算法3.3 二叉查找树
算法意义
对比链表和数组实现的符号表,要实现高效的插入,需要链式结构,但单链表无法实现二分查找,因为后者的高效来自于可以快速通过索引取得任何子数组的中间元素,而链表只能顺序查找.为了将二分查找的高效和链表的灵活性结合,需要复杂的数据结构—二叉查找树
符号表的6种实现
| 数据结构 | 实现 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 单链表(顺序查找) | SequentialSearchST | 适合小型问题 | 对大型表很慢 |
| 有序数组(二分查找) | BinarySearchST | 最优的查找和空间,有序 | 插入操作很慢 |
| 二叉查找树 | BST | 实现简单,有序 | 没有性能上界保证,需额外空间 |
| 平衡查找树 | RedBlackBST | 最优的查找,插入,有序 | 链接需额外空间 |
| 散列表 | SeparateChainHashST LinearProbingHashST | 可快速查找与插入常见类型数据 | 需计算不同散列,无法有序操作,链接和空结点占空间 |
二叉查找树的描述
BST时一棵二叉树,每个结点都有一个Comparable的键(以及关联的值),且每个结点的键都大于其左子树的任意结点键而小于(有的书中包含等于)右子树的任意结点的键
API
| 方法 | 注释 |
|---|---|
| ST() | 创建符号表 |
| void put(Key key, Value val) | 存入键值对 |
| Value get(Key key) | 获取键key的对应值 |
| void delete(Key key) | 删去键值对key |
| boolean contains(Key key) | 判断键是否存在 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 表是否为空 |
| int size() | 表中键值对数量 |
| Key min() | 最小的键 |
| Key max() | 最大的键 |
| Key floor(Key key) | 小于等于key的最大键 |
| Key ceiling(Key key) | 大于等于key的最小键 |
| int rank(Key key) | 小于key的键个数 |
| Key select(int k) | 排名为k的键 |
基本实现
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn;import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;public class BST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {//内部私有结点类private class Node{public Node(Key key, Value val, int N){}}//根结点指针Node root;//结点个数private int size(){ return root.N; }//全部节点个数public int size(Node x){//指定子树节点个数if (x == null) return 0;else return x.N;}//查询键所对应的值public Value get(Key key){}private Value gethelp(Node root, Key key){ }//插入/更新键值对public void put(Key key, Value val){}private Node puthelp(Node root, Key key, Value val){ }//或许子树上最大/最小结点private Node getmin(Node root){}private Node getmax(Node root){}//删除以及相关函数private Node deletemin(Node root){}public Value delete(Key key){}private Node deletehelp(Node root, Key key){}//返回小于等于key的最大键(向下取整)public Key floor(Key key){}private Node floorhelp(Node root, Key key){ }//返回大于等于key的最小件(向上取整)public Key ceiling(Key key){ }private Node ceilinghelp(Node root, Key key){ }//排名:获取小于指定键的键数,即为指定键的名词,如size = 3,则最大键名词为2.public int rank(Key key){ }private int rankhelp(Node root, Key key){}//选择:获取排名为k的键,即恰好有k个小于它的键public Key select(int rank){}private Node selecthelp(Node root, int rank){}//中序遍历,分层次打印private void printhelp(Node root, int level){ }public void print(){}//测试用例public static void main(String[] args){BST<String, Integer> tree = new BST<>();while (!StdIn.isEmpty()){tree.put(StdIn.readString(), StdIn.readInt());}tree.print();}}
数据表示
