保护因子的作用

保护因子的作用:是决定对一组媒体包产生多少个FEC包。
NumFecPackets

protection_factor 保护因子。
向右移8位,也就是除以256的原因,是因为webrtc的对包计算,是以256为单位计算的,也就是在256个包中,有多少个包丢失了。
保护因子从哪里来?

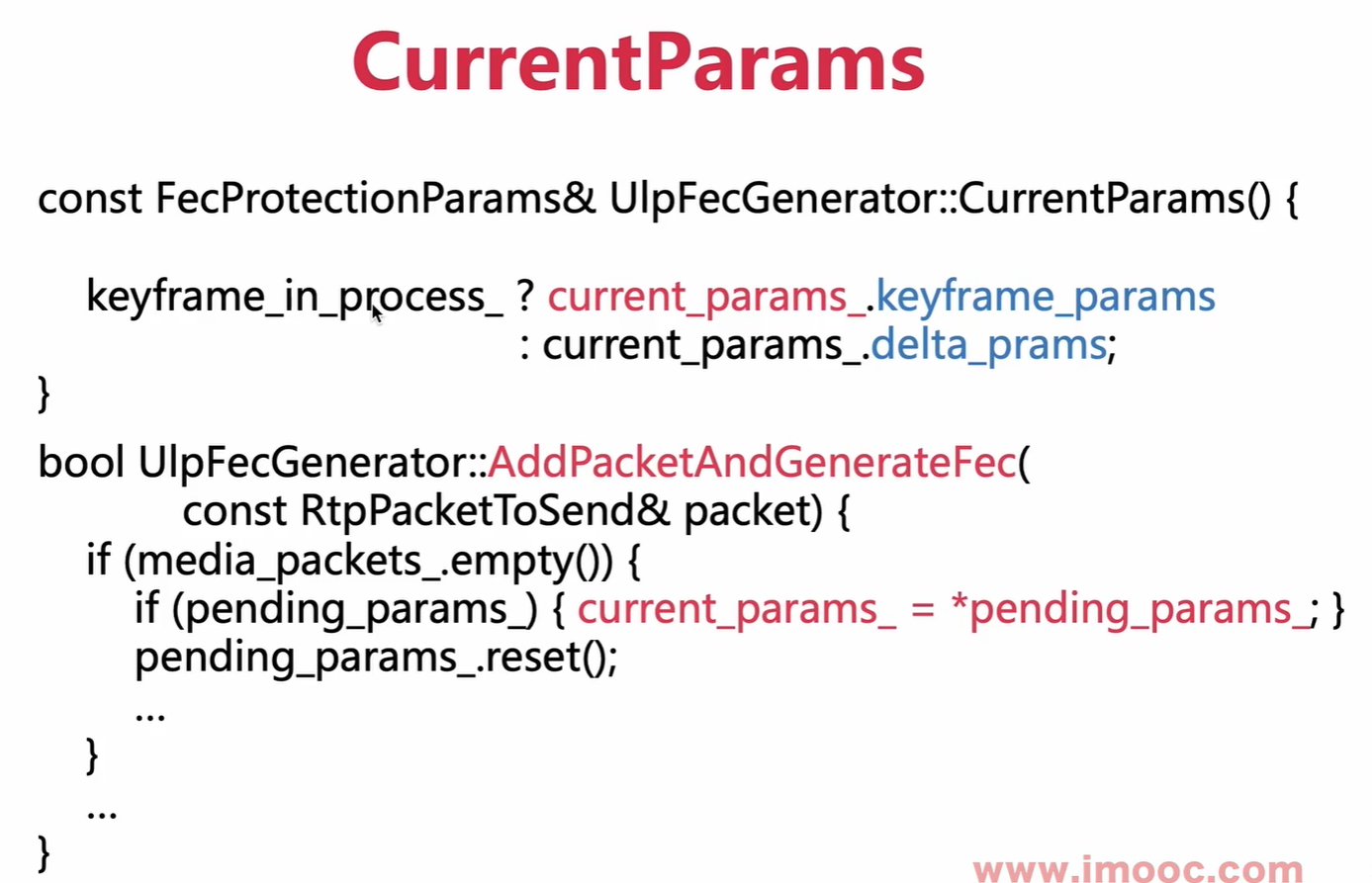
这类发现保护因子是从函数CurrentParams()函数得来的。
CurrentParams
后面查看是pendingparams是从SetProtectionParameters函数得来的。
SetProtectionParameters
更新FEC码调用栈
UpdateFecRate
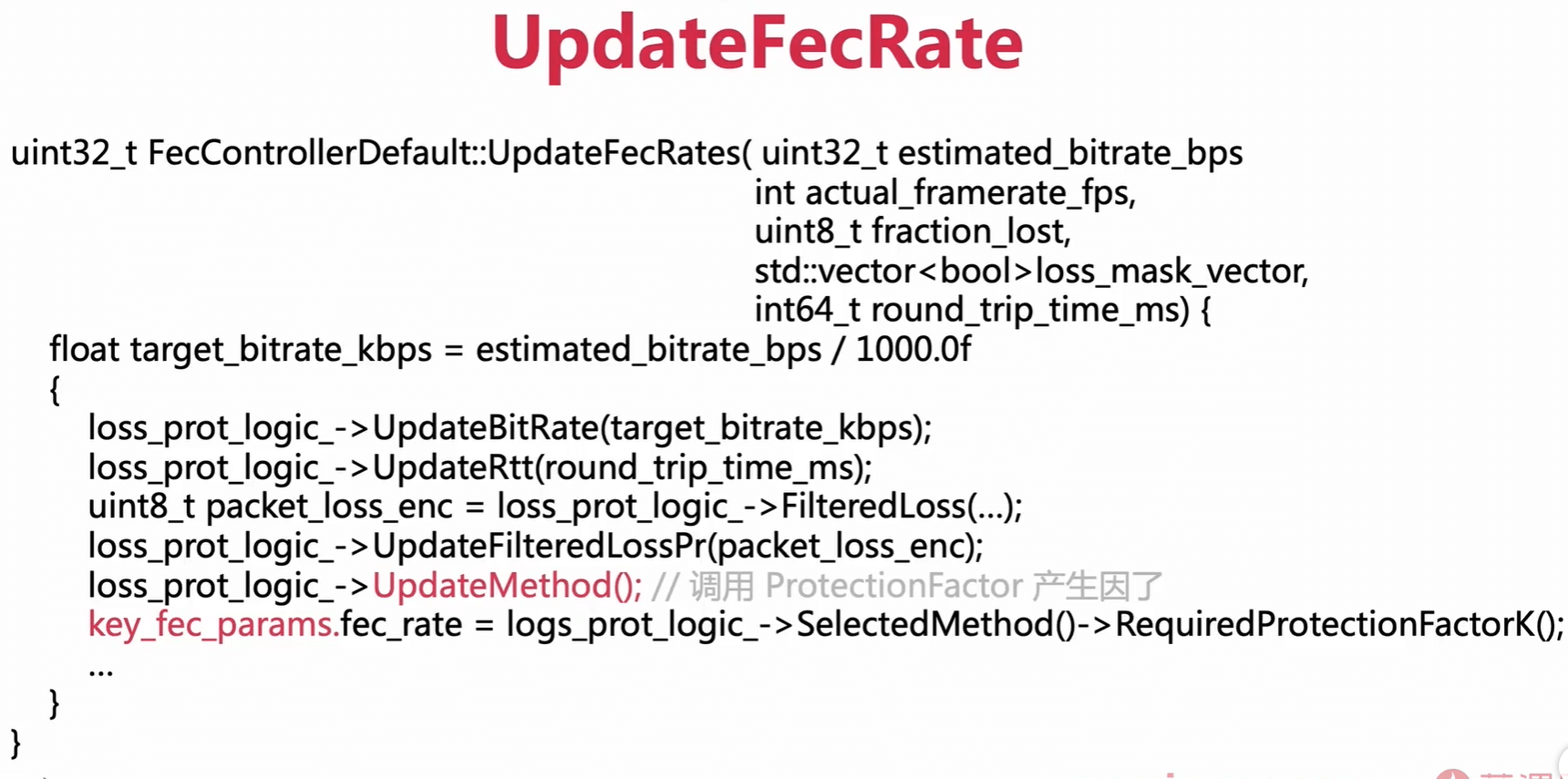
UpdateFecRate(评估码率, 真实帧率,丢包率,丢包的掩码数组,rtt时间)
ProtectionFactor计算保护因子
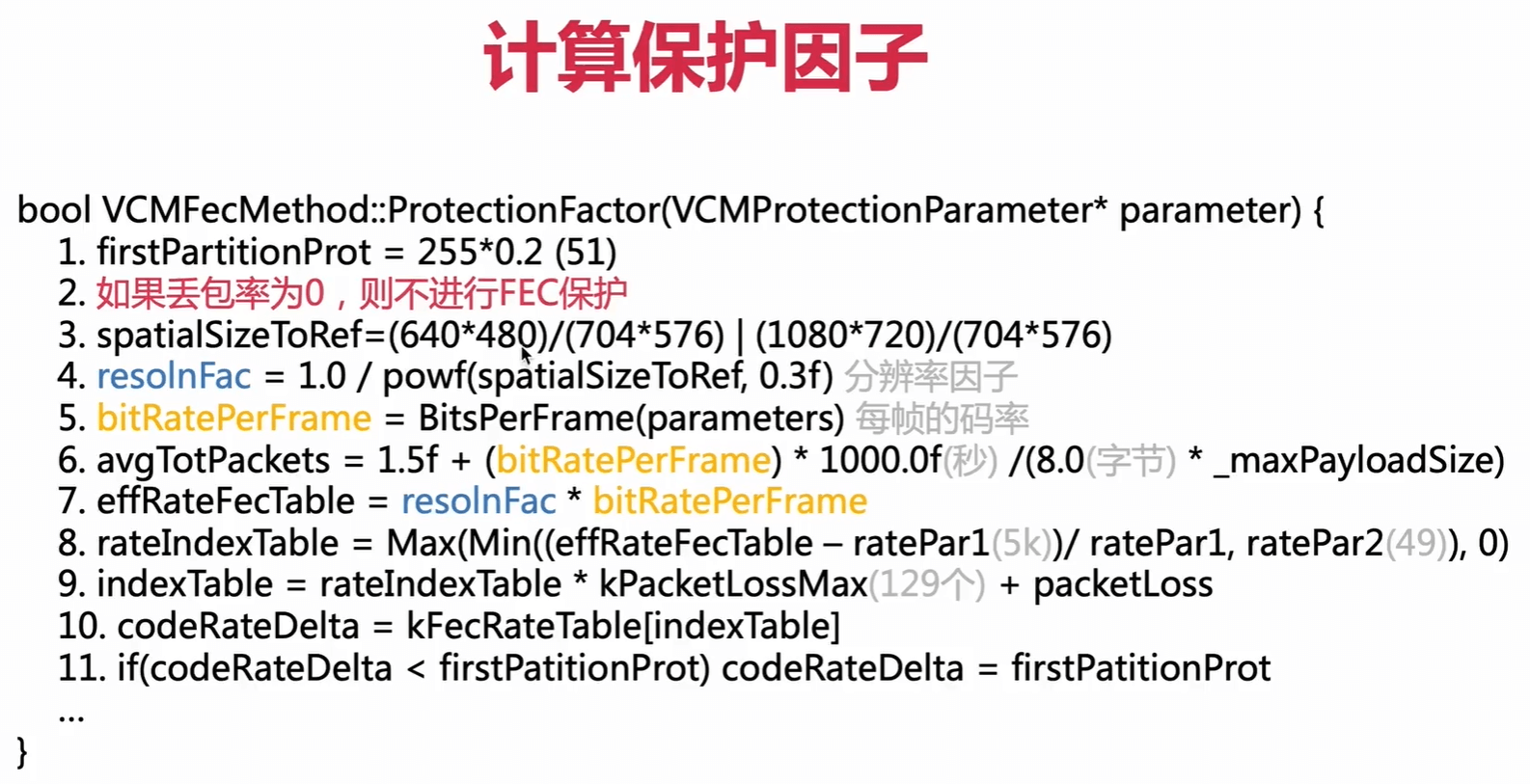
_maxPayloadSize : rtp包的最大字节,1460个。
effRateFecTable 有效码率
codeRateDelta 非关键帧的保护因子。关键帧的保护因子的计算方式跟这个差不多。
kFecRateTable 看《12-29 -FEC基础知识和原理》
bool VCMFecMethod::ProtectionFactor(const VCMProtectionParameters* parameters) {// FEC PROTECTION SETTINGS: varies with packet loss and bitrate// No protection if (filtered) packetLoss is 0uint8_t packetLoss = rtc::saturated_cast<uint8_t>(255 * parameters->lossPr);if (packetLoss == 0) {_protectionFactorK = 0;_protectionFactorD = 0;return true;}// Parameters for FEC setting:// first partition size, thresholds, table pars, spatial resoln fac.// First partition protection: ~ 20%uint8_t firstPartitionProt = rtc::saturated_cast<uint8_t>(255 * 0.20);// Minimum protection level needed to generate one FEC packet for one// source packet/frame (in RTP sender)uint8_t minProtLevelFec = 85;// Threshold on packetLoss and bitRrate/frameRate (=average #packets),// above which we allocate protection to cover at least first partition.uint8_t lossThr = 0;uint8_t packetNumThr = 1;// Parameters for range of rate