Linux三剑客
- grep:查找过滤
- sed:编辑
- awk:分析
这三个命令合称Linux的三剑客,从三剑客这个名字上大家可想而知它们有多厉害,如果把它们的全部内容都讲完的话,至少讲三天三夜,最可怕的是讲了三天三夜,最后你会发现里面很多的知识点是我们搞测试压根用不到的,那个时候你会怀疑人生的,所以在这里为了不让大家怀疑人生,我们就功利一点,只把我们常用的操作掌握了就可以了,学习技术有时候可以功利,但是做人可是不能功利哦 😃。
Linux三剑客之grep
基本使用: 搜索文件中的关键字
grep 关键字 文件路径
grep 常用于查找文件里符合条件的字符串。我们先演示一个基本的操作,这样可以实现一个简单的过滤查找操作。
[root@localhost ~]# cat hello.txthello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!abc[root@localhost ~]# grep abc hello.txtabc
练习
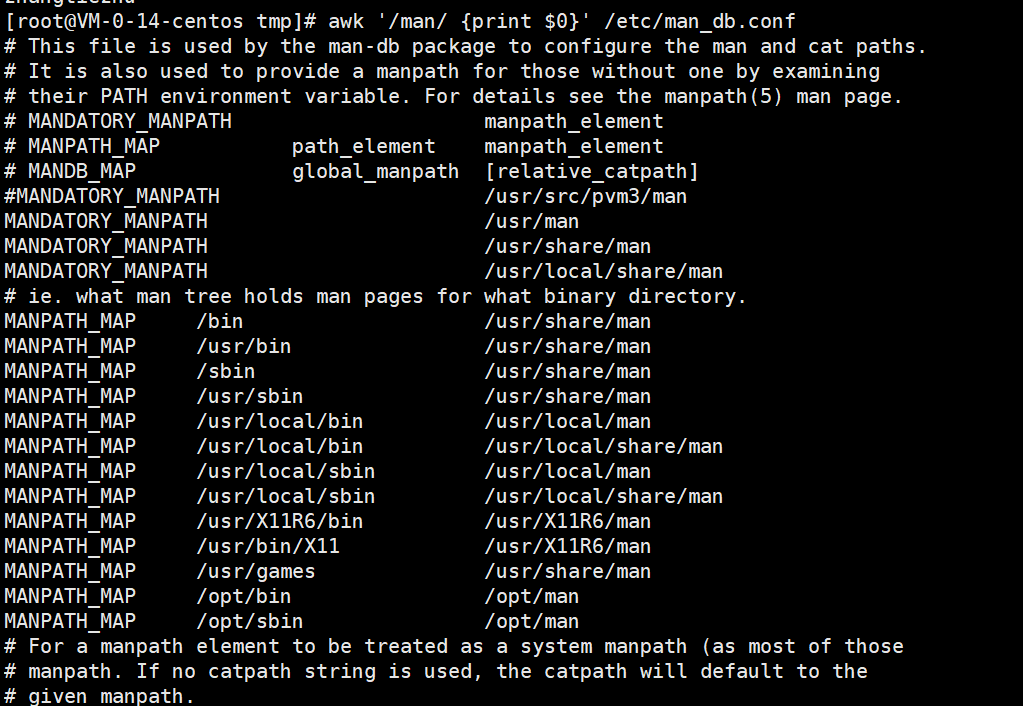
搜索 /etc/man_db.conf 文件中 包含 man的内容。
grep man /etc/man_db.conf

统计 /etc/man_db.conf 文件中 包含 man 总共有多少行。
grep man /etc/man_db.conf | wc

grep后面跟的这个字符串是可以支持正则表达式的,我们可以把这个调整一下查询hello.txt中以字母a开头的内容,这样写也是可以的
^a 以a开头
[root@localhost ~]# grep ^a hello.txtabc
查找 /etc/man_db.conf 文件中以MAN开头的内容。
grep ^MAN /etc/man_db.conf

