- 144. 二叉树的前序遍历">144. 二叉树的前序遍历
- 145. 二叉树的后序遍历">145. 二叉树的后序遍历
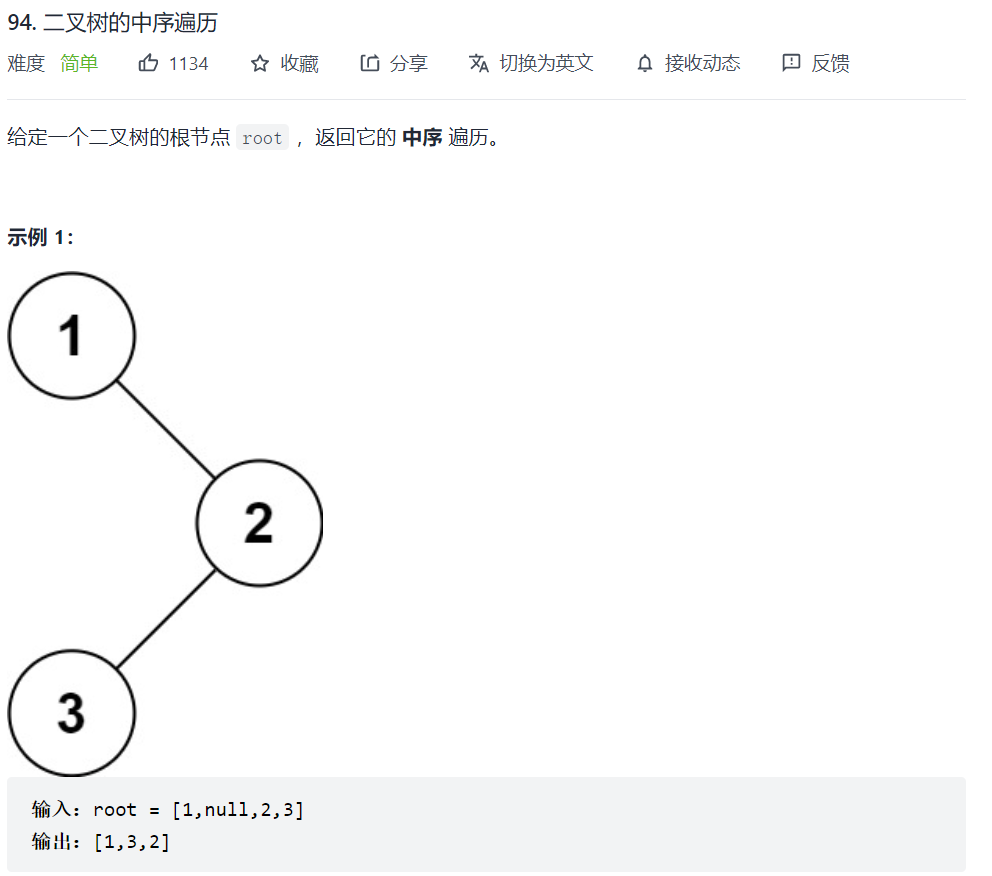
- 94. 二叉树的中序遍历">94. 二叉树的中序遍历
- 复杂度分析
- 102. 二叉树的层序遍历">102. 二叉树的层序遍历
- 107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II">107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II
- 199. 二叉树的右视图">199. 二叉树的右视图
- 637. 二叉树的层平均值">637. 二叉树的层平均值
- 429. N 叉树的层序遍历">429. N 叉树的层序遍历
- 515. 在每个树行中找最大值">515. 在每个树行中找最大值
- 116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针">116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
- 117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II">117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II
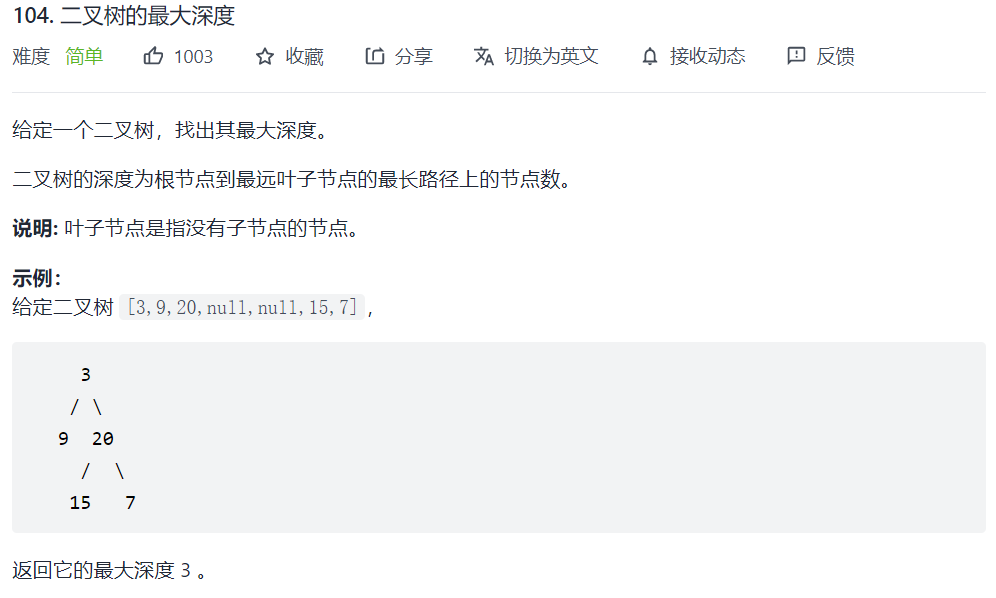
- 104. 二叉树的最大深度">104. 二叉树的最大深度
- 559. N 叉树的最大深度">559. N 叉树的最大深度
- 111. 二叉树的最小深度">111. 二叉树的最小深度
144. 二叉树的前序遍历
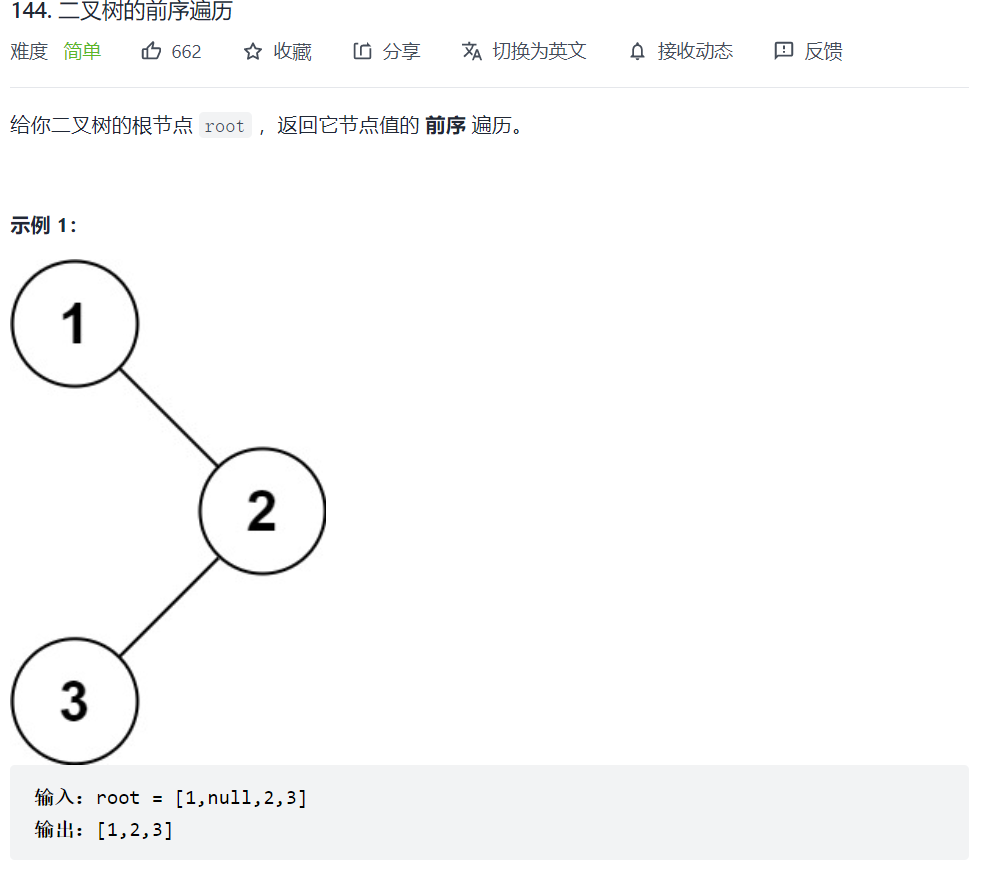

先序遍历:先根再左再右
二叉树的定义:
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/
递归遍历
C++代码:
public:vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {vector<int> res;traversal(root, res);return res;}void traversal(TreeNode * cur, vector<int> &v) {// 递归出口if (cur == nullptr)return;// 先访问根结点,然后再递归遍历左右子树v.push_back(cur->val);traversal(cur->left, v);traversal(cur->right, v);}};
迭代遍历
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
stack<TreeNode*> stk;
if (root == nullptr) return res;
stk.push(root);
while (!stk.empty()) {
// 访问根结点
TreeNode* cur = stk.top();
stk.pop();
res.push_back(cur->val);
// 右孩子先入栈,先入的后被访问
if (cur->right)
stk.push(cur->right);
if (cur->left)
stk.push(cur->left);
}
return res;
}
};
145. 二叉树的后序遍历

递归遍历
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
traversal(root, res);
return res;
}
void traversal(TreeNode *cur, vector<int> &v) {
