在本教程中,您将学习冒泡排序的工作原理。 此外,您还将找到 C,C++ ,Java 和 Python 中冒泡排序的工作示例。
冒泡排序是一种算法,用于比较相邻元素,如果相邻元素之间的位置不符合预期顺序,则会交换它们的位置。 顺序可以是升序或降序。
冒泡排序如何工作?
从第一个索引开始,比较第一个和第二个元素,如果第一个元素大于第二个元素,则将它们交换。
现在,比较第二个和第三个元素。 如果它们不正常,请交换它们。
上面的过程一直进行到最后一个元素。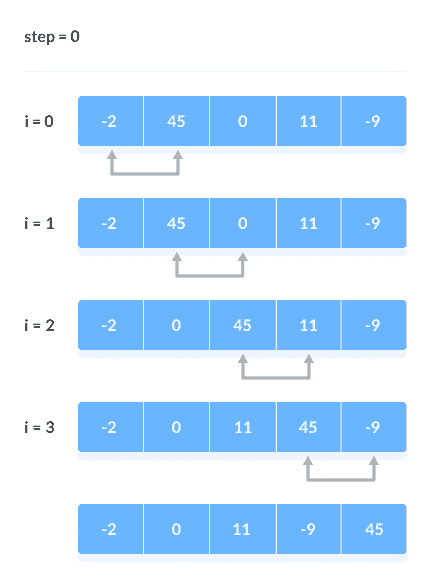
比较相邻元素其余迭代将继续相同的过程。 每次迭代后,未排序元素中的最大元素将放置在末尾。
在每次迭代中,都会进行比较直到最后一个未排序的元素。
当所有未排序的元素都放在其正确位置时,对数组进行排序。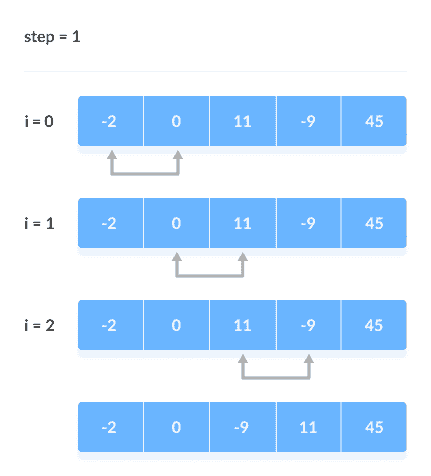
比较相邻的元素
[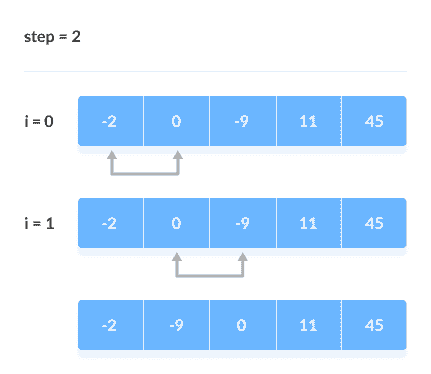
比较相邻的元素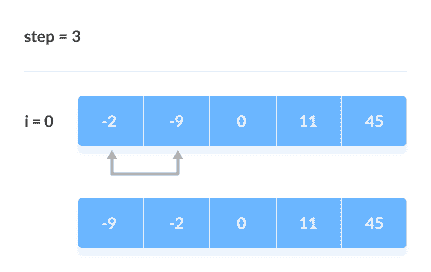
比较相邻的元素
冒泡排序算法
bubbleSort(array)for i <- 1 to indexOfLastUnsortedElement-1if leftElement > rightElementswap leftElement and rightElementend bubbleSort
Python,Java 和 C/C++ 示例
# Bubble sort in Pythondef bubbleSort(array):# run loops two times: one for walking throught the array# and the other for comparisonfor i in range(len(array)):for j in range(0, len(array) - i - 1):# To sort in descending order, change > to < in this line.if array[j] > array[j + 1]:# swap if greater is at the rear position(array[j], array[j + 1]) = (array[j + 1], array[j])data = [-2, 45, 0, 11, -9]bubbleSort(data)print('Sorted Array in Asc ending Order:')print(data)
// Bubble sort in Java
import java.util.Arrays;
class BubbleSort {
void bubbleSort(int array[]) {
int size = array.length;
// run loops two times: one for walking throught the array
// and the other for comparison
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < size - i - 1; j++)
// To sort in descending order, change > to < in this line.
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// swap if greater is at the rear position
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
// driver code
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] data = { -2, 45, 0, 11, -9 };
BubbleSort bs = new BubbleSort();
bs.bubbleSort(data);
System.out.println("Sorted Array in Ascending Order:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
}
}
// Bubble sort in C
#include <stdio.h>
void bubbleSort(int array[], int size) {
// run loops two times: one for walking throught the array
// and the other for comparison
for (int step = 0; step < size - 1; ++step) {
for (int i = 0; i < size - step - 1; ++i) {
// To sort in descending order, change">" to "<".
if (array[i] > array[i + 1]) {
// swap if greater is at the rear position
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[i + 1];
array[i + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
// function to print the array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// driver code
int main() {
int data[] = {-2, 45, 0, 11, -9};
int size = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
bubbleSort(data, size);
printf("Sorted Array in Ascending Order:\n");
printArray(data, size);
}
// Bubble sort in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void bubbleSort(int array[], int size) {
// run loops two times: one for walking throught the array
// and the other for comparison
for (int step = 0; step < size - 1; ++step) {
for (int i = 0; i < size - step - 1; ++i) {
// To sort in descending order, change > to < in this line.
