- 剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表">剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表
- 剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点">(双指针)剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点
- 剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点">(双指针)剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点
- (双指针)剑指 Offer 23. 链表中环的入口节点
- 剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表">剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表
- 剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表">剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表
- 剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制">剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
- 剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点">剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点
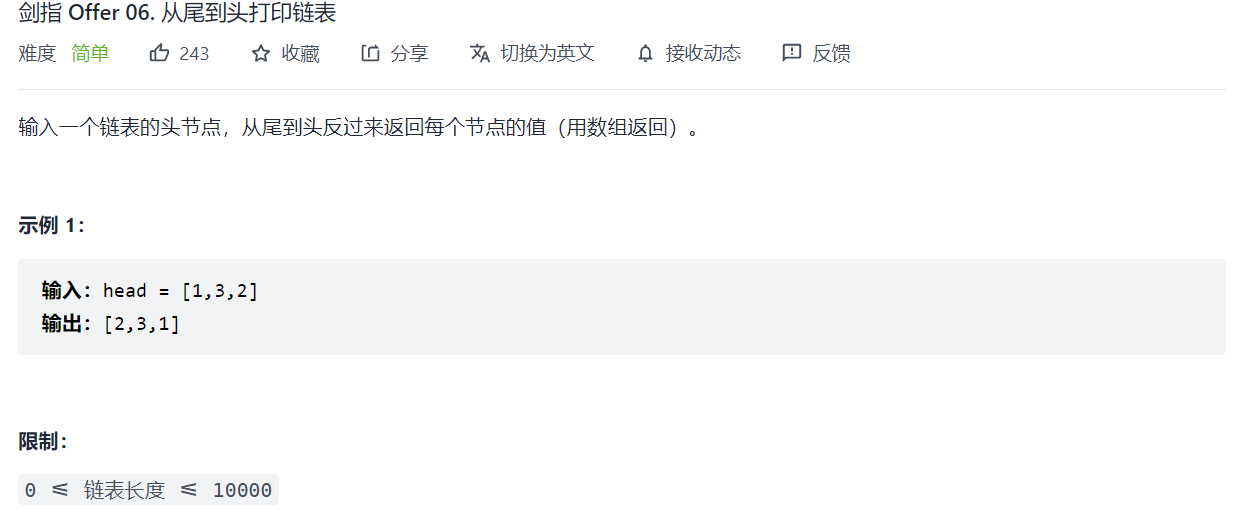
剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表
先正向打印链表再反转数组
class Solution {public:vector<int> reversePrint(ListNode* head) {ListNode* cur = head;vector<int> res;while (cur) {res.push_back(cur->val);cur = cur->next;}reverse(res.begin(), res.end());return res;}};
递归(dfs)
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(ListNode* cur, vector<int>& v) {
if (!cur) return;
dfs(cur->next, v);
v.push_back(cur->val);
}
vector<int> reversePrint(ListNode* head) {
vector<int> res;
dfs(head, res);
return res;
}
};
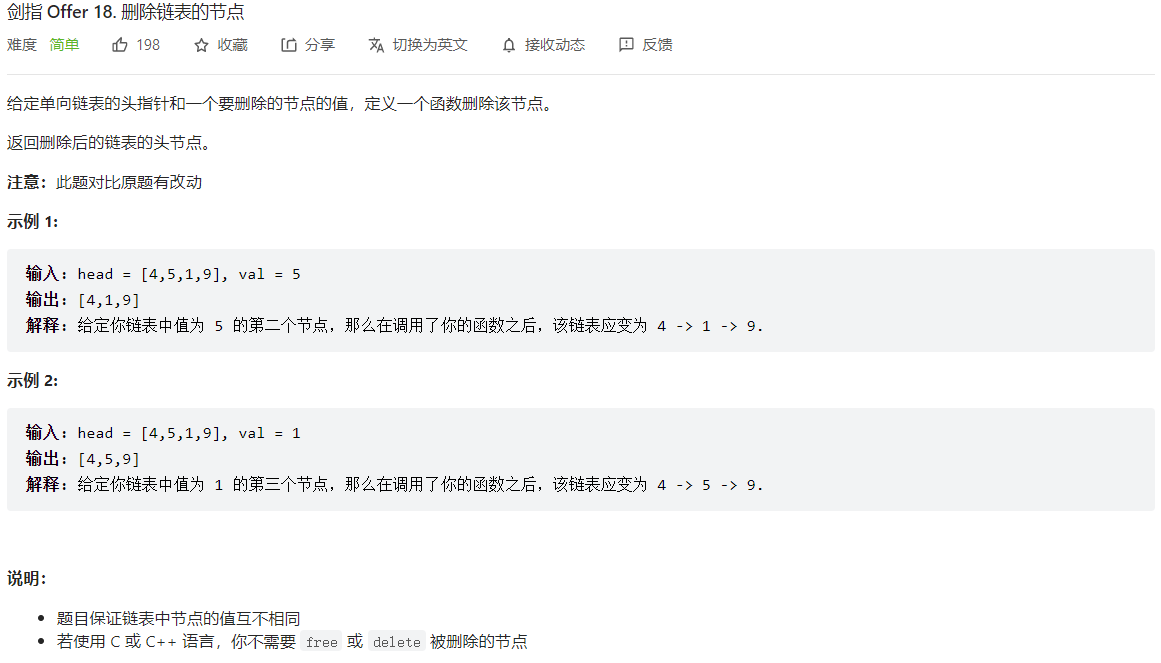