// 递归出口
if (cur == nullptr)
return;
// 先遍历左右子树,最后访问根结点
traversal(cur->left, v);
traversal(cur->right, v);
v.push_back(cur->val);
}
};
迭代遍历
后序遍历的关键在于,当访问完节点的左子树后,如果右子树为空或者已经访问过,才能访问这个节点
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return {};
stack<TreeNode*> st;
vector<int> res;
TreeNode* cur = root;
TreeNode* pre = nullptr; // 用于判断右子树是否处理
while (cur != nullptr || !st.empty()) {
while (cur != nullptr) { // 处理左子树
st.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
// 左子树处理完毕,处理根和右子树
cur = st.top();
st.pop();
if (cur->right == nullptr || pre == cur->right) { // 如果没有右孩子或者右孩子已经访问过,访问根
res.push_back(cur->val);
pre = cur; // 记住此次访问的节点
cur = nullptr; // 表示这根子树处理完毕,接下来从栈中取节点处理
} else {
st.push(cur); // 右子树未处理,先处理右子树,因此将根节点再次放回栈中
cur = cur->right;
}
}
return res;
}
};
当然,先序遍历是中左右,后续遍历是左右中,那么我们只需要调整一下先序遍历的代码顺序,就变成中右左的遍历顺序,然后在反转result数组,输出的结果顺序就是左右中了,如下图:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
vector<int> result;
if (root == NULL) return result;
st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top();
st.pop();
result.push_back(node->val);
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 相对于前序遍历,这更改一下入栈顺序 (空节点不入栈)
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 空节点不入栈
}
reverse(result.begin(), result.end()); // 将结果反转之后就是左右中的顺序了
return result;
}
};
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
递归遍历
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
traversal(root, res);
return res;
}
void traversal(TreeNode *cur, vector<int> &v) {
// 递归出口
if (cur == nullptr)
return;
// 先左再根最后右
traversal(cur->left, v);
v.push_back(cur->val);
traversal(cur->right, v);
}
};
迭代遍历
