描述
给定单链表的头节点 head ,请反转链表,并返回反转后的链表的头节点。
示例
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
提示
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5000] -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
解题思路
方法一:迭代
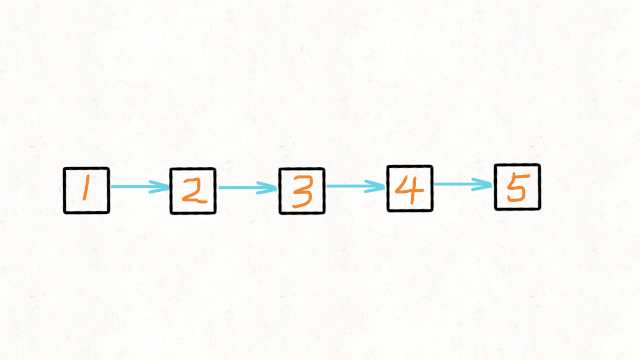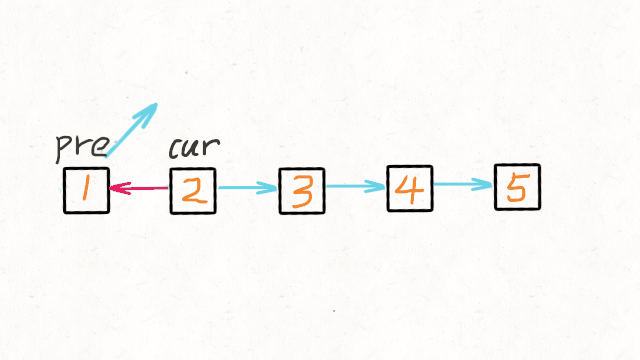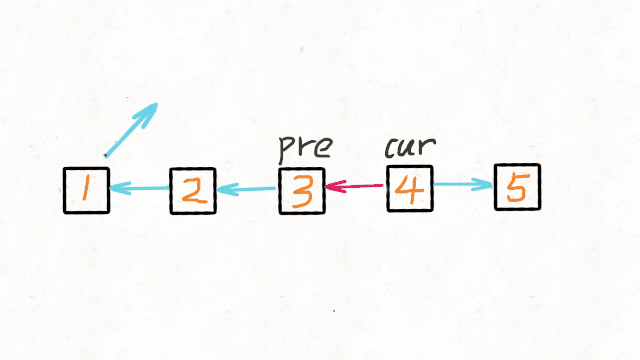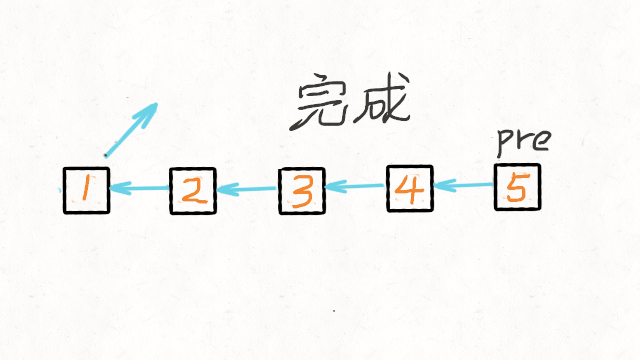
- 维护两个节点
curr,prev。curr代表当前节点,prev代表上一个节点,每次迭代时,将curr节点的next指针指向prev节点。同时,需要用另一个指针保存下一个节点。
代码
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode nextTemp = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = nextTemp;
}
return prev;
}
}
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:O(n),假设 n 是列表的长度,时间复杂度是 O(n)。
- 空间复杂度:O(1)。
方法二:递归
- 递归其实就是从右往左,逐步地构建反转链表,这样能保证当我们进行反转指针时,即
cur.next.next = cur操作时,不能因为丢失后面一个节点的 next 指针而无法操作,因为当前节点后面的指针已经反转好了,所以不需要再去关心这个问题。
代码
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode p = reverseList(head.next); // p 是反转前最后一个节点
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null; // 防止循环
return p;
}
}
递归过程如下:
reverseList: head=1
reverseList: head=2
reverseList: head=3
reverseList:head=4
reverseList:head=5
终止返回
cur = 5
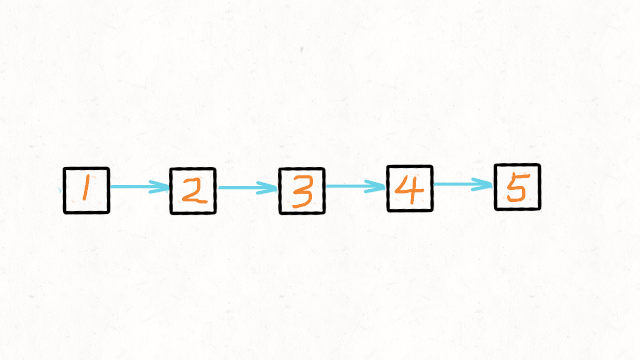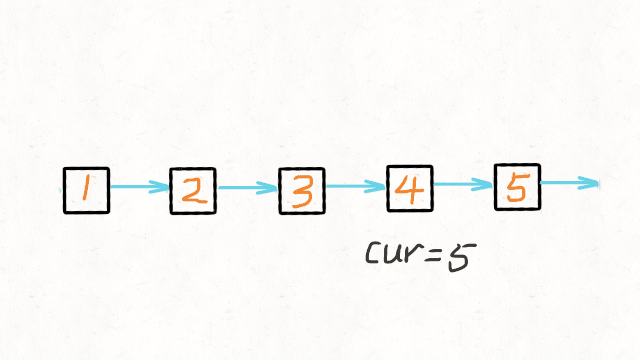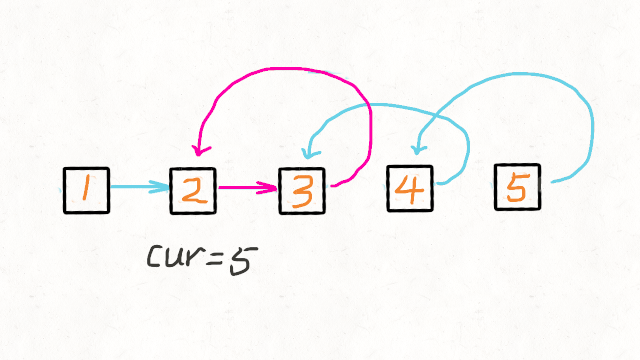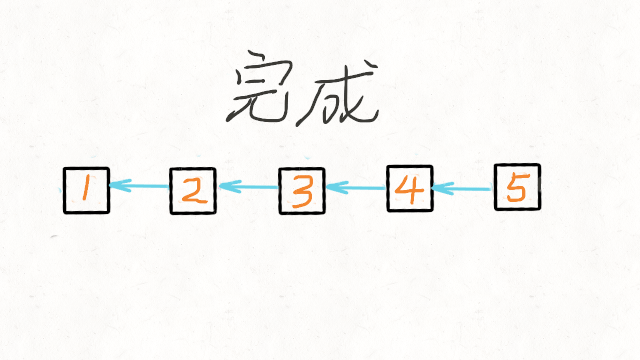
4.next.next->4,即5->4
cur=5
3.next.next->3,即4->3
cur = 5
2.next.next->2,即3->2
cur = 5
1.next.next->1,即2->1
最后返回cur
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n),假设 n 是列表的长度,那么时间复杂度为 O(n)。
空间复杂度:O(n),由于使用递归,将会使用隐式栈空间。递归深度可能会达到 n 层。