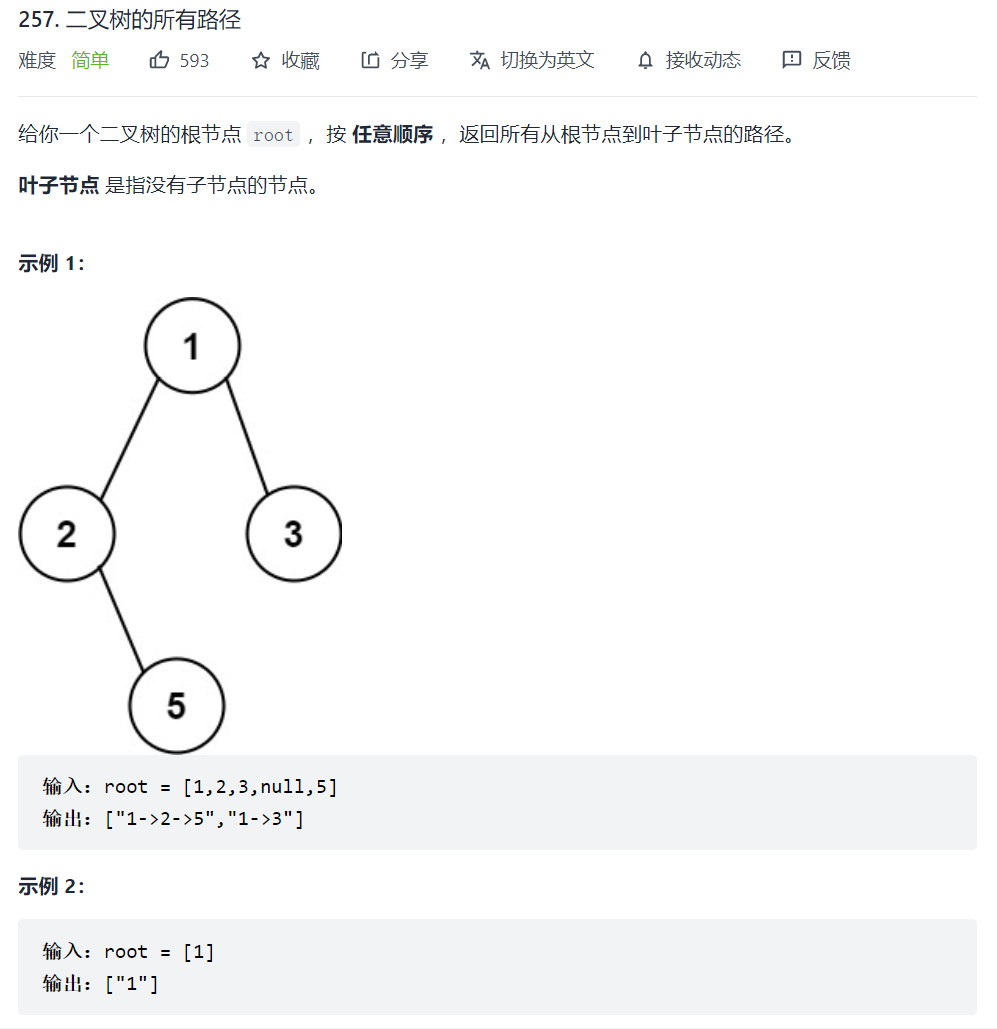
257. 二叉树的所有路径
这道题目要求从根节点到叶子的路径,所以需要前序遍历,这样才方便让父节点指向孩子节点,找到对应的路径。
在这道题目中将第一次涉及到回溯,因为我们要把路径记录下来,需要回溯来回退一一个路径在进入另一个路径。
前序遍历以及回溯的过程如图: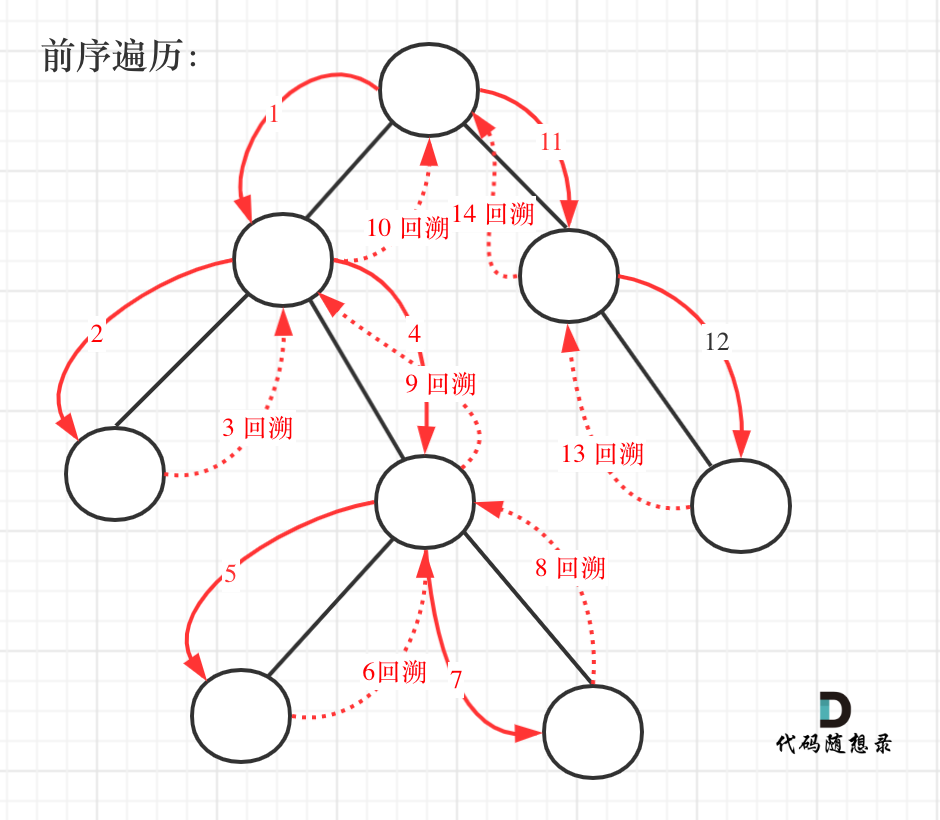
递归法
class Solution {private:void traversal(TreeNode* cur, vector<int>& path, vector<string>& result) {path.push_back(cur->val);// 这才到了叶子节点if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL) {string sPath;for (int i = 0; i < path.size() - 1; i++) {sPath += to_string(path[i]);sPath += "->";}sPath += to_string(path[path.size() - 1]);result.push_back(sPath);return;}if (cur->left) {traversal(cur->left, path, result);path.pop_back(); // 回溯}if (cur->right) {traversal(cur->right, path, result);path.pop_back(); // 回溯}}public:vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {vector<string> result;vector<int> path;if (root == NULL) return result;traversal(root, path, result);return result;}};
精简后:
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> res;
void dfs(TreeNode* root, string path) {
path += to_string(root->val);
if (!root->left && !root->right) {
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
// 保证不访问空节点
if (root->left) dfs(root->left, path + "->");
if (root->right) dfs(root->right, path + "->");