(双指针)剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点
查找并删除
写法一:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteNode(ListNode* head, int val) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode();
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode* pre = dummyHead;
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur != NULL) {
if (cur->val == val) {
pre->next = cur->next;
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
return dummyHead->next;
}
};
写法二:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteNode(ListNode* head, int val) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode();
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode* cur = dummyHead;
while(cur != NULL && cur->next != NULL) {
if (cur->next->val == val) {
cur->next = cur->next->next;
break;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return dummyHead->next;
}
};
单指针,单独处理头结点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteNode(ListNode* head, int val) {
if (!head) return head;
if (head->val == val) return head->next;
// 删除一个节点需要记录其前面的节点
ListNode *cur = head;
while (cur->next && cur->next->val != val) {
cur = cur->next;
}
if (cur->next->val == val) {
cur->next = cur->next->next;
}
return head;
}
};
时间复杂度为O(1)的办法💦
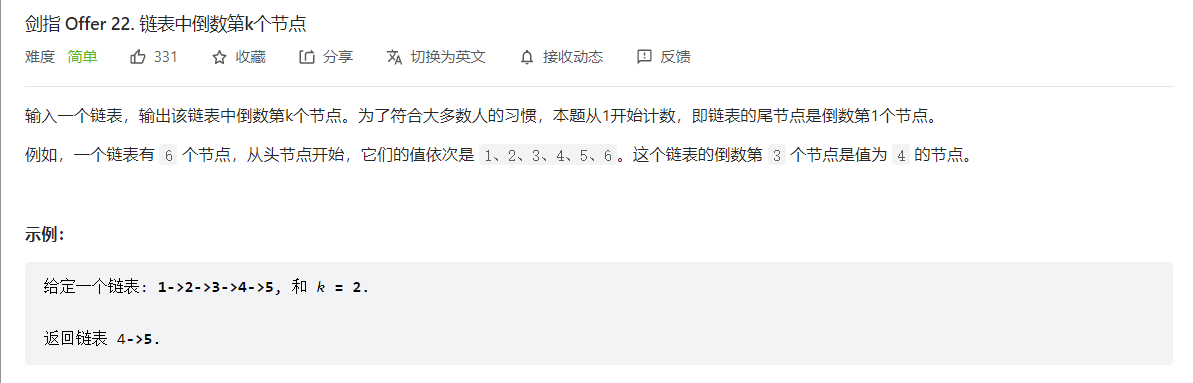
(双指针)剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点
用栈
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* getKthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int k) {
