在本教程中,您将学习二叉搜索树的工作原理。 此外,您还将找到 C,C++ ,Java 和 Python 中的二叉搜索树的工作示例。
二叉搜索树是一种数据结构,可快速使我们维护一个排序的数字列表。
- 之所以称为二叉树,是因为每个树节点最多有两个子节点。
- 之所以称为搜索树,是因为它可用于在
O(log(n))时间中搜索数字的存在。
将二叉搜索树与常规二叉树分开的属性是
- 左子树的所有节点均小于根节点
- 右子树的所有节点均大于根节点
- 每个节点的两个子树也是 BST,即它们具有上述两个属性
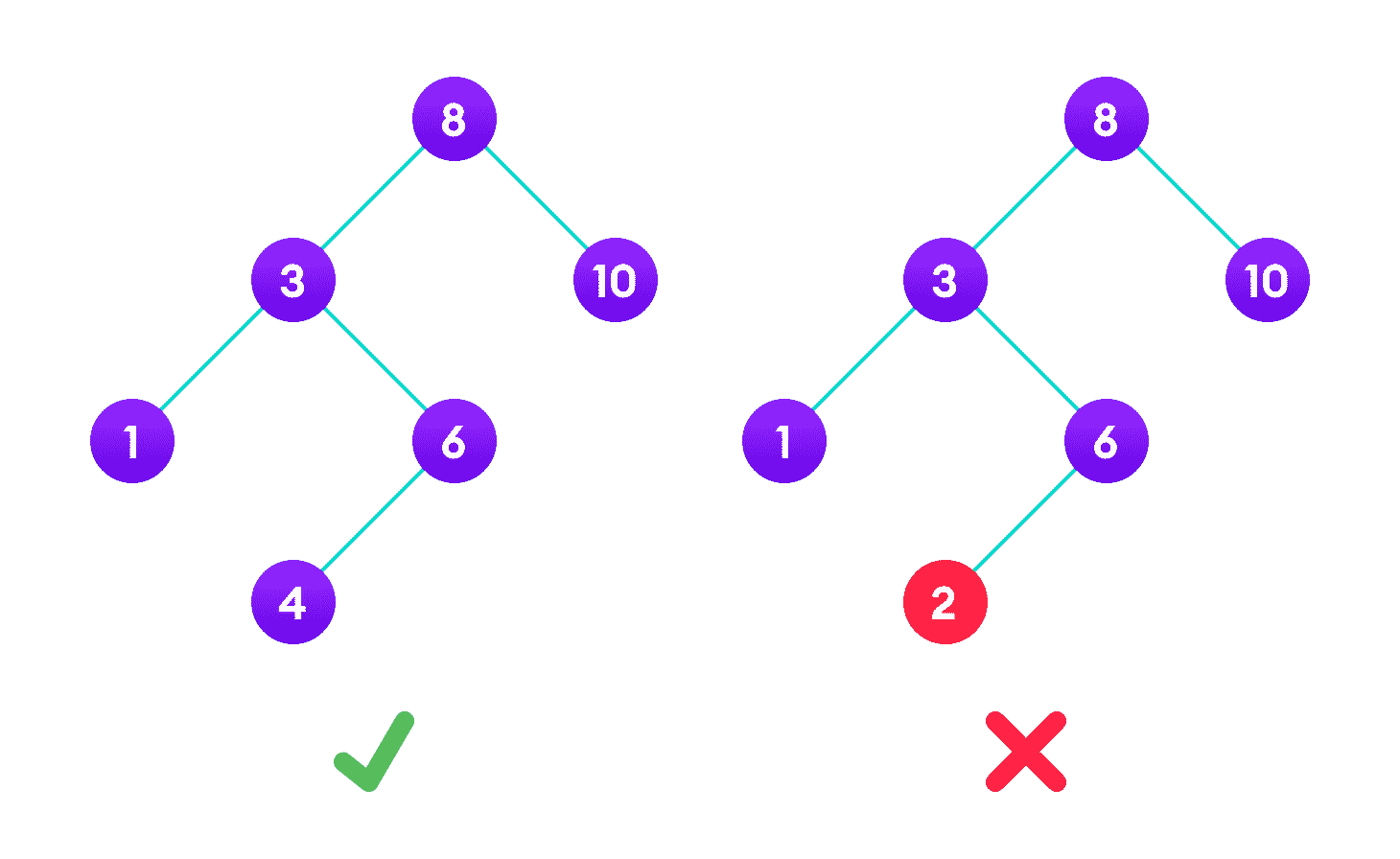
显示了一个树,该树的右子树的值小于根,表明该树不是有效的二叉搜索树
右边的二叉树不是二叉搜索树,因为节点“3”的右子树包含的值小于它。
您可以对二叉搜索树执行两个基本操作:
搜索操作
该算法取决于 BST 的属性,即每个左子树的值都低于根,而每个右子树的值都高于根。
如果该值低于根,则可以确定该值不在正确的子树中。 我们只需要在左子树中搜索,如果该值在根之上,则可以肯定地说该值不在左子树中; 我们只需要在正确的子树中搜索。
算法:
If root == NULLreturn NULL;If number == root->datareturn root->data;If number < root->datareturn search(root->left)If number > root->datareturn search(root->right)
让我们尝试通过图表将其可视化。

找不到 4,因此遍历 8 的左子树
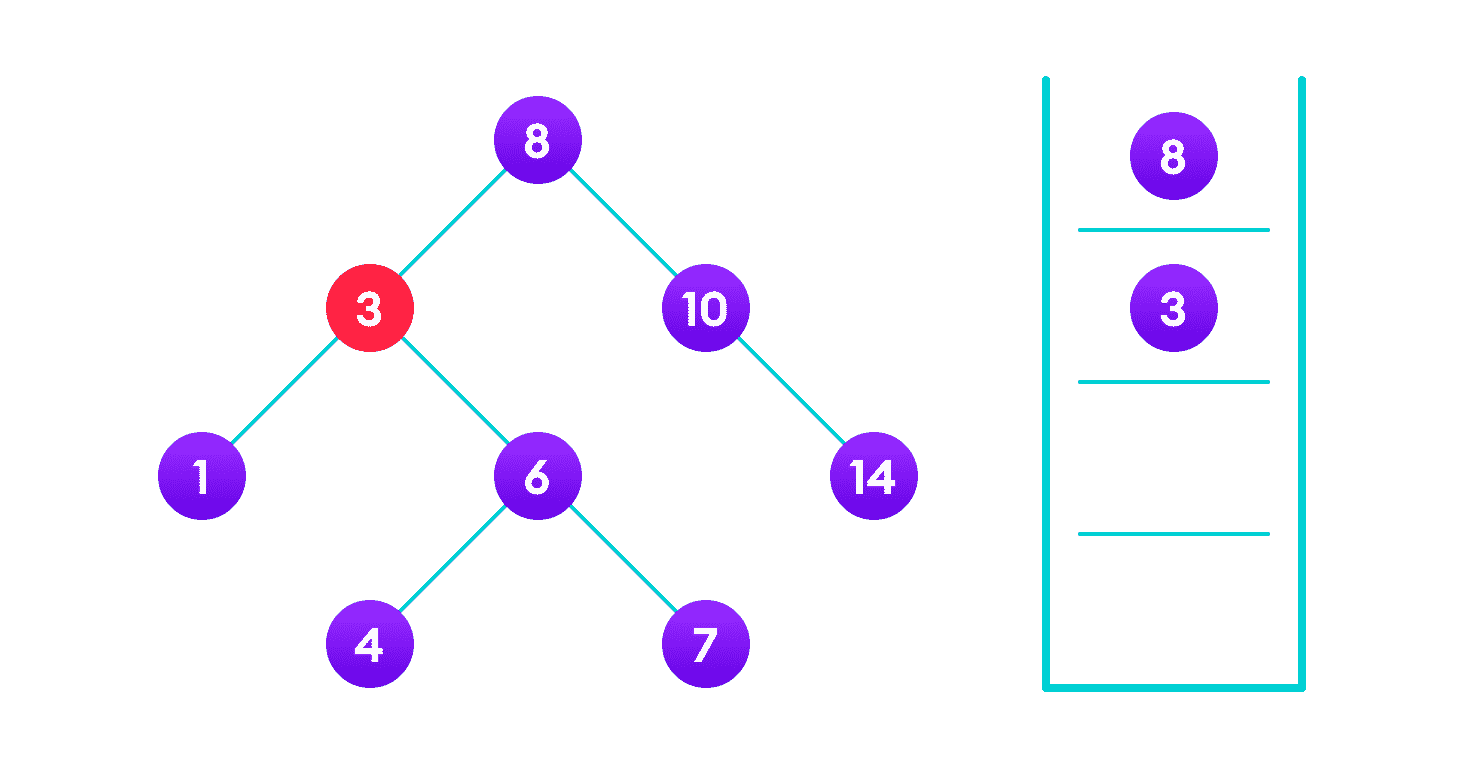
找不到 4,因此遍历 3 的右子树
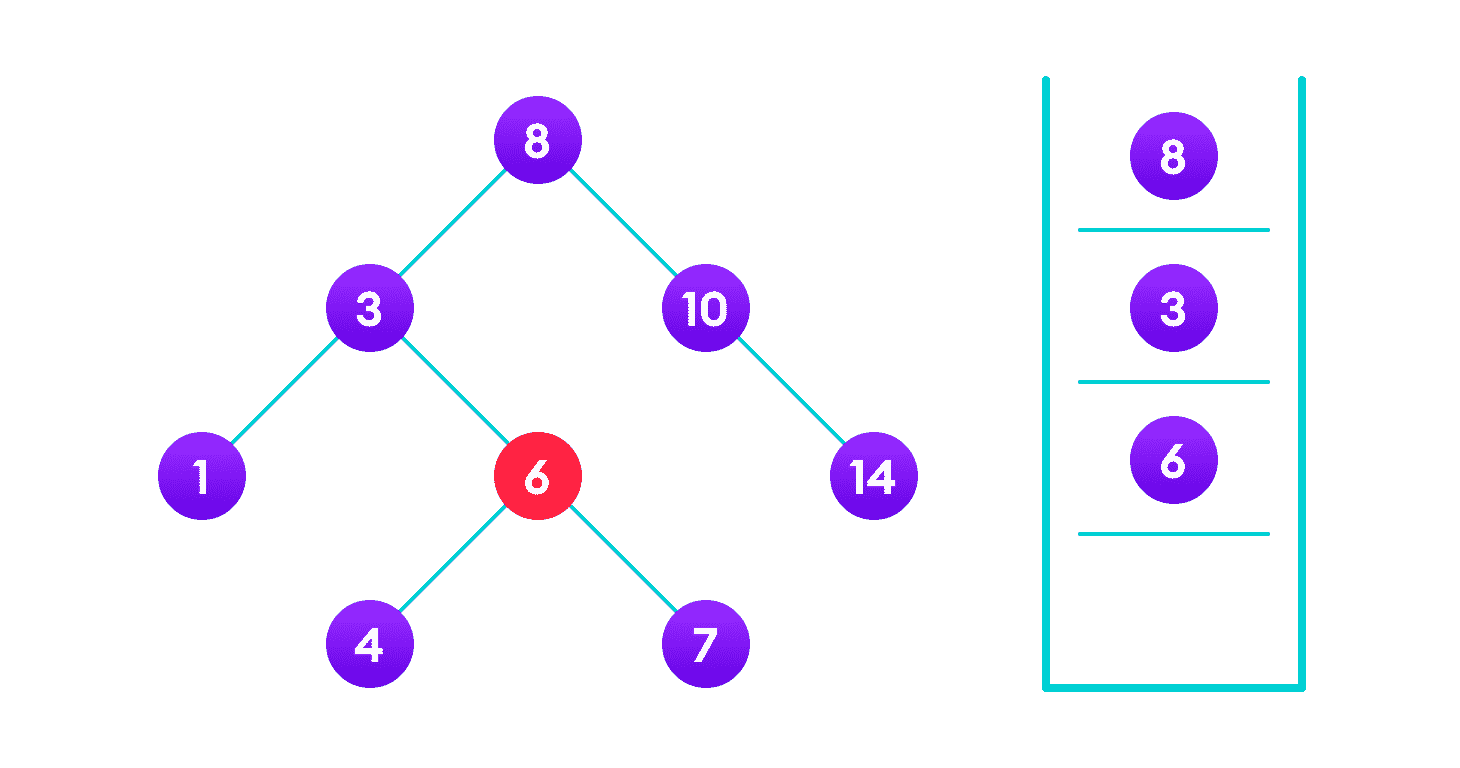
找不到 4,因此遍历 6 的左子树
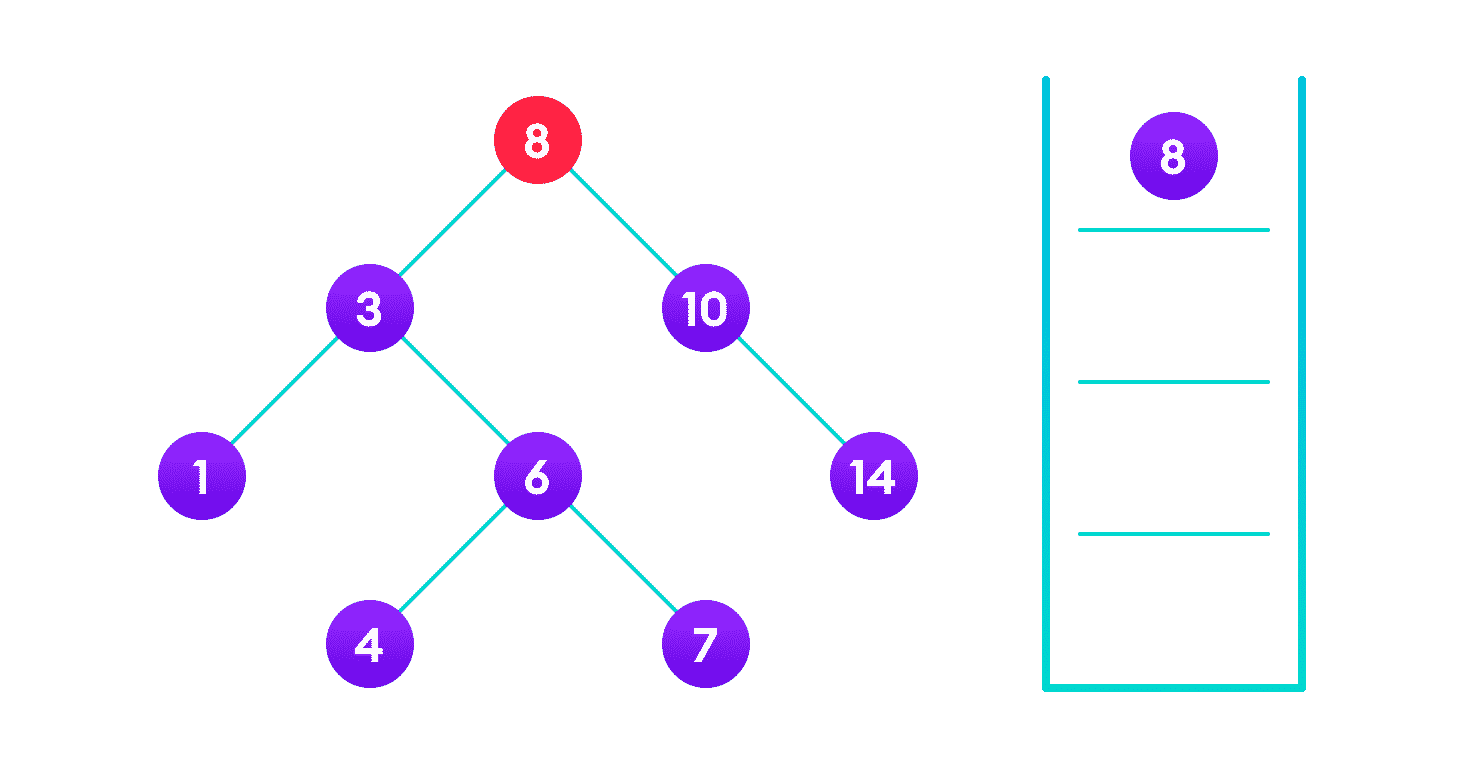
找到了 4
如果找到该值,则返回该值,以便在每个递归步骤中将其传播,如下图所示。
如果您可能已经注意到,我们已经四次调用return search(struct node *)。 当我们返回新节点或NULL时,该值会一次又一次返回,直到search(root)返回最终结果。
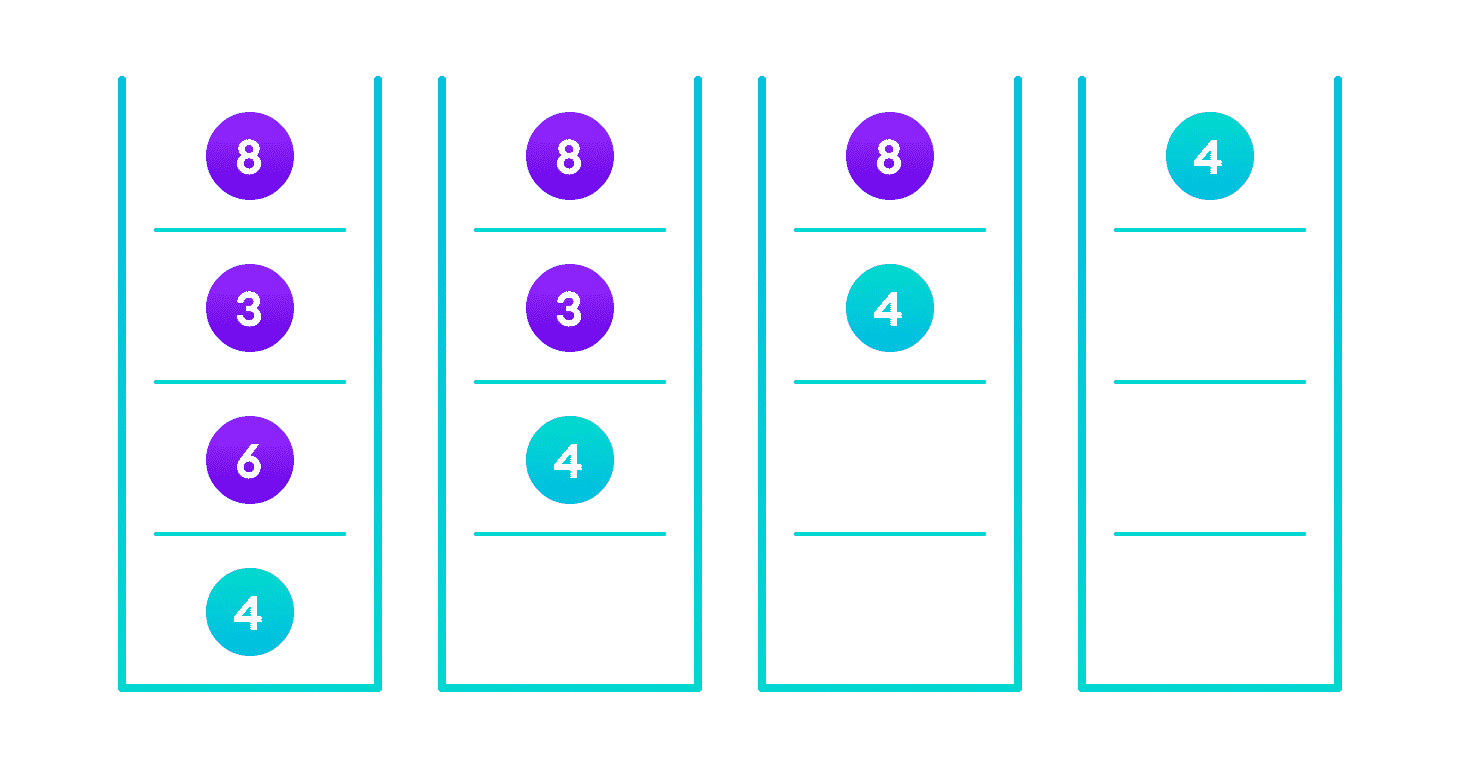
如果在任何子树中找到该值,则将其向上传播,以便最后返回,否则返回null。
如果找不到该值,则最终到达叶节点的左或右子节点,该子节点为NULL,并传播并返回。
插入操作
在正确的位置插入值类似于搜索,因为我们尝试维护以下规则:左子树小于根,右子树大于根。
我们继续根据值去右子树或左子树,当我们到达左或右子树为null的点时,将新节点放在那里。
算法:
If node == NULLreturn createNode(data)if (data < node->data)node->left = insert(node->left, data);else if (data > node->data)node->right = insert(node->right, data);return node;
