快速限流
限流,限制用户访问频率,例如:用户1分钟最多访问100次 或者 短信验证码一天每天可以发送50次, 防止盗刷。
- 对于匿名用户,使用用户IP作为唯一标识。
- 对于登录用户,使用用户ID或名称作为唯一标识。
缓存={用户标识:[12:33,12:32,12:31,12:30,12,] 1小时/5次 12:34 11:34{
pip3 install django-redis
先启动redis
配置参考 https://pypi.org/project/django-redis/
# settings.pyCACHES = {"default": {"BACKEND": "django_redis.cache.RedisCache","LOCATION": "redis://127.0.0.1:6379","OPTIONS": {"CLIENT_CLASS": "django_redis.client.DefaultClient","PASSWORD": "", # redis默认密码为空}}}
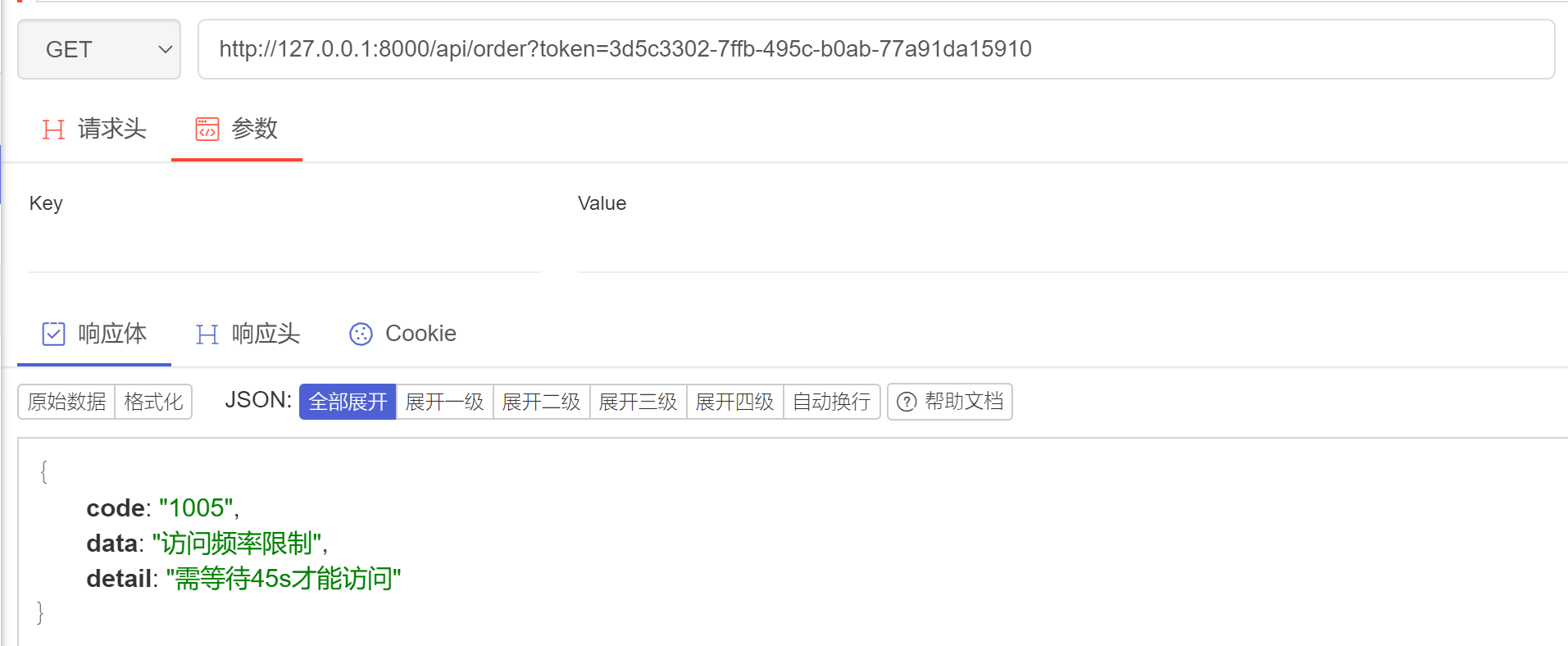
# views.pyfrom rest_framework.views import APIViewfrom rest_framework.response import Responsefrom rest_framework import exceptionsfrom rest_framework import statusfrom rest_framework.throttling import SimpleRateThrottlefrom django.core.cache import cache as default_cacheclass ThrottledException(exceptions.APIException):status_code = status.HTTP_429_TOO_MANY_REQUESTSdefault_code = 'throttled'class MyRateThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):cache = default_cache # 访问记录存放在django的缓存中(需设置缓存)scope = "user" # 构造缓存中的keycache_format = 'throttle_%(scope)s_%(ident)s'# 设置访问频率,例如:1分钟允许访问10次# 其他:'s', 'sec', 'm', 'min', 'h', 'hour', 'd', 'day'THROTTLE_RATES = {"user": "10/m"}def get_cache_key(self, request, view):if request.user:ident = request.user.pk # 用户IDelse:ident = self.get_ident(request) # 获取请求用户IP(去request中找请求头)# throttle_u # throttle_user_11.11.11.11ser_2return self.cache_format % {'scope': self.scope, 'ident': ident}def throttle_failure(self):wait = self.wait()detail = {"code": 1005,"data": "访问频率限制",'detail': "需等待{}s才能访问".format(int(wait))}raise ThrottledException(detail)class OrderView(APIView):throttle_classes = [MyRateThrottle, ]def get(self, request):return Response({"code": 0, "data": "数据..."})
多个限流类
本质,每个限流的类中都有一个 allow_request 方法,此方法内部可以有三种情况
- 返回True,表示当前限流类允许访问,继续执行后续的限流类。
- 返回False,表示当前限流类不允许访问,继续执行后续的限流类。所有的限流类执行完毕后,读取所有不允许的限流,并计算还需等待的时间。
- 抛出异常,表示当前限流类不允许访问,后续限流类不再执行。
写法一(推荐)
所有的限流类执行完后,再返回报错
# views.pyfrom rest_framework.views import APIViewfrom rest_framework.response import Responsefrom rest_framework import exceptionsfrom rest_framework import statusfrom rest_framework.throttling import SimpleRateThrottlefrom django.core.cache import cache as default_cacheclass ThrottledException(exceptions.APIException):status_code = status.HTTP_429_TOO_MANY_REQUESTSdefault_code = 'throttled'class MyRateThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):cache = default_cache # 访问记录存放在django的缓存中(需设置缓存)scope = "user" # 构造缓存中的keycache_format = 'throttle_%(scope)s_%(ident)s'# 设置访问频率,例如:1分钟允许访问10次# 其他:'s', 'sec', 'm', 'min', 'h', 'hour', 'd', 'day'THROTTLE_RATES = {"user": "10/m"}def get_cache_key(self, request, view):if request.user:ident = request.user.pk # 用户IDelse:ident = self.get_ident(request) # 获取请求用户IP(去request中找请求头)# throttle_u # throttle_user_11.11.11.11ser_2return self.cache_format % {'scope': self.scope, 'ident': ident}class MyRateThrottleB(SimpleRateThrottle):cache = default_cache # 访问记录存放在django的缓存中(需设置缓存)scope = "xx" # 构造缓存中的keycache_format = 'throttle_%(scope)s_%(ident)s'# 设置访问频率,例如:1分钟允许访问3次# 其他:'s', 'sec', 'm', 'min', 'h', 'hour', 'd', 'day'THROTTLE_RATES = {"xx": "3/m"}def get_cache_key(self, request, view):if request.user:ident = request.user.pk # 用户IDelse:ident = self.get_ident(request) # 获取请求用户IP(去request中找请求头)# throttle_u # throttle_user_11.11.11.11ser_2return self.cache_format % {'scope': self.scope, 'ident': ident}class OrderView(APIView):throttle_classes = [MyRateThrottle, ]def get(self, request):return Response({"code": 0, "data": "数据..."})def throttled(self, request, wait):detail = {"code": 1005,"data": "访问频率",'detail': "需等待{}s才能访问".format(int(wait))}raise ThrottledException(detail)
写法二
前面的限流类执行完后,马上返回报错
class ThrottledException(exceptions.APIException):status_code = status.HTTP_429_TOO_MANY_REQUESTSdefault_code = 'throttled'class MyRateThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):cache = default_cache # 访问记录存放在django的缓存中(需设置缓存)scope = "user" # 构造缓存中的keycache_format = 'throttle_%(scope)s_%(ident)s'# 设置访问频率,例如:1分钟允许访问10次# 其他:'s', 'sec', 'm', 'min', 'h', 'hour', 'd', 'day'THROTTLE_RATES = {"user": "10/m"}def get_cache_key(self, request, view):if request.user:ident = request.user.pk # 用户IDelse:ident = self.get_ident(request) # 获取请求用户IP(去request中找请求头)# throttle_u # throttle_user_11.11.11.11ser_2return self.cache_format % {'scope': self.scope, 'ident': ident}def throttle_failure(self):wait = self.wait()detail = {"code": 1005,"data": "访问频率限制",'detail': "需等待{}s才能访问".format(int(wait))}raise ThrottledException(detail)class MyRateThrottleB(SimpleRateThrottle):cache = default_cache # 访问记录存放在django的缓存中(需设置缓存)scope = "xx" # 构造缓存中的keycache_format = 'throttle_%(scope)s_%(ident)s'# 设置访问频率,例如:1分钟允许访问10次# 其他:'s', 'sec', 'm', 'min', 'h', 'hour', 'd', 'day'THROTTLE_RATES = {"xx": "20/h"}def get_cache_key(self, request, view):if request.user:ident = request.user.pk # 用户IDelse:ident = self.get_ident(request) # 获取请求用户IP(去request中找请求头)# throttle_u # throttle_user_11.11.11.11ser_2return self.cache_format % {'scope': self.scope, 'ident': ident}def throttle_failure(self):wait = self.wait()detail = {"code": 1005,"data": "访问频率限制",'detail': "需等待{}s才能访问".format(int(wait))}raise ThrottledException(detail)class OrderView(APIView):throttle_classes = [MyRateThrottle, MyRateThrottleB]def get(self, request):return Response({"code": 0, "data": "数据..."})
全局配置
REST_FRAMEWORK = {"DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES":["xxx.xxx.xx.限流类", ],"DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES": {"user": "10/m","xx":"100/h"}}