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if (root == nullptr) return res;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* cur = root;
while (cur || !st.empty()) {
while (cur != nullptr) { // 有左子树的话,将根结点先入栈
st.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
// 访问根结点
cur = st.top(); st.pop();
res.push_back(cur->val);
cur = cur->right;
}
return res;
}
};
复杂度分析
- 空间复杂度:无论是迭代还是递归,都需要用栈来保存节点信息,只不过一个是自己定义的栈,一个是系统栈,因此空间复杂度都为O(n)
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
[
](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-tilt/)记住层序遍历,稍微修改一下,就能完成下面道题
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
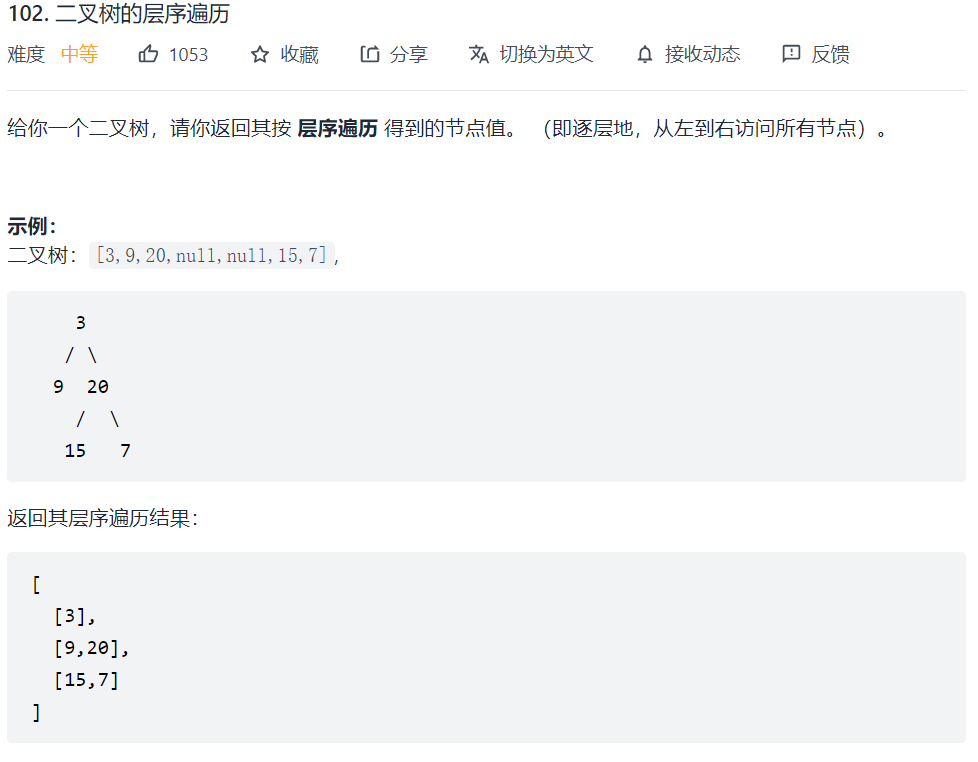
需要借用一个辅助数据结构即队列来实现,队列先进先出,符合一层一层遍历的逻辑,而是用栈先进后出适合模拟深度优先遍历也就是递归的逻辑。
而这种层序遍历方式就是图论中的广度优先遍历,只不过我们应用在二叉树上。
使用队列实现二叉树广度优先遍历,动画如下: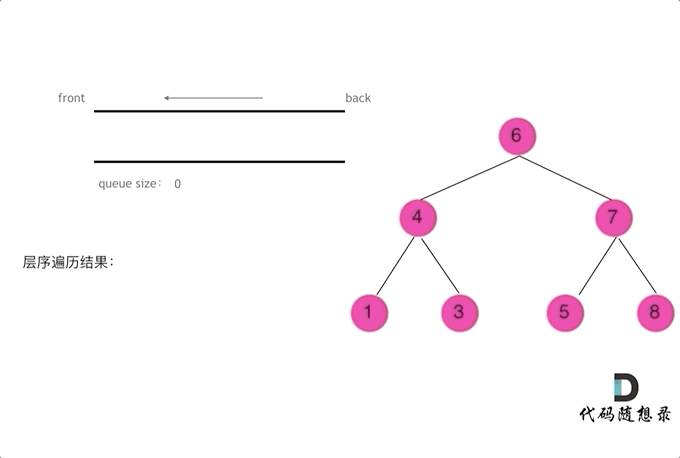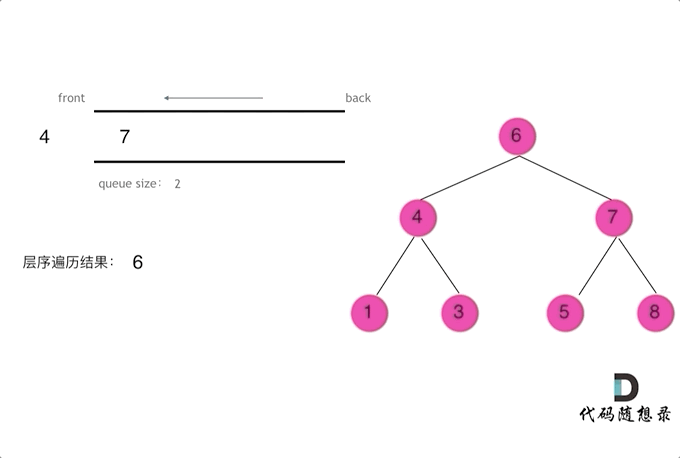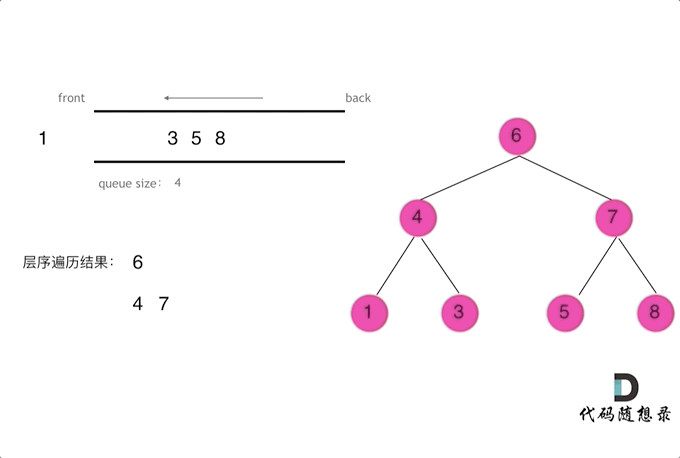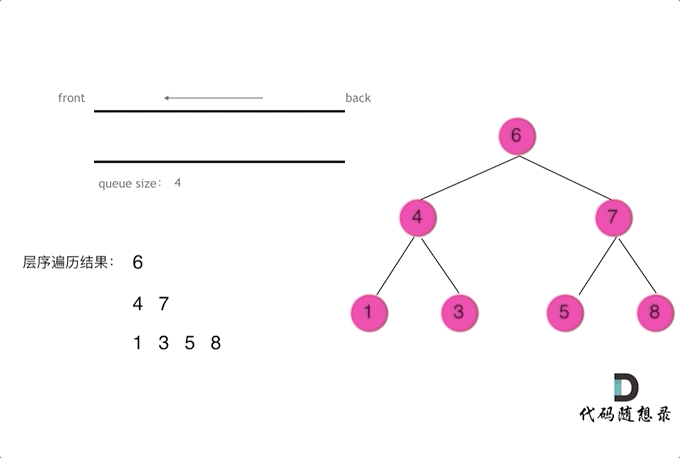
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
vector<vector<int>> res;
if (root == nullptr) return res;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size(); // 当前层的节点个数
vector<int> level;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
level.push_back(node->val);
if (node->left != nullptr) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right != nullptr) que.push(node->right);
}
res.push_back(level);
}
return res;
}
};
107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II
102题是返回从顶层向下的结果,这一题要求返回自底向上的层序遍历结果,那么我们直接对结果进行反转即可。
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if (root == nullptr) return res;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
vector<int> level;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
level.push_back(node->val);