private class Node{Key key;Value val;Node lc;Node rc;int N;public Node(Key key, Value val, int N){this.key = key;this.val = val;this.N = N;}}Node root;private int size(){ return root.N; }//全部节点个数public int size(Node x){//指定子树节点个数if (x == null) return 0;else return x.N;}
- 数据结构选择具有两个链接和一对键值对以及一个结点计数器(N)的结点类,对于结点计数器,即以该结点为根结点的子树所具有的结点个数,size()返回值即为N,对任意一个结点x,size(x) = size(x.lc)+size(x.rc)+1
- 要使用一个针对整棵BST的根结点指针root
get():查找
public Value get(Key key){ return gethelp(root, key); }private Value gethelp(Node root, Key key){if(root == null) return null;int cmp = key.compareTo(root.key);if (cmp < 0) return gethelp(root.lc, key);//小于结点键,进入左子树else if (cmp > 0) return gethelp(root.rc, key);//大于结点键,进入右子树else return root.val;//相等则返回值}
- 查找:若树是空的,返回null;若查找键和根结点键相等,命中,否则就递归地进入子树查找,小于根结点键进入左子树,反之进入右子树
put():插入
public void put(Key key, Value val){root = puthelp(root, key, val);}private Node puthelp(Node root, Key key, Value val){if (root == null) return new Node(key, val, 1);int cmp = key.compareTo(root.key);//小于结点键,进入左子树if (cmp < 0) root.lc = puthelp(root.lc, key, val);//大于结点键,进入右子树else if (cmp > 0) root.rc = puthelp(root.rc, key, val);else root.val = val;root.N = size(root.lc)+size(root.rc)+1;return root;//返回插入结点后的子树(结点)}
- 插入键值对的思想和查找类似,但注意如果发现表中已经有待插键,则直接更新值
- root.N也要随之更新, root.N = size(root.lc)+size(root.rc)+1;
有序性有关的方法和删除操作
getmin()/getmax():获得最大键和最小键
private Node getmin(Node root){if (root.lc == null) return root;return getmin(root.lc);}private Node getmax(Node root){if (root.rc == null) return root;return getmax(root.rc);}
- 最大键沿着根结点右侧链接不断向下到右侧链接到头,最大键就是此结点的键,最小键类似
ceiling()/floor():向上取整和向下取整
//返回小于等于key的最大键(向下取整)public Key floor(Key key){Node floorNode = floorhelp(root, key);if (floorNode == null) return null;else return floorNode.key;}private Node floorhelp(Node root, Key key){if (root == null) return null;int cmp = root.key.compareTo(key);if (cmp == 0) return root;//父结点键值恰好等于key,返回keyif (cmp < 0) return floorhelp(root.lc, key);//若key小于父结点键值,只可能出现在左子树//只有右子树中存在小于等于key的结点,小于等于key的最大键才会出现在右子树,因为之后的cmp始终>0,不断进入右子树,最终返回null//否则满足条件的就是根结点Node temp = floorhelp(root.rc, key);if (temp != null) return temp;else return root;}//返回大于等于key的最小件(向上取整)public Key ceiling(Key key){Node ceilingNode = ceilinghelp(root, key);if (ceilingNode == null) return null;else return ceilingNode.key;}private Node ceilinghelp(Node root, Key key){if (root == null) return null;int cmp = key.compareTo(root.key);if (cmp == 0) return root;if (cmp > 0) return ceilinghelp(root.rc, key);Node temp = ceilinghelp(root.lc, key);if (temp != null) return temp;else return root;}
- 向下取整,给定key小于root.key,则小于等于key的最大键只能出现在左子树;当key大于root.key时,只有root的右子树中存在小于等于key的结点时,小于等于key的最大键才会出现在右子树中,否则根结点就是小于等于key的最大结点.
