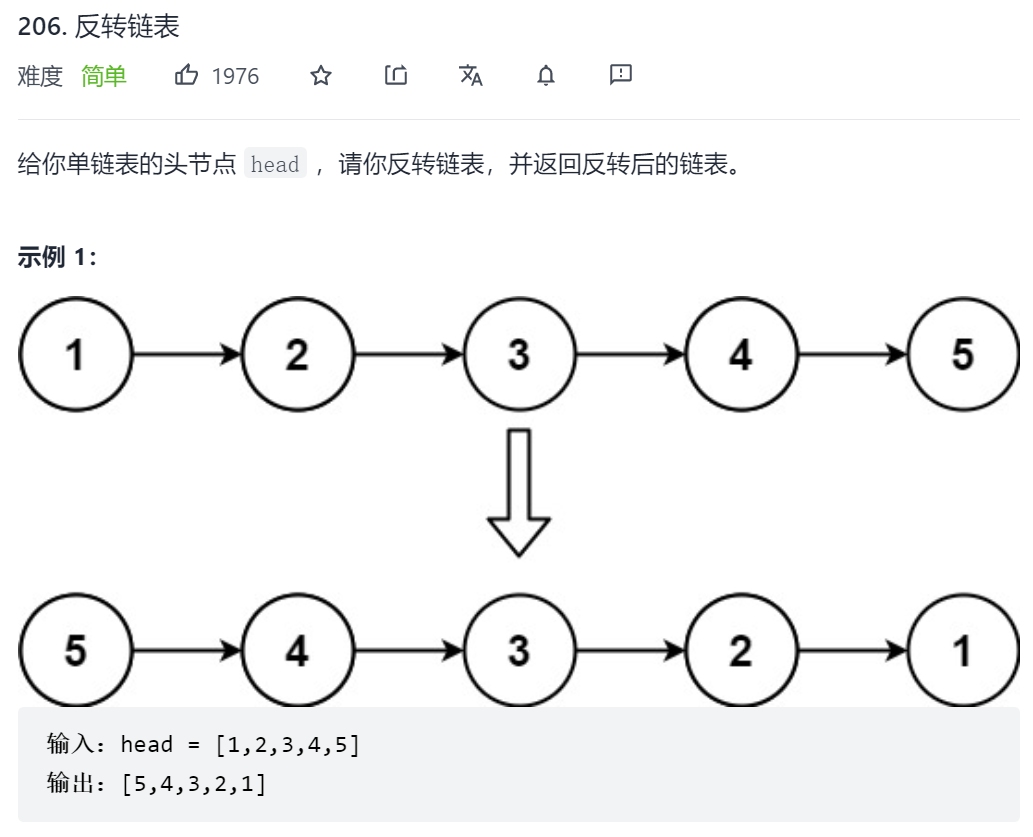
206. 反转链表
思路一:改变指针方向
可以再创建一个链表,然后通过头插法实现链表的翻转,但是这样会很浪费空间,其实可以直接通过改变指针方向来实现链表的翻转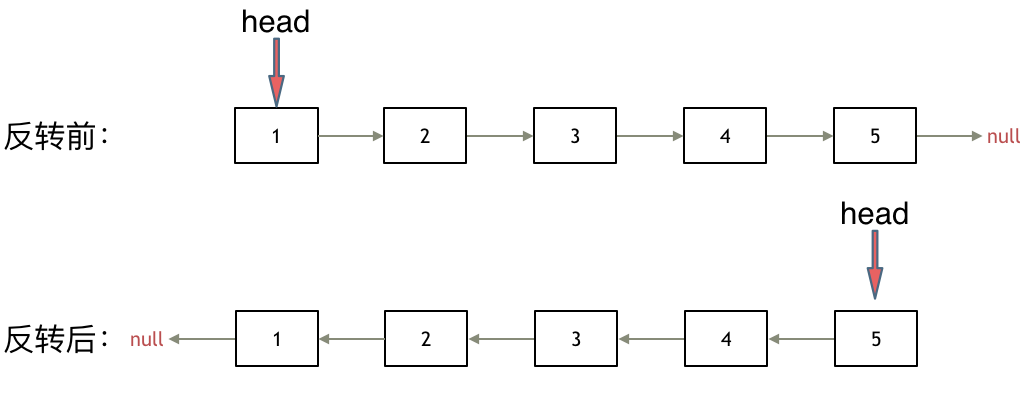
定义三个指针pre、cur、nxt:
- cur:指向当前节点,初始为head
- pre:指向前一个节点,初始为nullptr
- nxt:指向下一个节点,防止断链
动画演示翻转过程: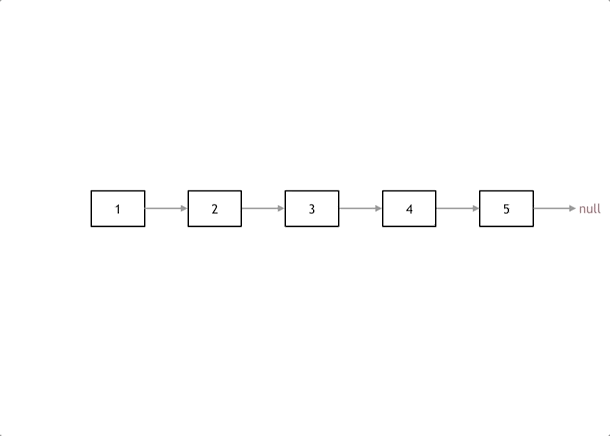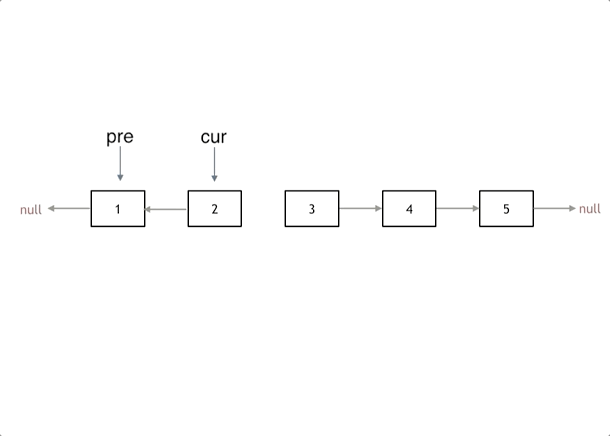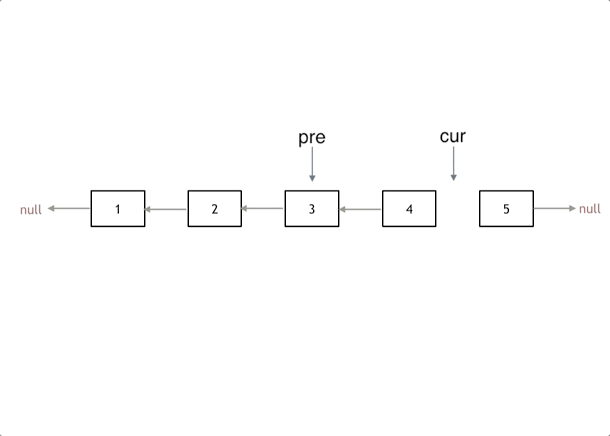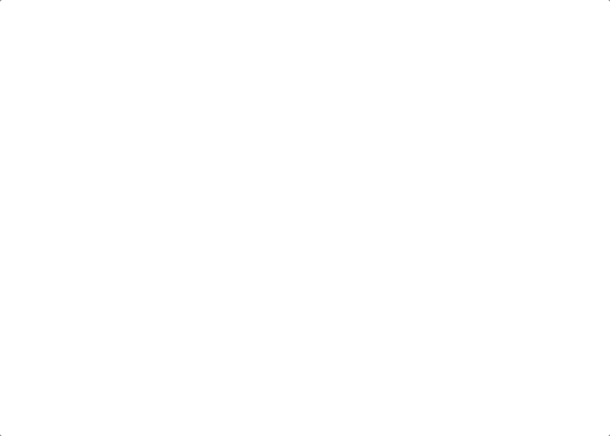
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/class Solution {public:ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {if (head == nullptr)return nullptr;ListNode* pre = nullptr;ListNode* cur = head;while(cur) {ListNode* nxt = cur->next;//保存下一个节点防止断链cur->next = pre;pre = cur;cur = nxt;}return pre;}};
思路二:递归法
递归法其实和改变指针方向的思路是一样的,每次递归改变一次指针朝向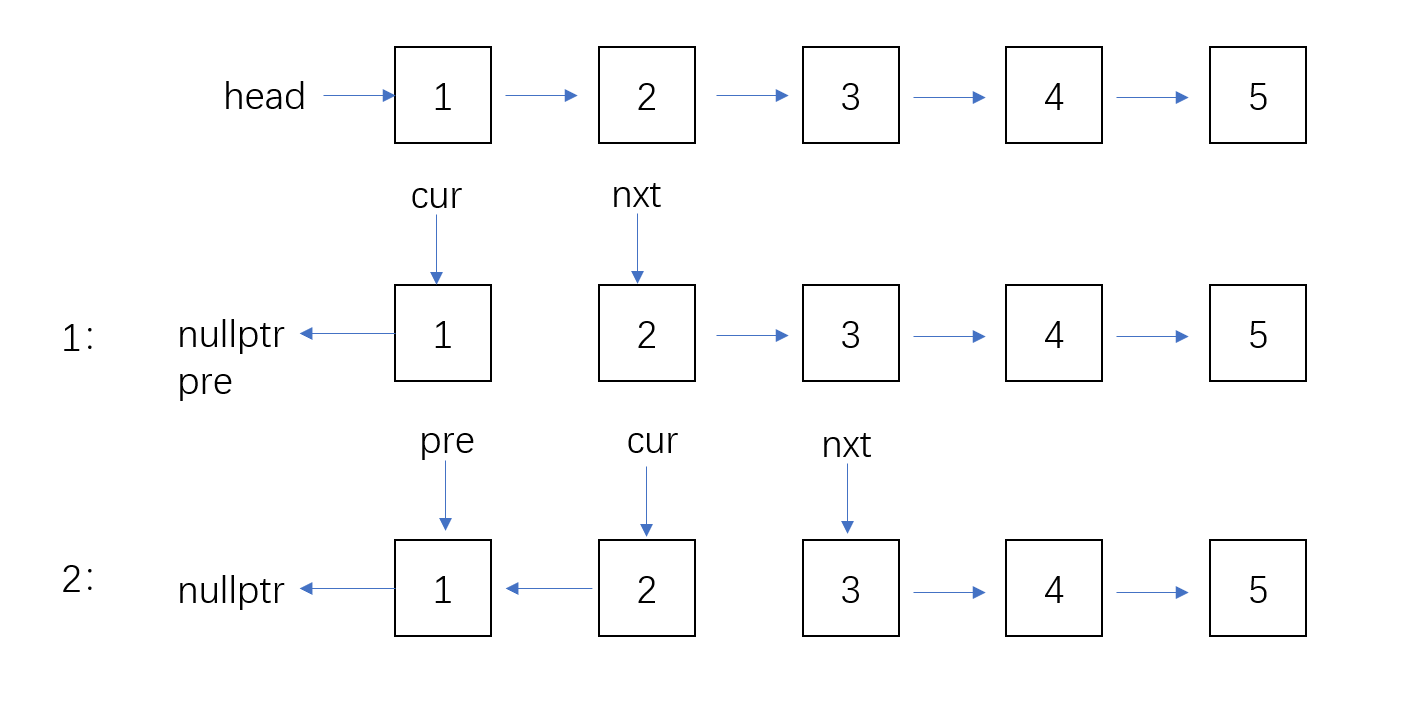
递归函数的参数为:
- pre:改变后的指向
- cur:要改变方向的节点
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/class Solution {public:ListNode* reverse(ListNode* pre, ListNode* cur) {if (cur == nullptr)return pre;ListNode* nxt = cur->next;cur->next = pre;return reverse(cur, nxt);}ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {return reverse(nullptr, head);}};