if (node->left != nullptr) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right != nullptr) que.push(node->right);
}
res.push_back(level);
}
reverse(res.begin(), res.end()); // 反转自顶向下的结果
return res;
}
};

199. 二叉树的右视图
所谓,二叉树的右视图,实际上就是得到每一层的最后一个节点值,因此,在层序遍历的基础上,我们直接把每一层的最后一个元素放入res中。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if (root == nullptr) return res;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (i == size - 1)
res.push_back(node->val);
if (node->left != nullptr) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right != nullptr) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return res;
}
};
637. 二叉树的层平均值

将层序每一层的结果求个平均值就可。
class Solution {
public:
vector<double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode* root) {
vector<double> res;
if (root == nullptr) return res;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
sum += node->val;
if (node->left != nullptr) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right != nullptr) que.push(node->right);
}
res.push_back(sum / size); //保存当前层的平均值
}
return res;
}
};
429. N 叉树的层序遍历
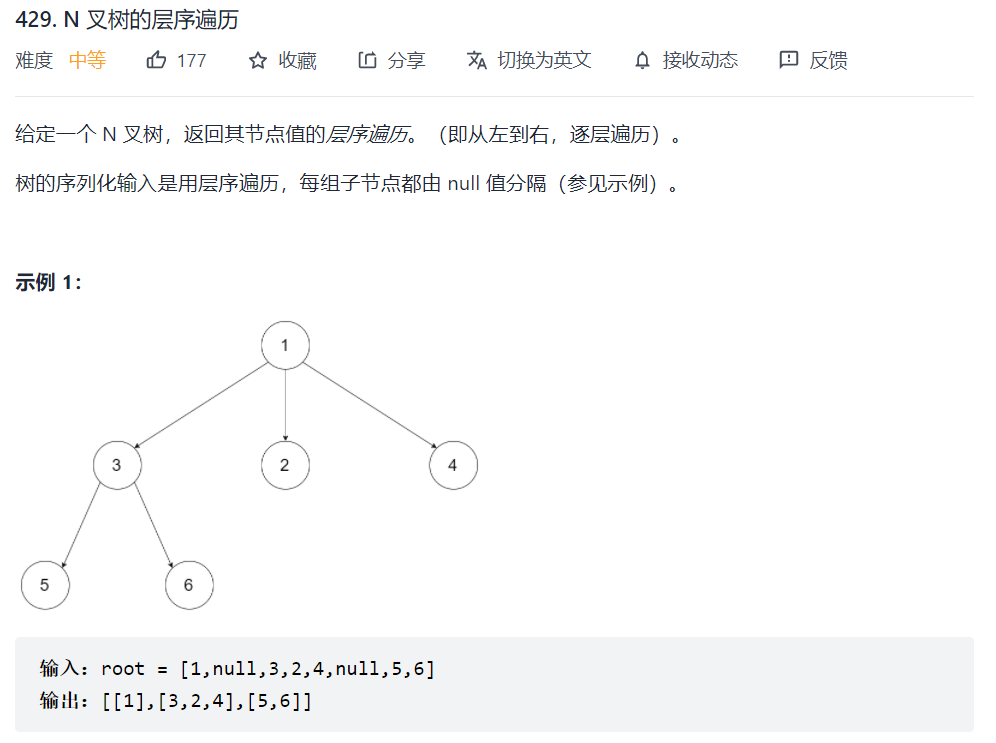
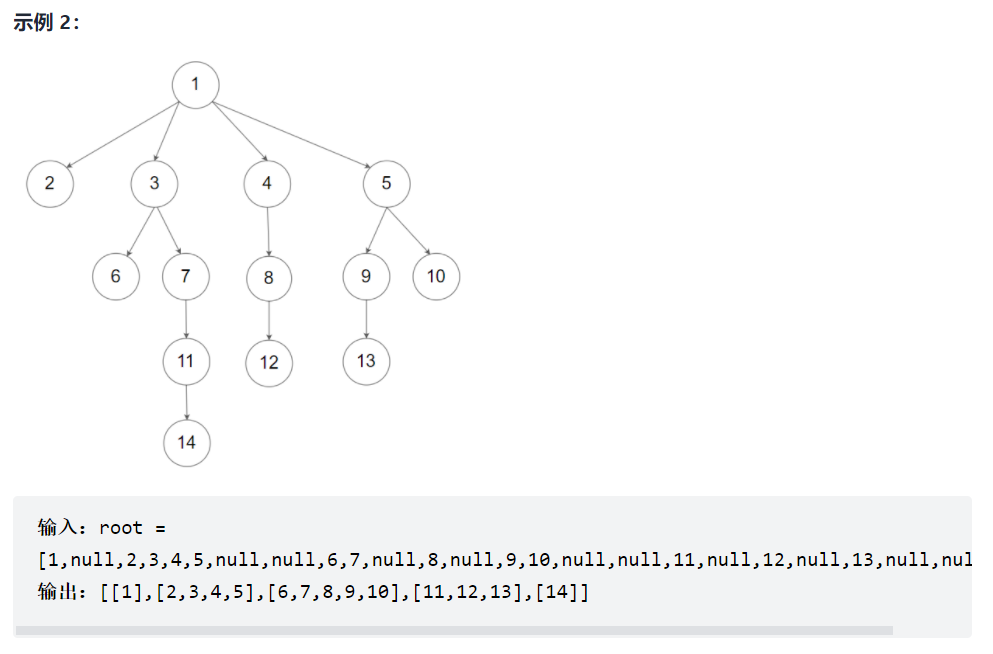
N叉树的定义
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
套层序遍历的模板
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if (root == nullptr) return res;
queue<Node*> que;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
vector<int> level;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node* node = que.front();
que.pop();
level.push_back(node->val);
// 孩子的数量不确定,用循环
for (auto child : node->children) {
que.push(child);
}
}
res.push_back(level);
}
return res;
}
};
515. 在每个树行中找最大值
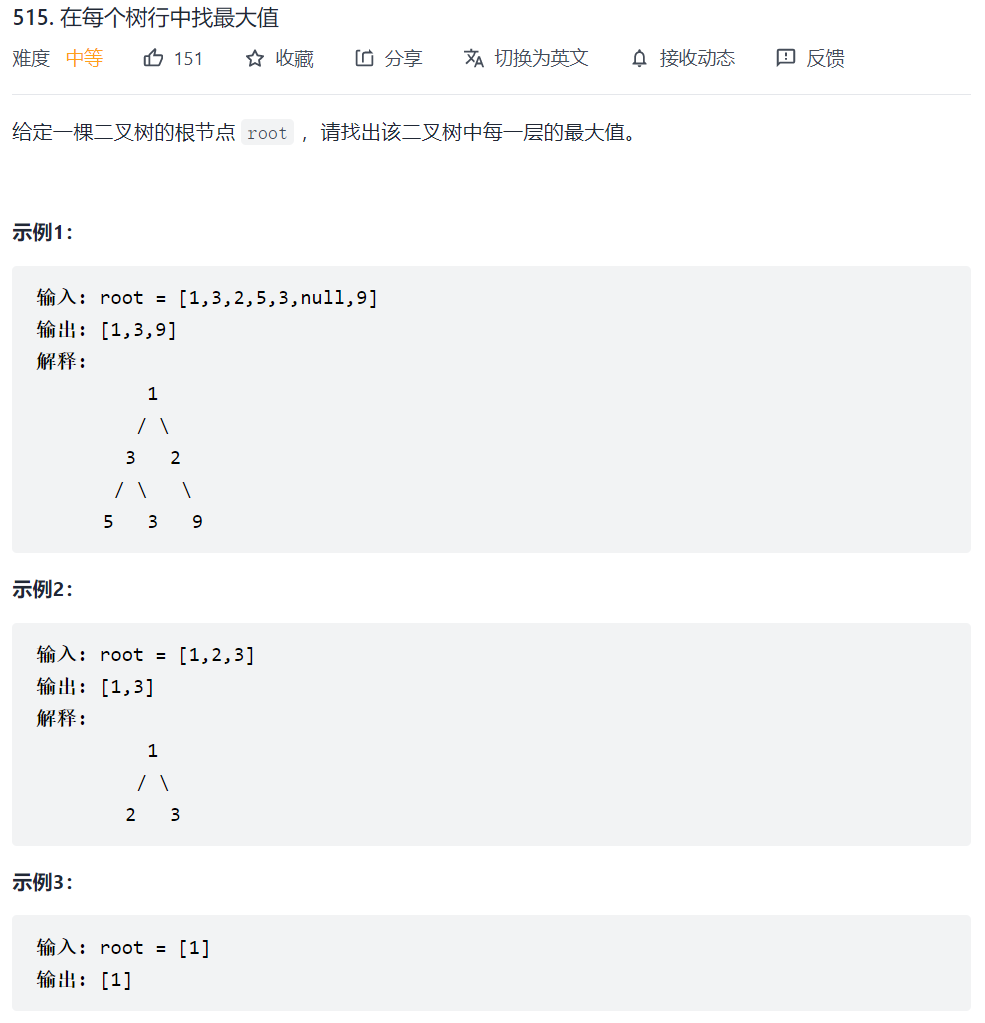
