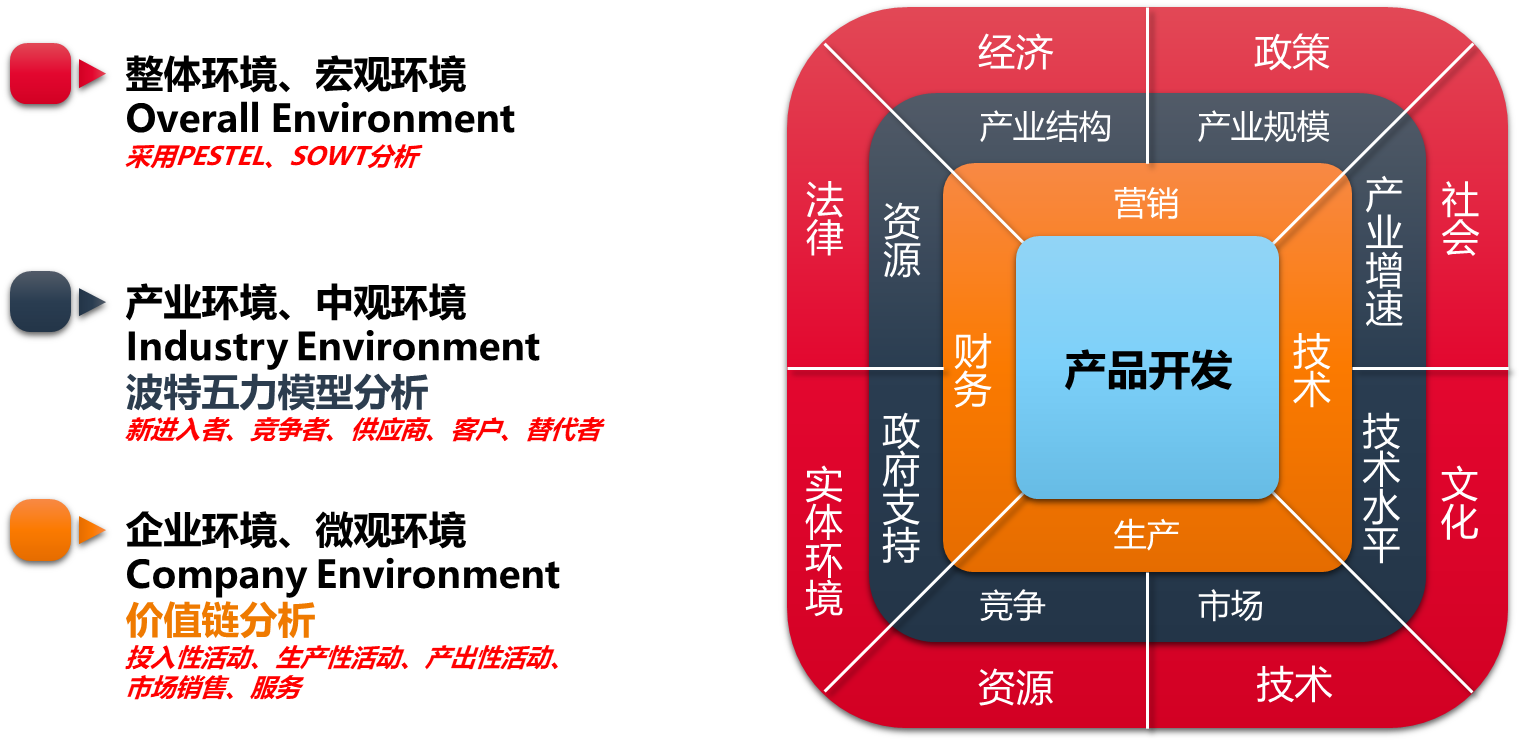
整体环境、宏观环境(Overall Environment)
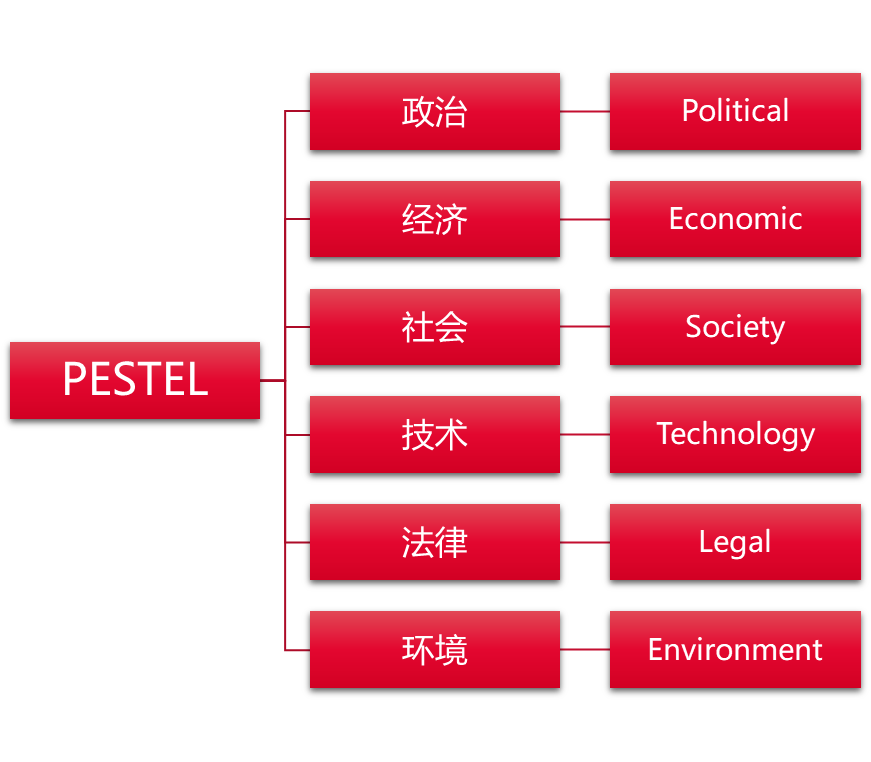
PESTEL
针对宏观环境采用PESTEL分析法,研究对象是目标市场的【宏观环境】
| Political | Economic | Society | Technology | Legal | Environment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Government policy Political stability Foreign trade policy Tax policy Labor law Trade restrictions |
Economic growth Exchange rates Interest rates Inflation rates Disposable income Unemployment rates |
Population growth rate Age distribution Educational levels Safety emphasis Lifestyle attitudes Cultural barriers |
Technology incentives Level of innovation Automation R&D activity Technological change Technological awareness |
Discrimination laws Antitrust laws Employment laws Consumer protection laws Patent laws Health and safety laws |
Weather Environmental politics Climate change Pressure from NGOs |
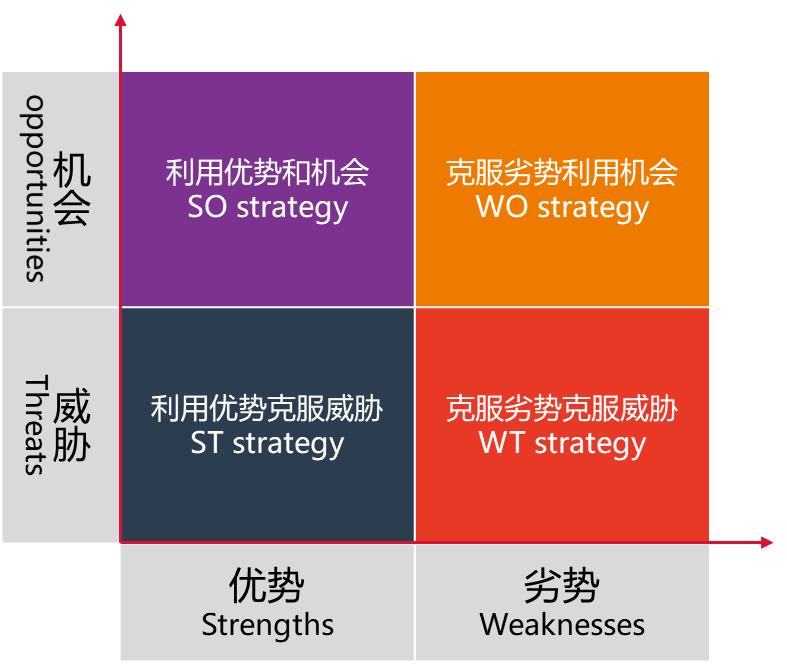
SWOT
