- 剑指 Offer 12. 矩阵中的路径💦">剑指 Offer 12. 矩阵中的路径💦
- 剑指 Offer 13. 机器人的运动范围">剑指 Offer 13. 机器人的运动范围
- 剑指 Offer 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径">剑指 Offer 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
- 剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表">剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
- 剑指 Offer 38. 字符串的排列">剑指 Offer 38. 字符串的排列
- 剑指 Offer 54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点">剑指 Offer 54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点
- 剑指 Offer 55 - I. 二叉树的深度">剑指 Offer 55 - I. 二叉树的深度
- 剑指 Offer 55 - II. 平衡二叉树">剑指 Offer 55 - II. 平衡二叉树
- 剑指 Offer 64. 求1+2+…+n">剑指 Offer 64. 求1+2+…+n
- 剑指 Offer 68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先">剑指 Offer 68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
- 剑指 Offer 68 - II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先">剑指 Offer 68 - II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
- 剑指 Offer 37. 序列化二叉树">剑指 Offer 37. 序列化二叉树
剑指 Offer 12. 矩阵中的路径💦

本题考察dfs + 回溯
class Solution {public:int len = 0;bool backtracking(vector<vector<char>>& board, vector<vector<bool>>& used, int i, int j, const string& word) {if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= board.size() || j >= board[0].size() || used[i][j] || board[i][j] != word[len]) return false; // 剪枝used[i][j] = true; // 使用当前字母len++;if (len == word.size()) return true;// 向四个方向搜索bool flag = backtracking(board, used, i + 1, j, word) || backtracking(board, used, i, j + 1, word) || backtracking(board, used, i - 1, j, word) || backtracking(board, used, i, j - 1, word);used[i][j] = false;len--;return flag;}bool exist(vector<vector<char>>& board, string word) {if (board.size() == 0) return false;int m = board.size(), n = board[0].size();vector<vector<bool>> used(m, vector<bool>(n, false));// 以board[i][j]为起始位置for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {if (backtracking(board, used, i, j, word)) return true;}}return false;}};
剑指 Offer 13. 机器人的运动范围
class Solution {
public:
// 计算数位和
int compute(int n) {
int ans = 0;
while (n) {
int temp = n % 10;
ans += temp;
n /= 10;
}
return ans;
}
// dfs
int backtracking(int i, int j, int& m, int& n, int& k, vector<vector<bool>>& used) {
// 到不了这个格子
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= m || j >= n || used[i][j] || compute(i) + compute(j) > k) {
return 0;
}
// 可以走到当前格子
used[i][j] = true;
return backtracking(i + 1, j, m, n, k, used) + backtracking(i - 1, j, m, n, k, used) + backtracking(i, j + 1, m, n, k, used) + backtracking(i, j - 1, m, n, k, used) + 1;
}
int movingCount(int m, int n, int k) {
vector<vector<bool>> used(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
return backtracking(0, 0, m, n, k, used);
}
};
剑指 Offer 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
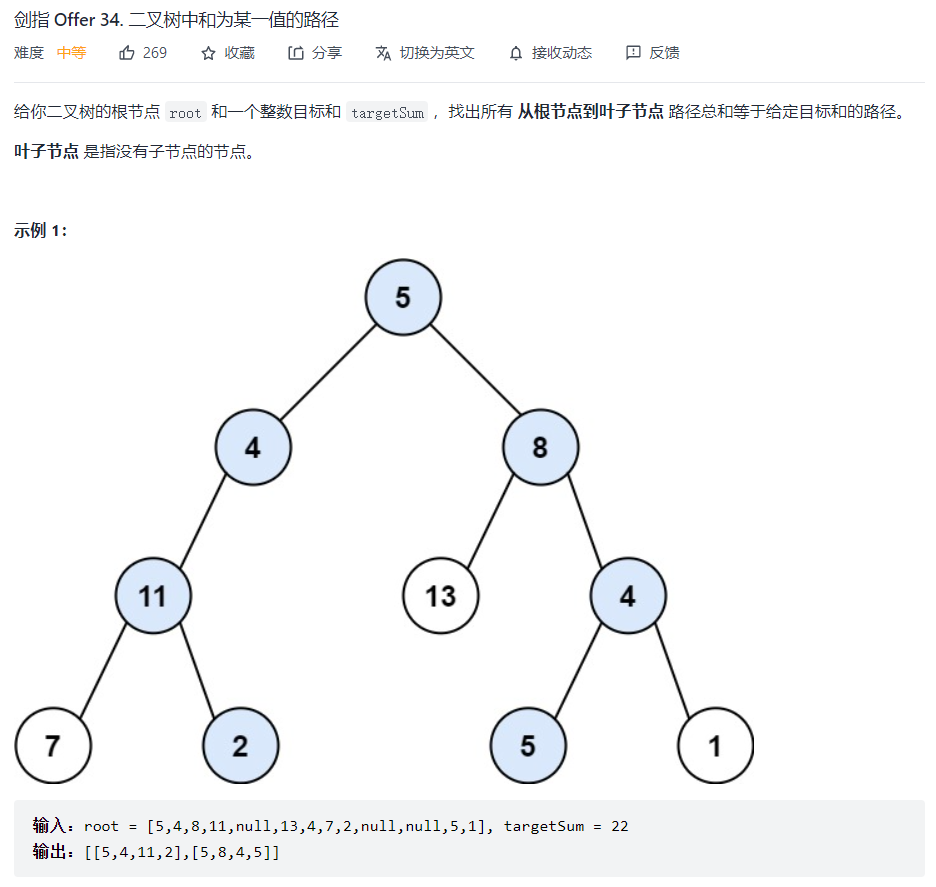
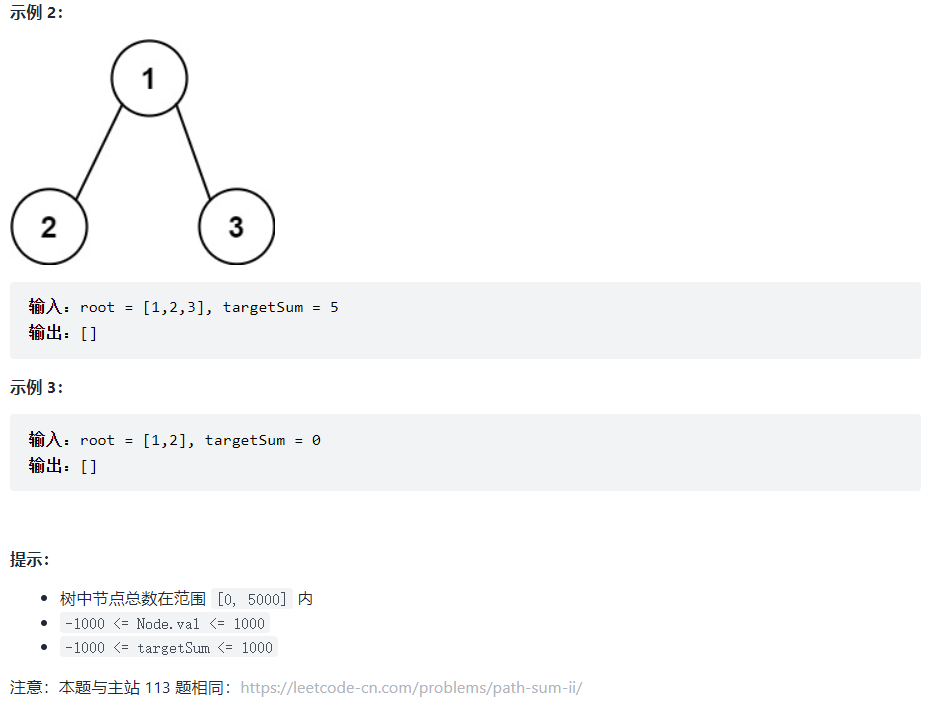