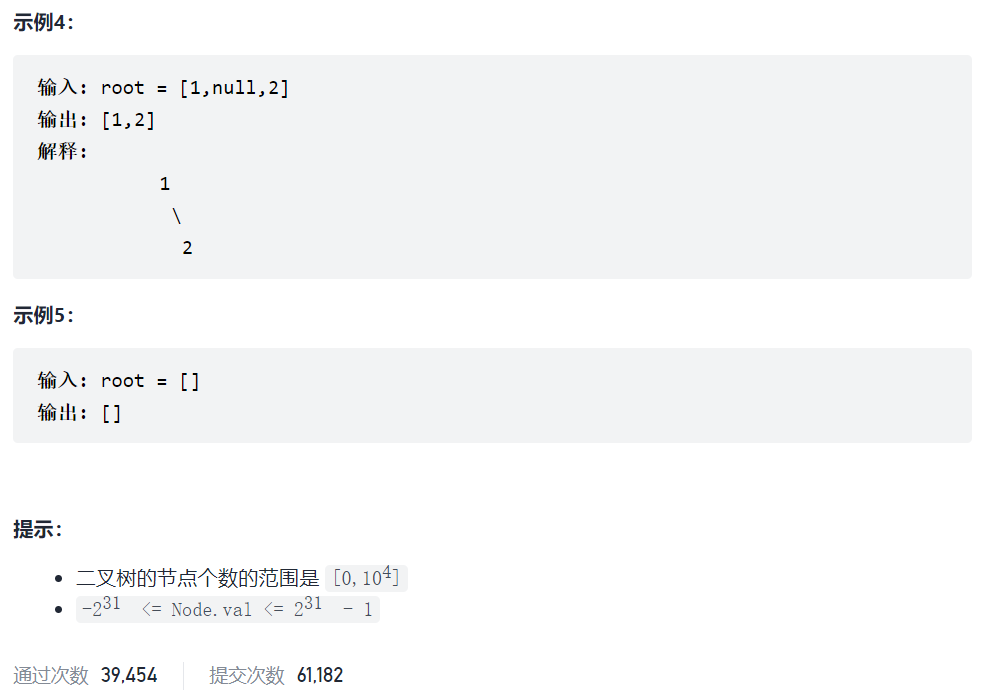
依然套用层序遍历的模板
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> largestValues(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
vector<int> res;
if (root == nullptr) return res;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size(); // 当前层的节点个数
int max = INT_MIN; // 记录每层的最大值
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (node->val > max) max = node->val;
if (node->left != nullptr) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right != nullptr) que.push(node->right);
}
res.push_back(max);
}
return res;
}
};
116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
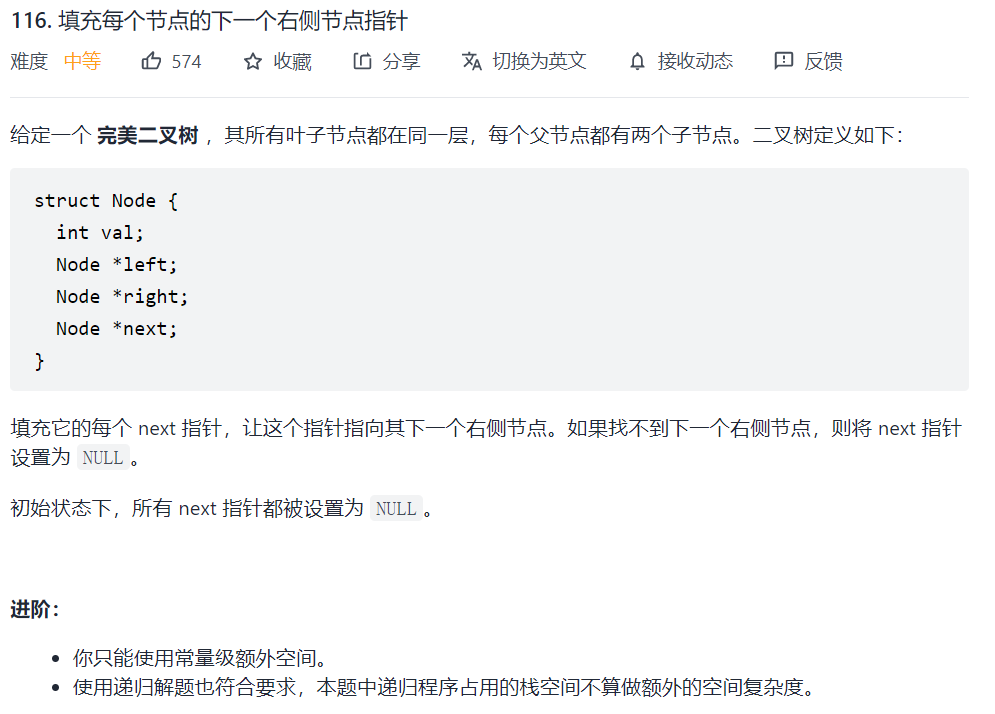
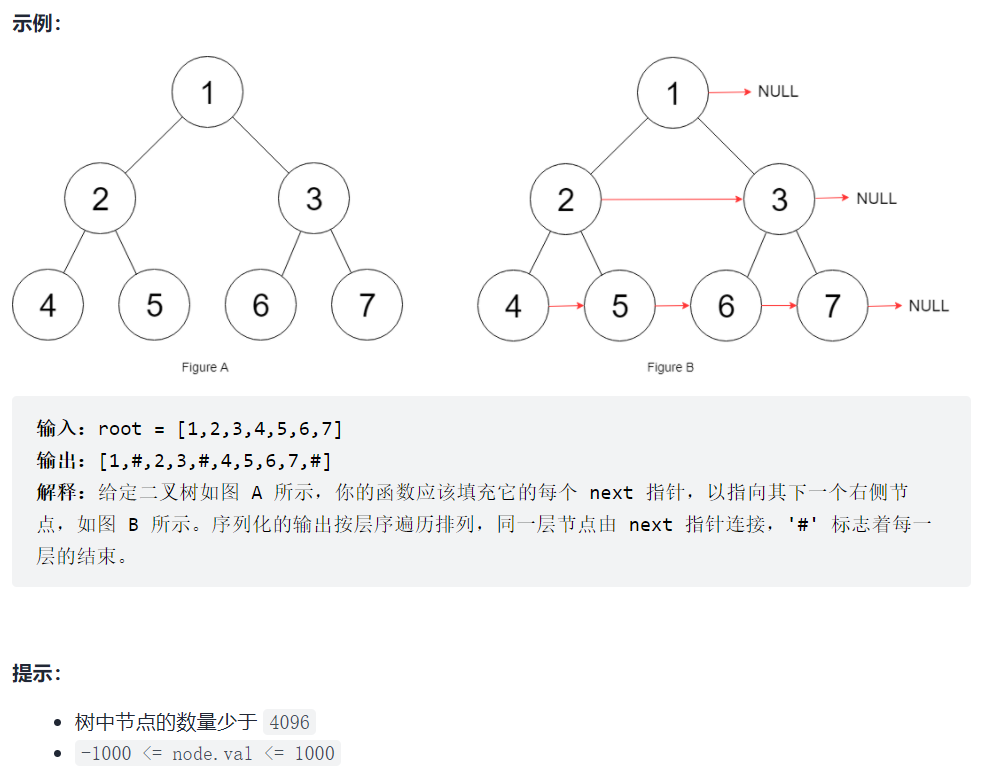
套用层序遍历的模板,遍历每一层元素,如果元素不是最后一个,对其赋值
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node* next;
Node() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}
Node(int _val) : val(_val), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}
Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right, Node* _next)
: val(_val), left(_left), right(_right), next(_next) {}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
if (!root) return root;
queue<Node*> que;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size(); // 当前层的节点个数
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (i < size - 1) // 不是层的最后一个元素
node->next = que.front();
// 默认next都为null,因此不用再设置最后一个元素的next
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return root;
}
};
117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II
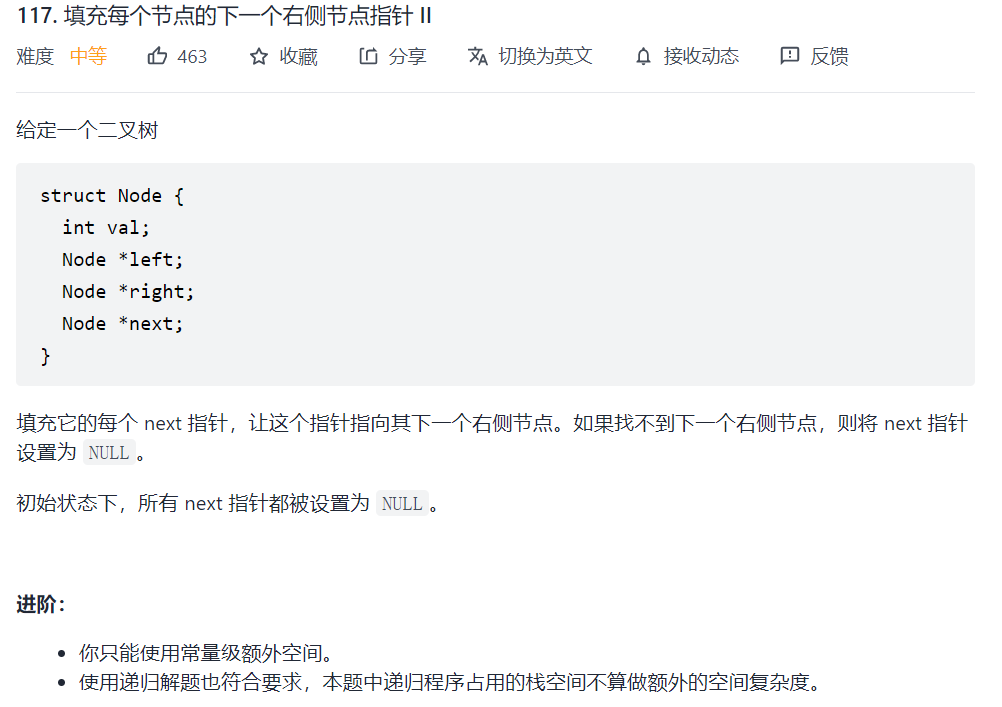
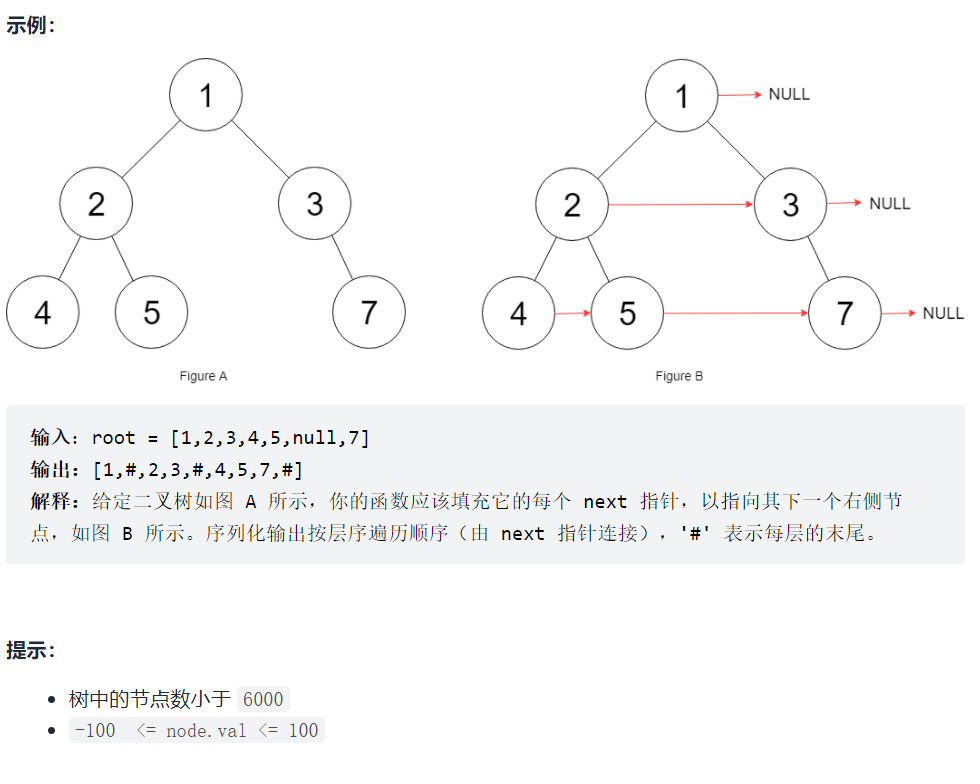
上一道题,使用层序遍历模板的解法,不需要考虑二叉树是否完美,因此,本题代码与上一题一样
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
if (!root) return root;