92. 反转链表 II
思路一:先反转,再拼接
class Solution {private:void reverseLinkedList(ListNode *head) {// 也可以使用递归反转一个链表ListNode *pre = nullptr;ListNode *cur = head;while (cur != nullptr) {ListNode *next = cur->next;cur->next = pre;pre = cur;cur = next;}}public:ListNode *reverseBetween(ListNode *head, int left, int right) {// 因为头节点有可能发生变化,使用虚拟头节点可以避免复杂的分类讨论ListNode *dummyNode = new ListNode(-1);dummyNode->next = head;ListNode *pre = dummyNode;// 第 1 步:从虚拟头节点走 left - 1 步,来到 left 节点的前一个节点// 建议写在 for 循环里,语义清晰for (int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++) {pre = pre->next;}// 第 2 步:从 pre 再走 right - left + 1 步,来到 right 节点ListNode *rightNode = pre;for (int i = 0; i < right - left + 1; i++) {rightNode = rightNode->next;}// 第 3 步:切断出一个子链表(截取链表)ListNode *leftNode = pre->next;ListNode *curr = rightNode->next;// 注意:切断链接pre->next = nullptr;rightNode->next = nullptr;// 第 4 步:同第 206 题,反转链表的子区间reverseLinkedList(leftNode);// 第 5 步:接回到原来的链表中pre->next = rightNode;leftNode->next = curr;return dummyNode->next;}};
思路二:头插法,扫描一遍
使用头节点方便处理
