准备数据
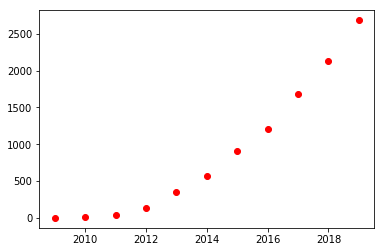
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression# 1. 数据展示:了解数据,可以是csv读取,也可以直接copy进来years = np.arange(2009, 2020)sales = np.array([0.52, 9.36, 33.6, 132, 352, 571, 912, 1207, 1682, 2135, 2684])print(years)print(sales)
可视化
一般使用散点图
plt.scatter(years, sales, c='red')
初步判断
多项式回归(3阶)
y = a*x^3 + b*x^2 + c*x + d1: 1 1 12: 8 4 23: 27 9 3
数据预处理
model_y = salesmodel_x = (years - 2008).reshape(-1, 1) # 任意行,一列print(model_x)model_x = np.concatenate([model_x ** 3, model_x ** 2, model_x], axis=1)print(model_x)
建模
# 4. 创建回归模型(多项式->1元3次)model = LinearRegression()# 5. 数据训练model.fit(model_x, model_y)# 6. 获取系数、截距 -> 声明方程式print('系数:', model.coef_) # 系数: [ -0.20964258 34.42433566 -117.85390054]print('截距:', model.intercept_) # 截距: 90.12060606060629
y = -0.20964258*x^3 + 34.42433566*x^2 + -117.85390054*x + 90.12060606060629
绘图
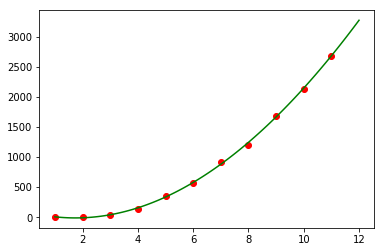
# 7. 添加趋势线:想象成画折线图,x:1~11,12 y:带入公式之后得到的trend_x = np.linspace(1, 12, 100)fun = lambda x: -0.20964258 * x ** 3 + 34.42433566 * x ** 2 + -117.85390054 * x + 90.12060606060629trend_y = fun(trend_x)# print(type(fun))# print(trend_x)# print(trend_y)years_no = years - 2008plt.scatter(years_no, sales, c='red') # 画散点图plt.plot(trend_x, trend_y, c='green') # 画趋势线plt.show()
预测
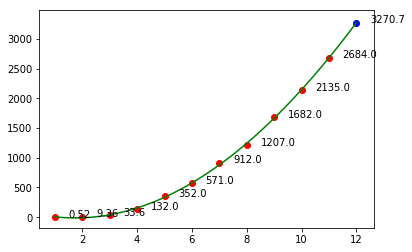
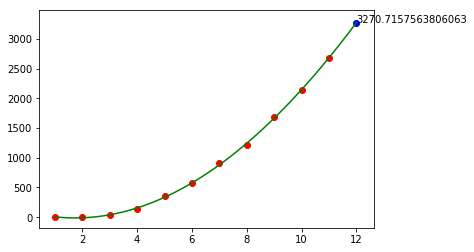
# 8. 预测2020年的销售额print('2020年销售额预测:', fun(12))years_no = years - 2008plt.scatter(years_no, sales, c='red')plt.scatter(12, fun(12), c='blue')plt.plot(trend_x, trend_y, c='green')# 加数据标签plt.annotate(fun(12), xy=(12, fun(12))) # annotate : (参数1:注释文本的内容, 参数2:被注释的坐标点)
给其它坐标加标签
for i in range(11):plt.annotate(sales[i], xy=(years_no[i], sales[i]))plt.show()
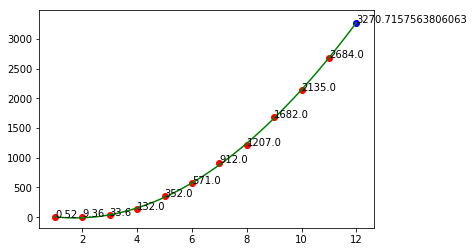
调整标签的位置
# x右移0.5,y下移0.5plt.annotate(round(fun(12), 1), xy=(12, fun(12)), xytext=(12 + 0.5, fun(12) - 0.5))for i in range(11):plt.annotate(sales[i], xy=(years_no[i], sales[i]), xytext=(years_no[i] + 0.5, sales[i] - 0.5))plt.show()