queue<Node*> que;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size(); // 当前层的节点个数
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (i < size - 1) // 不是层的最后一个元素
node->next = que.front();
// 默认next都为null,因此不用再设置最后一个元素的next
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return root;
}
};
104. 二叉树的最大深度
思路一:广度优先
套用层序遍历的模板
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
int depth = 0;
if (root == nullptr) return depth;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size(); // 当前层的节点个数
depth++; // 记录深度
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (node->left != nullptr) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right != nullptr) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return depth;
}
};
思路二:深度优先
知道了左右子树的最大深度,那么树的最大深度就是左右子树的最大深度之中最大的那个+1
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return 0;
return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};
通过递归三部曲更加深刻的理解这个深度优先方法:
精简的写法看不出这道题是先序遍历还是后续遍历:
- 先序遍历求的是深度
- 后序遍历求的是高度,根节点的高度就是树的深度
使用后序遍历计算树的高度:
确定递归函数的参数和返回值:参数就是传入树的根节点,返回就返回这棵树的深度,所以返回值为int类型。
int getdepth(treenode* node)确定终止条件:如果节点为空的话,返回0,表示高度为0
if (!node) return 0;确定单层递归的逻辑:先求它的左子树的深度,再求的右子树的深度,最后取左右深度最大的数值 再+1 (加1是因为算上当前中间节点)就是目前节点为根节点的树的深度
int leftdepth = getdepth(node->left); // 左 int rightdepth = getdepth(node->right); // 右 int depth = 1 + max(leftdepth, rightdepth); // 中 return depth;整体代码如下:
class solution { public: int getdepth(treenode* node) { if (node == null) return 0; int leftdepth = getdepth(node->left); // 左 int rightdepth = getdepth(node->right); // 右 int depth = 1 + max(leftdepth, rightdepth); // 中 return depth; } int maxdepth(treenode* root) { return getdepth(root); } };代码精简后就是最开始的代码了!!!