例子:head = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5], left = 2, right = 4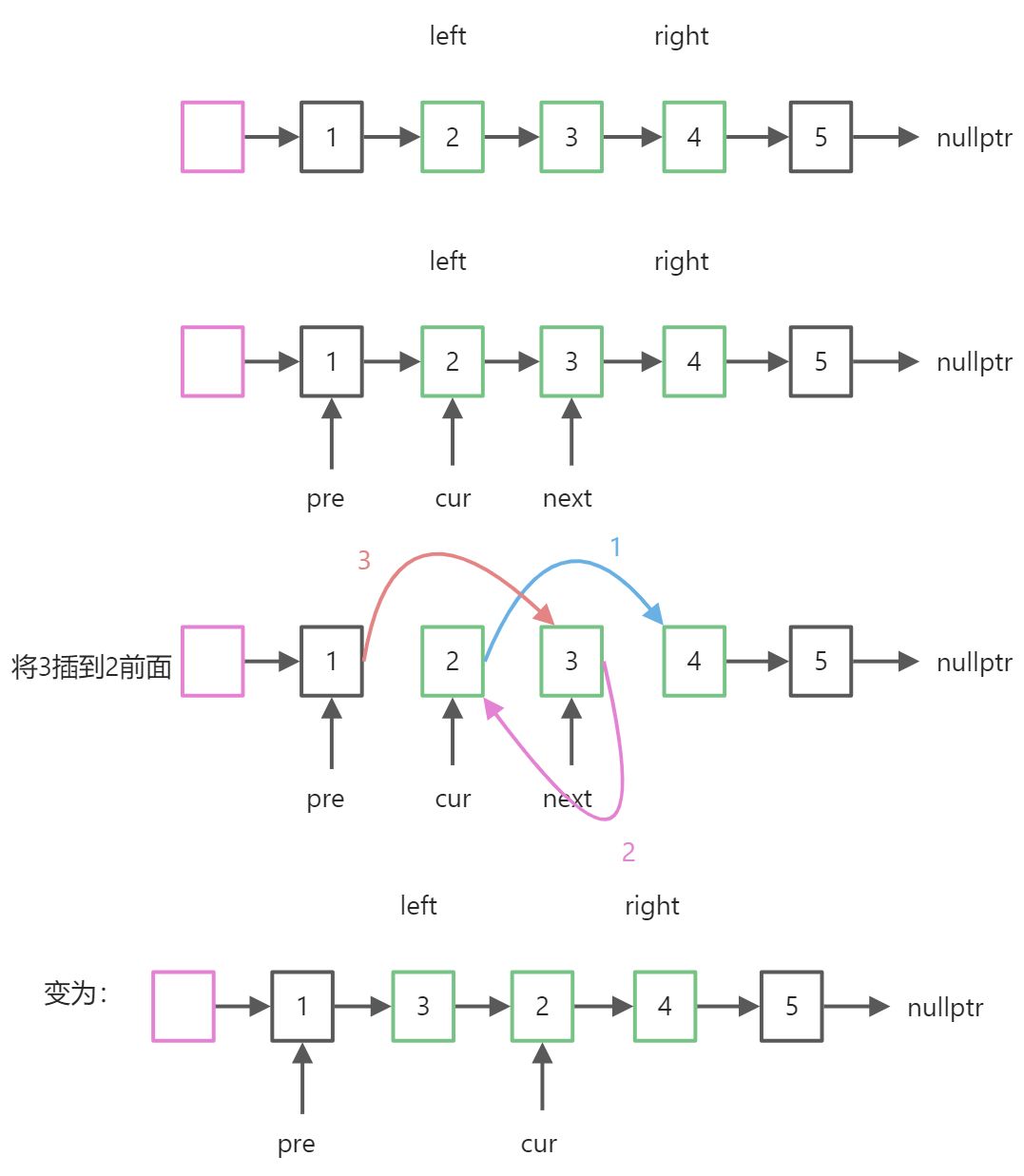
class Solution {public:ListNode *reverseBetween(ListNode *head, int left, int right) {// 设置 dummyNode 是这一类问题的一般做法ListNode *dummyNode = new ListNode(-1);dummyNode->next = head;ListNode *pre = dummyNode;for (int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++) {pre = pre->next;}ListNode *cur = pre->next;ListNode *next;for (int i = 0; i < right - left; i++) {next = cur->next;cur->next = next->next;next->next = pre->next;pre->next = next;}return dummyNode->next;}};
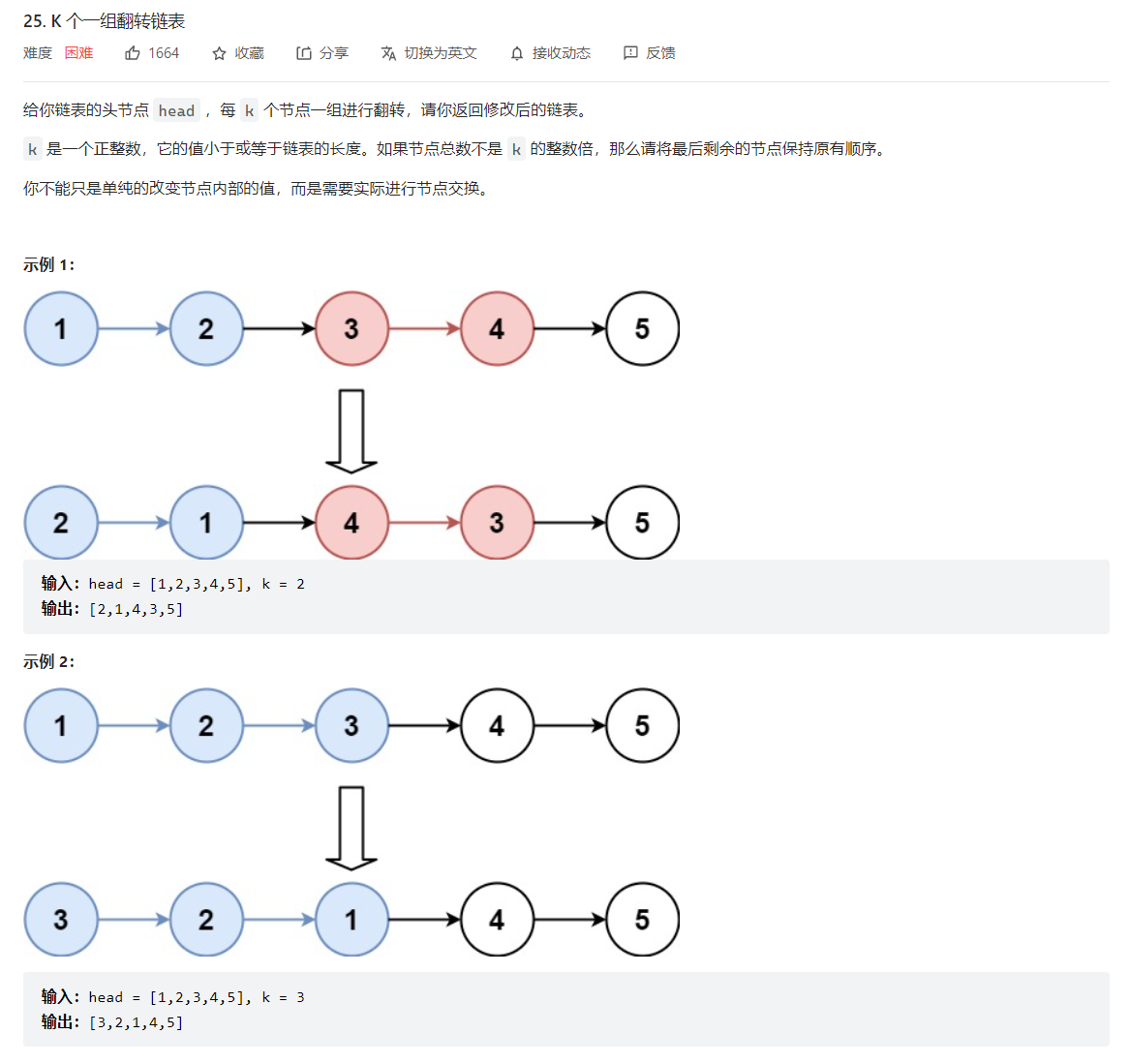
25. K 个一组翻转链表
迭代
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/class Solution {public:ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {if (head == nullptr || k == 1) return head;ListNode* dummy = new ListNode();dummy->next = head;ListNode* cur = head;ListNode* pre = dummy;int len = 0; // 链表长度while (cur) {len++;cur = cur->next;}cur = head;for (int i = 0; i < len / k; i++) { // 一共反转len/k组for (int j = 1; j < k; j++) { // 使用头插法反转该组链表ListNode* ne = cur->next;cur->next = ne->next;ne->next = pre->next;pre->next = ne;}pre = cur;cur = cur->next;}return dummy->next;}};