该算法并不像看起来那样简单。 让我们尝试可视化如何将数字添加到现有的 BST。
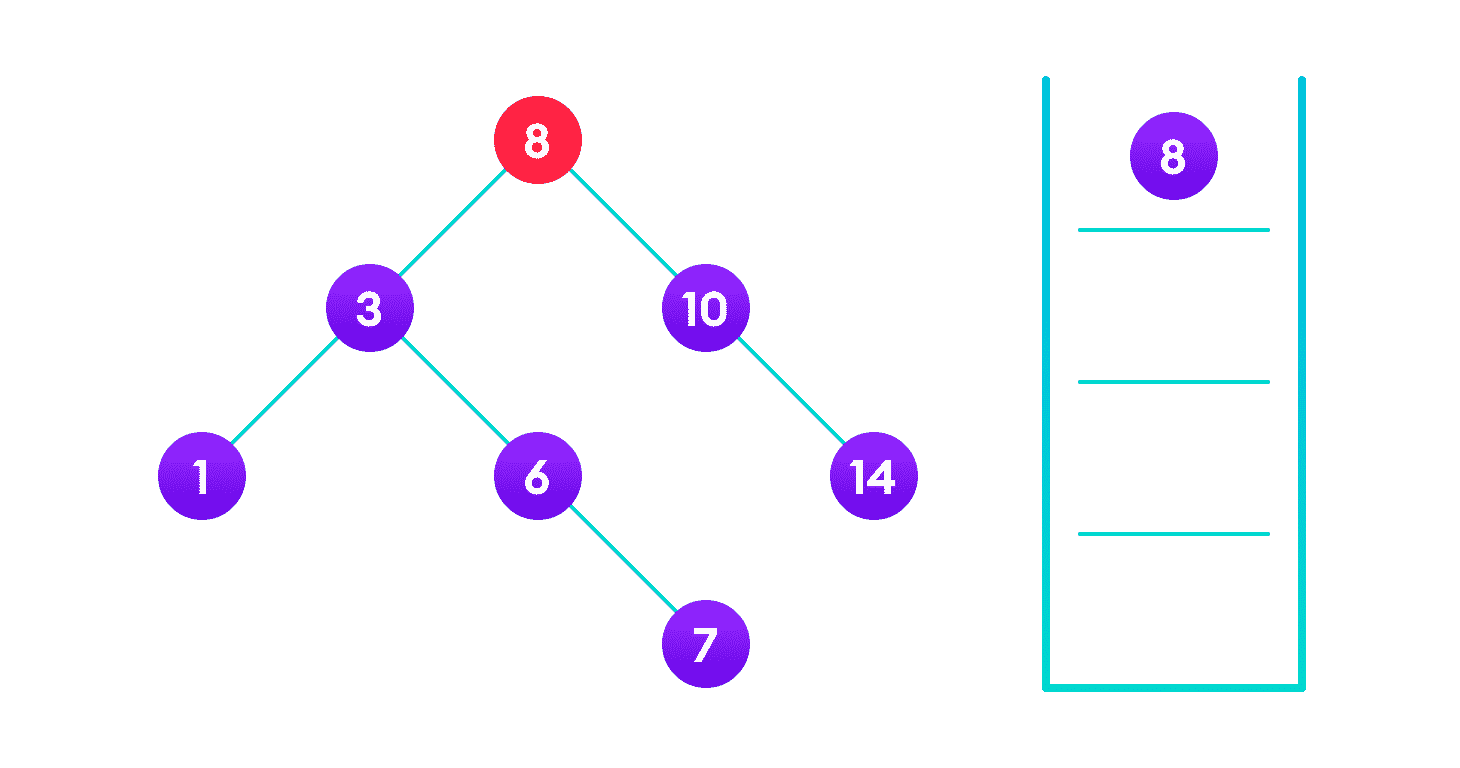
因为4 < 8,遍历 8 的左子树
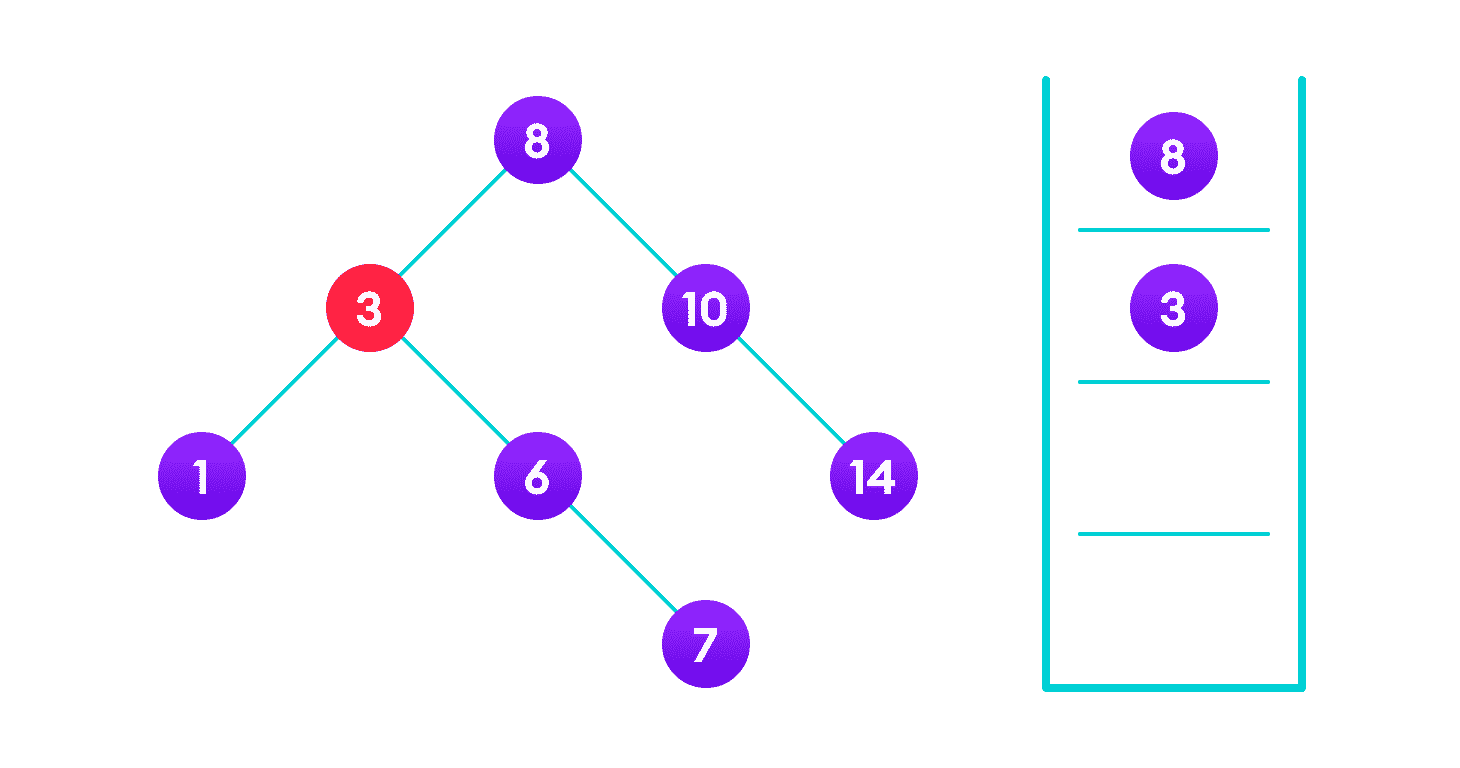
因为4 > 3,遍历 3 的右子树
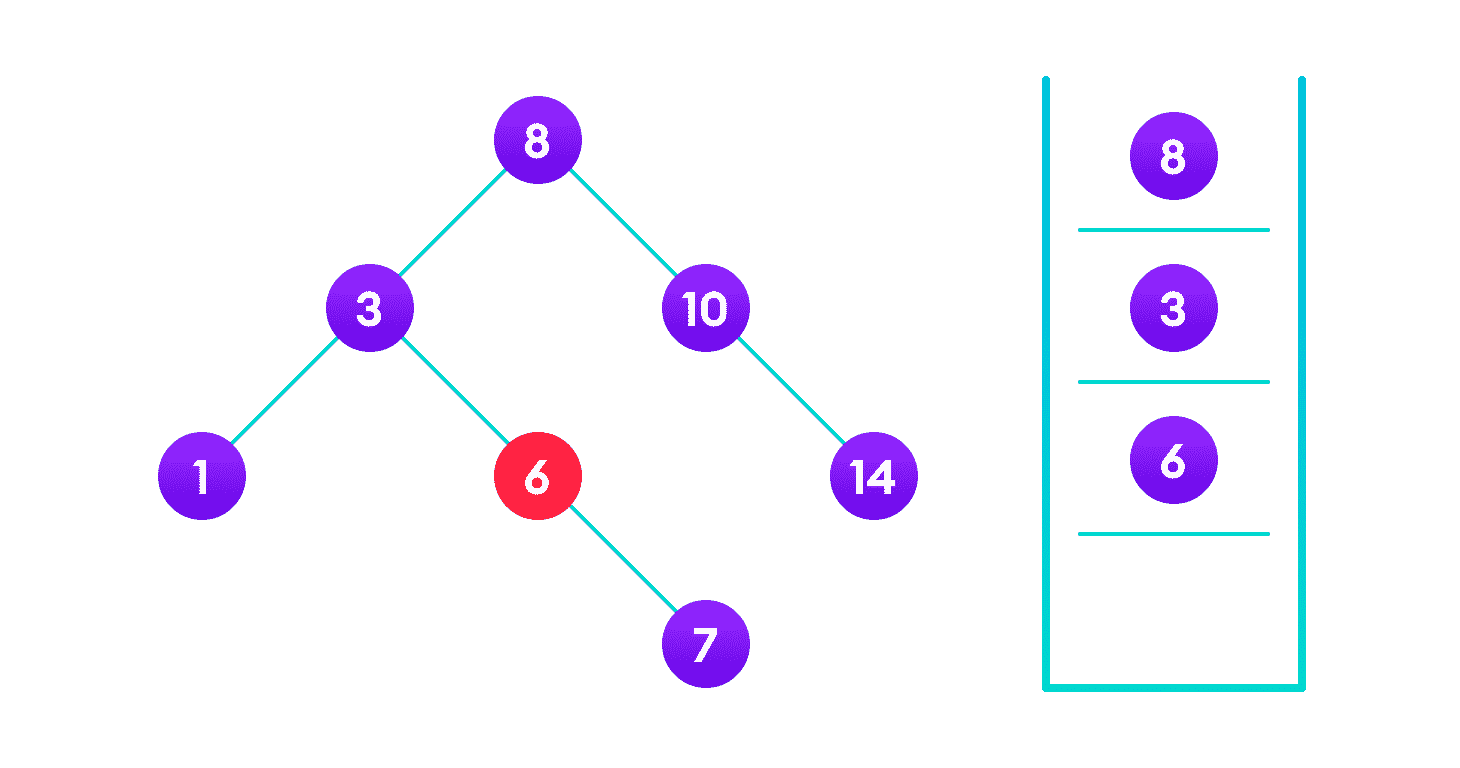
因为4 < 6,遍历 6 的左子树
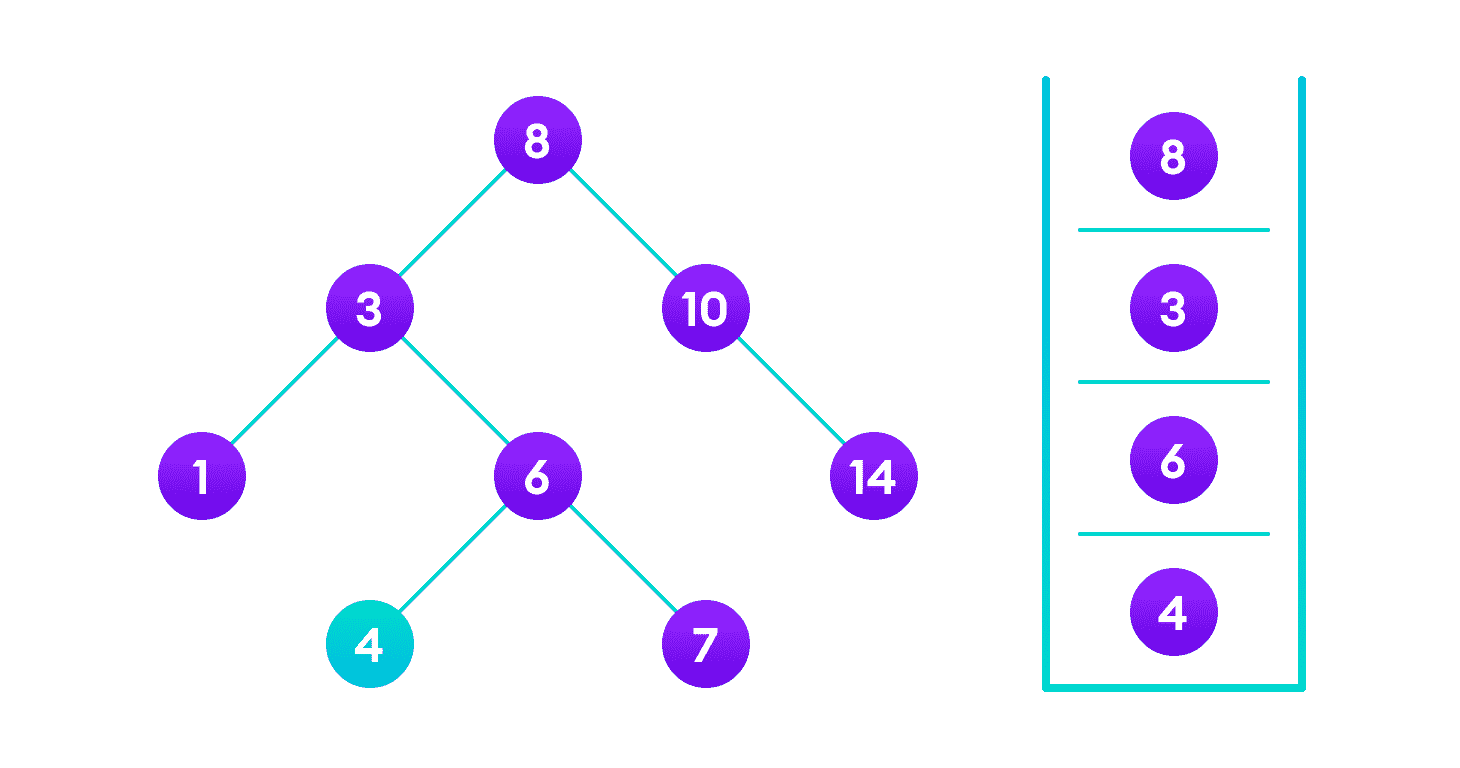
插入 4 作为 6 的左子级
我们已经附加了节点,但是我们仍然必须退出该函数,而不会损坏树的其余部分。 这是最后的return node;派上用场的地方。 在NULL的情况下,将返回新创建的节点并将其附加到父节点,否则在返回到根节点之前,将返回相同的节点,而不会进行任何更改。
这可以确保当我们向后移动树时,其他节点连接不会更改。
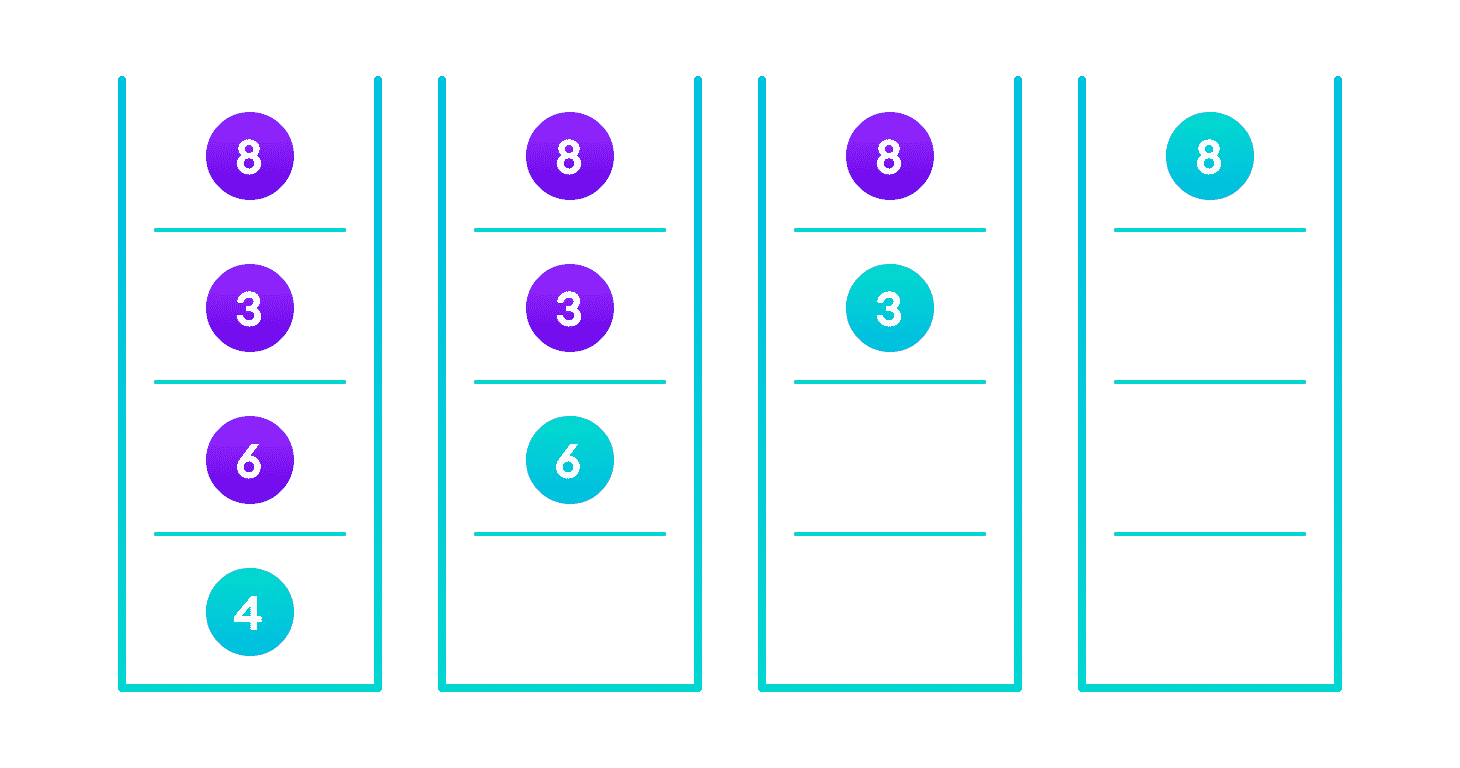
该图显示了在最后返回根元素的重要性,这样根元素才能在向上递归步骤中不丢失其位置。
删除操作
从二叉搜索树中删除节点的情况有三种。
情况一
在第一种情况下,要删除的节点是叶节点。 在这种情况下,只需从树中删除该节点即可。
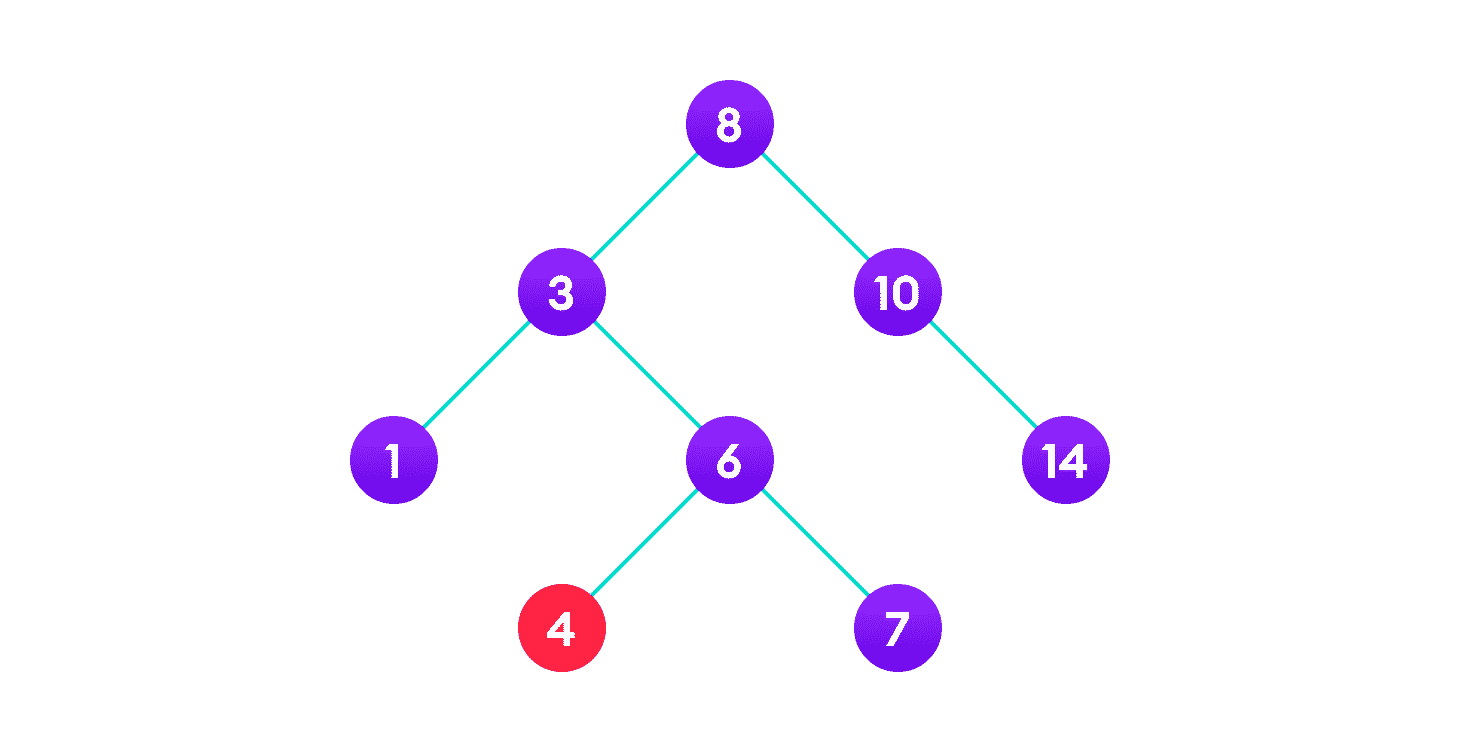
4 将被删除
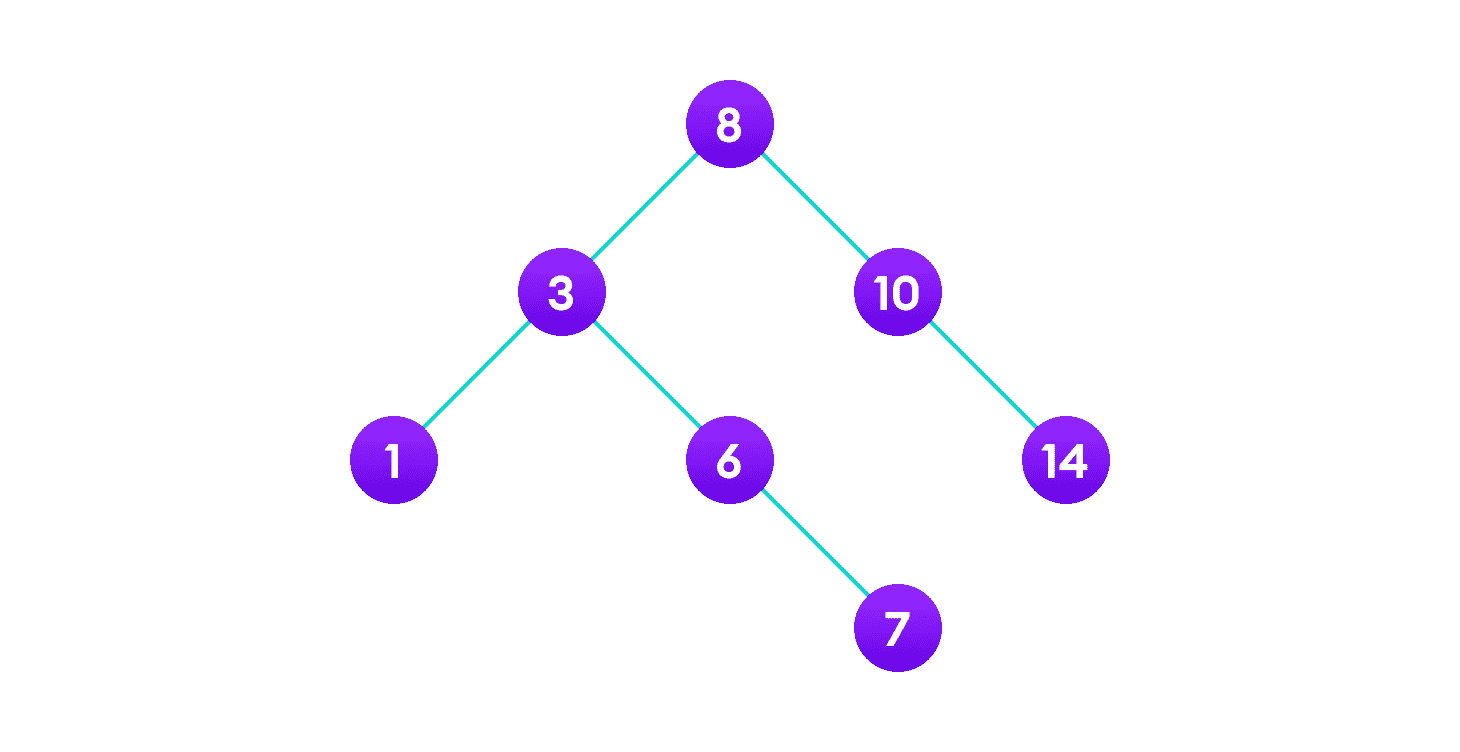
删除节点
情况二
在第二种情况下,要删除的节点只有一个子节点。 在这种情况下,请执行以下步骤:
- 将该节点替换为其子节点。
- 从其原始位置删除子节点。
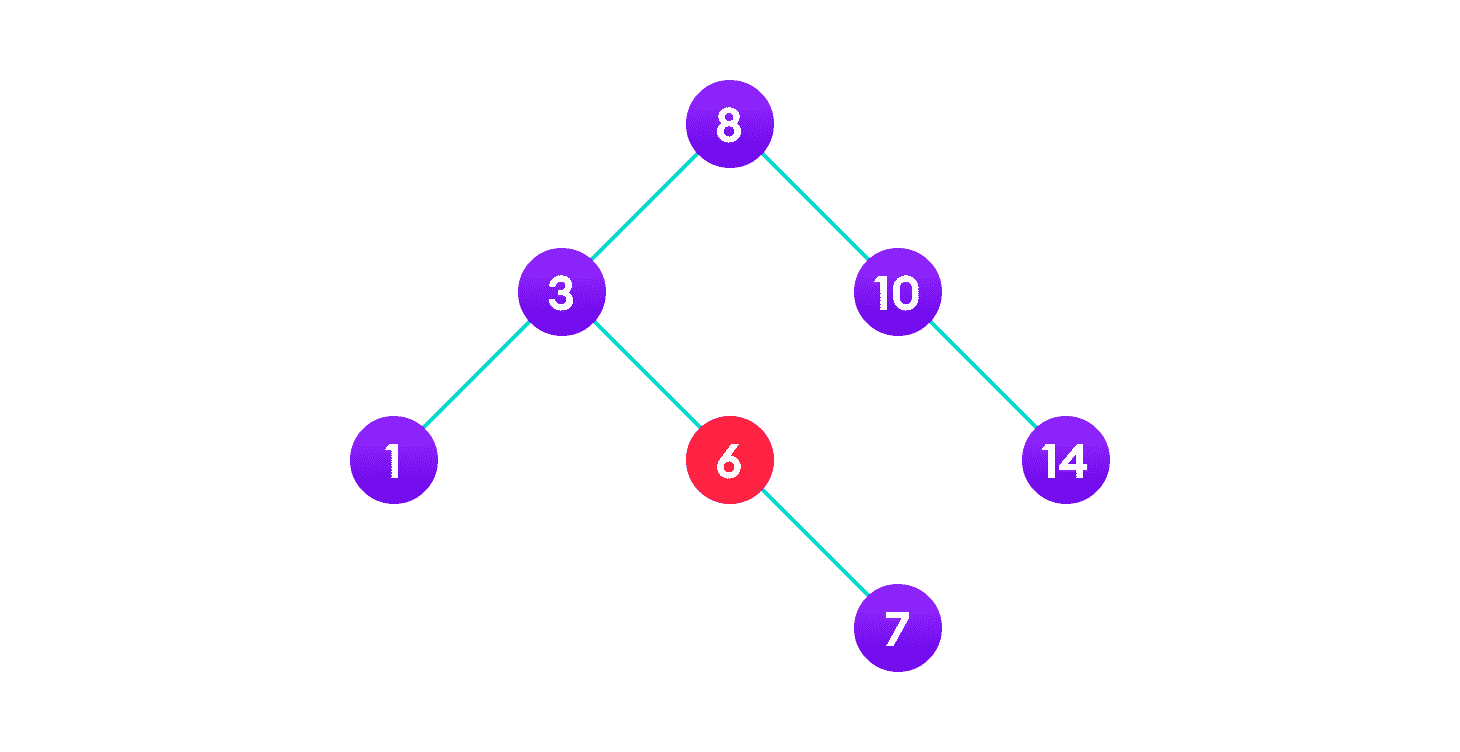
6 将被删除
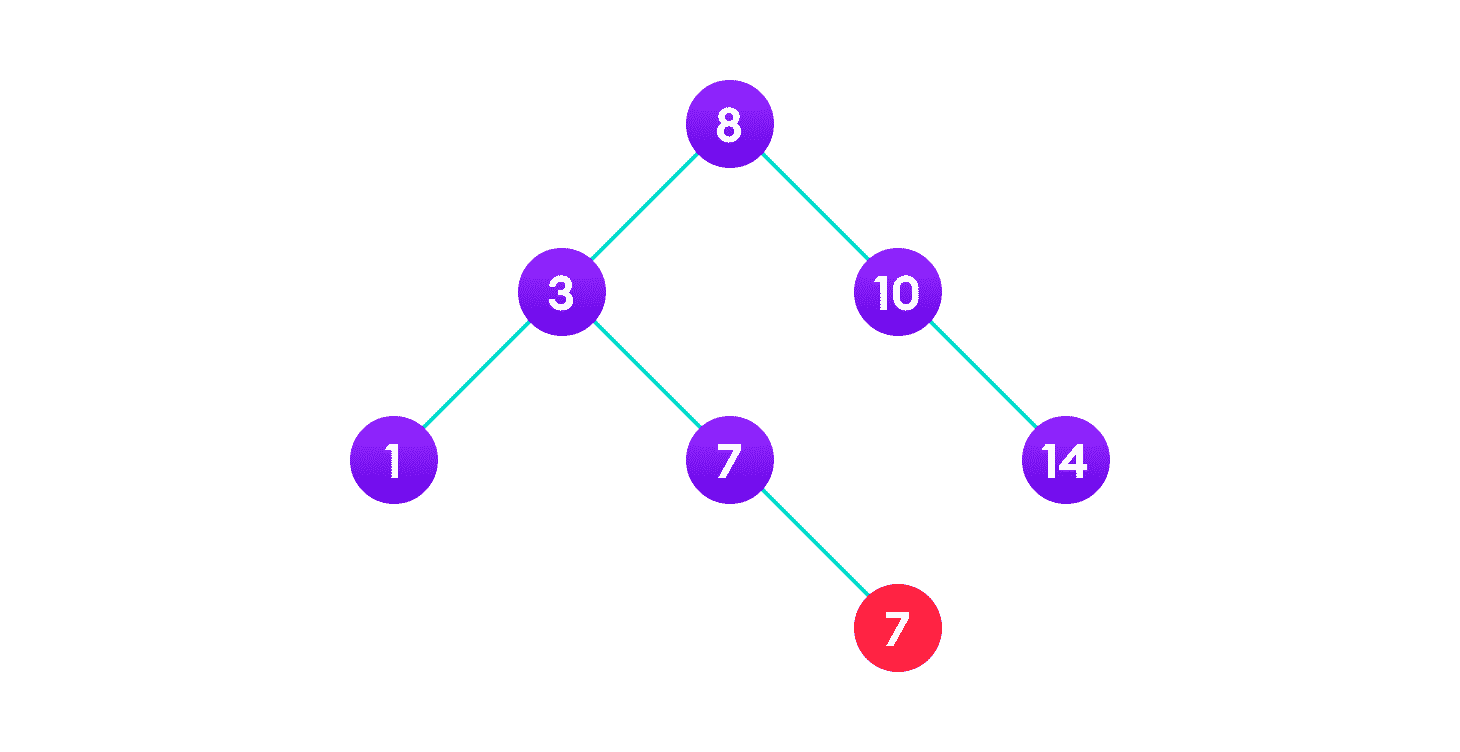
将其子项的值复制到节点并删除该子项
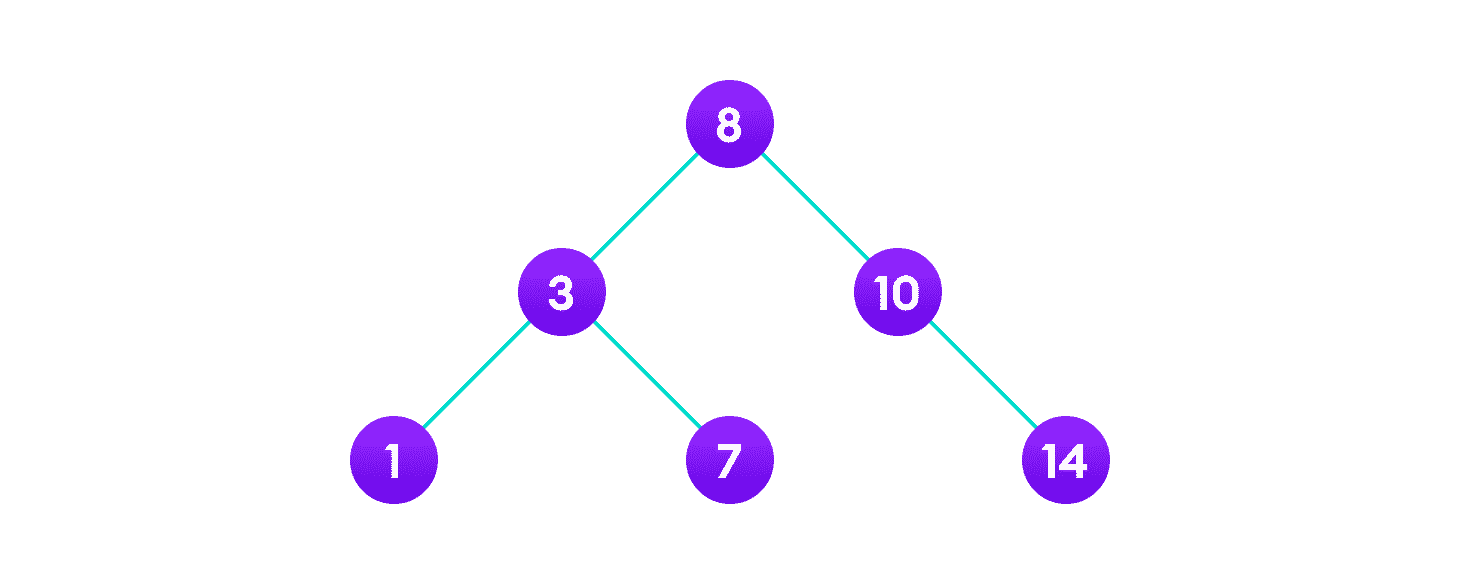
最终的树
情况三
在第三种情况下,要删除的节点有两个子级。 在这种情况下,请执行以下步骤:
- 获取该节点的有序后继。
- 将节点替换为有序后继节点。
- 从原始位置卸下有序后继。

3 将被删除
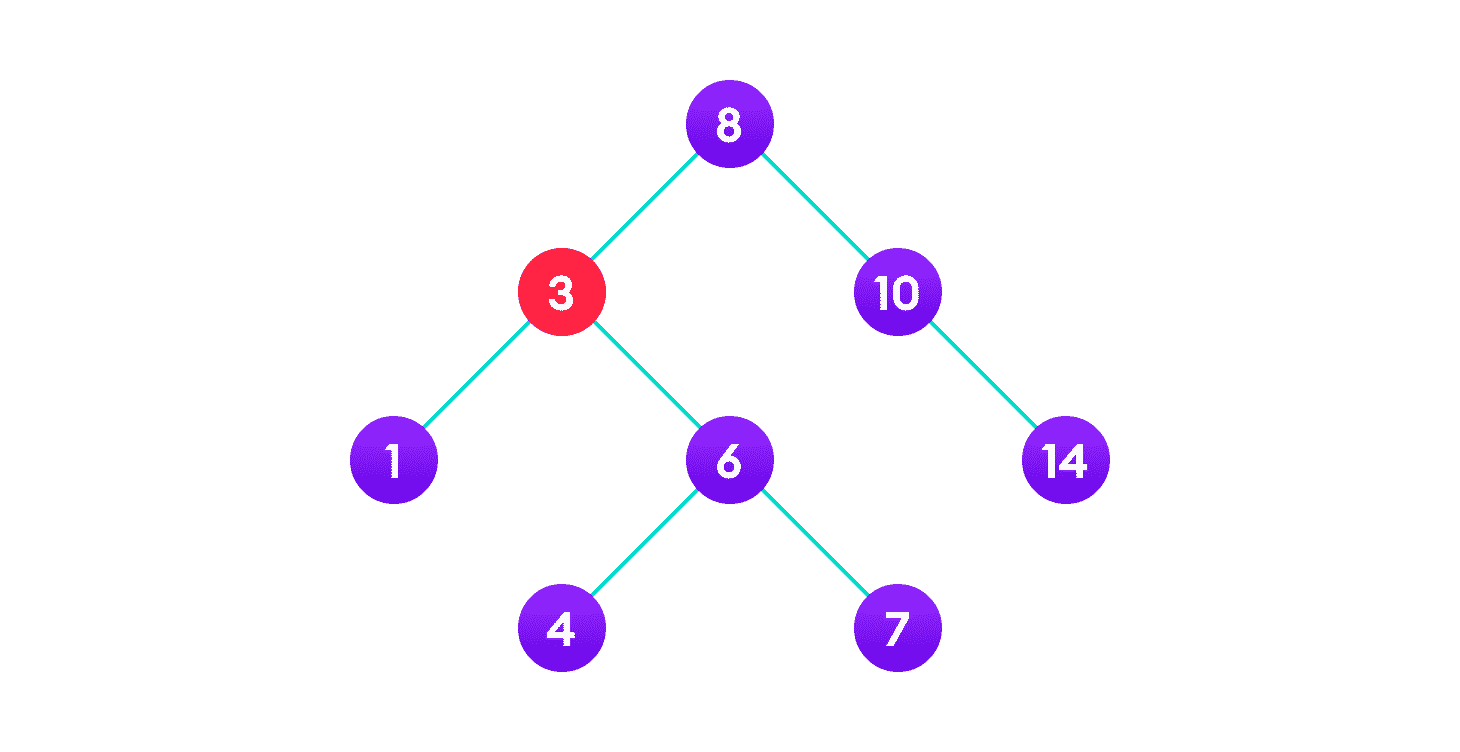
将有序后继(4)的值复制到节点
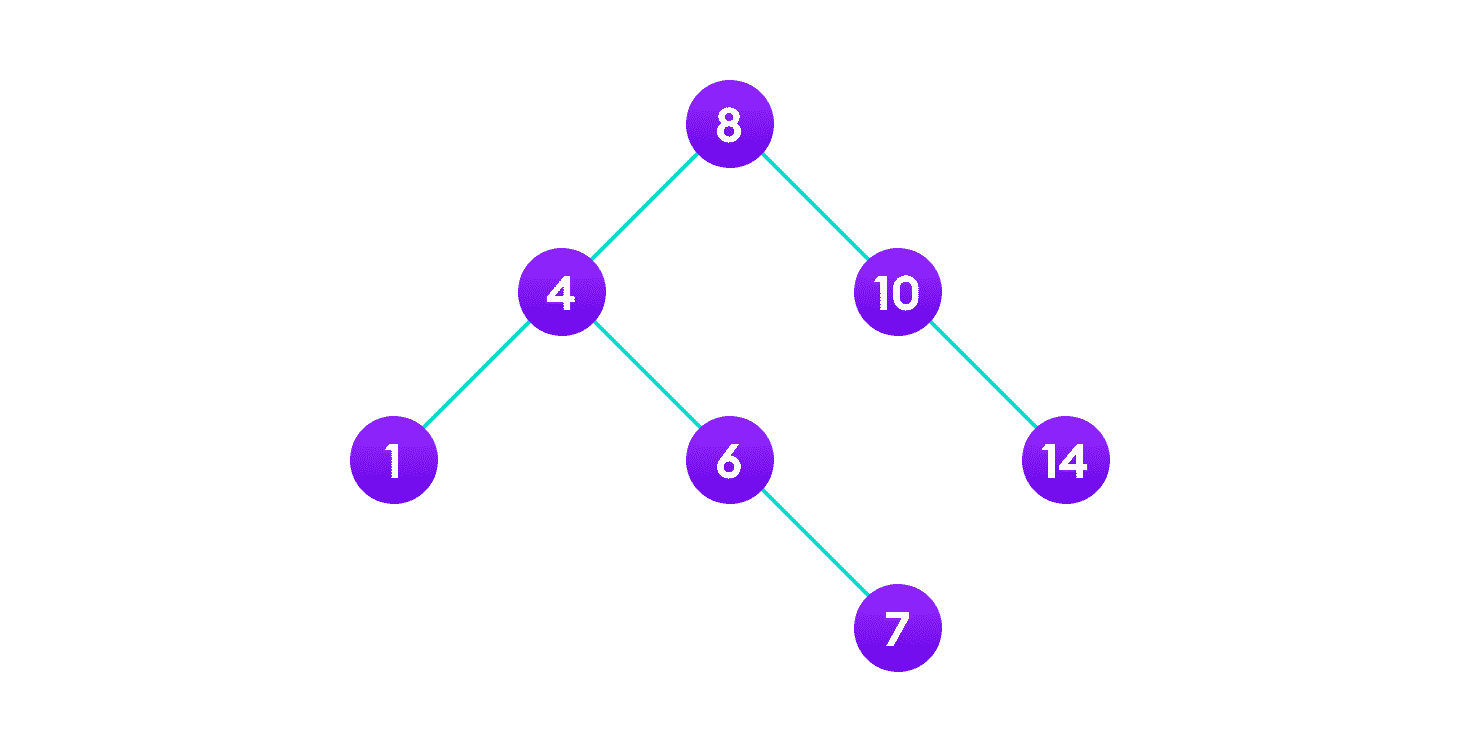
删除顺序后继
Python,Java 和 C/C++ 示例
# Binary Search Tree operations in Python# Create a nodeclass Node:def __init__(self, key):self.key = keyself.left = Noneself.right = None# Inorder traversaldef inorder(root):if root is not None:# Traverse leftinorder(root.left)# Traverse