针对宏观环境采用SWOT分析法,研究对象是【公司】对外界的反应以及影响。包括:考察公司优势能够抵消威胁的程度;机会可以克服劣势的程度。
SOWT是结构化分析方法,广泛用于包括产品开发在内的商业领域
- 优势 Strength:企业或项目优于其他企业的特点
- 劣势 Weakness:企业或项目相对于其他企业的劣势
- 机会 Opportunities:企业能利用的优势的要素
- 威协 Threats:环境中能给企业或项目带来麻烦的要素
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
| —- | —- |
|
- What the company does well, e.g., technical development, market research
- What separates the company from competitors, e.g., strong brand recognition
- Company resources such as specialized manufacturing or skilled staff
- Tangible assets such as IP or capital
|
- What the company lacks, e.g., specific skills or capital
- Things that competitors do better, e.g., distribution, consumerrelationships
- Resource limitations, e.g., specific skills, access to raw materials
- Unclear value proposition
| | Opportunities | Threats | |
- Significant identified gaps in product offerings
- Few or weak competition
- Market trends supporting need for the company’s products
- Availability of specialist technical knowledge through licensing or acquisition
|
- Emerging competitors
- Changing regulatory environment
- Potential for disruptive technologies
- Trends counter to current product attributes
- Potential loss of valuable skills
- Potential loss of critical raw materials
|
产业环境、中观环境(Industry Environment)
波特五力竞争模型
是最流行的产业结构分析工具,可有效的分析客户当下的产业竞争环境,进而帮助选择成本领先、差异化、聚焦(细分)三大战略
1. 进入壁垒
- 规模经济
- 产品差异化
- 品牌认同
- 转移成本
- 资本需求
- 销售渠道
- 绝对成本优势
- 独有的学习曲线
- 必要的进货渠道
- 独有的低成本产品设计
- 政府政策
-
2. 竞争决定因素
固定(或不变)成本/附加价值
- 间歇的产能过剩
- 产品差别
- 品牌的认同
- 转移成本
- 集中度额均衡
- 信息的复杂性
- 竞争者的多样性
- 公司权益
-
3. 客户力量的决定因素
促销手段
- 客户集中度VS供应商集中度
- 与供应商转移成本相关的客户转移成本
- 客户信息
- 向后整合的能力
- 替代产品
- 客户拉动
- 价格敏感度
- 价格/整体采购
- 产品差别
- 品牌的认同
- 对质量性能的影响
- 客户利益
-
4. 替代者威胁的决定因素
替代品的价格影响
- 转移成本
-
5. 供应商力量的决定因素
进货差别
- 行业内公司和供应商的转移成本
- 替代货源的出现
- 供应商集中度
- 采购商对供应商的重要性
- 行业内与整体采购有关的成本
- 进货成本或差别的影响
- 行业内公司的前向和后向整合的威胁
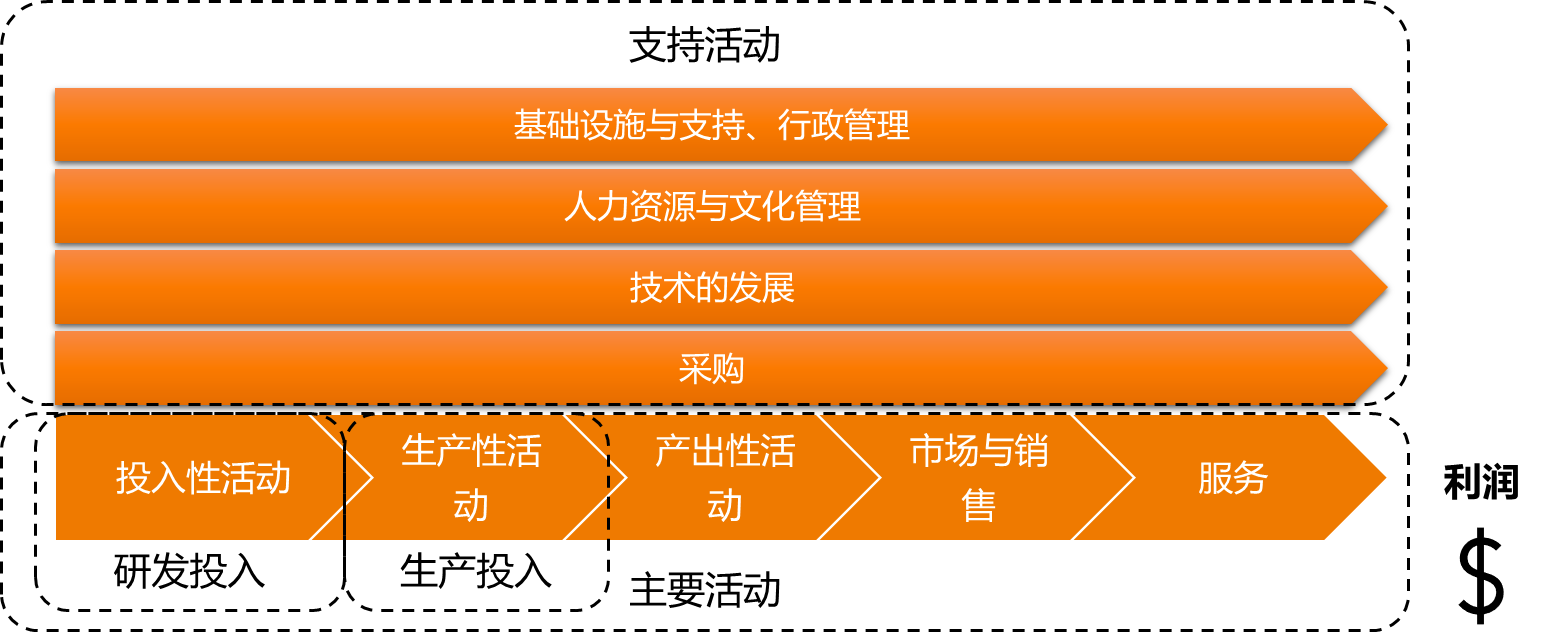
企业环境分析
价值链模型