index of table.const uint8_t ratePar1 = 5;const uint8_t ratePar2 = 49;// Spatial resolution size, relative to a reference size.float spatialSizeToRef = rtc::saturated_cast<float>(parameters->codecWidth *parameters->codecHeight) /(rtc::saturated_cast<float>(704 * 576));// resolnFac: This parameter will generally increase/decrease the FEC rate// (for fixed bitRate and packetLoss) based on system size.// Use a smaller exponent (< 1) to control/soften system size effect.const float resolnFac = 1.0 / powf(spatialSizeToRef, 0.3f);const int bitRatePerFrame = BitsPerFrame(parameters);// Average number of packets per frame (source and fec):const uint8_t avgTotPackets = rtc::saturated_cast<uint8_t>(1.5f + rtc::saturated_cast<float>(bitRatePerFrame) * 1000.0f /rtc::saturated_cast<float>(8.0 * _maxPayloadSize));// FEC rate parameters: for P and I frameuint8_t codeRateDelta = 0;uint8_t codeRateKey = 0;// Get index for table: the FEC protection depends on an effective rate.// The range on the rate index corresponds to rates (bps)// from ~200k to ~8000k, for 30fpsconst uint16_t effRateFecTable =rtc::saturated_cast<uint16_t>(resolnFac * bitRatePerFrame);uint8_t rateIndexTable = rtc::saturated_cast<uint8_t>(VCM_MAX(VCM_MIN((effRateFecTable - ratePar1) / ratePar1, ratePar2), 0));// Restrict packet loss range to 50:// current tables defined only up to 50%if (packetLoss >= kPacketLossMax) {packetLoss = kPacketLossMax - 1;}uint16_t indexTable = rateIndexTable * kPacketLossMax + packetLoss;// Check on table