无论其文化或语言如何,应用程序中涉及到的文本,应该是任何地方,任何人都可以理解的。
Text should be understandable by anyone, anywhere, regardless of their culture or language.
原则
UI 中的文本不能出现语法错误并且可以建立设计者与用户之间的信任。
文字应该保持:
- 清晰
- 准确
- 简洁
UI text can make interfaces more usable and build trust. Text should be clear, accurate, and concise.
精炼
为了便于用户快速找到文本并且进行阅读,请使用简练的文字编写文本,设计者需要严格控制字数。
To facilitate navigation and discovery, write UI text in short, scannable segments that focus on a limited number of concepts at a time.
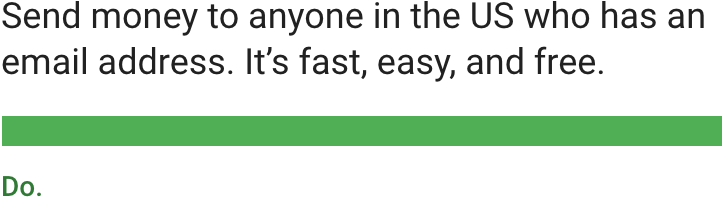
通过简练的语言来传递信息或描述操作。
Express information and actions concisely.

描述重要的操作或信息时,请不要使用过于复杂的语言。
Don’t list many complex implications when introducing a key action or concept.

正确:通过简练的语言来说明重要的信息。
Write instructions that focus on a small number of key concepts.
错误:避免冗长的叙述。
Don’t embed instructions within lengthy descriptions.
简单直接
使用简单,直接的语言使内容易于理解。
Use simple, direct language that makes content easy to understand.

正确:简单直接。
Keep UI text short.
错误:避免冗长的叙述。
Don’t write instructions that are longer than necessary to communicate an action.
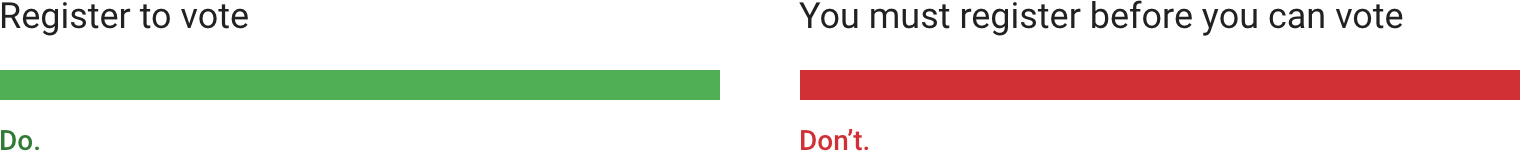
正确:撰写文案要以任务目标为核心。
Write UI text focused on the current task.
错误:告诉用户如何采取行动,而不是告诉他们应该或必须采取行动。
Tell the user how to take action, not that they should or must do so.
对话
在与用户对话的过程中,需要根据实际情况选用第二人称(您或您的用户)或第一人称(我,我或我的用户)。
两种人称的使用情况:
第二人称(“您”或“您的”):第二人称在部分情况下都适用,让用户觉得自己在跟 UI 直接对话。
第一人称(“我”或“我的”):在某些情况下,第一人称用于强调用户对内容或操作的所有权。
Address users in either the second person (you or your) or the first person (I, me, or my), depending on which is suitable and clearest for the situation.
Each form of address is recommended for the following contexts:
- Second person, “you” or “your”: This conversational style is appropriate in most situations; as though the UI is speaking directly to the user.
- First person, “I” or “my”: In some cases, this form of address emphasizes the user’s ownership of content or actions.

Speak directly to the user in the second person.
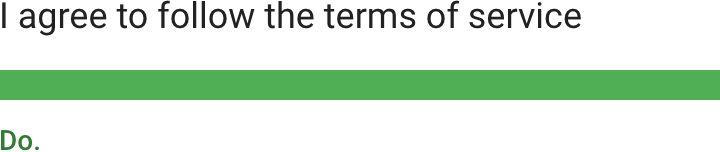
通过第二人称直接与用户对话。
Emphasize ownership of actions using the first person.