}
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return {};
dfs(root, "");
return res;
}
};

精简后的代码传入的path参数不能引用,必须拷贝,否则无法回溯
如果把 **path + "->"**作为函数参数就是可以的,因为并有没有改变path的数值,执行完递归函数之后,path依然是之前的数值(相当于回溯了)
迭代法
用一个栈模拟递归,用一个栈来存放遍历路径
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> treeSt;// 保存树的遍历节点
stack<string> pathSt; // 保存遍历路径的节点
vector<string> result; // 保存最终路径集合
if (root == NULL) return result;
treeSt.push(root);
pathSt.push(to_string(root->val));
while (!treeSt.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = treeSt.top(); treeSt.pop(); // 取出节点 中
string path = pathSt.top();pathSt.pop(); // 取出该节点对应的路径
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) { // 遇到叶子节点
result.push_back(path);
}
if (node->right) { // 右
treeSt.push(node->right);
pathSt.push(path + "->" + to_string(node->right->val));
}
if (node->left) { // 左
treeSt.push(node->left);
pathSt.push(path + "->" + to_string(node->left->val));
}
}
return result;
}
};
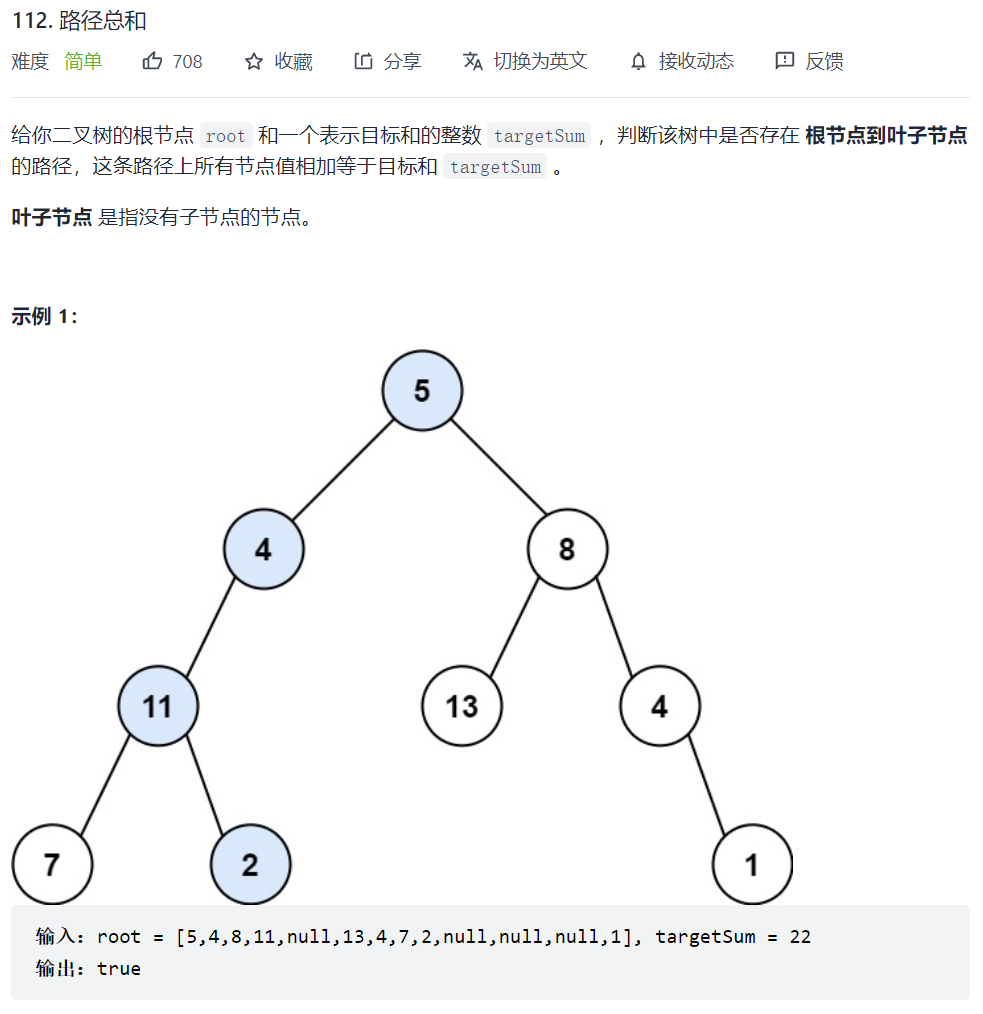
112. 路径总和
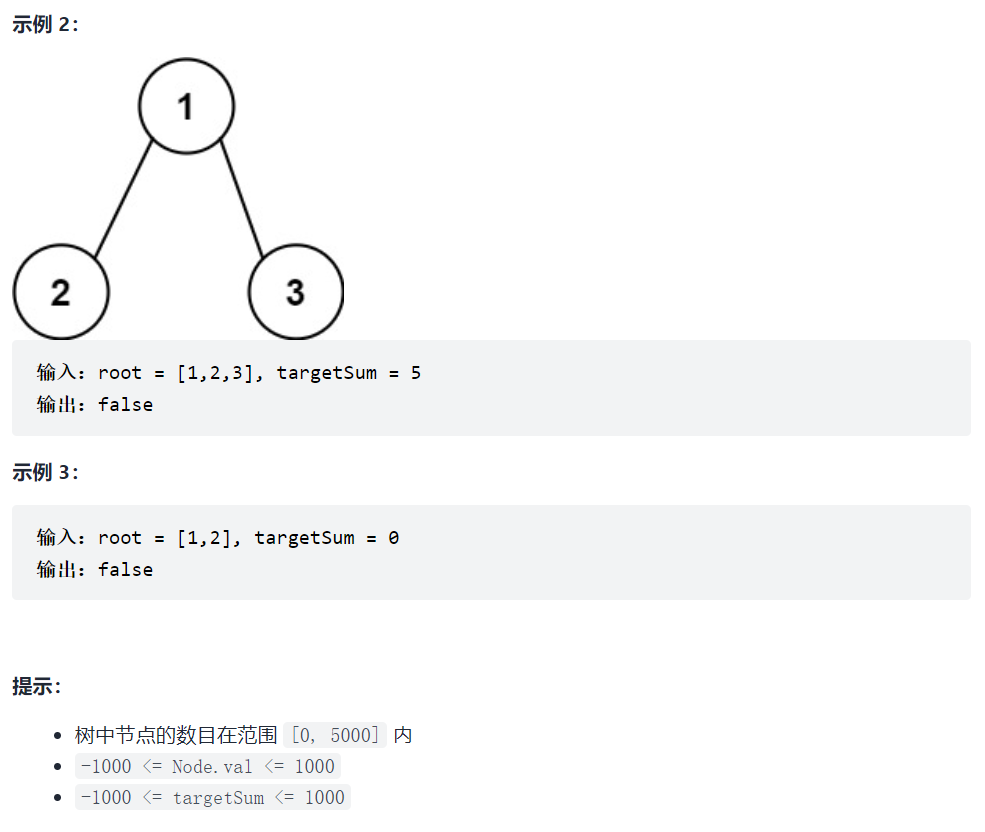
思路一:记录所有路径
可以将所有的路径和保存,看是否存在targetSum,这里需要回溯,和257.二叉树的所有路径是一样的思路,只不过这一题保存的是路径上节点的和
class Solution {
public:
void traversal(TreeNode* cur, int& pathSum, vector<int>& res) {