stack<ListNode*> st;
ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur != NULL) {
st.push(cur);
cur = cur->next;
}
while (k > 1) {
st.pop();
k--;
}
return st.top();
}
};
计数,遍历两遍
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* getKthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int k) {
ListNode* cur = head;
int n = 0;
while (cur != NULL) {
n++;
cur = cur->next;
}
cur = head;
int num = n - k;
while (num--) {
cur = cur->next;
}
return cur;
}
};
双指针
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* getKthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int k) {
if (k == 0 || head == NULL)
return NULL;
ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head;
// 快指针先走k-1步
for (int i = 0; i < k - 1; i++) {
fast = fast->next;
}
// 当快指针指向最后一个节点时,慢指针指向倒数第k个节点
while (fast->next != NULL) {
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
};
要考虑鲁棒性,开头的判断很重要
推广:如果链表中节点个数为奇数求链表中间节点,或者链表个数为偶数求中间两个节点中的任意一个,那么可以定义两个指针,快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,当快指针指向尾节点时,慢指针指向中间节点
(双指针)剑指 Offer 23. 链表中环的入口节点
141. 环形链表
142. 环形链表 II
剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表
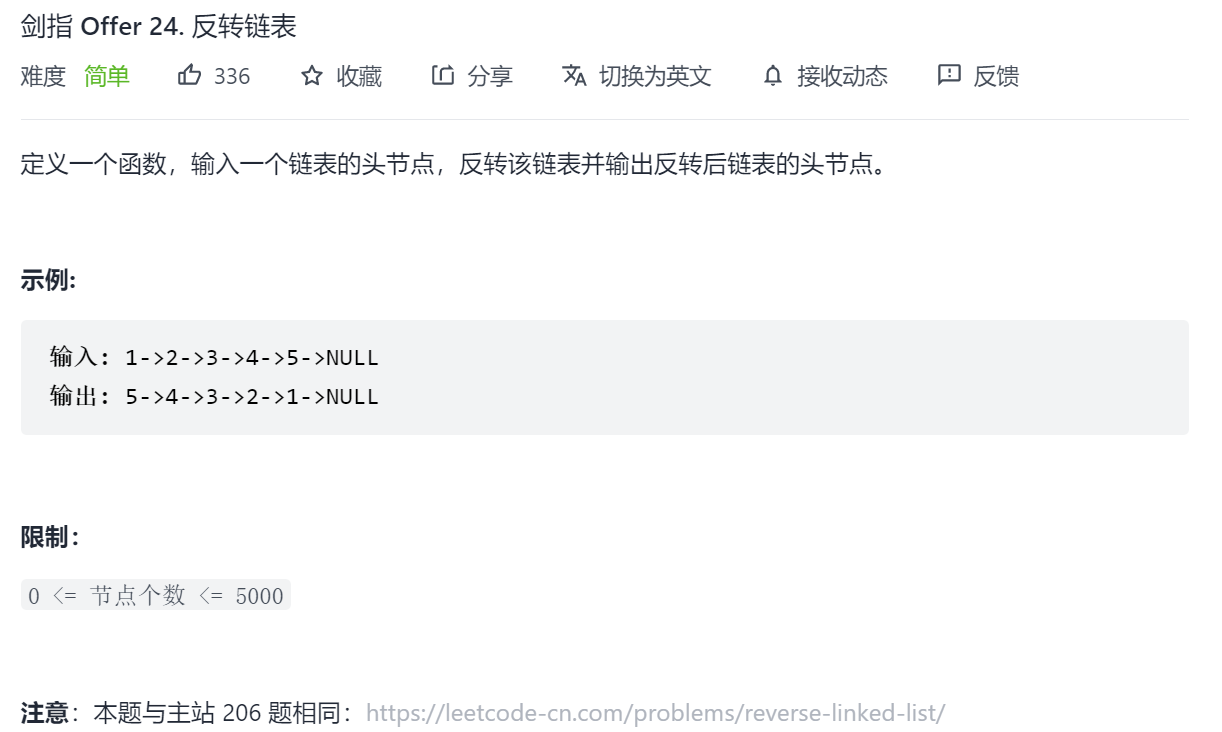
思路一:迭代
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* pre = NULL;
ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur) {
ListNode* post = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = post;
}