使用前序遍历的话,就能体现出回溯的过程
class solution {
public:
int result;
void getdepth(treenode* node, int depth) {
result = depth > result ? depth : result; // 中
if (node->left == null && node->right == null) return ;
if (node->left) { // 左
depth++; // 深度+1
getdepth(node->left, depth);
depth--; // 回溯,深度-1
}
if (node->right) { // 右
depth++; // 深度+1
getdepth(node->right, depth);
depth--; // 回溯,深度-1
}
return ;
}
int maxdepth(treenode* root) {
result = 0;
if (root == 0) return result;
getdepth(root, 1);
return result;
}
};
精简后:
class solution {
public:
int result;
void getdepth(treenode* node, int depth) {
result = depth > result ? depth : result; // 中
if (node->left == null && node->right == null) return ;
if (node->left) { // 左
getdepth(node->left, depth + 1);
}
if (node->right) { // 右
getdepth(node->right, depth + 1);
}
return ;
}
int maxdepth(treenode* root) {
result = 0;
if (root == 0) return result;
getdepth(root, 1);
return result;
}
};
559. N 叉树的最大深度
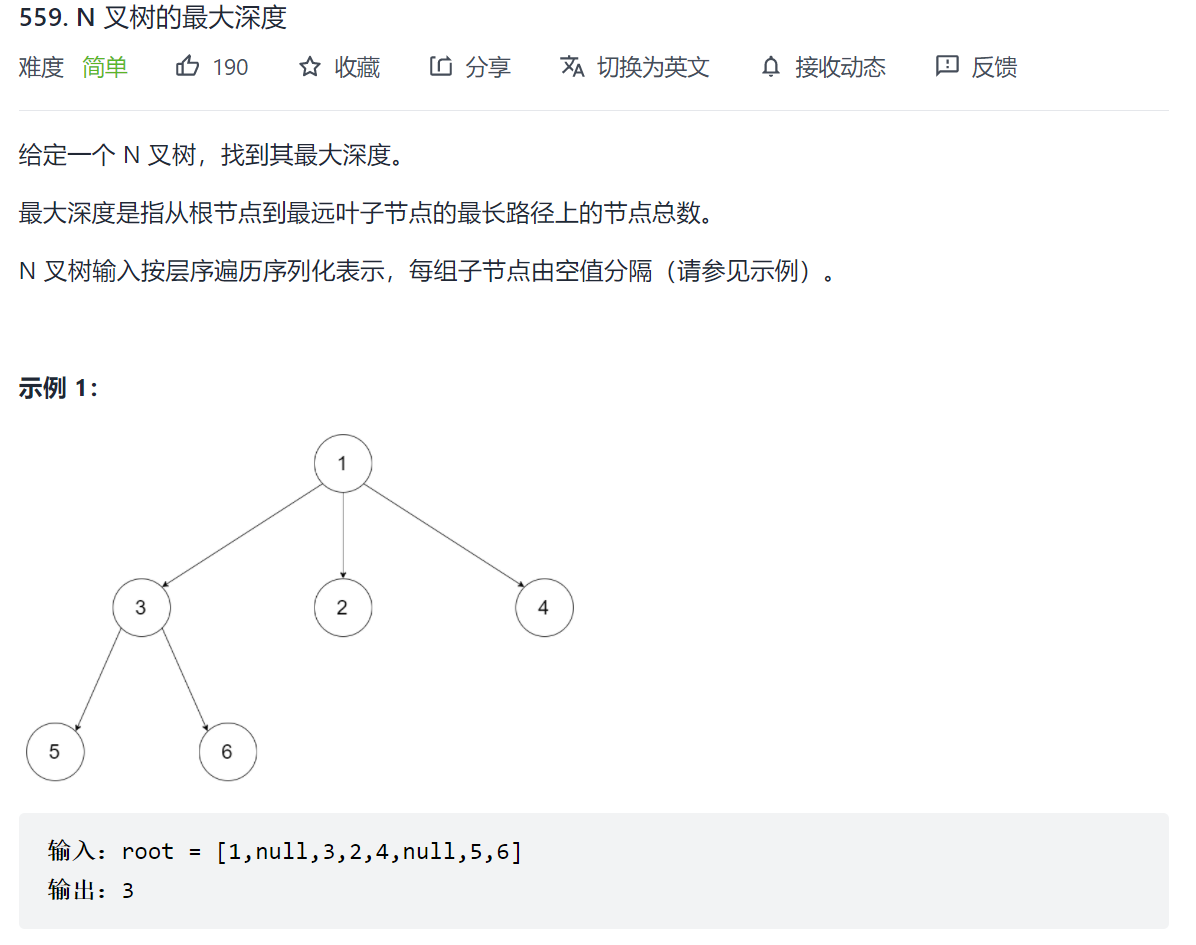
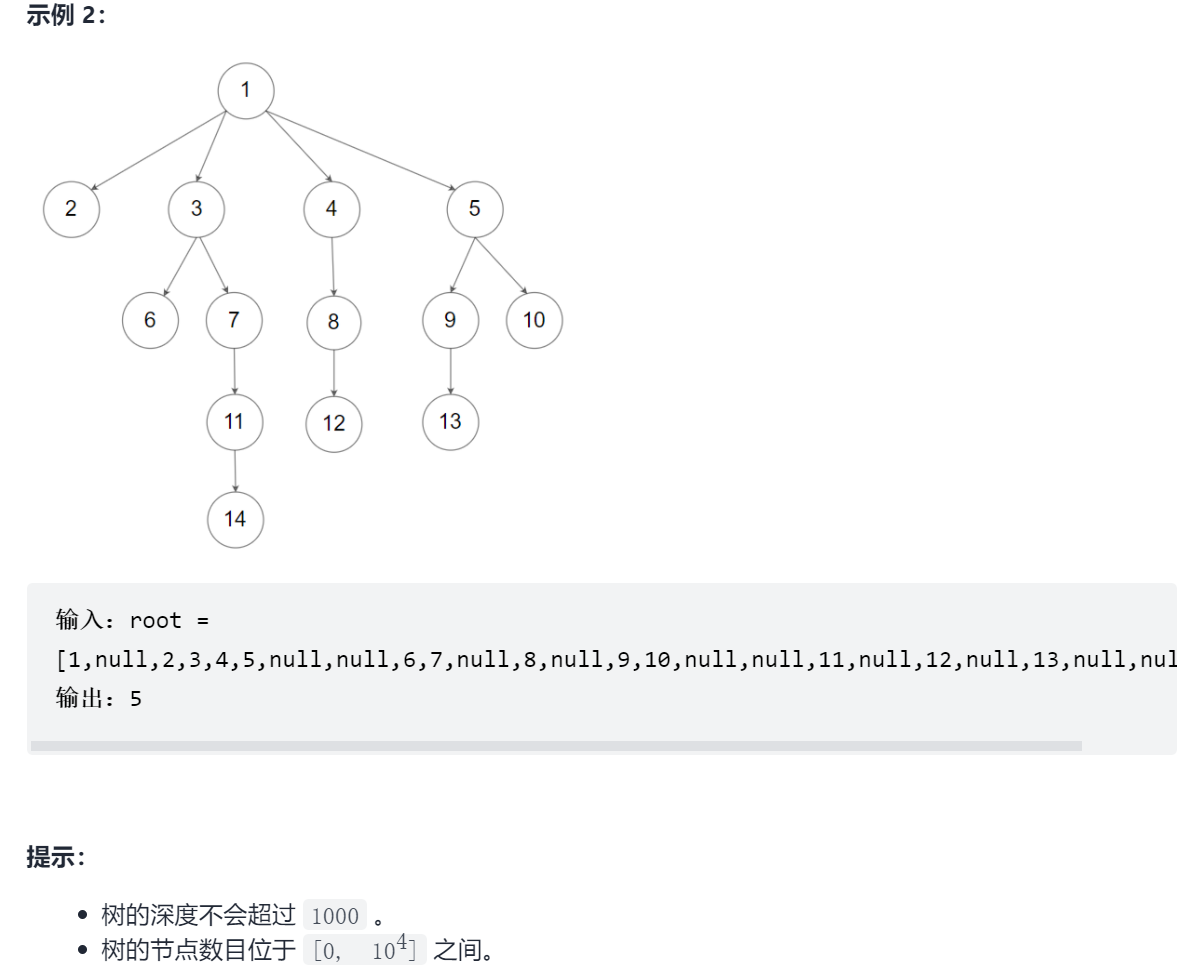
N叉树的定义如下:
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
递归法
确定参数和返回值:参数为节点,返回值为int
int getDepth(Node* root)确定递归出口:如果节点为空的话,返回0
if (!root) return 0;确定单层递归的逻辑:求每个子树的高度,树的高度为最大的子树高度加1
int maxdep = 0; for (auto node : root->children) { maxdep = max(maxdep, getDepth(node)); } return maxdep + 1;完整代码如下:
class Solution { public: int maxDepth(Node* root) { return getDepth(root); } int getDepth(Node* root) { if (!root) return 0; int maxdep = 0; for (auto node : root->children) { maxdep = max(maxdep, getDepth(node)); } return maxdep + 1; } };简化后的代码如下:
class Solution { public: int maxDepth(Node* root) { if (!root) return 0; int maxdep = 0; for (auto node : root->children) { maxdep = max(maxdep, maxDepth(node)); } return maxdep + 1; } };迭代法