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
void backtracking(TreeNode* cur, int target) {
if (!cur) return;
// 处理当前节点
path.push_back(cur->val);
target -= cur->val;
// 如果当前节点是叶子节点并且路径值为target
if (cur->left == nullptr && cur->right == nullptr && target == 0) {
res.push_back(path);
}
backtracking(cur->left, target);
backtracking(cur->right, target);
target += cur->val;
path.pop_back();
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int target) {
if (!root) return {};
backtracking(root, target);
return res;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
void traversal(TreeNode* cur, int count) {
if (!cur->left && !cur->right && count == 0) {// 当前节点是叶子节点,保存根结点到叶子节点的路径
res.push_back(path);
}
if (cur->left) {
path.push_back(cur->left->val);
traversal(cur->left, count - cur->left->val);
path.pop_back();
}
if (cur->right) {
path.push_back(cur->right->val);
traversal(cur->right, count - cur->right->val);
path.pop_back();
}
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (!root) return res;
path.push_back(root->val);
traversal(root, targetSum - root->val);
return res;
}
};
剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
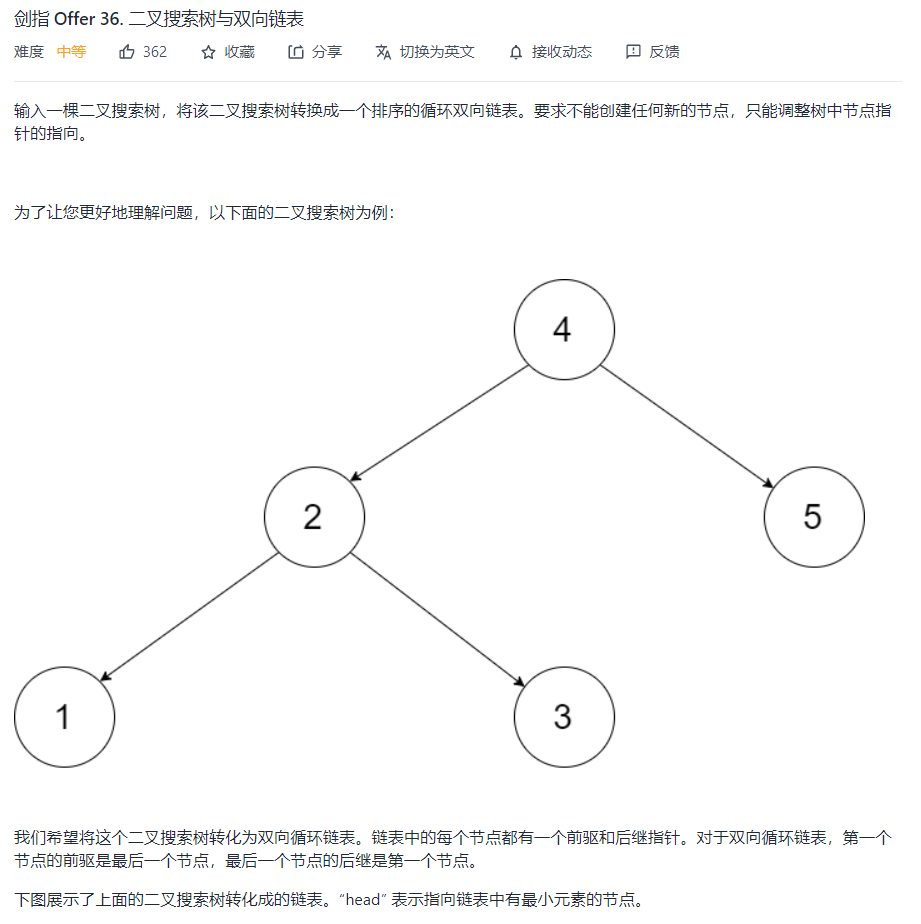

class Solution {
Node head, pre;
public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) {
if(root==null) return null;
dfs(root);
pre.right = head;
head.left =pre;//进行头节点和尾节点的相互指向,这两句的顺序也是可以颠倒的
return head;
}
public void dfs(Node cur){