有时候在查询的时候,我们也忘记需要查询的字符串是大写还是小写了,这个时候可以使用忽略大小写功能。
-i 忽略大小写
[root@localhost ~]# grep ABC hello.txt[root@localhost ~]# grep -i ABC hello.txtabc
统计 /etc/man_db.conf 文件 以man开头的内容 (不区分大小写)。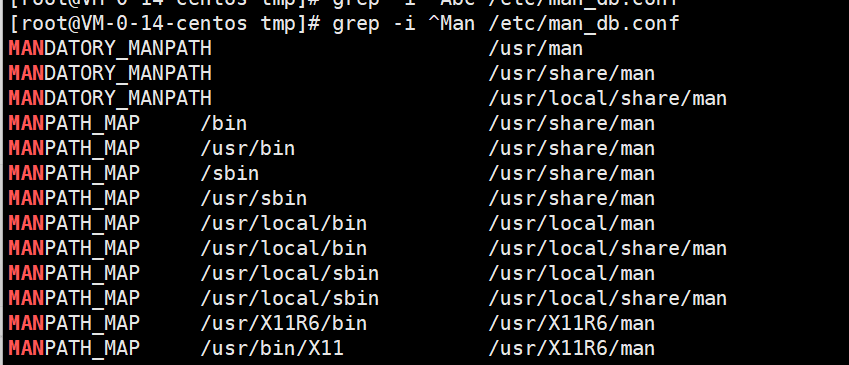
还有一些场景需要查询出来对应字符串所在的行号,方便我们快速在文件中定位字符串所在的位置,这个也很简单,通过-n参数就可以实现。
-n 显示行号
[root@localhost ~]# grep -i ABC -n hello.txt7:abc
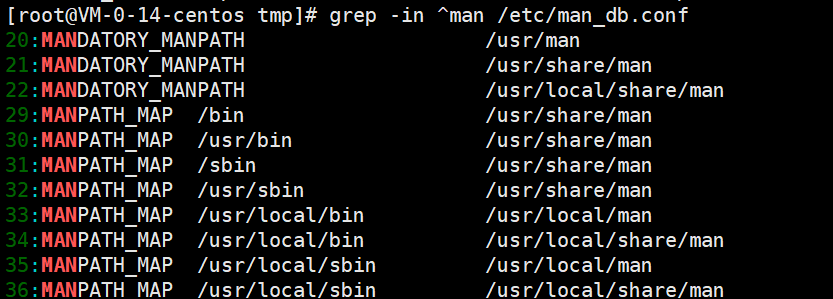
显示行号,并忽略大小写,从/etc/man_db.conf 文件中搜索 man
grep -in ^man /etc/man_db.conf
最后再教大家一招,假设我们想要查看一下服务器中运行的java进程,那我们可以使用前面讲的ps命令加上grep命令来实现ps -ef | grep java显示出这个信息其实说明没有找到java进程信息,下面返回的这一行表示是grep进程本身,这样容易给我们造成错觉,想把它去掉,怎么去掉呢?
[root@localhost ~]# ps -ef | grep javaroot 2497 2247 0 22:34 pts/1 00:00:00 grep --color=auto java
很简单,使用grep加上-v参数再做一次过滤即可,表示忽略包含指定字符串的数据。
-v 屏蔽指定的字符串
[root@localhost ~]# ps -ef | grep java | grep -v grep
显示行号,并忽略大小写,从/etc/man_db.conf 文件中搜索 man,如果搜索结果中包含 share,请将这一行屏蔽掉。
grep -in ^man /etc/man_db.conf | grep -v share

