定义了创新战略之后,当务之急是正确地建立一组执行该战略所需的能力
来源途径
- 聚焦与内部能力(internal capabilities)
- 依靠外部能力(external capabilities)
- 部分
- 全部
- 结合内部、外部能力

- Having defined the innovation strategy, it is imperative to establish the right set of capabilities to implement this strategy.
- Some key definitions:
- Competencies refer to the combination of skills, knowledge, and ability that lead to superior performance in an organization and that allow it to be competitive in the marketplace. There are two main types, commonly referred to as “soft” or “behavioral” competencies and “hard” or “technical” competencies.
- Behavioral competencies include cognitive and personality characteristics while technical competencies include learned expertise such as project management. Behavioral competencies involve characteristics such as analytical thinking, interpersonal ability and initiative. Abilities rely on natural or inherent behaviors as opposed to learned. Although abilities can be developed to some extent, the majority of what constitutes ability cannot be learned. Technical competencies involve the knowledge and skills elements which are learned through study and practice. Skills are the application of knowledge in work or leisure, in a trade or profession.
- Core competencies are what give an organization one or more competitive advantages in creating and delivering value to customers. Whereas a standard set of competencies allow an organization to compete in the marketplace, core competencies are those that give the organization a truly competitive edge.
- Resources are the operational inputs that allow an organization to perform its business activities. Resources are often divided into three categories:
- Physical assets,
- Human resources,
- Organizational capital.
- Capabilities are the activities and functions an organization performs to utilize its resources — physical assets, organizational capital and human resources (competencies) — in an integrated way. Capabilities are practiced and developed over time. As they become stronger, the organization enhances its expertise in a particular functional or operational area. This expertise allows the organization to differentiate itself from competitors.
- Capability-based strategies, sometimes referred to as the resource-based view of the firm, are determined by those internal resources and capabilities that provide the platform for the organization’s strategy and those resources and capabilities that are the primary source of profit. A key management function is to identify what resource gaps need to be filled in order to maintain a competitive edge where these capabilities are required.
A basic roadmap for developing capability-based strategies for product innovation:
- Ensure a clear definition of organizational mission, goals, business strategy, and innovation strategy. As discussed in previous sections of this chapter, these underpin all organization decision-making. Refer to Figure 1.22.
- Carry out a SWOT analysis, specifically focusing on the organization’s capability to take advantage of opportunities and to combat threats. What specific resources — physical assets, organizational capital, and human resources — are required?
- Carry out a “capability audit” to identify current organizational resources and their strengths.
- dentify the gaps between required capability and the current capability. Specifically:
- What new resources need to be added?
- Where do current resources need to be strengthened?
- What competencies are required to compete?
- What core competencies are required to provide a truly competitive edge?
- How should the organization develop the desired capability and acquire the required resources?
- Specifically:
- Develop internally, e.g., train or re-train existing staff
- New appointments to supplement or complement existing competencies
- Mergers, acquisitions, joint ventures, open innovation
- Specifically:
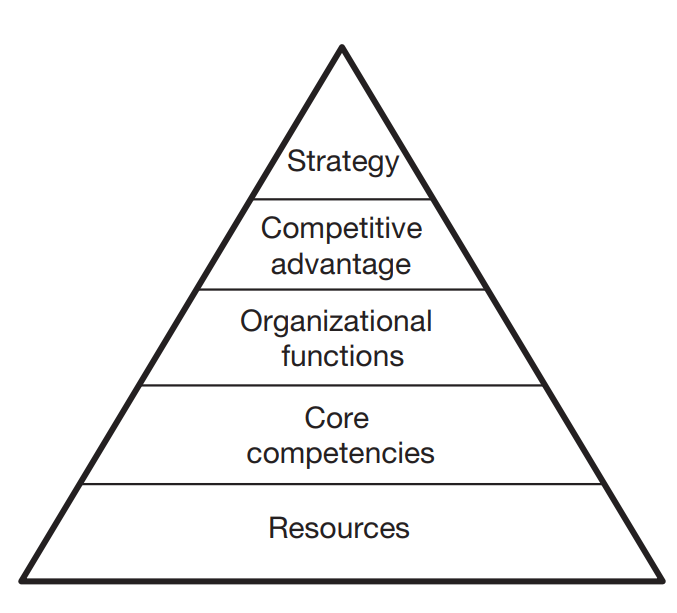
The hierarchy of capability-based strategy