第一人称用于强调用户对于操作或内容的所有权。
Speak directly to the user in the second person.
Emphasize content ownership using the first person.
避免第一人称和第二人称混用
第一人称和第二人称混用会让混淆用户的认知。
To avoid confusing the user, avoid using “me” or “my,” and “you” or “your,” in the same phrase.
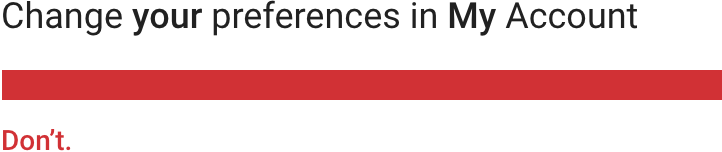
避免第一人称和第二人称混用。
Don’t refer to the user in both the second person and the first person within the same phrase.
基本信息
仅传达基本信息,以便用户可以专注于自己的任务。
优秀的 UI 设计能够不通过文本来传达信息。
Communicate only essential details so users can focus on their own tasks. Sometimes the most effective UI contains no text at all.
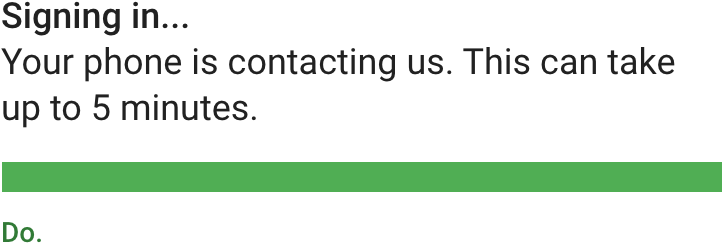
仅传达基本信息(当前的状态以及操作信息)。
Communicate the details that are essential to understanding a current state or action.
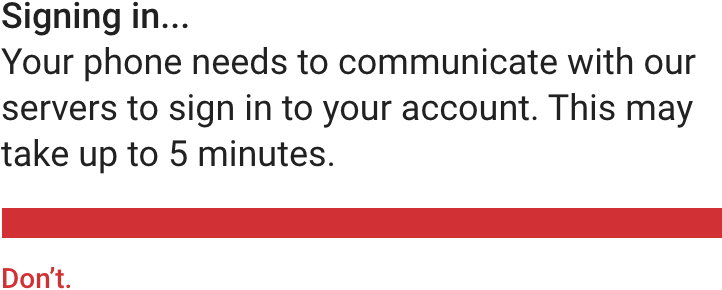
用户不需要了解所有的细节(比如系统是如何执行用户操作的)。
Avoid providing details that aren’t essential for the user to know, such as how an action or process is performed.
为大多数人设计
设计者需要根据大多数人的阅读能力来设计文本。
Use common words that are clearly and easily understandable across all reading levels.

使用常用的词汇。
Use common words.
行业术语和功能名称
避免使用针对 UI 功能而发明的行业专用术语或名称。
Avoid industry-specific terminology or names invented for UI features.
Use common words.
Don’t use technical jargon, unless it’s critical to understanding the context.

除非是对当前场景十分重要的信息,否则请不要使用专业术语。
Use common ways of describing both the UI and devices.
Don’t use technical language to describe, unless it’s necessary to understanding the context.
时态
使用现在时来描述应用程序的行为。
当您需要使用过去或将来时态书写时,请使用简单的动词形式。
Use the present tense to describe product behavior. Avoid using the future tense to describe the way a product always acts.
When you need to write in the past or future tenses, use simple verb forms.

请勿使用现在时态的其他变化形式,例如现在完成时态。
Write in the present tense.
Don’t write in different variations of the present tense, such as the present perfect tense.
数字
除非需要混合输入(”Enter two 3s”),否则请使用阿拉伯数字(“1, 2, 3,” not “one, two, three”)。
Use numerals ( “1, 2, 3,” not “one, two, three”) unless writing copy that mixes uses of numbers, such as “Enter two 3s.”

Use numerals.
Don’t spell out numbers.

