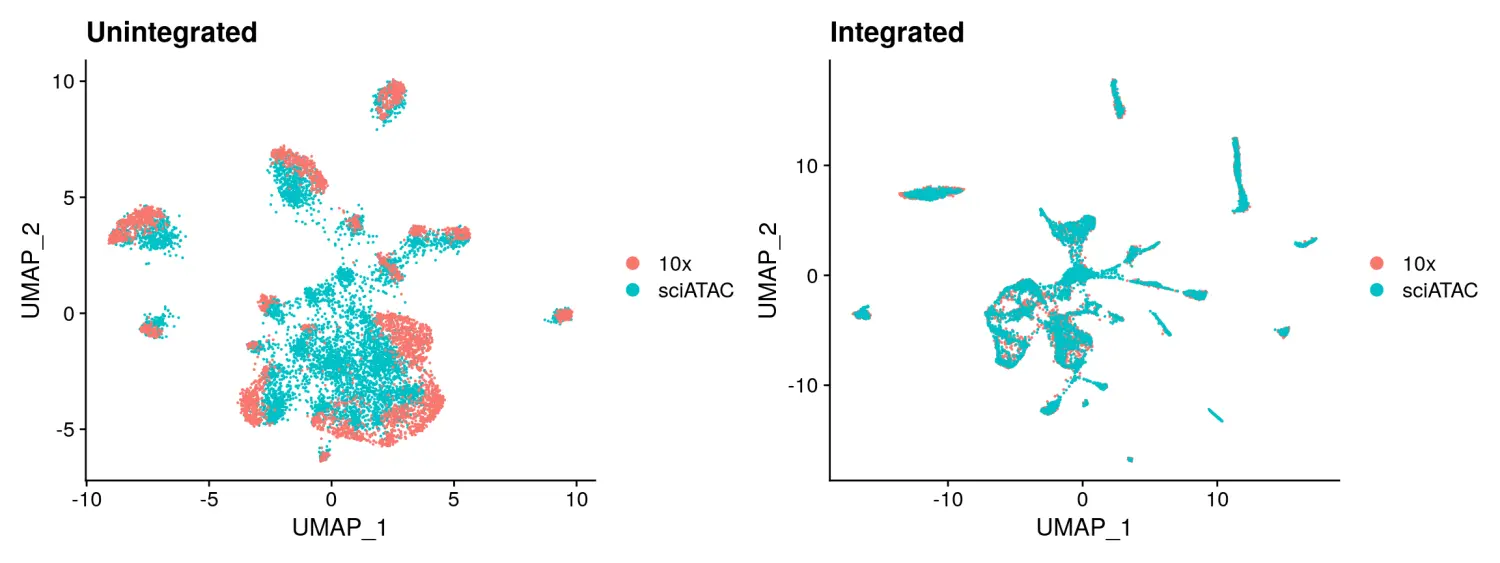
在进行数据整合之前,我们最好先检查下是否存在数据集特异的差异,并将其删除。如果没有,我们可以简单地将多个对象进行合并而不执行整合。在本示例中,由于使用不同的测序技术,两个数据集之间存在很大的差异。我们可以使用Seurat v3中的数据整合方法来消除这种影响。
# 先简单的将两个数据集进行合并看一下聚类的效果# Look at the data without integration first# 使用MergeWithRegions函数将两个数据对象进行合并unintegrated <- MergeWithRegions(object.1 = sci,object.2 = tenx,assay.1 = 'peaks',assay.2 = 'sciPeaks',sep.1 = c("-", "-"),sep.2 = c("-", "-"))# 对合并后数据进行归一化,特征选择和降维可视化unintegrated <- RunTFIDF(unintegrated)unintegrated <- FindTopFeatures(unintegrated, min.cutoff = 50)unintegrated <- RunSVD(unintegrated, n = 30, reduction.name = 'lsi', reduction.key = 'LSI_')unintegrated <- RunUMAP(unintegrated, reduction = 'lsi', dims = 2:30)p1 <- DimPlot(unintegrated, group.by = 'tech', pt.size = 0.1) + ggplot2::ggtitle("Unintegrated")# 使用Seurat v3的数据整合方法进行数据集的整合# find integration anchors between 10x and sci-ATAC# 使用FindIntegrationAnchors函数识别共享的整合anchorsanchors <- FindIntegrationAnchors(object.list = list(tenx, sci),anchor.features = peaks.use,assay = c('sciPeaks', 'peaks'),k.filter = NA)# integrate data and create a new merged object# 使用IntegrateData函数根据识别的anchors进行数据整合integrated <- IntegrateData(anchorset = anchors,weight.reduction = sci[['lsi']],dims = 2:30,preserve.order = TRUE)# we now have a "corrected" TF-IDF matrix, and can run LSI again on this corrected matrix# 对整合后的数据进行降维可视化integrated <- RunSVD(object = integrated,n = 30,reduction.name = 'integratedLSI')integrated <- RunUMAP(object = integrated,dims = 2:30,reduction = 'integratedLSI')p2 <- DimPlot(integrated, group.by = 'tech', pt.size = 0.1) + ggplot2::ggtitle("Integrated")p1 + p2
Label transfer
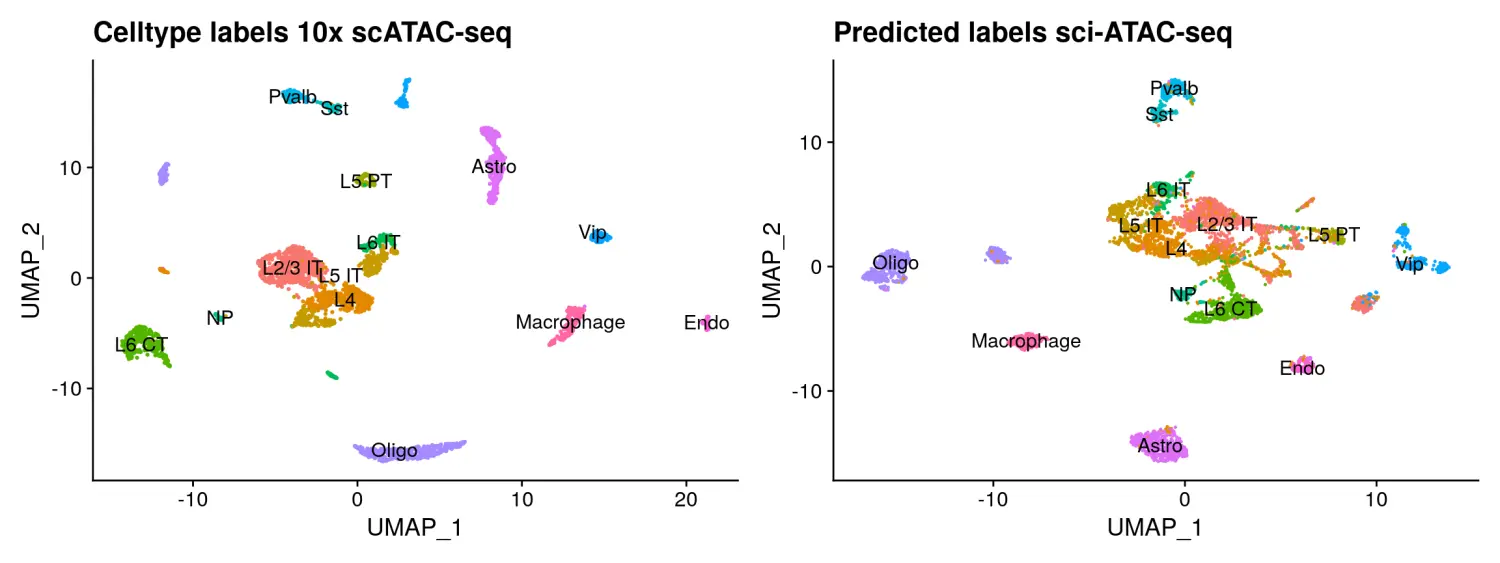
我们还可以使用Seurat v3中的Label transfer方法进行数据集的整合,它将数据从一个query数据集映射到另一个reference数据集中。在这里,我们通过将细胞类型标签从10x Genomics scATAC-seq数据映射到到sci-ATAC-seq数据中。
# 使用FindTransferAnchors函数识别整合的anchorstransfer.anchors <- FindTransferAnchors(reference = tenx,query = sci,reference.assay = 'sciPeaks',query.assay = 'peaks',reduction = 'cca',features = peaks.use,k.filter = NA)# 使用TransferData函数基于识别好的anchors进行数据映射整合predicted.id <- TransferData(anchorset = transfer.anchors,refdata = tenx$celltype,weight.reduction = sci[['lsi']],dims = 2:30)sci <- AddMetaData(object = sci,metadata = predicted.id)sci$predicted.id <- factor(sci$predicted.id, levels = levels(tenx$celltype)) # to make the colors match# 数据可视化p3 <- DimPlot(tenx, group.by = 'celltype', label = TRUE) + NoLegend() + ggplot2::ggtitle("Celltype labels 10x scATAC-seq")p4 <- DimPlot(sci, group.by = 'predicted.id', label = TRUE) + NoLegend() + ggplot2::ggtitle("Predicted labels sci-ATAC-seq")p3 + p4
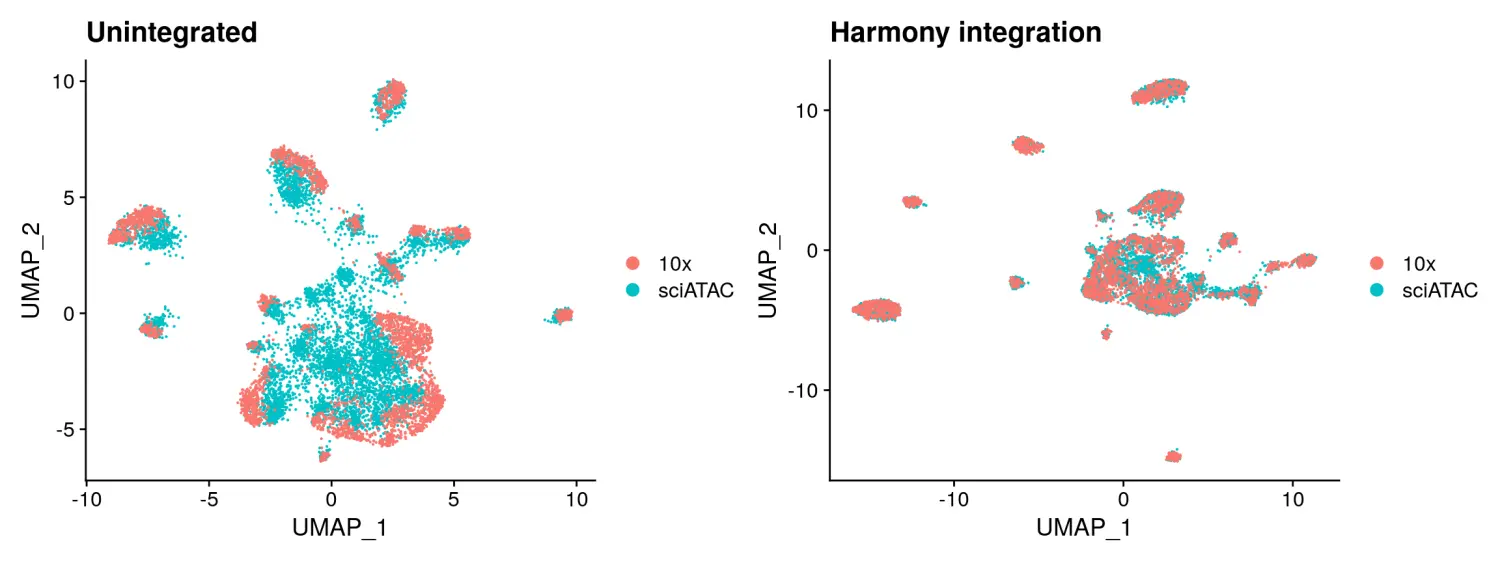
Integration with Harmony 使用Harmony包进行数据整合
Harmony需要一个对象作为输入,因此这里我们使用MergeWithRegions函数以coordinate-aware的方式将sci-ATAC-seq数据集和10x的scATAC-seq数据集进行合并,然后对合并后的对象进行LSI线性降维。数据降维后,我们可以使用RunHarmony函数调用Harmony的方法进行数据的整合,并提供用作分组变量的技术来消除sci-ATAC-seq和10x Genomics scATAC-seq数据集之间的批次差异。这会产生一组“校正”的LSI嵌入,可以进一步用于UMAP或tSNE降维,并进行细胞聚类分群。
# 加载harmony包library(harmony)# 使用RunHarmony函数进行数据整合hm.integrated <- RunHarmony(object = unintegrated,group.by.vars = 'tech',reduction = 'lsi',assay.use = 'peaks',project.dim = FALSE)# re-compute the UMAP using corrected LSI embeddings# 数据降维可视化hm.integrated <- RunUMAP(hm.integrated, dims = 2:30, reduction = 'harmony')p5 <- DimPlot(hm.integrated, group.by = 'tech', pt.size = 0.1) + ggplot2::ggtitle("Harmony integration")p1 + p5