使用层序遍历的模板,稍微修改下即可
代码如下:class Solution { public: int maxDepth(Node* root) { if (!root) return 0; queue<Node*> que; que.push(root); int depth = 0; while (!que.empty()) { depth++; int size = que.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { Node* node = que.front(); que.pop(); for (auto n : node->children) { que.push(n); } } } return depth; } };
111. 二叉树的最小深度
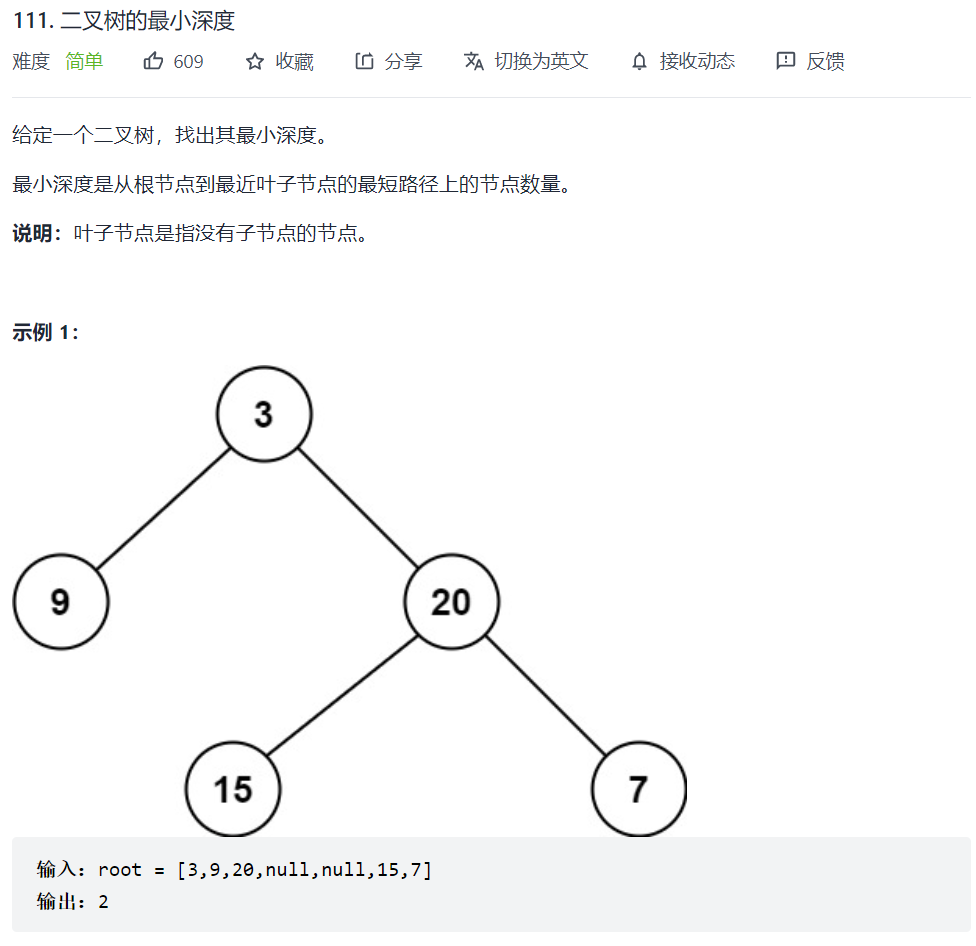

这道题要注意的一点就是,只有当一个节点左孩子和右孩子都不存在时,这个节点才是叶子节点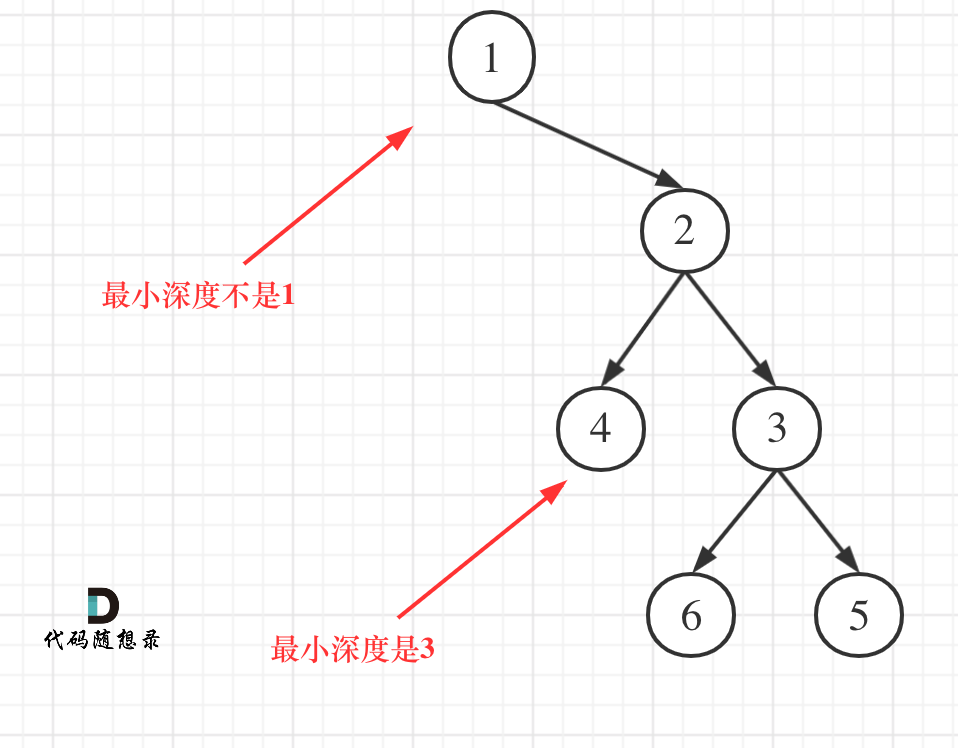
思路一:广度优先
套用层序遍历的模板,在最大深度的基础上,加一个判断条件,如果出队时某节点是叶子节点,那么返回当前深度。
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
int depth = 0;
if (root == nullptr) return depth;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size(); // 当前层的节点个数
depth++; // 记录深度
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (!node->left && !node->right)//当前节点为叶子节点,返回当前深度
return depth;
if (node->left != nullptr) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right != nullptr) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return depth;
}
};
思路二:深度优先
对于每个非叶子节点,都可以考虑其左子树和右子树的最小叶子结点深度,那么就可以递归的解决这个问题
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
if (root->left != nullptr && root->right == nullptr) {
return minDepth(root->left) + 1;
}
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right != nullptr) {
return minDepth(root->right) + 1;
}
return min(minDepth(root->left), minDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};
或
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
else if (!root->left) return minDepth(root->right) + 1;
else if (!root->right) return minDepth(root->left) + 1;
else return min(minDepth(root->left), minDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};
[