递归
class Solution {public:ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr || k < 2) return head;ListNode* dummy = new ListNode();dummy->next = head;ListNode* cur = head;for (int i = 1; i < k; i++) {cur = cur->next;if (cur == nullptr) return head; // 不足k个}ListNode* neGroup = cur->next; // 记录下一组的头结点for (int i = 1; i < k; i++) {ListNode* ne = head->next;head->next = ne->next;ne->next = dummy->next;dummy->next = ne;}head->next = reverseKGroup(neGroup, k);return dummy->next;}};
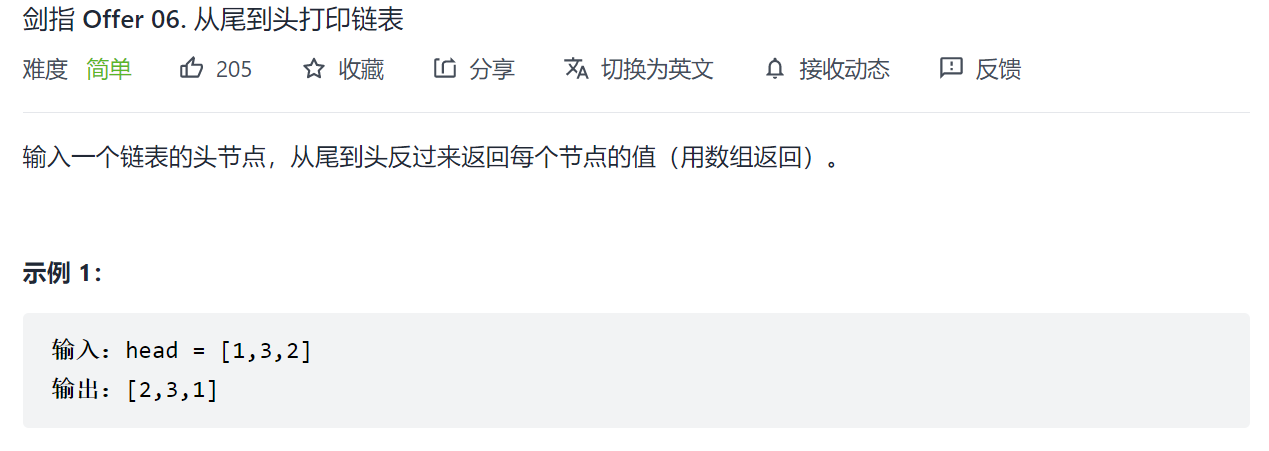
剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表
思路一:反转数组
class Solution {public:vector<int> reversePrint(ListNode* head) {vector<int> res;while (head) {res.push_back(head->val);head = head->next;}reverse(res.begin(), res.end());return res;}};
思路二:dfs
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> res;
void dfs(ListNode* head) {
if (!head) return;
dfs(head->next);
res.push_back(head->val);
}
vector<int> reversePrint(ListNode* head) {
