描述
给定一个可包含重复数字的整数集合 nums ,按任意顺序 返回它所有不重复的全排列。
示例
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,1,2]输出:[[1,1,2],[1,2,1],[2,1,1]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [1,2,3]
输出:[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
提示
1 <= nums.length <= 8-10 <= nums[i] <= 10
解题思路
- 这道题的关键是想清楚什么时候会出现 重复的全排列,为什么会出现 , 如何去重(剪枝)
- 先对数组排序,这是剪枝的前提,对于相同的元素,同一层的相同元素的全排列是一样的,所以需要进行剪枝。参考下图:
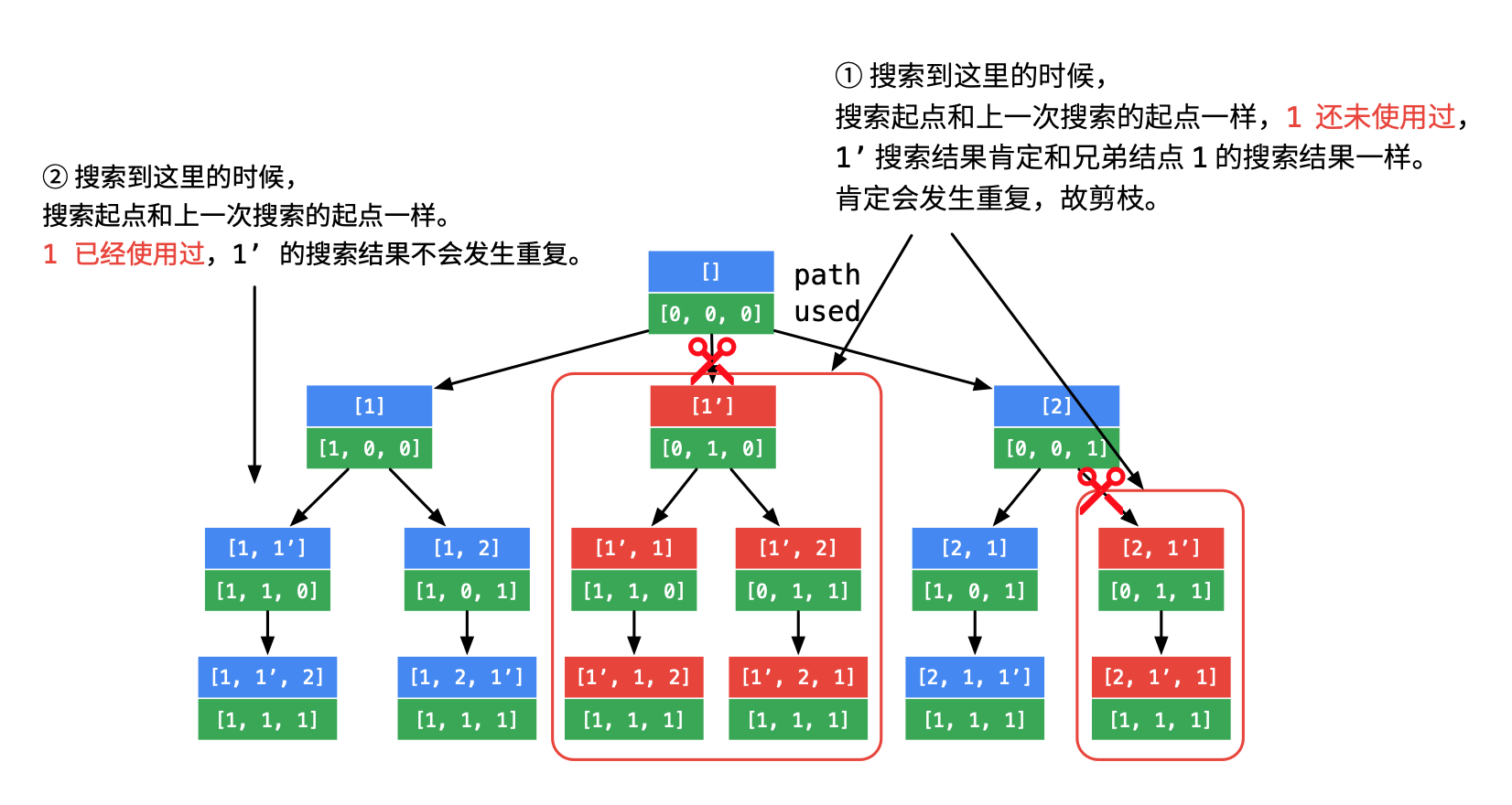
剪枝代码:
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && !used[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
这里要重点思考下为什么是 !used[i - 1],因为 i - 1 未被使用时,正好说明 i - 1 和 i 在同一层。
代码
class Solution {
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<Integer>();
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
boolean[] used = new boolean[n];
Arrays.sort(nums);
dfs(0, used, nums);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(int cur, boolean[] used, int[] nums) {
if (path.size() == nums.length) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (used[i]) {
continue;
}
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && !used[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
path.add(nums[i]);
used[i] = true;
dfs(i + 1, used, nums);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
used[i] = false;
}
}
}

