给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
说明:不允许修改给定的链表。
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:tail connects to node index 1
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。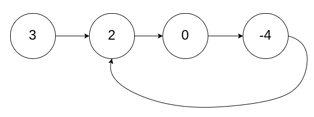
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:tail connects to node index 0
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。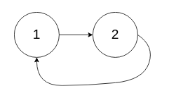
示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:no cycle
解释:链表中没有环。
法一:双指针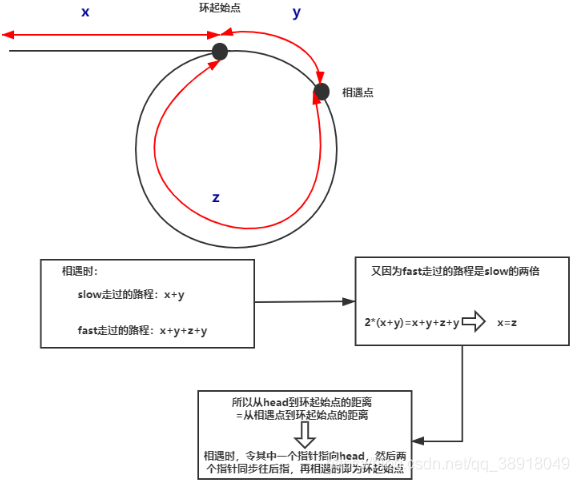
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) {* val = x;* next = null;* }* }*/public class Solution {public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;while (true) {if (fast == null || fast.next ==null) return null;slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;if (slow == fast) break;}fast = head;while (fast != slow) {fast = fast.next;slow = slow.next;}return fast;}}
法二:哈希表
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
如果我们用一个 Set 保存已经访问过的节点,我们可以遍历整个列表并返回第一个出现重复的节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
HashSet<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
ListNode node = head;
while (node != null) {
if (set.contains(node)) return node;
set.add(node);
node = node.next;
}
return null;
}
}