if (array[i] > array[i + 1]) {
// swap if greater is at the rear position
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[i + 1];
array[i + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
// function to print the array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
cout << " " << array[i];
}
cout << "\n";
}
// driver code
int main() {
int data[] = {-2, 45, 0, 11, -9};
int size = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
bubbleSort(data, size);
cout << "Sorted Array in Ascending Order:\n";
printArray(data, size);
}
优化冒泡排序
在上面的代码中,即使数组已经排序,也进行了所有可能的比较。 它增加了执行时间。
通过引入swapped额外变量可以优化代码。 每次迭代之后,如果没有交换发生,则无需执行其他循环。
在这种情况下,将变量swapped设置为false。 因此,我们可以防止进一步的迭代。
优化冒泡排序的算法是
bubbleSort(array)
swapped <- false
for i <- 1 to indexOfLastUnsortedElement-1
if leftElement > rightElement
swap leftElement and rightElement
swapped <- true
end bubbleSort
优化的冒泡排序示例
# Optimized bubble sort in python
def bubbleSort(array):
# Run loops two times: one for walking throught the array
# and the other for comparison
for i in range(len(array)):
# swapped keeps track of swapping
swapped = True
for j in range(0, len(array) - i - 1):
# To sort in descending order, change > to < in this line.
if array[j] > array[j + 1]:
# Swap if greater is at the rear position
(array[j], array[j + 1]) = (array[j + 1], array[j])
swapped = False
# If there is not swapping in the last swap, then the array is already sorted.
if swapped:
break
data = [-2, 45, 0, 11, -9]
bubbleSort(data)
print('Sorted Array in Ascending Order:')
print(data)
// Optimized bubble sort in Java
import java.util.Arrays;
class BubbleSort {
void bubbleSort(int array[]) {
int size = array.length;
// Run loops two times: one for walking throught the array
// and the other for comparison
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
// swapped keeps track of swapping
boolean swapped = true;
for (int j = 0; j < size - i - 1; j++) {
// To sort in descending order, change > to < in this line.
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// Swap if greater is at the rear position
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
swapped = false;
}
}
// If there is not swapping in the last swap, then the array is already sorted.
if (swapped == true)
break;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] data = { -2, 45, 0, 11, -9 };
BubbleSort bs = new BubbleSort();
bs.bubbleSort(data);
System.out.println("Sorted Array in Ascending Order:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
}
}
// Optimized bubble sort in C
#include <stdio.h>
void bubbleSort(int arrayay[], int size) {
for (int step = 0; step < size - 1; ++step) {
// Swapped keeps track of swapping
int swapped = 0;
// Run loops two times: one for walking throught the array
// and the other for comparison
for (int i = 0; i < size - step - 1; ++i) {
// To sort in descending order, change > to < in this line.
if (arrayay[i] > arrayay[i + 1]) {
// Swap if greater is at the rear position
int temp = arrayay[i];
arrayay[i] = arrayay[i + 1];
arrayay[i + 1] = temp;
swapped = 1;
}
}
// If there is not swapping in the last swap, then the array is already sorted.
if (swapped == 0)
break;
}
}
// Function to print an array
void printarrayay(int arrayay[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
printf("%d ", arrayay[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int data[] = {-2, 45, 0, 11, -9};
int size = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
bubbleSort(data, size);
printf("Sorted Array in Ascending Order:\n");
printarrayay(data, size);
}
// Optimized bubble sort in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void bubbleSort(int array[], int size) {
for (int step = 0; step < size - 1; ++step) {
// Run loops two times: one for walking throught the array // and the other for comparison
int swapped = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size - step - 1; ++i) {
// To sort in descending order, change > to < in this line.
if (array[i] > array[i + 1]) {
// Swap if greater is at the rear position
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[i + 1];
array[i + 1] = temp;
swapped = 1;
}
}
// If there is not swapping in the last swap, then the array is already sorted.
if (swapped == 0)
break;
}
}
// Function to print an array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
cout << " " << array[i];
}
cout << "\n";
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int data[] = {-2, 45, 0, 11, -9};
int size = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
bubbleSort(data, size);
cout << "Sorted Array in Ascending Order:\n";
printArray(data, size);
}
复杂度
冒泡排序是最简单的排序算法之一。 该算法实现了两个循环。
| 周期 | 比较次数 |
|---|---|
| 第一 | (n-1) |
| 第二 | (n-2) |
| 第三 | (n-3) |
| ……. | …… |
| 最后 | 1 |
比较次数:(n-1) + (n-2) + (n-3) + ..... + 1 = n(n-1) / 2几乎等于n^2
复杂度: O(n^2)
同样,我们可以通过简单地观察循环数来分析复杂度。 有 2 个循环,因此复杂度为n*n = n^2
时间复杂度:
最坏情况的复杂度:
O(n^2)
如果我们要以升序排序,而数组是以降序排序,那么会发生最坏情况。最佳情况复杂度:
O(n)
如果数组已经排序,则无需排序。平均情况复杂度:
O(n^2)
当数组的元素处于混乱顺序(既不升也不降)时,会发生这种情况。
空间复杂度:
空间复杂度为O(1),因为交换使用了额外的变量temp。
在优化算法中,变量swapped会增加空间复杂度,从而使其成为O(2)。
冒泡排序应用
在以下情况下使用冒泡排序:
- 代码的复杂程度无关紧要。
- 短代码是首选的。

