算法步骤
- 首先将待排序的数组构造成一个大根堆,此时,整个数组的最大值就是堆结构的顶端
- 将顶端的数与末尾的数交换,此时,末尾的数为最大值,剩余待排序数组个数为n-1
- 将剩余的n-1个数再构造成大根堆,再将顶端数与n-1位置的数交换,如此反复执行,便能得到有序数组
动图演示
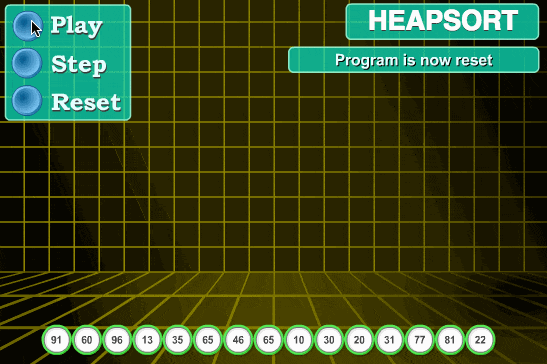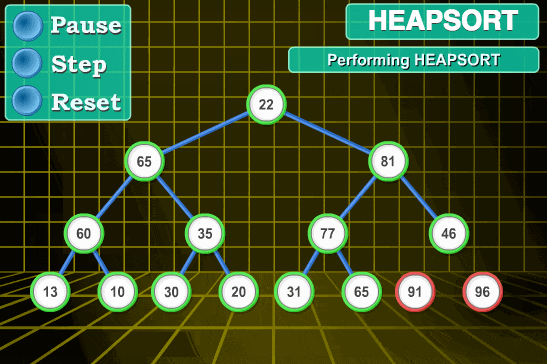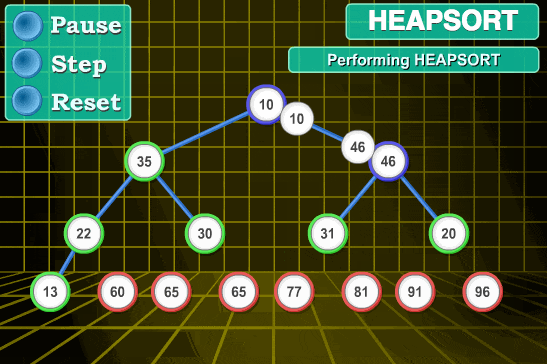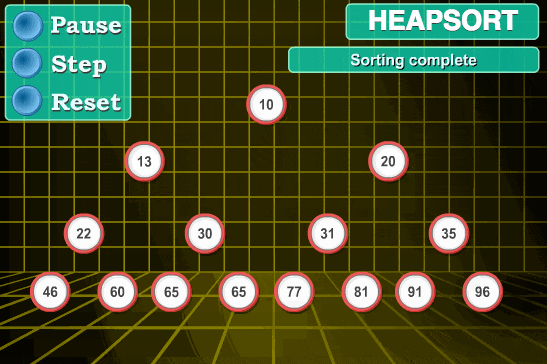
代码
//堆排序 public static void heapSort(int[] arr) { //构造大根堆 heapInsert(arr); int size = arr.length; while (size > 1) { //固定最大值 swap(arr, 0, size - 1); size--; //构造大根堆 heapify(arr, 0, size); } } //构造大根堆(通过新插入的数上升) public static void heapInsert(int[] arr) { for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { //当前插入的索引 int currentIndex = i; //父结点索引 int fatherIndex = (currentIndex - 1) / 2; //如果当前插入的值大于其父结点的值,则交换值,并且将索引指向父结点 //然后继续和上面的父结点值比较,直到不大于父结点,则退出循环 while (arr[currentIndex] > arr[fatherIndex]) { //交换当前结点与父结点的值 swap(arr, currentIndex, fatherIndex); //将当前索引指向父索引 currentIndex = fatherIndex; //重新计算当前索引的父索引 fatherIndex = (currentIndex - 1) / 2; } } } //将剩余的数构造成大根堆(通过顶端的数下降) public static void heapify(int[] arr, int index, int size) { int left = 2 * index + 1; int right = 2 * index + 2; while (left < size) { int largestIndex; //判断孩子中较大的值的索引(要确保右孩子在size范围之内) if (arr[left] < arr[right] && right < size) { largestIndex = right; } else { largestIndex = left; } //比较父结点的值与孩子中较大的值,并确定最大值的索引 if (arr[index] > arr[largestIndex]) { largestIndex = index; } //如果父结点索引是最大值的索引,那已经是大根堆了,则退出循环 if (index == largestIndex) { break; } //父结点不是最大值,与孩子中较大的值交换 swap(arr, largestIndex, index); //将索引指向孩子中较大的值的索引 index = largestIndex; //重新计算交换之后的孩子的索引 left = 2 * index + 1; right = 2 * index + 2; } } //交换数组中两个元素的值 public static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) { int temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = temp; }
参考:堆排序算法(图解详细流程)


