在本文中,您将学习使用for循环的不同变体对元素序列进行迭代。
什么是 Python 中的for循环?
Python 中的for循环用于迭代序列(列表,元组,字符串)或其他可迭代对象。 在序列上进行迭代称为遍历。
for循环的语法
for val in sequence:Body of for
在这里,val是在每次迭代中获取序列内项目值的变量。
循环继续,直到我们到达序列中的最后一项。 for循环的主体使用缩进与其余代码分开。
for循环流程图
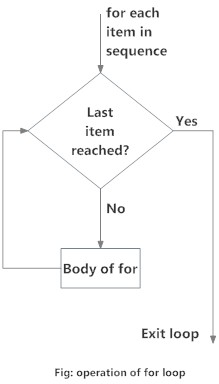
Python 中for循环的流程图
示例:Python for循环
# Program to find the sum of all numbers stored in a list# List of numbersnumbers = [6, 5, 3, 8, 4, 2, 5, 4, 11]# variable to store the sumsum = 0# iterate over the listfor val in numbers:sum = sum+valprint("The sum is", sum)
运行该程序时,输出为:
The sum is 48
range()函数
我们可以使用range()函数生成数字序列。range(10)将生成 0 到 9 之间的数字(10 个数字)。
我们还可以将开始,停止和步长定义为range(start, stop,step_size)。 如果未提供,则step_size默认为 1。
从某种意义上讲,range对象是“惰性”的,因为在创建它时,它不会生成它“包含”的每个数字。 但是,它不是迭代器,因为它支持in,len和__getitem__操作。
此函数不会将所有值存储在内存中; 这将是低效的。 因此它会记住开始,停止,步长并在旅途中生成下一个数字。
要强制此函数输出所有项目,我们可以使用函数list()。
以下示例将阐明这一点。
print(range(10))print(list(range(10)))print(list(range(2, 8)))print(list(range(2, 20, 3)))
输出
range(0, 10)[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9][2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7][2, 5, 8, 11, 14, 17]
我们可以在for循环中使用range()函数来迭代数字序列。 它可以与len()函数结合使用索引来遍历序列。 这是一个例子。
# Program to iterate through a list using indexinggenre = ['pop', 'rock', 'jazz']# iterate over the list using indexfor i in range(len(genre)):print("I like", genre[i])
输出:
I like popI like rockI like jazz
循环与else
for循环也可以具有可选的else块。 如果for循环的序列中的项目用尽,则会执行else部分。
break关键字可用于停止for循环。 在这种情况下,其他部分将被忽略。
因此,如果没有中断发生,则for循环的else部分将运行。
这是一个例子来说明这一点。
digits = [0, 1, 5]for i in digits:print(i)else:print("No items left.")
当你运行程序时,输出将是:
015No items left.
在这里,for循环打印列表中的项目,直到循环用尽。 当for循环用完时,它将执行else中的代码块并打印。
仅当未执行break关键字时,此for...else语句才能与break关键字一起使用以运行else块。 让我们举个例子:
# program to display student's marks from recordstudent_name = 'Soyuj'marks = {'James': 90, 'Jules': 55, 'Arthur': 77}for student in marks:if student == student_name:print(marks[student])breakelse:print('No entry with that name found.')
输出:
No entry with that name found.