if(cur==null) return;
dfs(cur.left);
//pre用于记录双向链表中位于cur左侧的节点,即上一次迭代中的cur,当pre==null时,cur左侧没有节点,即此时cur为双向链表中的头节点
if(pre==null) head = cur;
//反之,pre!=null时,cur左侧存在节点pre,需要进行pre.right=cur的操作。
else pre.right = cur;
cur.left = pre;//pre是否为null对这句没有影响,且这句放在上面两句if else之前也是可以的。
pre = cur;//pre指向当前的cur
dfs(cur.right);//全部迭代完成后,pre指向双向链表中的尾节点
}
}
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return nullptr;
dfs(root);
head->left = pre;
pre->right = head;
return head;
}
Node *pre, *head;
void dfs(Node* cur) {
if(cur == nullptr) return;
dfs(cur->left);
if(pre != nullptr) pre->right = cur;
else head = cur;
cur->left = pre;
pre = cur;
dfs(cur->right);
}
};
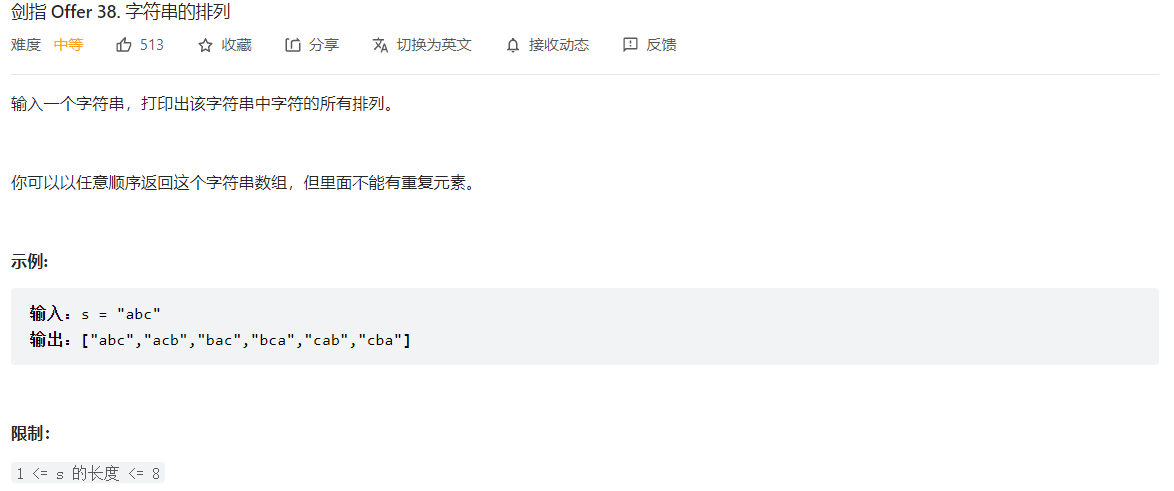
剑指 Offer 38. 字符串的排列
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> res;
string path;
void dfs(string& s, vector<bool>& used) {
if (path.size() == s.size()) {
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
if (i > 0 && s[i] == s[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false) {
continue;
}
if (used[i] == false) {
path.push_back(s[i]);
used[i] = true;
dfs(s, used);
used[i] = false;
path.pop_back();
}
}
}
vector<string> permutation(string s) {
vector<bool> used(s.size(), false);
sort(s.begin(), s.end());
dfs(s, used);
return res;
}
};
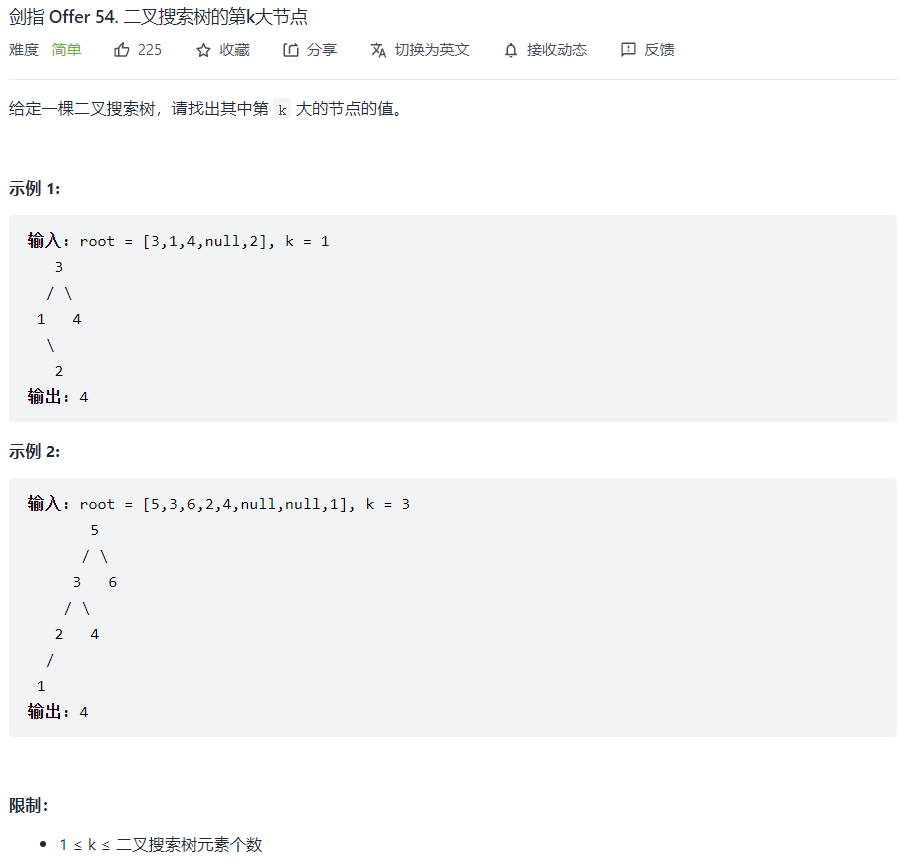
剑指 Offer 54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点
二叉搜索树左中右的中序遍历得到的是升序数组,如果将遍历顺序改为右中左,得到的就是降序序列,也就是先访问的元素是最大的。
