化二进制
- 整数:除2取余(自下而上,直到商为0)
- 小数:乘2取整(自上到下,直到小数部分为0)
C位运算
- 反码ONES’ COMPLEMENT ( ~ ),
- 位移SHIFT ( << and >> )
- 左移时丢弃高位,低位补0
- 右移有符号数,算术右移,丢弃低位,高位补符号位
- 右移无符号数,逻辑右移,丢弃低位,高位补0
- 与AND ( & ),
- 或OR ( | ),
- 异或EXCLUSIVE OR ( ^ ):同假异真
- 注意!为逻辑非,C中对除0以为任何数使用!都得到0
CSAPP datalab⭐
参考链接: 实验二 datalab-handout
实现按位&,|,^操作
/** bitAnd - x&y using only ~ and |* Example: bitAnd(6, 5) = 4* Legal ops: ~ |*/int bitAnd(int x, int y) {// ~(~A∪~B)=A∩Breturn ~(~x|~y);}/** bitOr - x|y using only ~ and &* Example: bitOr(6, 5) = 7* Legal ops: ~ &*/int bitOr(int x, int y) {// ~(~A∩~B)=A∪Breturn ~(~x&~y);}/** bitXor - x^y using only ~ and &* Example: bitXor(4, 5) = 1* Legal ops: ~ &*/int bitXor(int x, int y) {return (x & ~y) | (~x & y);}
求-1
1表示为32bits二进制000…001,数据位补码111…111,加符号位后转换为16进制,0xffffffff
/** minusOne - return a value of -1* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>* Max ops: 2*/int minusOne(void) {return ~0;}
求2s补码下最大整数
正常int的最大整数为0111…..1111,对齐取反1000…0000,那么通过0000…0001左移即可
/** TMax - return maximum two's complement integer* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>* Max ops: 4*/int tmax(void) {return ~(1 << 31);}
字节提取
/** getByte - Extract byte n from word x* Bytes numbered from 0 (LSB) to 3 (MSB)* Examples: getByte(0x12345678,1) = 0x56* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>*/int getByte(int x, int n) {return (x >> (n << 3)) & 0x000000ff;}
求相反数
即求2s补码
/** negate - return -x* Example: negate(1) = -1.* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>*/int negate(int x) {return (~x)+1;}
判断相等/等于0
/** isEqual - return 1 if x == y, and 0 otherwise* Examples: isEqual(5,5) = 1, isEqual(4,5) = 0* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>*/int isEqual(int x, int y) {return !(x^y);}/** isZero - returns 1 if x == 0, and 0 otherwise* Examples: isZero(5) = 0, isZero(0) = 1* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>*/int isZero(int x) {return ! (0^x);}
判断为正数,判断非负数
- 为正数:符号位为0,且非0
- 非负数:符号位为0,或为0
```c
/*
- isPositive - return 1 if x > 0, return 0 otherwise
- Example: isPositive(-1) = 0.
- Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >> */ int isPositive(int x) { return !((x >> 31) | (!x)); }
/ isNonNegative - return 1 if x >= 0, return 0 otherwise
- Example: isNonNegative(-1) = 0. isNonNegative(0) = 1.
- Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >> */ int isNonNegative(int x) { return !(x >> 31); }
---<a name="2Yy0J"></a>### 浮点数IEEE Standard 754浮点数格式<br />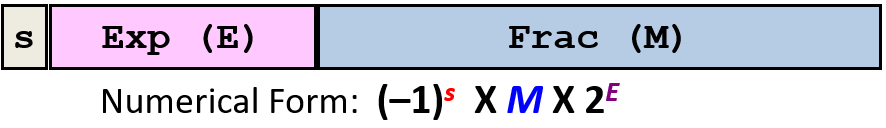| **结构** | 符号位sign: **正0负1**<br />阶码 Exponent: 决定小数点的位置: **Exp(阶码) = E (真值)+Bias(偏移量)**<br />分数 Fraction:指示[1 , 2]之间的数: **Frac = M - 1** || --- | --- || **规格** | 单精度: 8 Exp, 23 Frac, 1 sign = 32<br />双精度: 11 Exp, 52 Frac, 1 sign =64 || **举例** | **float F = 15213.0化为单精度浮点数求Exp: **<br />15213 = 11101101101101 = 1.1101101101101 X 213<br />得到E=13,偏移量27-1=127,13+127=140化为二进制10001100作为Exp<br />**求Frac:**<br />M = 1.1101101101101,Frac = 11011011011010000000000(补齐23bits)<br />最终:0,10001100, 11011011011010000000000<br />逆运算根据IEEE表达求出原数**(-1)****S**** * 2**** exp - 127 ***** (1 + frac * 2****-23****)**<br /> |---<a name="qQY9N"></a>### 浮点数加法浮点数加法需要经过"对阶",容易丢失精度:十进制下10.375 + 6.34375 = **16.71875**<br />---<a name="9F1JN"></a>### 选择题知识点1. 在4byte为一个word的计算机中,下列哪一个表达式测试指针ptr是否包含某个word的地址```c(ptr & 3) == 0(ptr | 3) == 0(ptr % 4) == 0
选Ⅰ和Ⅲ(指针不可以做%或&运算,需要强转)
- Ⅰ计算机4bytes为一个word,见指针,每个字节有一个地址,所以每个word的地址都以4对齐,下图为VS调试时内存窗口4字节显示结果,明显看到16进制表示时最后字节以0,4,8,c变化,对应0000 0000, 0000 0100, 0000 1000, 0000 1100
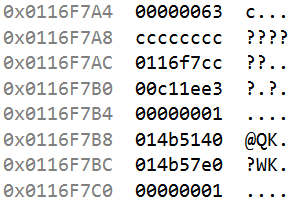
最后2bit始终为00与0011按位与的结果永远是0
- Ⅲ把最后字节化为int类型:0,4,8,12对4取余恒为0
关于溢出
- C程序对整型加法中的溢出不会产生提醒,会得到错误结果;
- 对浮点数溢出,即阶码部分超过其能表示的最大值时报错#INF:infinity
以下结果是false的是:0x00 ^ 0x00
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdbool.h>void main(){bool a = !(0);bool b = ~(0xFF);bool c = ~(0x00);bool d = 0x00 ^ 0x00;}
|
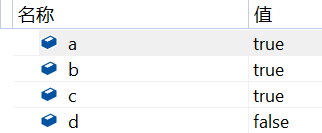 | 在bd中犹豫,实际上C语言没有bool,所有bool都根据int截取,b按位取反:0x000000ff->0xffffff00,结果为负数,求二进制下31bits数据位原码,取反加一(100)2即-256,在C中只要非0的数都为true,因此b是true |
| —- | —- |
| 在bd中犹豫,实际上C语言没有bool,所有bool都根据int截取,b按位取反:0x000000ff->0xffffff00,结果为负数,求二进制下31bits数据位原码,取反加一(100)2即-256,在C中只要非0的数都为true,因此b是true |
| —- | —- |