rootprint(str(root.key) + "->", end=' ')# Traverse rightinorder(root.right)# Insert a nodedef insert(node, key):# Return a new node if the tree is emptyif node is None:return Node(key)# Traverse to the right place and insert the nodeif key < node.key:node.left = insert(node.left, key)else:node.right = insert(node.right, key)return node# Find the inorder successordef minValueNode(node):current = node# Find the leftmost leafwhile(current.left is not None):current = current.leftreturn current# Deleting a nodedef deleteNode(root, key):# Return if the tree is emptyif root is None:return root# Find the node to be deletedif key < root.key:root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key)elif(key > root.key):root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key)else:# If the node is with only one child or no childif root.left is None:temp = root.rightroot = Nonereturn tempelif root.right is None:temp = root.leftroot = Nonereturn temp# If the node has two children,# place the inorder successor in position of the node to be deletedtemp = minValueNode(root.right)root.key = temp.key# Delete the inorder successorroot.right = deleteNode(root.right, temp.key)return rootroot = Noneroot = insert(root, 8)root = insert(root, 3)root = insert(root, 1)root = insert(root, 6)root = insert(root, 7)root = insert(root, 10)root = insert(root, 14)root = insert(root, 4)print("Inorder traversal: ", end=' ')inorder(root)print("\nDelete 10")root = deleteNode(root, 10)print("Inorder traversal: ", end=' ')inorder(root)
// Binary Search Tree operations in Javaclass BinarySearchTree {class Node {int key;Node left, right;public Node(int item) {key = item;left = right = null;}}Node root;BinarySearchTree() {root = null;}void insert(int key) {root = insertKey(root, key);}// Insert key in the treeNode insertKey(Node root, int key) {// Return a new node if the tree is emptyif (root == null) {root = new Node(key);return root;}// Traverse to the right place and insert the nodeif (key < root.key)root.left = insertKey(root.left, key);else if (key > root.key)root.right = insertKey(root.right, key);return root;}void inorder() {inorderRec(root);}// Inorder Traversalvoid inorderRec(Node root) {if (root != null) {inorderRec(root.left);System.out.print(root.key + " -> ");inorderRec(root.right);}}void deleteKey(int key) {root = deleteRec(root, key);}Node deleteRec(Node root, int key) {// Return if the tree is emptyif (root == null)return root;// Find the node to be deletedif (key < root.key)root.left = deleteRec(root.left, key);else if (key > root.key)root.right = deleteRec(root.right, key);else {// If the node is with only one child or no childif (root.left == null)return root.right;else if (root.right == null)return root.left;// If