那么采取右中左的遍历方式遍历二叉搜索树,并用一个变量来记录当前访问的元素是第几个,当访问到第k个时,记录即可。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int count = 0, ans = 0;
void traversal(TreeNode* root, int &k) {
if (!root) return;
traversal(root->right, k);
if (++count == k) {
ans = root->val;
return;
}
traversal(root->left, k);
}
int kthLargest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
traversal(root, k);
return ans;
}
};
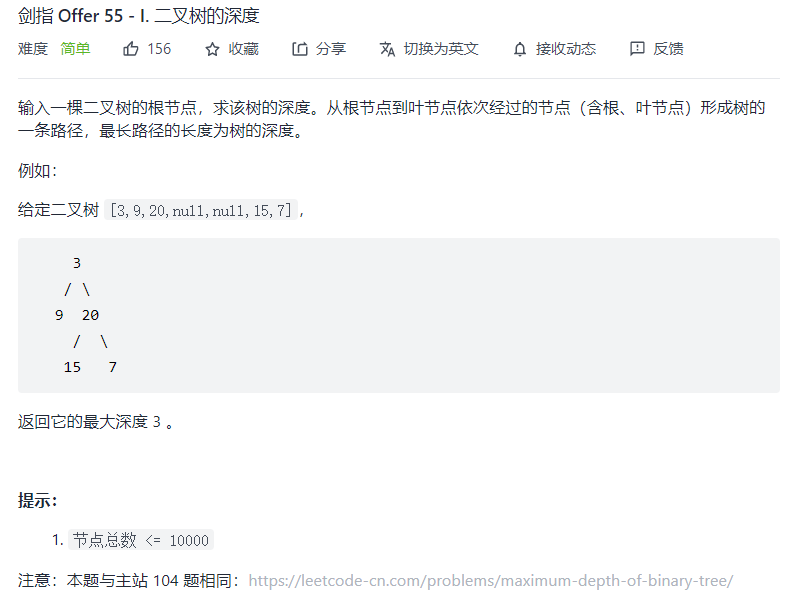
剑指 Offer 55 - I. 二叉树的深度
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};
剑指 Offer 55 - II. 平衡二叉树

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int getDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
int leftDepth = getDepth(root->left);
if (leftDepth == -1) return -1;
int rightDepth = getDepth(root->right);
if (rightDepth == -1) return -1;
return abs(leftDepth - rightDepth) <= 1 ? 1 + max(rightDepth, leftDepth) : -1;
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
return getDepth(root) == -1 ? false : true;
}
};
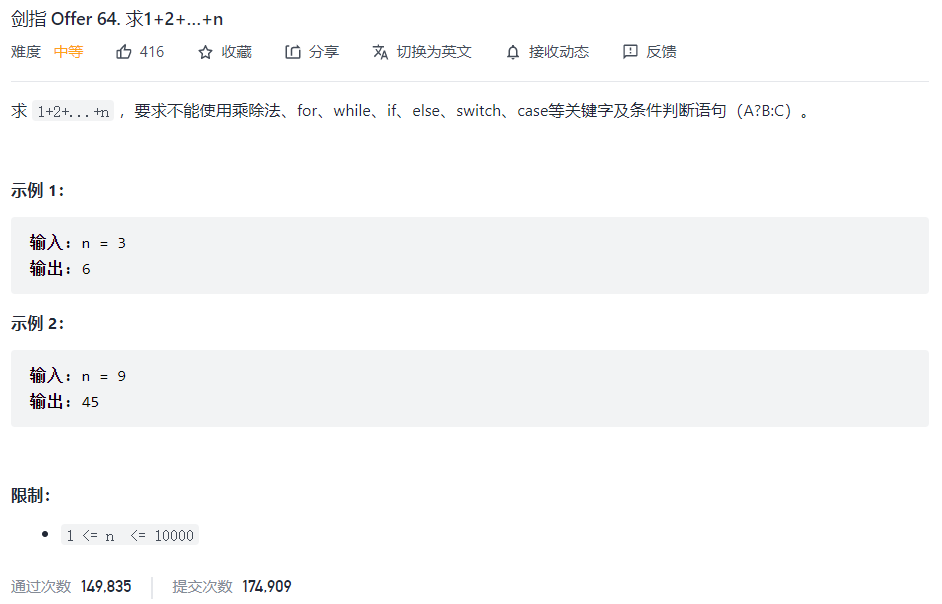
剑指 Offer 64. 求1+2+…+n
秀儿做法
bool类型占用一个字节,定义一个n n + 1的二维bool数组,大小为 n n + 1 个字节, 然后除以二。
class Solution {
public:
int sumNums(int n) {
bool arr[n][n + 1];
return sizeof(arr) >> 1;
}
};
递归
不能使用很多运算符,那么运用逻辑运算符短路的性质来进行判断
class Solution {
public:
int sumNums(int n) {
n && (n += sumNums(n - 1));
return n;
}
};
剑指 Offer 68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
按照一般二叉树来处理
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if (root == p || root == q || !root) return root;
TreeNode *left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
TreeNode *right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if (left && right) return root; // 当前节点是公共祖先
// 返回找到的那个或者空节点表示没有找到
if (!left) return right;
return left;
}
};
根据搜索二叉树的性质
递归
如果当前节点的值比p、q的都大,那么去左边查找,反之去右边查找
如果介于二者之间,那么该节点就是最近公共祖先
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if (!root) return root;
if (root->val > p->val && root->val > q->val) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
} else if (root->val < p->val && root->val < q->val) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
}
return root;
}
};
迭代
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
while (root) {
if (root->val > p->val && root->val > q->val) {
root = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
} else if (root->val < p->val && root->val < q->val) {
root = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
} else break;
}
return root;
}
};
剑指 Offer 68 - II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先

class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if (root == p || root == q || !root) return root;
TreeNode *left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
TreeNode *right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if (left && right)
return root;
if (!left)
return right;
return left;
}
};
剑指 Offer 37. 序列化二叉树



