在本教程中,您将学习分治算法的工作原理。 此外,您将发现分治方法与其他解决递归问题的方法之间的比较。
分治算法是一种通过以下方法解决较大问题的策略
- 将问题分解为较小的子问题
- 解决子问题,以及
- 合并它们以获得所需的输出。
要使用分治算法,请使用递归。 了解不同编程语言中的递归:
分治算法如何工作?
涉及的步骤如下:
- 划分:使用递归将给定问题划分为子问题。
- 解决:递归解决较小的子问题。 如果子问题足够小,则直接解决。
- 组合:组合子问题的解决方案,这是递归过程的一部分,以获取实际问题的解决方案。
让我们借助示例来理解这个概念。
在这里,我们将使用分治的方法对数组进行排序(即归并排序)。
假设给定数组为:

归并排序数组将数组分为两半。
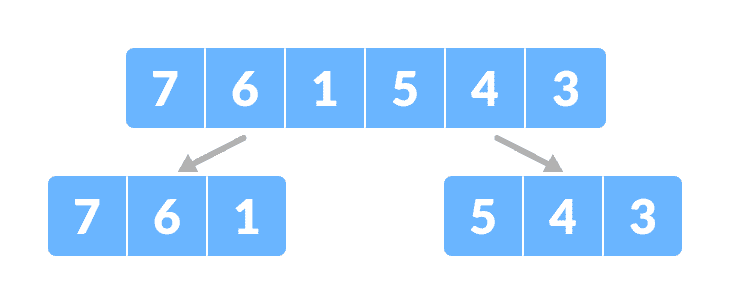
将数组分为两个子部分。
再次将每个子部分递归地分为两半,直到得到单个元素。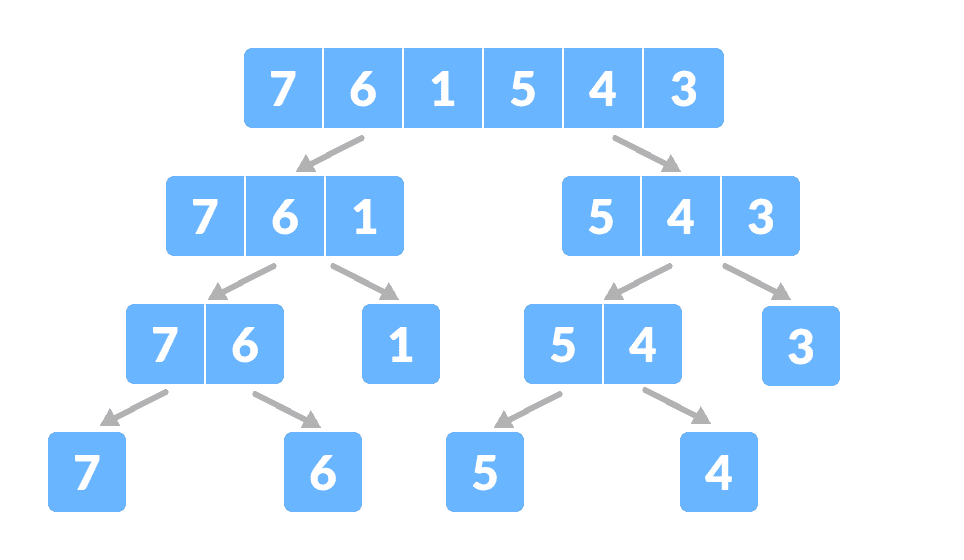
将数组分成较小的子部分现在,以排序的方式组合各个元素。 在这里,解决和组合步骤并排进行。
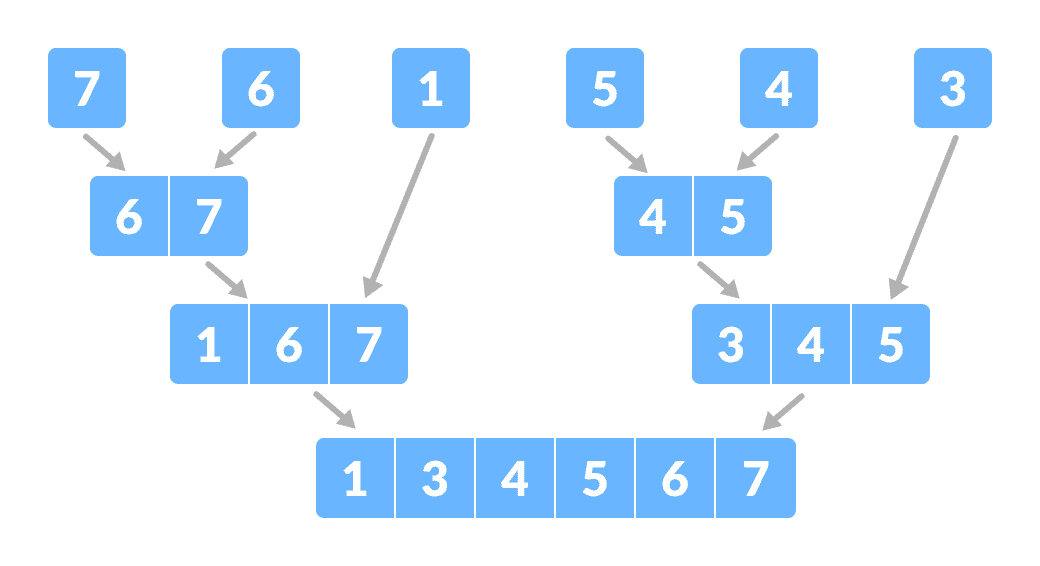
合并子部分
复杂度
分治法的复杂度是使用主定理计算的。
T(n) = aT(n/b) + f(n),where,n = size of inputa = number of subproblems in the recursionn/b = size of each subproblem. All subproblems are assumed to have the same size.f(n) = cost of the work done outside the recursive call, which includes the cost of dividing the problem and cost of merging the solutions
让我们举一个例子来发现递归问题的时间复杂度。
对于归并排序,等式可以写成:
T(n) = aT(n/b) + f(n)= 2T(n/2) + O(n)Where,a = 2 (each time, a problem is divided into 2 subproblems)n/b = n/2 (size of each sub problem is half of the input)f(n) = time taken to divide the problem and merging the subproblemsT(n/2) = O(n log n) (To understand this, please refer to the master theorem.)Now, T(n) = 2T(n log n) + O(n)≈ O(n log n)
分治 vs 动态方法
分治的方法将问题分为较小的子问题,这些子问题可以递归进一步解决。 每个子问题的结果都不存储以供将来参考,而在动态方法中,每个子问题的结果均存储以供将来参考。
当同一子问题无法多次解决时,请使用分治的方法。 当将来要多次使用子问题的结果时,请使用动态方法。
让我们通过一个例子来理解这一点。 假设我们试图找到斐波那契数列。 然后,
分治的方法:
fib(n)If n < 2, return 1Else , return f(n - 1) + f(n -2)
动态方法:
mem = [ ]fib(n)If n in mem: return mem[n]else,If n < 2, f = 1else , f = f(n - 1) + f(n -2)mem[n] = freturn f
在动态方法中,mem存储每个子问题的结果。
分治算法的优势
- 使用朴素方法将两个矩阵相乘的复杂度为
O(n^3),而使用分治法(即 Strassen 矩阵乘法)的复杂度为O(n^2.8074)。 这种方法还简化了诸如河内塔之类的其他问题。 - 这种方法适用于多处理系统。
- 它有效地利用了内存缓存。