res.clear();
dfs(head);
return res;
}
};
思路三:使用栈
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> reversePrint(ListNode* head) {
vector<int> res;
stack<int> st;
while (head) {
st.push(head->val);
head = head->next;
}
while (!st.empty()) {
res.push_back(st.top());
st.pop();
}
return res;
}
};
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
初始时,cur指向虚拟头结点,然后进行如下三步: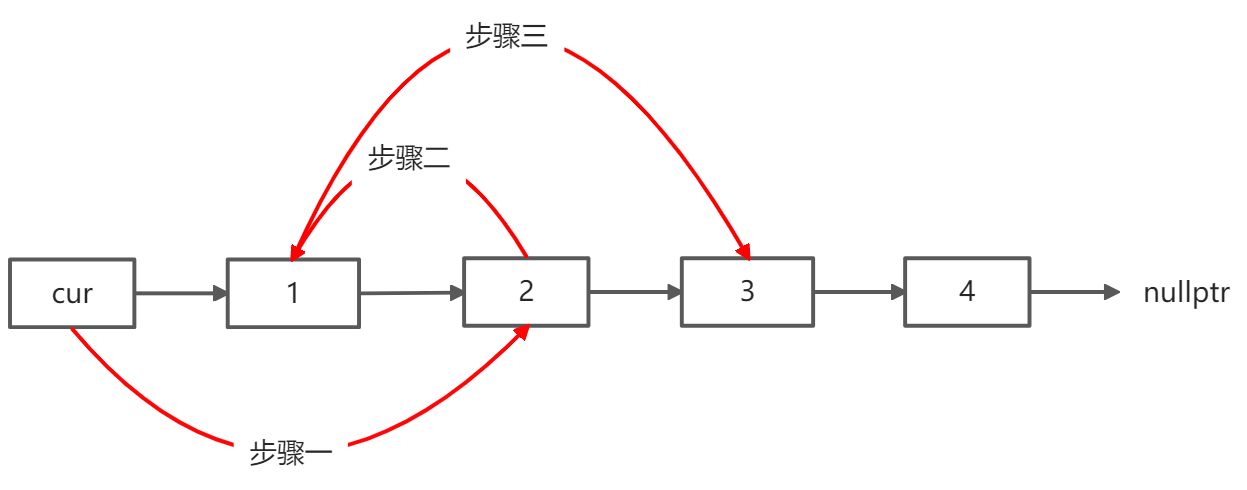
操作之后,链表如下: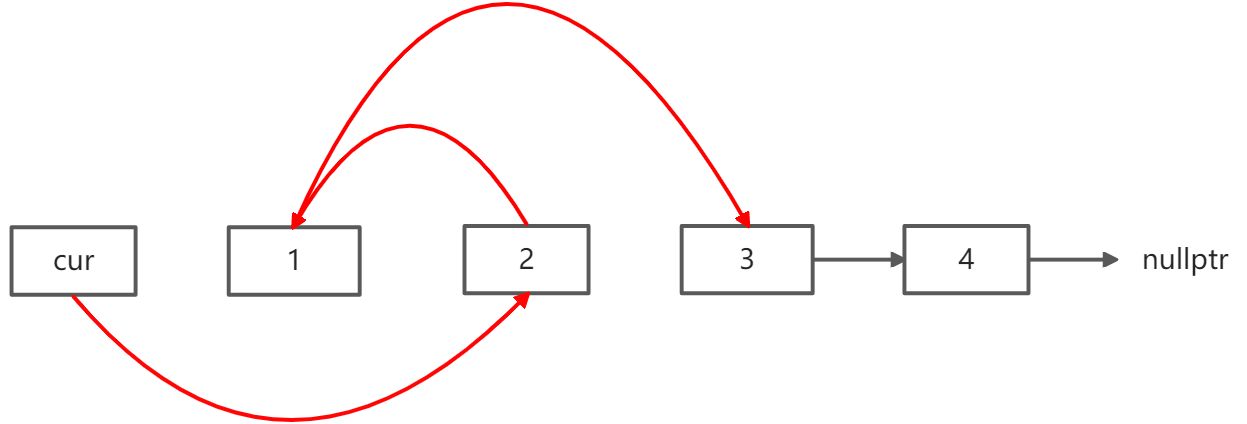
即;
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);//创建一个虚拟头结点
ListNode* cur = dummyHead;
while (cur->next != nullptr && cur->next->next != nullptr) {
ListNode* tmp1 = cur->next;
ListNode* tmp2 = cur->next->next->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;//步骤一
cur->next->next = tmp1;//步骤二
tmp1->next = tmp2;//步骤三
cur = cur->next->next;
}
return dummyHead->next;
}
};
143. 重排链表
- 双指针寻找链表中点
- 反转链表后半部分
合并两个链表
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) { ListNode* pre = nullptr; ListNode* cur = head; while (cur) { ListNode* next = cur->next; cur->next = pre; pre = cur; cur = next; } return