return pre;
}
};
思路二:递归
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* pre, ListNode* cur) {
// end recursion
if (!cur) return pre;
ListNode* post = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
return reverse(cur, post);
}
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
return reverse(NULL, head);
}
};
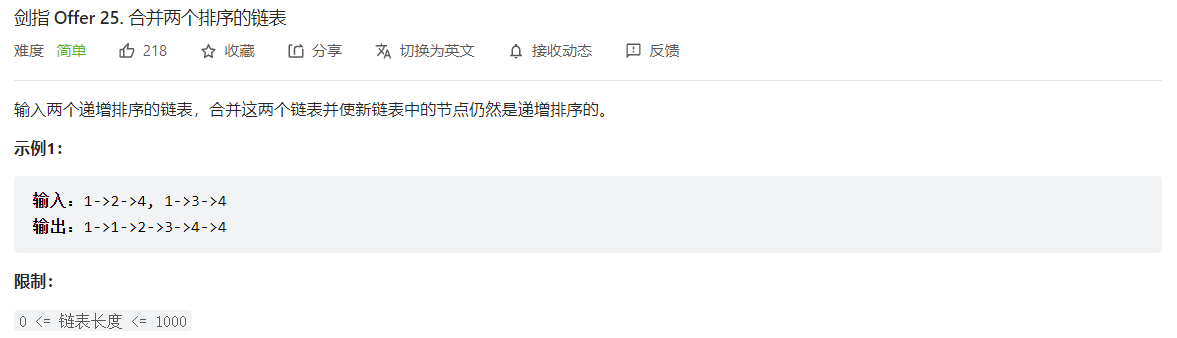
剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表
迭代
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode *head = new ListNode;
ListNode *cur = head;
ListNode *p1 = l1, *p2 = l2;
while (p1 && p2) {
if (p1->val < p2->val) {
cur->next = p1;
p1 = p1->next;
} else {
cur->next = p2;
p2 = p2->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = p1 ? p1 : p2;
return head->next;
}
};
递归
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
if (!l1) return l2;
if (!l2) return l1;
if (l1->val <= l2->val) {
l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2->next);
return l2;
}
}
剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
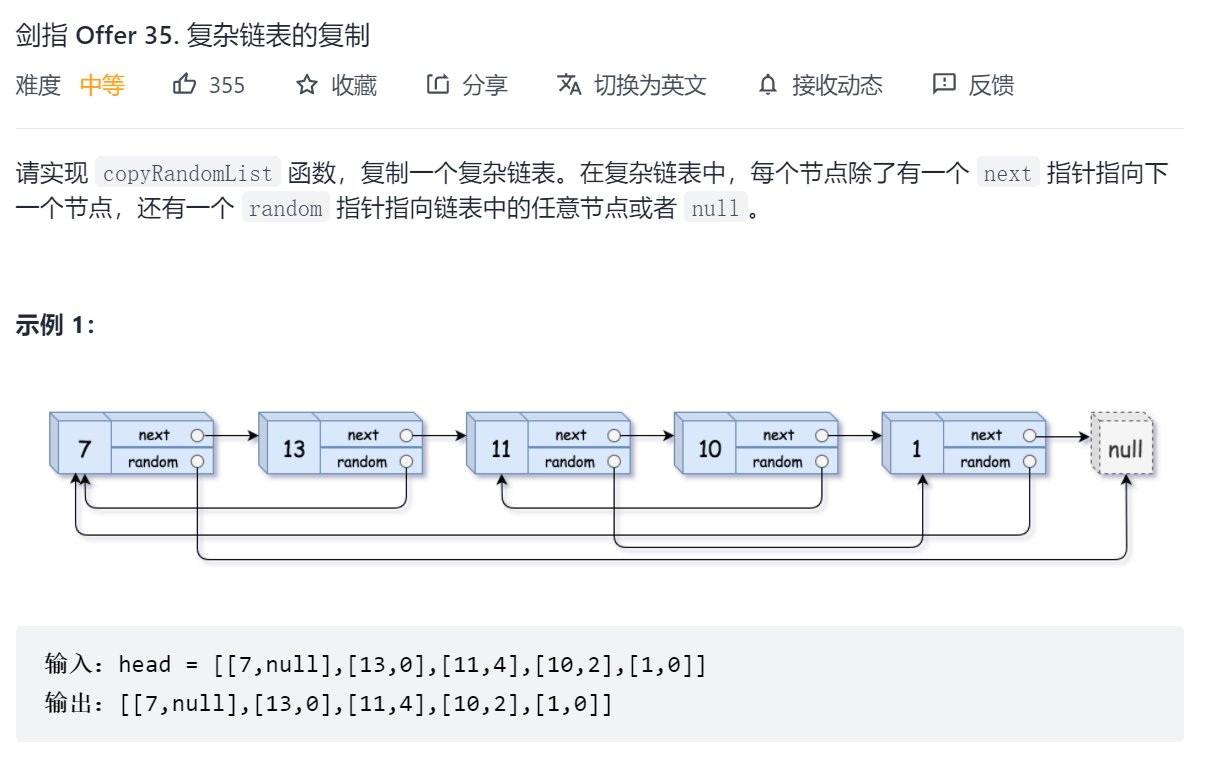

首先想到的是先将链表按照next复制一遍,然后再处理random,由于每次处理一个random都需要从第一个节点开始查找,所以时间复杂度为O(N^2),因此此题主要思考如何降低时间复杂度
思路一:哈希表+递归
使用哈希表空间换时间,复制节点时用哈希表记录其信息
可以顺着next和random指针进行拷贝,用一个哈希表记录当前节点是否拷贝过,如果拷贝过,直接返回,避免重复构造节点
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* next;
Node* random;
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
next = NULL;
random = NULL;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> um;