根据实际情况,可以混合输入。
When using numbers two different ways, refer to one in numerals and the other in text.
标点符号
为了帮助读者快速浏览文字,请避免在不必要的地方使用标点符号。
To help readers scan text at a glance, avoid using punctuation in places where it isn’t necessary.
句号
请避免在下面的 UI 元素内的单句中使用句号:
- 标签
- 悬停文字
- 项目符号列表
- 对话框正文
使用条件:
- 繁复句
- 链接后面的任何句子(链接本身不应该是完整的句子)
Avoid using periods on solitary sentences within these UI elements:
- Labels
- Hover text
- Bulleted lists
- Dialog body text
Use periods on:
- Multiple sentences
- Any sentence followed by a link (links themselves should not be full sentences)
长文本中的句点
在长文本或者复杂的句子中使用句子能够更好地帮助用户进行快速阅读。
Longer or complex sentences can use periods if doing so better suits the context. For example, if the rest of your app’s flow doesn’t use periods, introducing them in a few places may appear inconsistent.
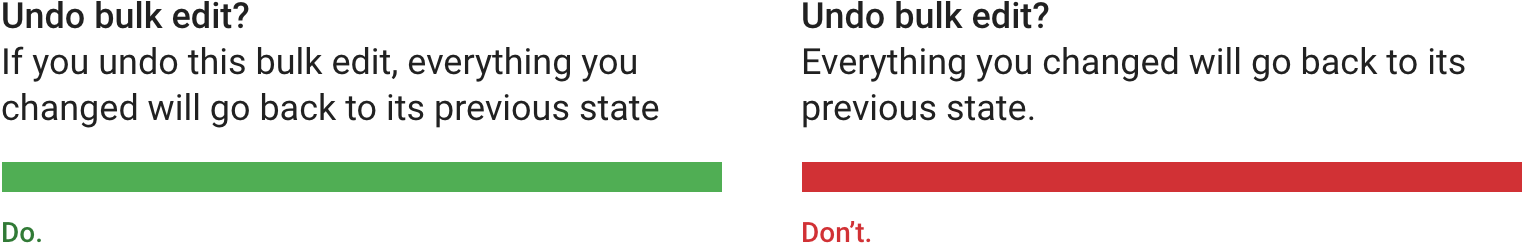
正文文本的单句之后可以不加句号;请不要在单句后面使用句号。
冒号
表情后面不使用冒号。
Skip colons after labels.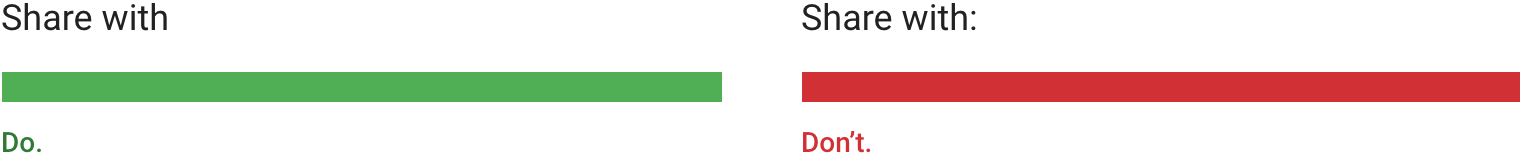
Skip periods after solo sentences of body text.
If there is only a single sentence, don’t place periods after body text.
组织结构
从目标开始
当我们使用短句来描述一个目标以及实现该目标所需才去的行动时,请以目标相关的内容作为文本的开头。
When a phrase describes a goal and the action needed to achieve it, start the sentence with the goal.

正确
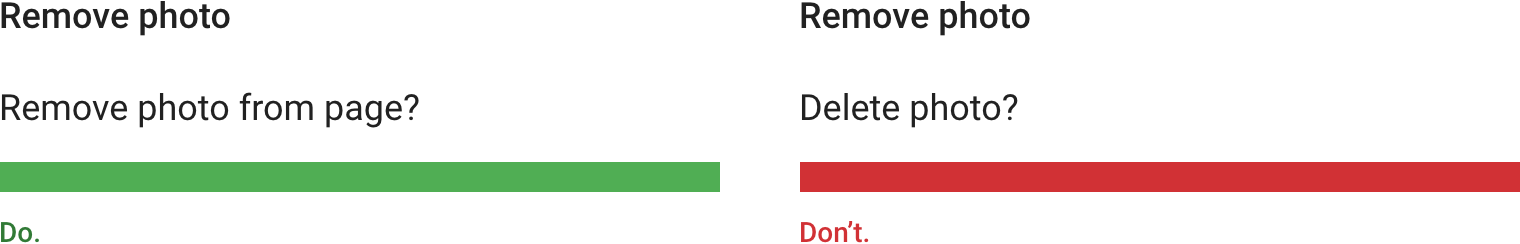
以目标开始(“删除照片”),以用户所需采取的操作结束(“拖入回收站”)。
Start a statement with the objective (“to remove a photo”) and end it with the user action (“drag it to the trash”).
错误
不要在描述目标(“删除照片”)之前描述用户所需采取的操作(“拖入回收站”)。
Don’t state the action the user takes (“drag a photo”) before the objective (“to remove it from this album”).
细节
根据需要逐步显示信息。不要在一开始就描述所有细节。
当用户浏览功能并需要更多信息时,将显示有关功能的更多详细信息。
Reveal information progressively and as it’s needed.
In a user’s first interaction, every detail doesn’t need to be described. Reveal more detail about features as the user explores them and needs more information.

风格一致
在 UI 的各个功能描述中的文风需要保持一致。
Use words in a consistent manner across your UI features.
通过标签来引用 UI 中的元素和控件
标签能够标识 UI 中元素或控件的功能。
它们出现在控件本身上或附近,例如按钮或开关上的文本。要引用UI控件或元素,请使用其标签文本进行提及。(不要说明元素或控件的类型)。
标签一般出现在控件上或者在其附近,例如按钮或开关上的文本。要引用 UI 中的元素或控件时,请使用标签文本。
不需要说明元素或控件的类型。
Labels identify what a control or element does. They appear either on or near the control itself, such as the text on a button or switch. To refer to a UI control or element, mention it using its label text. (don’t state the type of element or control).

标签仅用来说明 UI 中的元素;
State the UI element’s label only.
不要同时展示标签的内容以及标签对应的元素或控件类型。
Don’t state both the label and the element on which it appears.
组件文本
组件
以下组件需要特定的文本规范:
The following components have specific writing guidance:

