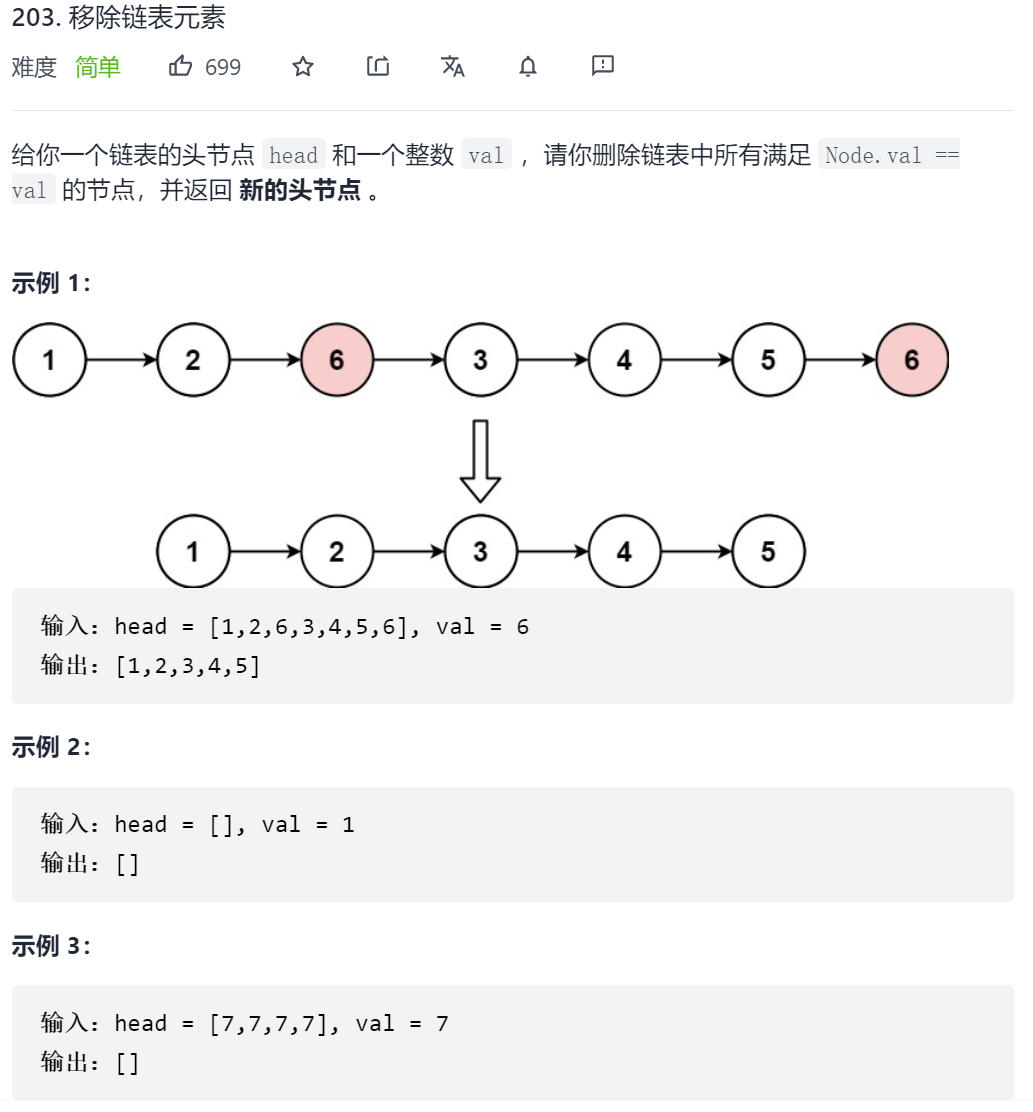
203. 移除链表元素
题目所给的链表是不带头结点的,如果直接操作原链表,删除第一个元素和其他元素的方法是不一样的,需要单独处理,因此有两种思路。
思路一
设置虚拟头结点,可以不单独处理删除第一个元素的情况
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/class Solution {public:ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0); //设置虚拟头结点dummyHead->next = head;ListNode *cur = dummyHead;while(cur->next != nullptr) {if (cur->next->val == val) {ListNode *q = cur->next;cur->next = q->next;delete q;} else {cur = cur->next;}}head = dummyHead->next;delete dummyHead;return head;}};
不考虑释放节点内存
class Solution {public:ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode();dummyHead->next = head;ListNode* pre = dummyHead;ListNode* cur = head;while (cur != nullptr) {if (cur->val == val) {pre->next = cur->next;} else {pre = cur;}cur = cur->next;}return dummyHead->next;}};
考虑释放节点内存
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode();
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode* pre = dummyHead;
ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur != nullptr) {
if (cur->val == val) {
pre->next = cur->next;
ListNode* q = cur;
cur = cur->next;
delete q;
} else {
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return dummyHead->next;
}
};
思路二
直接操作原链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
//删除头结点
while (head != nullptr && head->val == val) {
ListNode *q = head;
head = head->next;
delete q;
}
//删除非头结点,经过上个循环第一个节点值必不为val,因此可以把第一个节点看作头结点
ListNode *cur = head;
while(cur!= nullptr && cur->next != nullptr) {
if (cur->next->val == val) {
ListNode *q = cur->next;
cur->next = q->next;
delete q;
} else {
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return head;
}
};
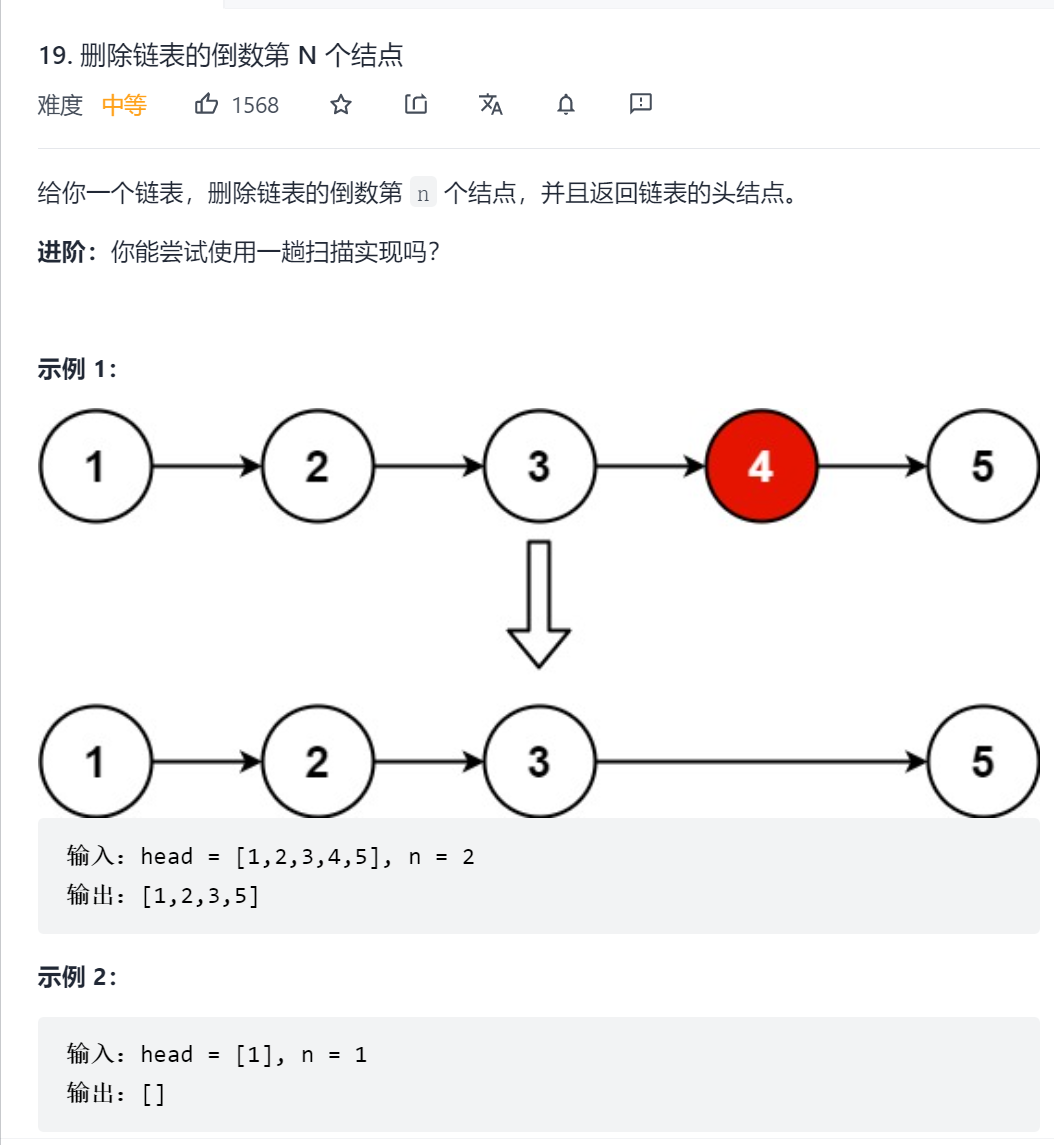
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
思路一:扫描两趟,计算链表长度
第一趟扫描,得到链表的长度len;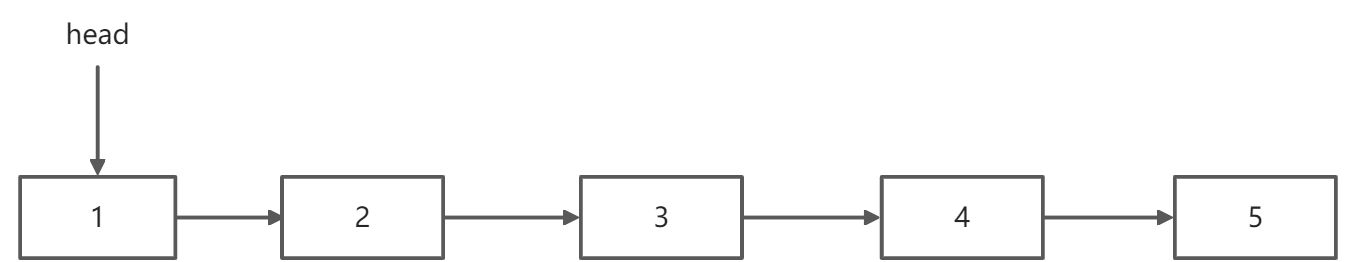
int len = 0;
ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur != nullptr) {
cur = cur->next;
len++;
}
对于例子,得到len = 5,
第二趟扫描,删除链表的第 len - n + 1个元素,假设n = 2,那么要删除的元素索引为 5-2+1=4,下标从0开始
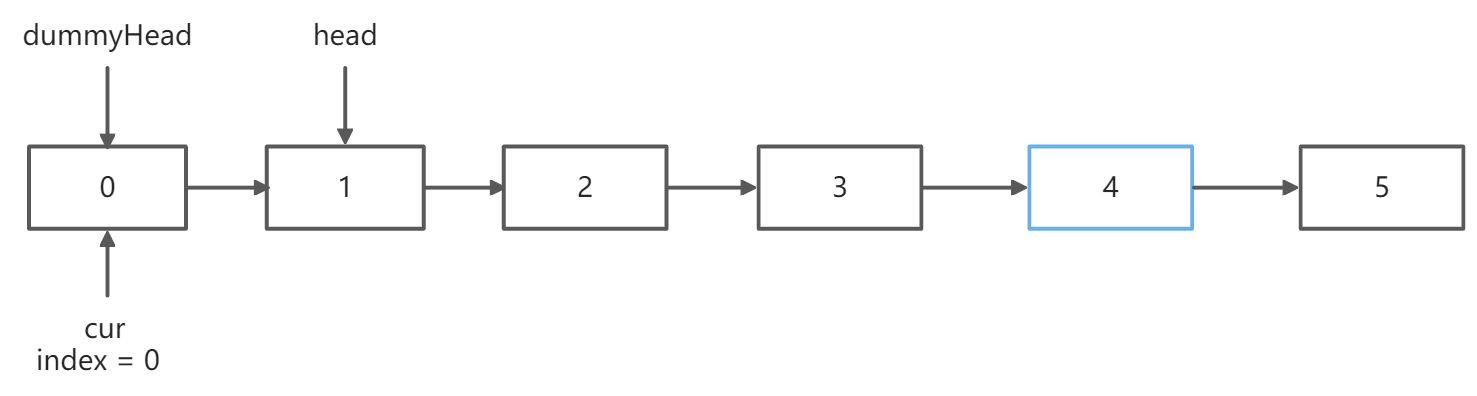
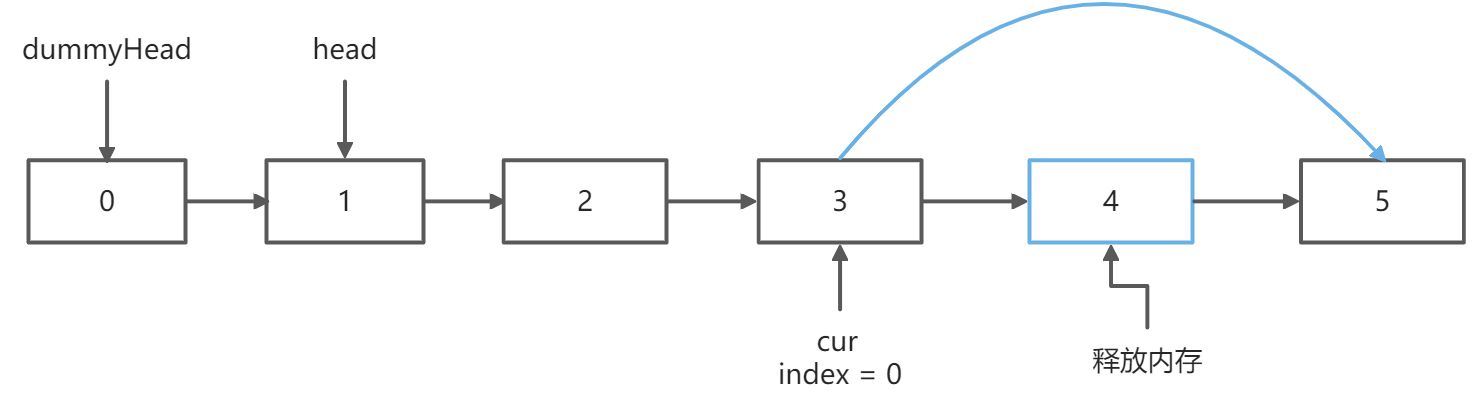
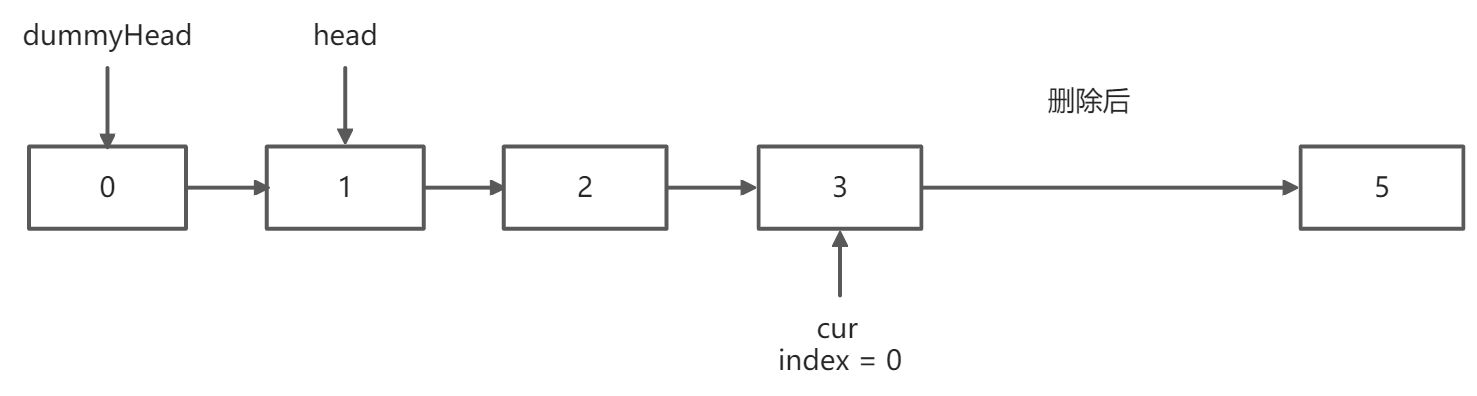
个虚拟头结点
cur = dummyHead;
while (index--) {
cur = cur->next;
}
ListNode* q = cur;
cur = cur->next->next;
delete q;
完整代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
int len = 0;
ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur != nullptr) {
cur = cur -> next;
++len;
}
int index = len - n;
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
cur = dummyHead;
while(index--) cur = cur->next;
ListNode* q = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
delete q;
return dummyHead->next;
}
};
思路二:双指针
先使用快指针fast前进n步,然后fast和slow一起前进,这样当fast指向末尾时,slow指向的元素为倒数第n个元素
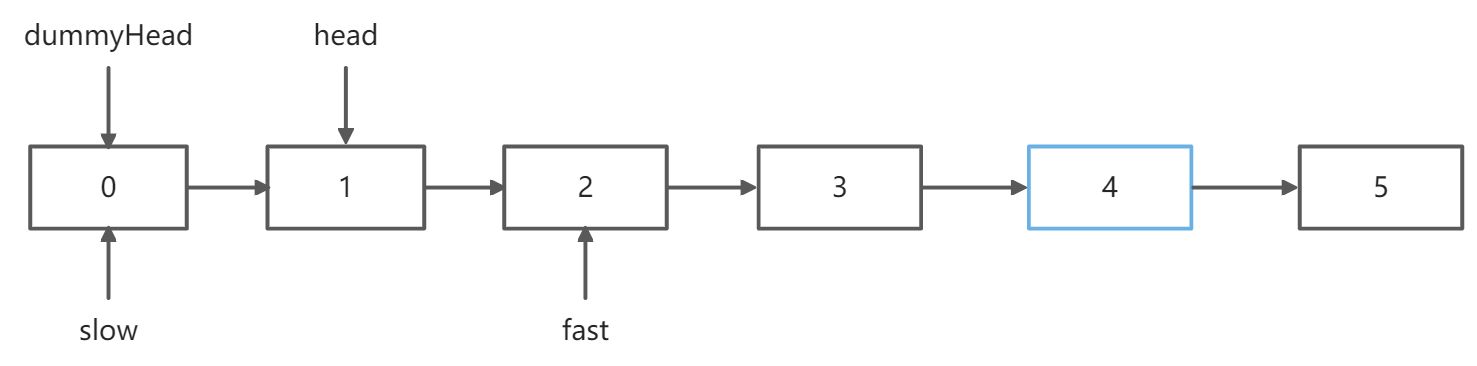
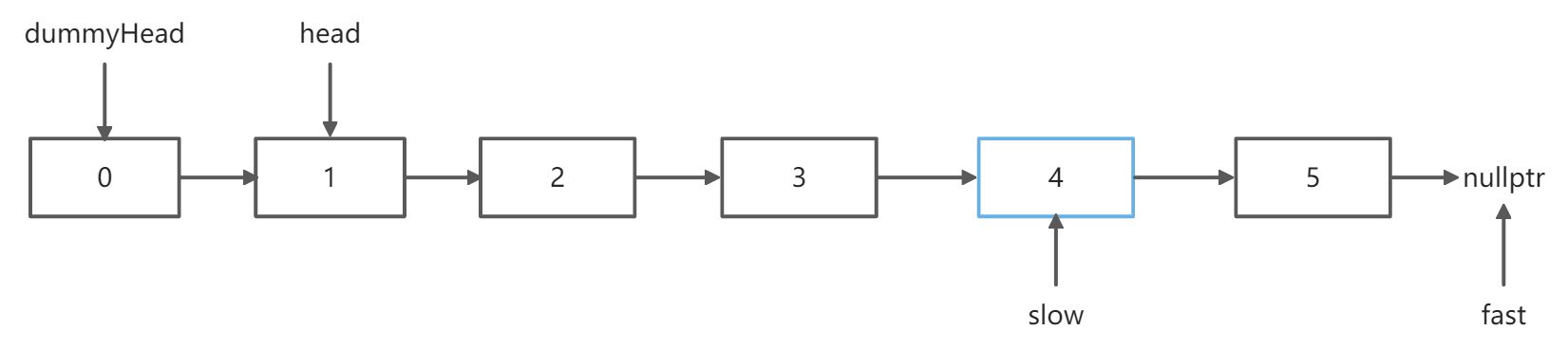
让fast多走一步,这样最后slow指向的元素是要删除的元素的前一个,方便删除操作的进行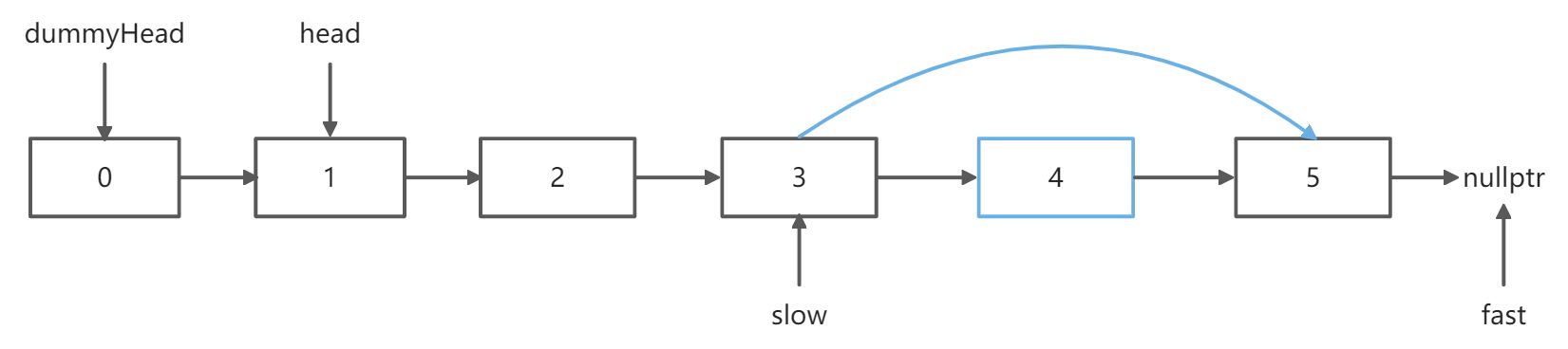
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode* slow = dummyHead;
ListNode* fast = dummyHead;
n++; // fast多走一步,这样会使slow最终指向倒数第n个节点的前一个
while(n--) fast = fast->next;
while(fast != nullptr) {
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
ListNode* q = slow->next;
slow->next = slow->next->next;
delete q;
return dummyHead->next;
}
};
思路三:栈
扫描节点的时候可以将节点放入栈中,当扫描完毕后开始出栈,出栈n个后,栈顶元素刚好是要删除节点的前一个节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
stack<ListNode*> stk;
ListNode* cur = dummyHead;
while(cur != nullptr) {
stk.push(cur);
cur = cur->next;
}
while(n--) stk.pop();
cur = stk.top();
ListNode* q = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
delete q;
return dummyHead->next;
}
};
82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
要舍得用变量,用一个变量来保存重复元素,可以少写很多代码
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
if (!head) return nullptr;
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode* cur = dummy;
while (cur->next && cur->next->next) {
if (cur->next->val == cur->next->next->val) {
int t = cur->next->val;
while (cur->next && cur->next->val == t) cur->next = cur->next->next;
} else {
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return dummy->next;
}
};