描述
给定一个有 n 个节点的有向无环图,用二维数组 graph 表示,请找到所有从 0 到 n-1 的路径并输出(不要求按顺序)。
graph 的第 i 个数组中的单元都表示有向图中 i 号节点所能到达的下一些结点(译者注:有向图是有方向的,即规定了 a→b 你就不能从 b→a ),若为空,就是没有下一个节点了。
示例
示例 1: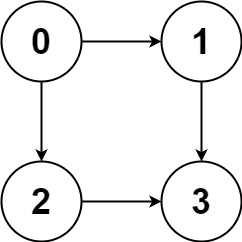
输入:graph = [[1,2],[3],[3],[]]输出:[[0,1,3],[0,2,3]]解释:有两条路径 0 -> 1 -> 3 和 0 -> 2 -> 3
示例 2:
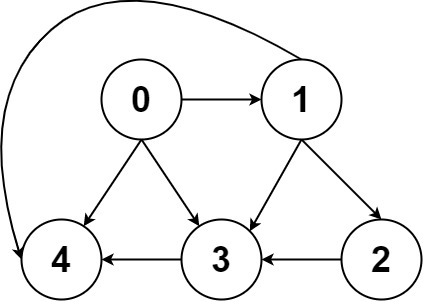
输入:graph = [[4,3,1],[3,2,4],[3],[4],[]]
输出:[[0,4],[0,3,4],[0,1,3,4],[0,1,2,3,4],[0,1,4]]
提示
n == graph.length2 <= n <= 150 <= graph[i][j] < ngraph[i][j] != i- 保证输入为有向无环图
(GAD)
解题思路
1、 深度优先搜索
我们可以使用深度优先搜索的方式求出所有可能的路径。具体地,我们从 0 号点出发,使用栈记录路径上的点。每次我们遍历到点 n−1,就将栈中记录的路径加入到答案中。
特别地,因为本题中的图为有向无环图(DAG),搜索过程中不会反复遍历同一个点,因此我们无需判断当前点是否遍历过。
代码
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public List<List<Integer>> allPathsSourceTarget(int[][] graph) {
int n = graph.length;
path.add(0);
dfs(0, graph, path);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(int index, int[][] graph, List<Integer> path) {
if (index == graph.length - 1) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(path));
return;
}
for (int num : graph[index]) {
path.add(num);
dfs(num, graph, path);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
2、 广度优先搜索
- 需要定义一个带有路径的数据结构 Node, 这样才能保证当前节点的路径是从 0 开始到这个节点的路径。
- 因为是有向无环图,所以不需要 visited 数组避免重复访问
- 剩下的事情就是套用 BFS 模板
代码
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> allPathsSourceTarget(int[][] graph) {
// bfs,从0开始一层一层向外搜索
List<List<Integer>> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
int n = graph.length;
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new Node(0));
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node node = queue.poll();
if (node.index == n - 1) {
resultList.add(node.path);
continue;
}
for (int next : graph[node.index]) {
queue.offer(new Node(next, node.path));
}
}
return resultList;
}
class Node {
int index;
List<Integer> path;
Node(int index) {
this.index = index;
this.path = new ArrayList<>();
// 把当前节点加入路径
this.path.add(index);
}
Node(int index, List<Integer> path) {
this.index = index;
// 复制一个新的List
this.path = new ArrayList<>(path);
// 把当前节点加入路径
this.path.add(index);
}
}
}

