描述
给定一个单链表 L 的头节点 head ,单链表 L 表示为:
L0 → L1 → … → Ln-1 → Ln
请将其重新排列后变为:L0 → Ln → L1 → Ln-1 → L2 → Ln-2 → …
不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
示例
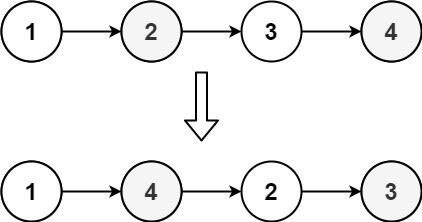
输入: head = [1,2,3,4]输出: [1,4,2,3]
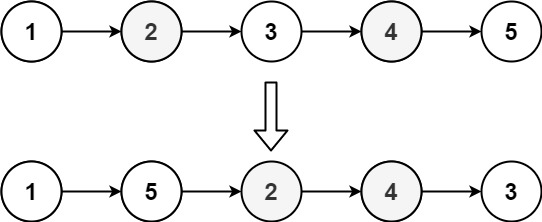
输入: head = [1,2,3,4,5]输出: [1,5,2,4,3]
提示
- 链表的长度范围为 [1, 5 * 104]
- 1 <= node.val <= 1000
解题思路
线性表
用线性表存储该链表,然后利用线性表可以下标访问的特点,直接按顺序访问指定元素,重建该链表即可。
代码
class Solution {public void reorderList(ListNode head) {if (head == null) {return;}List<ListNode> list = new ArrayList<ListNode>();ListNode node = head;while (node != null) {list.add(node);node = node.next;}int i = 0, j = list.size() - 1;while (i < j) {list.get(i).next = list.get(j);i++;if (i == j) {break;}list.get(j).next = list.get(i);j--;}list.get(i).next = null;}}
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:O(N), 其中 N 是链表中的节点数。
- 空间复杂度:O(N), 其中 N 是链表中的节点数。主要为线性表的开销。
寻找链表中点 + 链表逆序 + 合并链表
- 找到原链表的中点
- 我们可以使用快慢指针来 O(N) 地找到链表的中间节点。
- 将原链表的右半端反转
- 我们可以使用迭代法实现链表的反转。
- 将原链表的两端合并。
- 因为两链表长度相差不超过 1,因此直接合并即可。
代码
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/class Solution {public void reorderList(ListNode head) {if (head == null) return;ListNode mid = findMidNode(head);ListNode l1 = head;ListNode l2 = mid.next;mid.next = null;l2 = revertList(l2);merge(l1, l2);}public ListNode findMidNode(ListNode head) {if (head == null) return null;ListNode slow = head;ListNode fast = head;while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;}return slow;}public ListNode revertList(ListNode head) {if (head == null) return null;ListNode pre = null;ListNode curr = head;while (curr != null) {ListNode next = curr.next;curr.next = pre;pre = curr;curr = next;}return pre;}public void merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {ListNode l1_tmp;ListNode l2_tmp;while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {l1_tmp = l1.next;l2_tmp = l2.next;l1.next = l2;l1 = l1_tmp;l2.next = l1;l2 = l2_tmp;}}}
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是链表中的节点数。
- 空间复杂度:O(1)。