the node has two children// Place the inorder successor in position of the node to be deletedroot.key = minValue(root.right);// Delete the inorder successorroot.right = deleteRec(root.right, root.key);}return root;}// Find the inorder successorint minValue(Node root) {int minv = root.key;while (root.left != null) {minv = root.left.key;root = root.left;}return minv;}// Driver Program to test above functionspublic static void main(String[] args) {BinarySearchTree tree = new BinarySearchTree();tree.insert(8);tree.insert(3);tree.insert(1);tree.insert(6);tree.insert(7);tree.insert(10);tree.insert(14);tree.insert(4);System.out.print("Inorder traversal: ");tree.inorder();System.out.println("\n\nAfter deleting 10");tree.deleteKey(10);System.out.print("Inorder traversal: ");tree.inorder();}}
// Binary Search Tree operations in C#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>struct node {int key;struct node *left, *right;};// Create a nodestruct node *newNode(int item) {struct node *temp = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));temp->key = item;temp->left = temp->right = NULL;return temp;}// Inorder Traversalvoid inorder(struct node *root) {if (root != NULL) {// Traverse leftinorder(root->left);// Traverse rootprintf("%d -> ", root->key);// Traverse rightinorder(root->right);}}// Insert a nodestruct node *insert(struct node *node, int key) {// Return a new node if the tree is emptyif (node == NULL) return newNode(key);// Traverse to the right place and insert the nodeif (key < node->key)node->left = insert(node->left, key);elsenode->right = insert(node->right, key);return node;}// Find the inorder successorstruct node *minValueNode(struct node *node) {struct node *current = node;// Find the leftmost leafwhile (current && current->left != NULL)current = current->left;return current;}// Deleting a nodestruct node *deleteNode(struct node *root, int key) {// Return if the tree is emptyif (root == NULL) return root;// Find the node to be deletedif (key < root->key)root->left = deleteNode(root->left, key);else if (key > root->key)root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key);else {// If the node is with only one child or no childif (root->left == NULL) {struct node *temp = root->right;free(root);return temp;} else if (root->right == NULL) {struct node *temp = root->left;free(root);return temp;}// If the node has two childrenstruct node *temp = minValueNode(root->right);// Place the inorder successor in position of the node to be deletedroot->key = temp->key;// Delete the inorder successorroot->right = deleteNode(root->right, temp->key);}return root;}// Driver codeint main() {struct node *root = NULL;root = insert(root, 8);root = insert(root, 3);root = insert(root, 1);root = insert(root, 