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if (head == NULL) return NULL;
if (!um.count(head)) { // 当前节点未被拷贝过
Node* node = new Node(head->val); // 拷贝该节点
um[head] = node; //记录
node->next = copyRandomList(head->next);
node->random = copyRandomList(head->random);
}
return um[head];
}
};
思路二:原地操作💦
将拷贝的节点直接放在原节点的后面,比如 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> null 变为 1 -> 1’ -> 2 - > 2’ -> 3 -> 3’ - > null
然后拷贝处理random
最后将链表一分为二
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if (head == NULL) return NULL;
// 将拷贝节点置于原节点之后
Node* cur = head;
while (cur) {
Node* node = new Node(cur->val);
node->next = cur->next;
cur->next = node;
cur = node->next;
}
// 完成随机指针的复制
cur = head;
while (cur) {
if (cur->random) {
cur->next->random = cur->random->next;
}
cur = cur->next->next;
}
// 将链表一分为二
Node* newHead = head->next;
Node* copycur = head->next;
cur = head;
while (cur) {
cur->next = cur->next->next;
cur = cur->next;
if (copycur->next) {
copycur->next = copycur->next->next;
copycur = copycur->next;
}
}
return newHead;
}
};
这道题原地操作非常好,可以很好地锻炼处理链表的能力
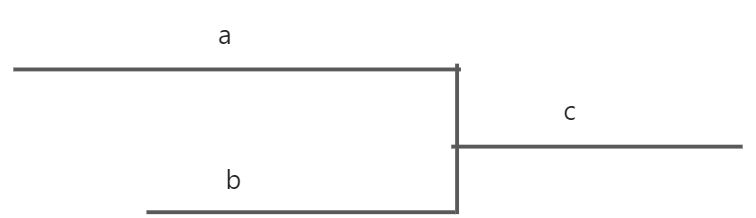
剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点
a + c + b = b + c + a
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
ListNode* curA = headA;
ListNode* curB = headB;
while (curA != curB) {
curA = curA == NULL ? headB : curA->next;
curB = curB == NULL ? headA : curB->next;
}
return curA;
}
};