pre; } ListNode* findMid(ListNode* head) { ListNode* right = head; ListNode* left = head; while (right->next && right->next->next) { right = right->next->next; left = left->next; } return left; } void merge(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) { ListNode* l1_ne; ListNode* l2_ne; while (l1 && l2) { l1_ne = l1->next; l2_ne = l2->next; l1->next = l2; l1 = l1_ne; l2->next = l1; l2 = l2_ne; } } void reorderList(ListNode* head) { if (!head) return; // 双指针将链表分割为两部分 ListNode* mid = findMid(head); ListNode* l1 = head; ListNode* l2 = mid->next; mid->next = nullptr; // 反转链表的后半部分 l2 = reverseList(l2); // 合并两个链表 merge(l1, l2); } };也可以先转化为数组,然后重新构造链表
61. 旋转链表
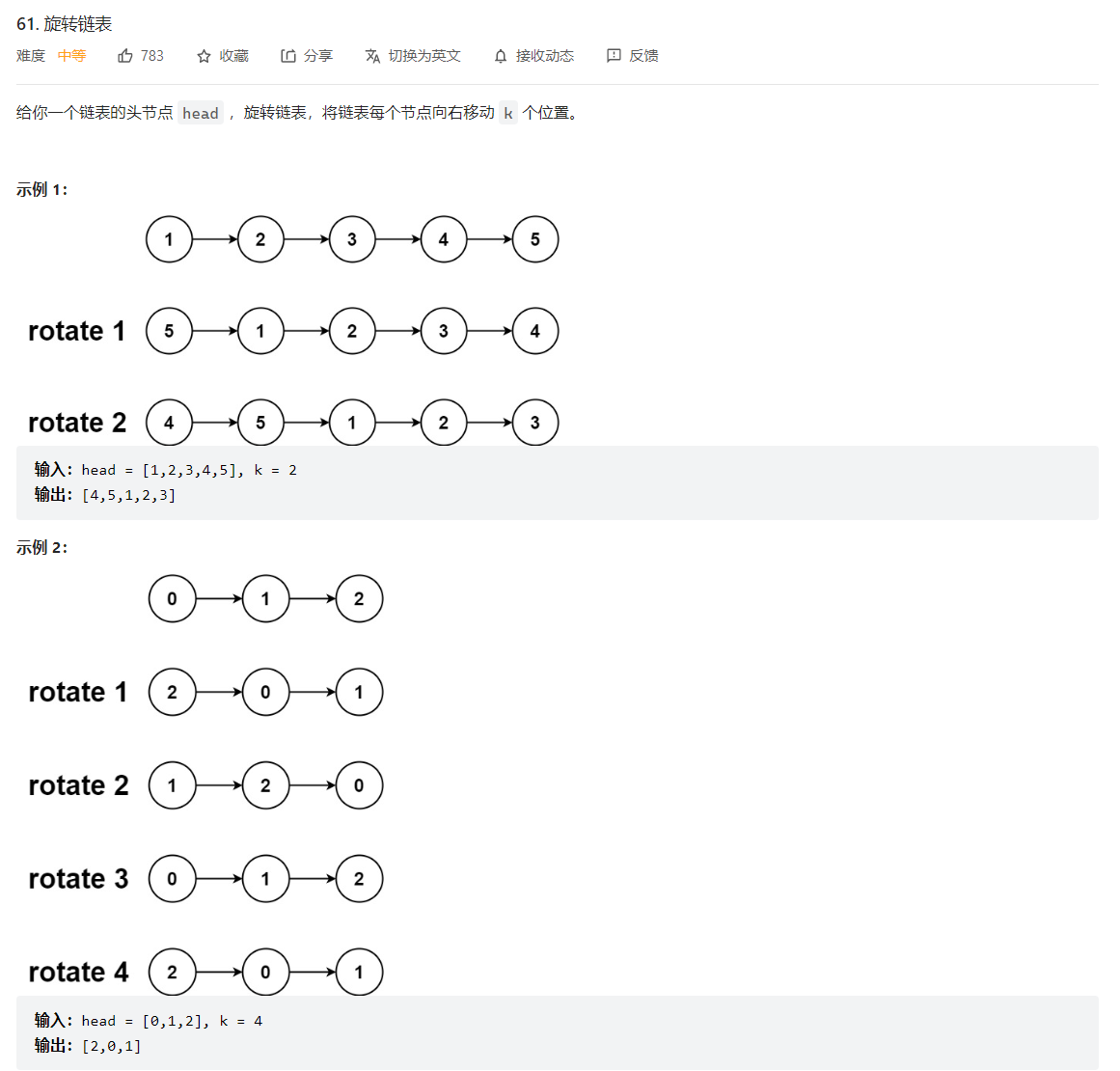
可以将后面的k个元素尾插法,插入到链表头部
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;
int len = 0;
ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur) {
len++;
cur = cur->next;
}
k %= len;
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
cur = head;
ListNode* slow = dummy;
while (k--) {
cur = cur->next;
}
while (cur) {
cur = cur->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