indexRTC_DCHECK_LT(indexTable, kFecRateTableSize);// Protection factor for P framecodeRateDelta = kFecRateTable[indexTable];if (packetLoss > lossThr && avgTotPackets > packetNumThr) {// Set a minimum based on first partition size.if (codeRateDelta < firstPartitionProt) {codeRateDelta = firstPartitionProt;}}// Check limit on amount of protection for P frame; 50% is max.if (codeRateDelta >= kPacketLossMax) {codeRateDelta = kPacketLossMax - 1;}// For Key frame:// Effectively at a higher rate, so we scale/boost the rate// The boost factor may depend on several factors: ratio of packet// number of I to P frames, how much protection placed on P frames, etc.const uint8_t packetFrameDelta =rtc::saturated_cast<uint8_t>(0.5 + parameters->packetsPerFrame);const uint8_t packetFrameKey =rtc::saturated_cast<uint8_t>(0.5 + parameters->packetsPerFrameKey);const uint8_t boostKey = BoostCodeRateKey(packetFrameDelta, packetFrameKey);rateIndexTable = rtc::saturated_cast<uint8_t>(VCM_MAX(VCM_MIN(1 + (boostKey * effRateFecTable - ratePar1) / ratePar1, ratePar2),0));uint16_t indexTableKey = rateIndexTable * kPacketLossMax + packetLoss;indexTableKey = VCM_MIN(indexTableKey, kFecRateTableSize);// Check on table indexassert(indexTableKey < kFecRateTableSize);// Protection factor for I framecodeRateKey = kFecRateTable[indexTableKey];// Boosting for Key frame.int boostKeyProt = _scaleProtKey * codeRateDelta;if (boostKeyProt >= kPacketLossMax) {boostKeyProt = kPacketLossMax - 1;}// Make sure I frame protection is at least larger than P frame