6);root = insert(root, 7);root = insert(root, 10);root = insert(root, 14);root = insert(root, 4);printf("Inorder traversal: ");inorder(root);printf("\nAfter deleting 10\n");root = deleteNode(root, 10);printf("Inorder traversal: ");inorder(root);}
// Binary Search Tree operations in C++#include <iostream>using namespace std;struct node {int key;struct node *left, *right;};// Create a nodestruct node *newNode(int item) {struct node *temp = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));temp->key = item;temp->left = temp->right = NULL;return temp;}// Inorder Traversalvoid inorder(struct node *root) {if (root != NULL) {// Traverse leftinorder(root->left);// Traverse rootcout << root->key << " -> ";// Traverse rightinorder(root->right);}}// Insert a nodestruct node *insert(struct node *node, int key) {// Return a new node if the tree is emptyif (node == NULL) return newNode(key);// Traverse to the right place and insert the nodeif (key < node->key)node->left = insert(node->left, key);elsenode->right = insert(node->right, key);return node;}// Find the inorder successorstruct node *minValueNode(struct node *node) {struct node *current = node;// Find the leftmost leafwhile (current && current->left != NULL)current = current->left;return current;}// Deleting a nodestruct node *deleteNode(struct node *root, int key) {// Return if the tree is emptyif (root == NULL) return root;// Find the node to be deletedif (key < root->key)root->left = deleteNode(root->left, key);else if (key > root->key)root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key);else {// If the node is with only one child or no childif (root->left == NULL) {struct node *temp = root->right;free(root);return temp;} else if (root->right == NULL) {struct node *temp = root->left;free(root);return temp;}// If the node has two childrenstruct node *temp = minValueNode(root->right);// Place the inorder successor in position of the node to be deletedroot->key = temp->key;// Delete the inorder successorroot->right = deleteNode(root->right, temp->key);}return root;}// Driver codeint main() {struct node *root = NULL;root = insert(root, 8);root = insert(root, 3);root = insert(root, 1);root = insert(root, 6);root = insert(root, 7);root = insert(root, 10);root = insert(root, 14);root = insert(root, 4);cout << "Inorder traversal: ";inorder(root);cout << "\nAfter deleting 10\n";root = deleteNode(root, 10);cout << "Inorder traversal: ";inorder(root);}
二叉搜索树的复杂度
时间复杂度
| 操作 | 最佳情况复杂度 | 平均情况复杂度 | 最坏情况复杂度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 搜索 | O(log n) |
O(log n) |
O(n) |
| 插入 | O(log n) |
O(log n) |
O(n) |
| 删除中 | O(log n) |
O(log n) |
O(n) |
这里,n是树中的节点数。
空间复杂度
所有操作的空间复杂度为O(n)。
二叉搜索树应用
- 在数据库中进行多级索引
- 用于动态排序
- 用于管理 Unix 内核中的虚拟内存区域