ListNode* next = slow->next;
slow->next = nullptr;
slow = next;
cur = dummy;
while (slow) {
next = slow->next;
slow->next = cur->next;
cur->next = slow;
cur = slow;
slow = next;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
也可以直接将k个元素打包过去
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
int len = 0;
ListNode* tail = dummy; // tail记录尾结点
while (tail->next) {
len++;
tail = tail->next;
}
k %= len;
if (k == 0) return head;
// 找到倒数第k个节点的前一个节点
ListNode* cur = dummy;
k = len - k;
while (k--) {
cur = cur->next;
}
// 将后面的k个节点插入头部
tail->next = dummy->next;
dummy->next = cur->next;
cur->next = nullptr;
cur = dummy;
return dummy->next;
}
};
也可以像旋转字符串或者数组那样,先整个反转,再部分反转
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* pre, ListNode* cur) {
if (!cur) return pre;
ListNode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
return reverseList(cur, next);
}
ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
int len = 0;
ListNode* tail = dummy; // tail记录尾结点
while (tail->next) {
len++;
tail = tail->next;
}
k %= len;
if (k == 0) return head;
// 找到倒数第k个节点的前一个节点
ListNode* cur = dummy;
k = len - k;
while (k--) {
cur = cur->next;
}
ListNode* right = cur->next; // 记录后半部分的起始节点
cur->next = nullptr;
head = reverseList(nullptr, head); // 反转左半部分
right = reverseList(nullptr, right); // 反转右半部分
dummy->next->next = right;
head =reverseList(nullptr, head); // 反转整个链表
return head;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> pathWithObstacles(vector<vector<int>>& obstacleGrid) {
int m = obstacleGrid.size();
int n = obstacleGrid[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> ans;
if (obstacleGrid[0][0]) return ans;
vector<vector<int>> dp(m, vector<int>(n, -1));
dp[0][0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if ((i == 0 && j == 0) || obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1) {
continue;
}
if (i > 0 && dp[i-1][j] >= 0) {
dp[i][j] = (i-1) * n + j;
}
if (j > 0 && dp[i][j-1] >= 0) {
dp[i][j] = i * n + j - 1;
}
}
}
if (dp[m-1][n-1] == -1) return ans;
int i = m - 1;
int j = n - 1;
while (i != 0 || j != 0) {
ans.push_back({i, j});
int tmp = dp[i][j];
i = tmp / n;
j = tmp % n;
}
ans.push_back({i, j});
reverse(ans.begin(), ans.end());
return ans;
}
};