- 向上取整:同上
select():选择
//选择:获取排名为k的键,即恰好有k个小于它的键public Key select(int rank){Node selectNode = selecthelp(root, rank);if (selectNode == null) return null;return selectNode.key;}private Node selecthelp(Node root, int rank){if (root == null) return null;int r = size(root.lc);if (r == rank) return root;else if (r > rank) return selecthelp(root.lc, rank);else return selecthelp(root.rc, rank-r-1);}
- 当给定rank(排名,小于查找键的键个数)等与size(root.lc)时,root.key即为查找键,若小于,进入左子树,若大于进入右子树,但进入右子树时,由于size和rank的区别,rank要改变为rank-size(root.lc)-1,可以理解为砍去左子树和父结点后的select()
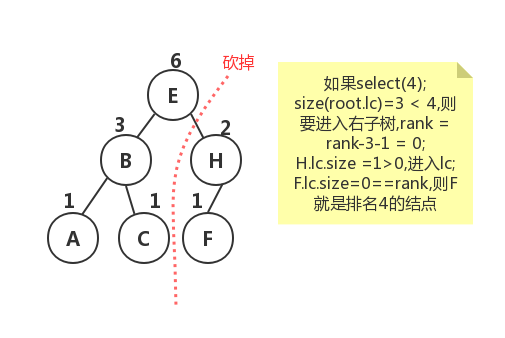
rank():排名
//排名:获取小于指定键的键数,即为指定键的名次,如size=3,则最大键名次为2public int rank(Key key){ return rankhelp(root, key); }private int rankhelp(Node root, Key key){if (root == null) return 0;int cmp = key.compareTo(root.key);if (cmp == 0) return size(root.lc);else if (cmp < 0) return rankhelp(root.lc, key);else return (root.lc.N + 1 + rankhelp(root.rc, key));}
- 当给定键和根结点键相等,返回左子树结点数;若给定结点小于根结点,则进入左子树递归;当大于根结点,则进入右子树,同时返回值上要加rc.lc.size()+1
delelemin():删除指定树最小键
private Node deletemin(Node root){if (root == null) return null;if (root.lc == null) return root.rc;root.lc = deletemin(root.lc);root.N--;return root;}
- 删除最小键,找最小键和getmin()一样,但找到后,需要将根结点的左子树设为返回值(即删除最小结点后的左子树),且N—.
delete():删除指定键值对
public Value delete(Key key){Value temp = get(key);//当键值对存在时再执行删除if(temp !=null) root = deletehelp(root, key);return temp;}private Node deletehelp(Node root, Key key){if (root == null) return null;int cmp = key.compareTo(root.key);if (cmp < 0) root.lc = deletehelp(root.lc, key);else if (cmp > 0) root.rc = deletehelp(root.rc, key);else{//找到待删除结点if (root.rc == null) root = root.lc;if (root.lc == null) root = root.rc;//单孩子结点Node temp = root;root = getmin(root.rc);//用待删结点右子树最大结点作为新结点root.rc = deletemin(root.rc);//新结点右子树即剔除原右子树最大结点后子树root.lc = temp.lc;//新结点左子树为待删结点左子树,无改变}root.N--;return root;//返回删除结点后的子树}
删除结点需要先找到指定键值对,有三种情况:
- 结点无右子树,只需root = root.lc
- 结点无左子树,只需root = root.rc
- 结点有两个子树,这是只需要让其位置被右子树最小结点代替(选左子树最大结点在某些规定可有重复键的二叉树中,不满足左结点恒小的定义)
- 将指向待删结点root的引用保存为temp
- 将root指向getmin(root.rc)
- root.lc = t.lc
- root.rc = deletemin(t.rc)
- N—
与C++实现的对比
Node *temp = getmin(root->rc());root->setval() = temp->val();root->setkey() = temp->key();root->setright() = deletemin(root->rc());delete temp;
C++版本采用赋值法,找到右子树最小结点后将键值对赋值给root,然后删除此结点.
print():中序遍历打印
//中序遍历,分层次打印private void printhelp(Node root, int level){if (root == null) return;printhelp(root.lc, level+1);for (int i = 0; i<level ; i++) StdOut.print(" ");StdOut.println(root.key);printhelp(root.rc, level+1);}public void print(){if (root == null) {StdOut.println("the BST is empty");return;}printhelp(root, 1);}
- 遍历分三种:前序,中序,后序,要切换打印方式,只需要调整
printhelp(root.lc, level+1),StdOut.println(root.key),printhelp(root.rc, level+1)的顺序 - 对BST,中序遍历结果即为从小到大的顺序排列
性能分析
| 算法(数据结构) | 最坏查找 | 最坏插入 | 平均查找 | 平均插入 | 是否有序 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 顺序查找(无序链表) | N | N | N/2 | N | 否 |
| 二分查找(有序数组) | lgN | N | lgN | N/2 | 是 |
| 二叉树查找(BST) | N | N | 1.39lgN | 1.39lgN | 是 |
- BST的基本操作性能依赖于其中的键分组足够随机(平衡)以消除长路径