protection,// and at least as high as filtered packet loss.codeRateKey = rtc::saturated_cast<uint8_t>(VCM_MAX(packetLoss, VCM_MAX(boostKeyProt, codeRateKey)));// Check limit on amount of protection for I frame: 50% is max.if (codeRateKey >= kPacketLossMax) {codeRateKey = kPacketLossMax - 1;}_protectionFactorK = codeRateKey;_protectionFactorD = codeRateDelta;// Generally there is a rate mis-match between the FEC cost estimated// in mediaOpt and the actual FEC cost sent out in RTP module.// This is more significant at low rates (small # of source packets), where// the granularity of the FEC decreases. In this case, non-zero protection// in mediaOpt may generate 0 FEC packets in RTP sender (since actual #FEC// is based on rounding off protectionFactor on actual source packet number).// The correction factor (_corrFecCost) attempts to corrects this, at least// for cases of low rates (small #packets) and low protection levels.float numPacketsFl =1.0f + (rtc::saturated_cast<float>(bitRatePerFrame) * 1000.0 /rtc::saturated_cast<float>(8.0 * _maxPayloadSize) +0.5);const float estNumFecGen =0.5f +rtc::saturated_cast<float>(_protectionFactorD * numPacketsFl / 255.0f);// We reduce cost factor (which will reduce overhead for FEC and// hybrid method) and not the protectionFactor._corrFecCost = 1.0f;if (estNumFecGen < 1.1f && _protectionFactorD < minProtLevelFec) {_corrFecCost = 0.5f;}if (estNumFecGen < 0.9f && _protectionFactorD < minProtLevelFec) {_corrFecCost = 0.0f;}// DONE WITH FEC PROTECTION SETTINGSreturn true;}