pathSum += cur->val;//将该节点的值加入
if (!cur->left && !cur->right) {// 当前节点是叶子节点,保存根结点到叶子节点的路径
res.push_back(pathSum);
}
if (cur->left) {
traversal(cur->left, pathSum, res);
pathSum -= cur->left->val;//回溯
}
if (cur->right) {
traversal(cur->right, pathSum, res);
pathSum -= cur->right->val;//回溯
}
}
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (!root) return false;
vector<int> res;
int pathSum = 0;
traversal(root, pathSum, res);
return find(res.begin(), res.end(), targetSum) != res.end();
}
};
还可以再精简一点:
class Solution {
public:
void traversal(TreeNode* cur, int pathSum, vector<int>& res) {
pathSum += cur->val;//将该节点的值加入
if (!cur->left && !cur->right) {// 当前节点是叶子节点,保存根结点到叶子节点的路径
res.push_back(pathSum);
}
if (cur->left) {
traversal(cur->left, pathSum, res); // pathSum是复制的,递归回来还是原来的值,相当于回溯
}
if (cur->right) {
traversal(cur->right, pathSum, res);
}
}
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (!root) return false;
vector<int> res;
traversal(root, 0, res);
return find(res.begin(), res.end(), targetSum) != res.end();
}
};
思路二:满足条件直接返回(递归)
其实没有必要保存所有的结果,只要pathSum = targetSum,便可以退出代码了,因此可以对遍历操作进行剪枝
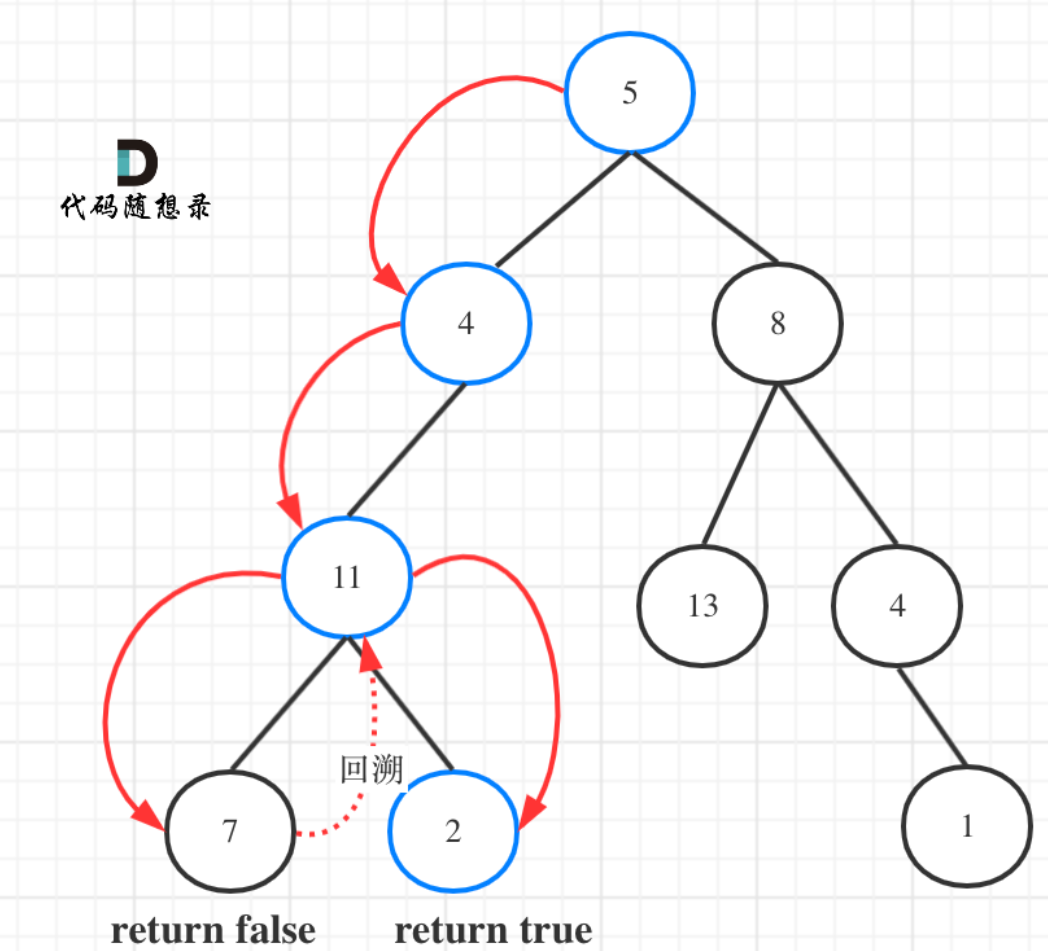
class Solution {
public:
bool traversal(TreeNode* cur, int count) {
if (!cur->left && !cur->right && count == 0) return true; // 是叶子节点,且路径和满足要求,返回true
if (!cur->left && !cur->right) return false; // 是叶子节点,但路径和不对,直接返回
if (cur->left) {
// 这条路径上有满足要求的叶子结点,直接返回true
if (traversal(cur->left, count - cur->left->val)) return true;
}
if (cur->right) {
if (traversal(cur->right, count - cur->right->val)) return true;
}
return false;
}
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (!root) return false;
return traversal(root, targetSum - root->val);
}
};
精简后:
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (!root) return false;
if (!root->left && !root->right && targetSum == root->val) return true;
return hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum - root->val) || hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum - root->val);
}
};
2022.3.30二刷写法
class Solution {
public:
bool dfs(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
sum -= root->val;
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr && sum == 0)
return true;
bool left = false, right = false;
if (root->left)
left = dfs(root->left, sum);
if (left) // 剪枝
return true;
if (root->right)
right = dfs(root->right, sum);
return left || right;
}
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (root == nullptr) return false;
return dfs(root, targetSum);
}
};
思路三:迭代法
用栈来模拟前序遍历,然后栈里记录节点时连当前节点的路径和也保存起来
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (!root) return false;
stack<pair<TreeNode*, int>> st;
st.push(pair<TreeNode*, int>(root, root->val));
while (!st.empty()) {
pair<TreeNode*, int> node = st.top();
st.pop();
// 当前节点为叶子节点并且路径值等于target
if (!node.first->left && !node.first->right && node.second == targetSum) return true;
// 右节点先入栈
if (node.first->right)
st.push(pair<TreeNode*, int>(node.first->right, node.second + node.first->right->val));
if (node.first->left)
st.push(pair<TreeNode*, int>(node.first->left, node.second + node.first->left->val));
}
return false;
}
};
113. 路径总和 II
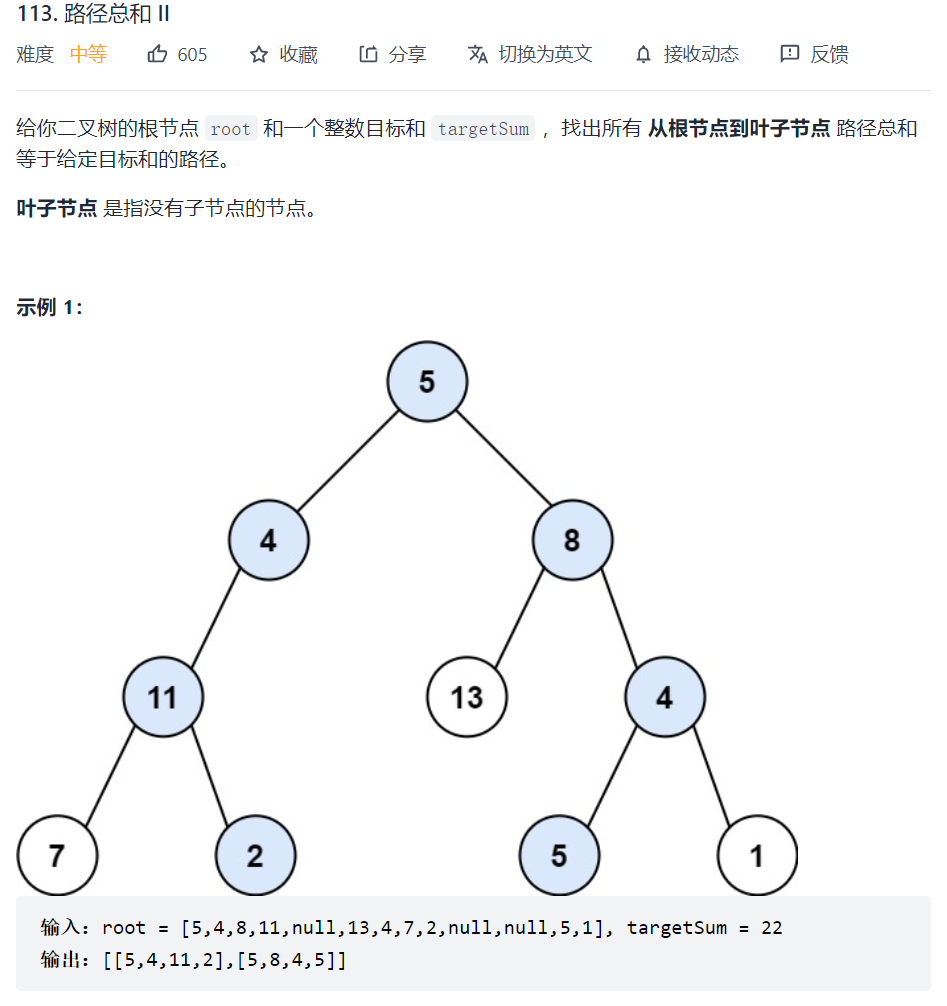
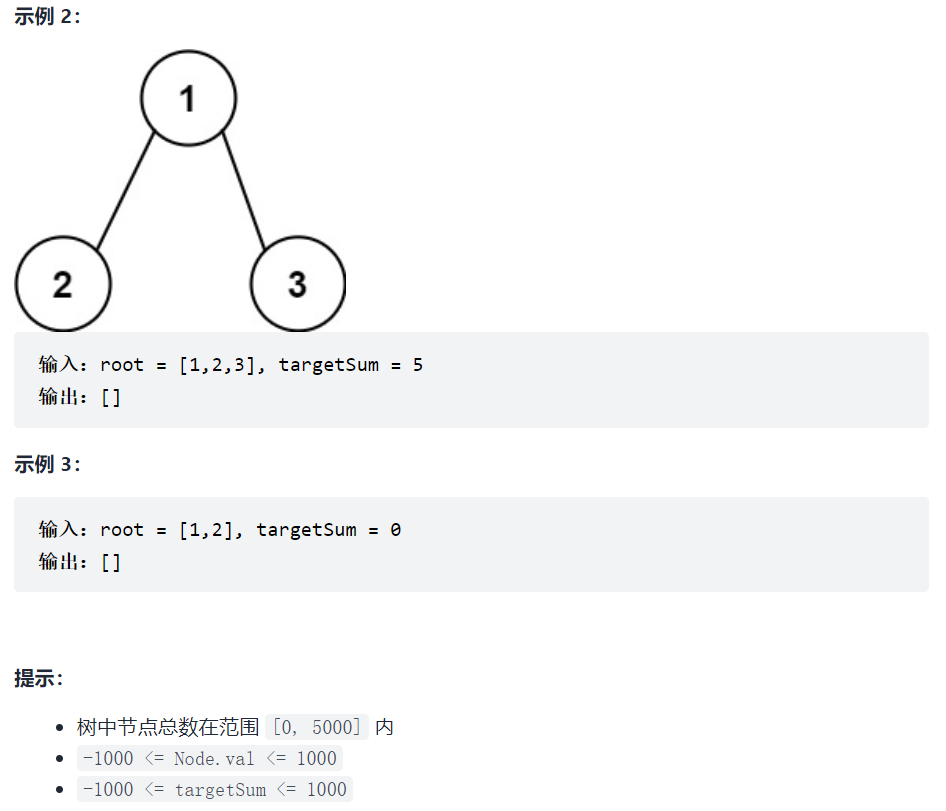
这道题和112.记录所有路径其实是一样的,不过需要遍历数的所有节点,并用全局变量来记录满足条件的路径
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
void traversal(TreeNode* cur, int count) {
if (!cur->left && !cur->right && count == 0) {// 当前节点是叶子节点,保存根结点到叶子节点的路径
res.push_back(path);
}
if (cur->left) {
path.push_back(cur->left->val);
traversal(cur->left, count - cur->left->val);
path.pop_back();
}
if (cur->right) {
path.push_back(cur->right->val);
traversal(cur->right, count - cur->right->val);
path.pop_back();
}
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (!root) return res;
path.push_back(root->val);
traversal(root, targetSum - root->val);
return res;
}
};
基于112题改造的写法
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
path.push_back(root->val);
sum -= root->val;
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr && sum == 0) {
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
if (root->left) {
dfs(root->left, sum);
path.pop_back();
}
if (root->right) {
dfs(root->right, sum);
path.pop_back();
}
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (root == nullptr) return {};
dfs(root, targetSum);
return res;
}
};
687. 最长同值路径
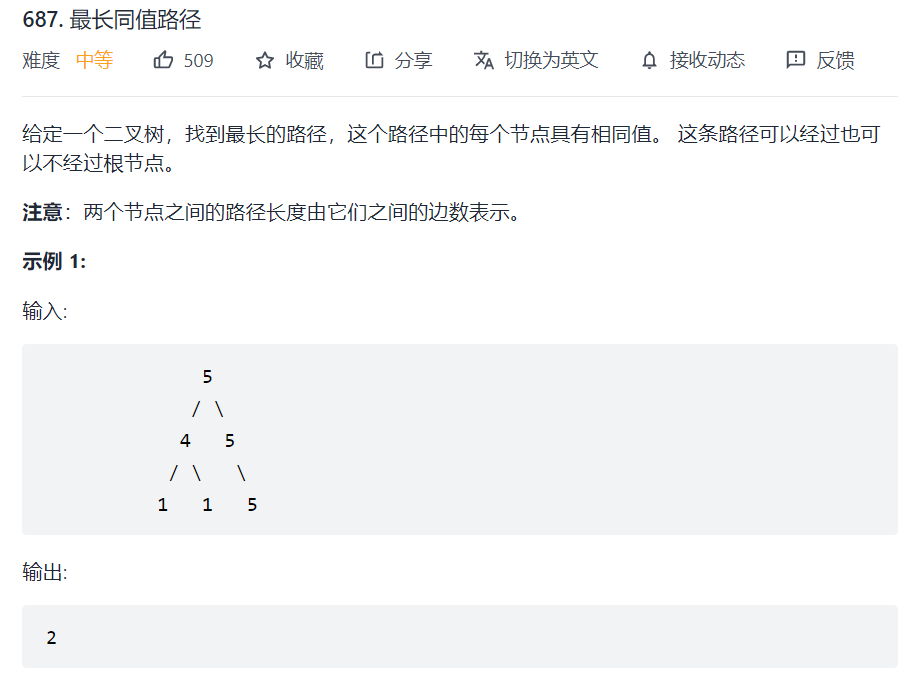
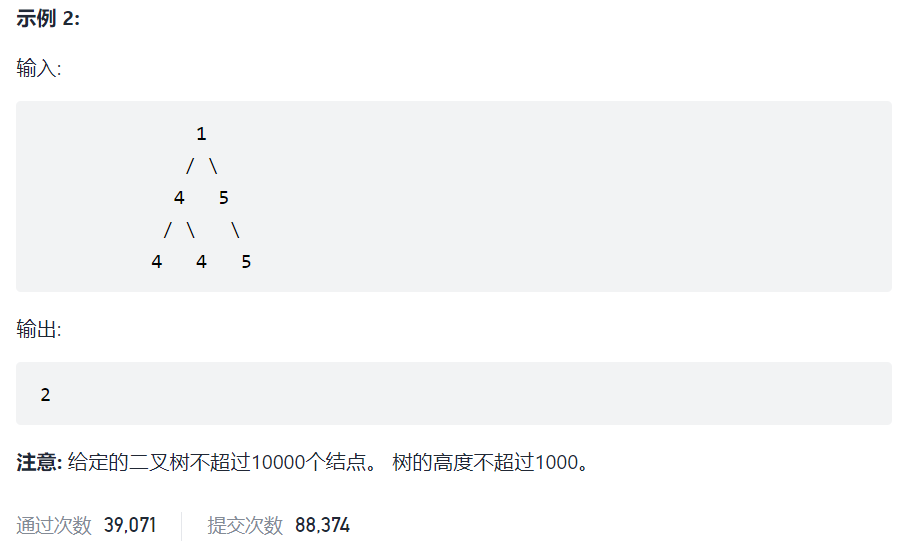
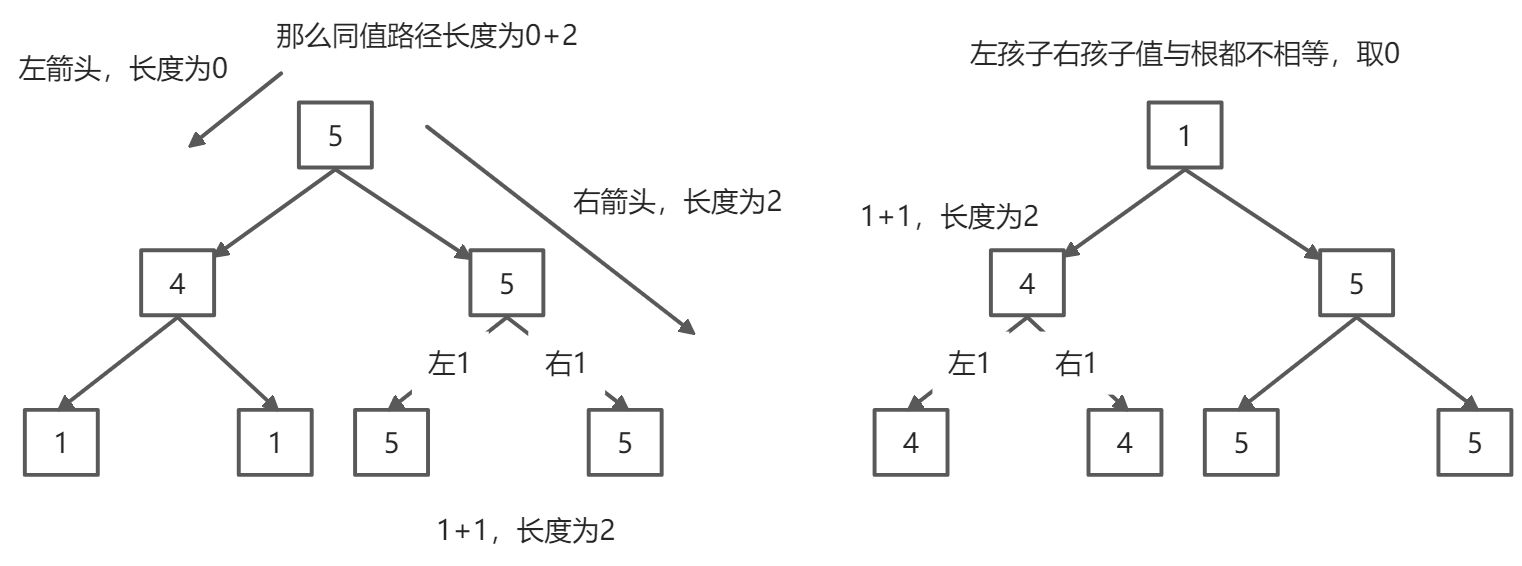
将路径看作是以当前节点为箭尾的箭头(总长度为指向左孩子的箭头和指向右孩子的箭头的长度之和):
- 如果左孩子的值和当前节点的值相等,那么向左的箭头长度+1
- 如果右孩子的值和当前节点的值相等,那么向右的箭头长度+1
需要用一个全局变量来记录最长的路径长度
class Solution {
public:
int res;
int traversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
int left = traversal(root->left);// 得到左右孩子中最大的箭头长度
int right = traversal(root->right);
int arrowLeft = 0, arrowRight = 0;// 初始向左向右的箭头长度都为0
if (root->left && root->val == root->left->val)
arrowLeft += left + 1;
if (root->right && root->val == root->right->val)
arrowRight += right + 1;
res = max(res, arrowLeft + arrowRight);
return max(arrowLeft, arrowRight); //向父节点返回左箭头和右箭头的最大值
}
int longestUnivaluePath(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
res = 0;
traversal(root);
return res;
}
};
124. 二叉树中的最大路径和
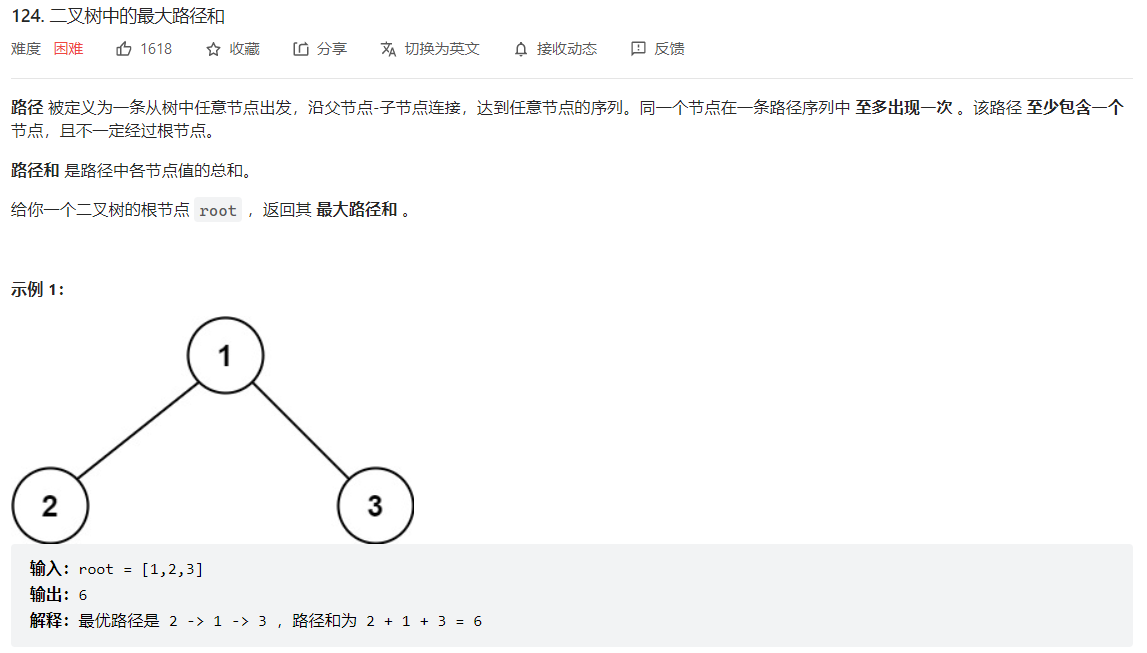
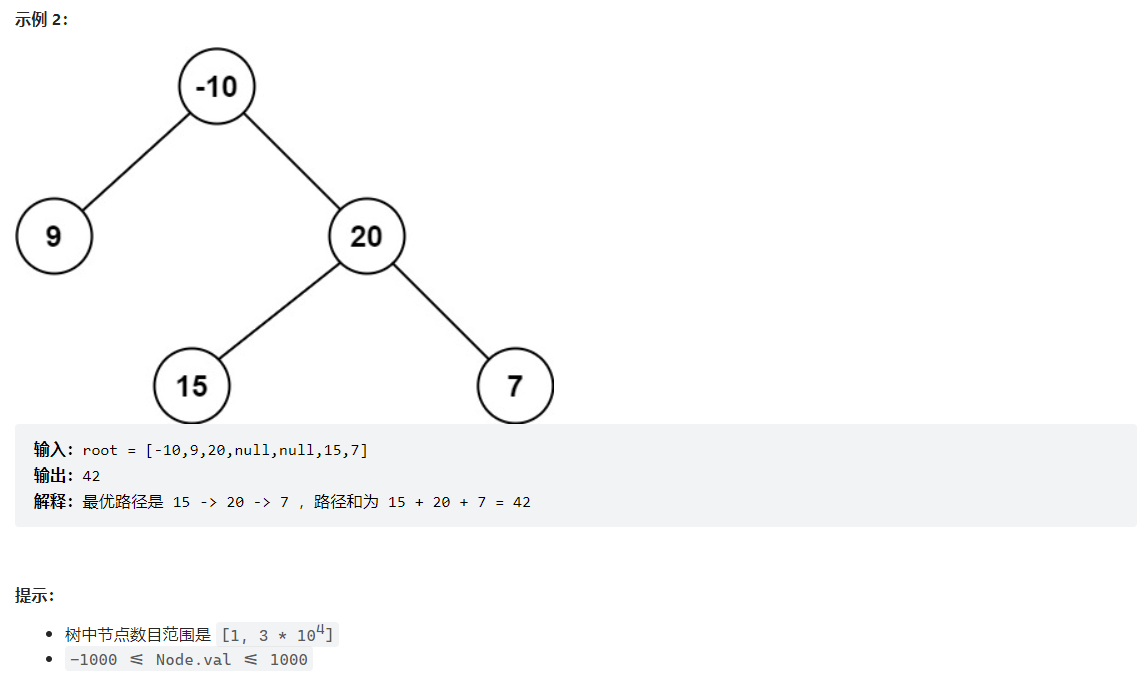
计算从每个节点出发,到某个节点的最大路径,以某个节点为枢纽,计算从该节点向左向右出发得到的最大路径长度,如果该节点不是枢纽,那么返回向左向右两条路径的最大长度(取左右子树最大的贡献值)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int res = INT32_MIN;
int getmax(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
// 只有左右路径和为整数时,才选择该路径
int l = max(getmax(root->left), 0);
int r = max(getmax(root->right), 0);
int path = root->val + l + r;
res = max(res, path);
// 返回一条最大的路径和
return root->val + max(l, r);
}
int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) {
getmax(root);
return res;
}
};
543. 二叉树的直径
124题的简化版本,后序遍历
class Solution {
public:
int res = 0;
int dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
int l = dfs(root->left);
int r = dfs(root->right);
res = max(l + r, res);
return max(l, r) + 1;
}
int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return res;
}
};
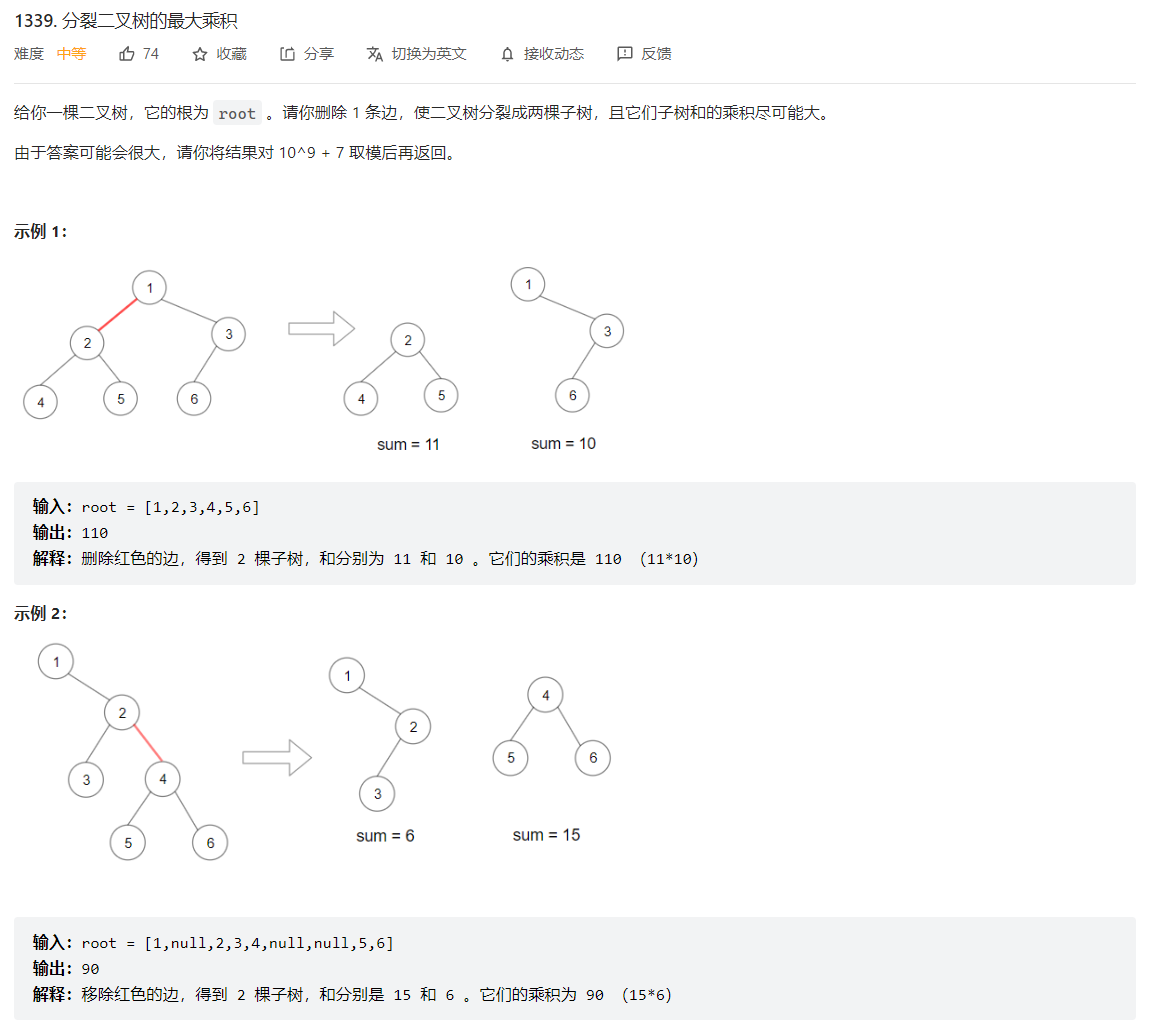
1339. 分裂二叉树的最大乘积
枚举删除某条边
class Solution {
public:
int sum = 0;
long long res = 1;
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
void dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return;
sum += root->val;
dfs(root->left);
dfs(root->right);
}
int compute(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
int l = compute(root->left);
int r = compute(root->right);
res = max(res, (long long) l * (sum - l)); // 删除到左子树的边
res = max(res, (long long) r * (sum - r)); // 删除到右子树的边
return l + r + root->val;
}
int maxProduct(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
compute(root);
return res % MOD; // 最后再取模,不然结果不对
}
};
数学
分裂的子树越接近总和的一半,乘积越大
class Solution {
public:
int sum = 0;
int best = 0;
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
void dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return;
sum += root->val;
dfs(root->left);
dfs(root->right);
}
int compute(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
int l = compute(root->left);
int r = compute(root->right);
int cur = l + r + root->val;
if (abs(2 * cur - sum) < abs(2 * best - sum)) best = cur; // 记录最接近一半的子树和
return cur;
}
int maxProduct(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
compute(root);
return (long long) best * (sum - best) % MOD;
}
};