$ 指定字符结尾
查找 /etc/man_db.conf 文件,找到以 man结尾 的内容。
grep -n man$ /etc/man_db.conf

ok 这些就是针对grep最常见的一些用法,前期大家掌握这些就足够使用了!
更多关于 grep 的使用。
Linux三剑客之sed
接下来我们看一下Linux的第二个剑客,sed之前我们修改文件是使用vi命令,大家可以想象一个场景,如果让你同时去修改上千个文件里面的某一行内容,你再使用vi去操作,是不是有点手软,虽然这个上千个文件有点夸张,但是在实际工作中类似这样同时修改10几个文件的场景还是有的,大家不要想着,就10几个文件,我使用vi命令不到10分钟就搞完了,如果你这样想,那就完了,程序员一定要懒,这个懒是指能用程序去做的,千万不要动手。假设你花费5分钟写一个自动化程序,然后可以在秒级别内解决掉这十几个文件,这样是不是还剩下5分钟时间。
首先看一下,如何通过sed命令向文件中添加一行内容,我的需求是这样的,我想要在hello.txt文件的第二行内容下面添加一行内容
- a 在指定位置之后添加 2a 在第二行之后添加
- i 在指定位置之前添加 2i 在第二行之前添加
[root@localhost ~]# cat hello.txthello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!abc[root@localhost ~]# sed '2a\haha' hello.txthello world!hello world!hahahello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!abc
但是你回头再来查看这个文件的内容发现数据并没有被真正添加进去,注意了,sed 默认不会直接修改源文件数据,而是会将数据复制到缓冲区中,修改也仅限于缓冲区中的数据,最终把缓冲区内的数据输出到控制台。
那能不能直接修改源文件数据呢? 当然可以了,具体的操作方法我们一会再说,现在这种方式我们测试起来非常方便,不会影响源文件。
刚才的a参数表示向指定行的下面添加数据,但是如果我们想要在第一行添加数据怎么办呢?sed ‘1a\haha’ hello.txt 此操作会将数据添加到第一行下面(也就是第二行的位置)sed ‘0a\haha’ hello.txt 此操作会报错,行号是从1开始的。
[root@localhost ~]# sed '1a\haha' hello.txthello world!hahahello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!abc[root@localhost ~]# sed '0a\haha' hello.txtsed: -e expression #1, char 2: invalid usage of line address 0
那这个时候怎么办呢? 不要着急,还有一个参数 1i的意思表示在指定行的前面插入一行,它的使用方式和参数a一样我们来演示一下
[root@localhost ~]# sed '1i\haha' hello.txthahahello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!abc
所以说这个a其实表示是append的意思,在指定行后面追加内容i表示是insert的意思,是在指定行的前面插入内容好 ,这是a和i的区别。
不知道大家有没有思考一个问题,如果我们想要在一个文件的最后一行的前面添加一行内容,这个时候怎么办呢?我们可以先去看一下文件的行数,然后再过来操作,这样当然是没有问题的,就是比较麻烦,那能不能快速定位到最后一行呢?可以的,在这里我们可以通过一个特殊参数 $ 它在这里表示是最后一行的意思
$ 表示最后一行
[root@localhost ~]# sed '$i\haha' hello.txthello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!hahaabc
ok,这就是增加数据的操作
下面我们来看一下删除操作,有时候我们想要删除文件中多余的行,这个时候只需要使用参数d就可以搞定假设我们想删除文件中的第7行内容
d (delete) 删除
[root@localhost ~]# sed '7d' hello.txthello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!
当然了这里也可以使用$参数,$d删除最后一行,更加便捷
[root@localhost ~]# sed '$d' hello.txthello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!
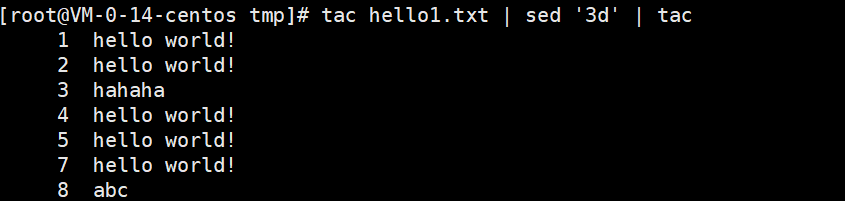
删除倒数第3行的内容。
tac hello1.txt | sed '3d' | tac
删除3,4,5行内容。
sed '3,5d' hello.txt

- 3,5d 表示从第3行到第5行。
修改文件内容
ok,这是删除数据的操作接下来我们来看一下替换操作,这个也是比较常见的,最常见的场景就是修改配置文件里面的服务器地址相关信息,以及账号密码什么的。
下面我们来操作修改一下文件内容中的l这个字符sed ‘s/l/a/1’ hello.txt
sed后面的参数格式为[address]s/pattern/replacement/flags这里的address 表示指定要操作的具体行,是一个可选项s 表示替换操作,pattern 指的是需要替换的内容,replacement 指的是要替换的新内容,flags有多种用法,我们挑两种说一下第一种就是flags可以表示为1~512之间的任意一个数字,表示指定要替换的字符串在这一行中出现第几次时才进行替换第二种就是flags可以直接表示为g,这样的意思就是对每一行数据中所有匹配到的内容全部进行替换如果flags位置的值为空,则只会在第一次匹配成功时做替换操作
- s/l/a/1 s 表示搜索 l ,将l替换为a, 最后的 1 表示每行的第一个
- s/l/a/2 s 表示搜索 l ,将l替换为a, 最后的 2 表示每行的第2个
[root@localhost ~]# sed 's/l/a/1' hello.txthealo world!healo world!healo world!healo world!healo world!healo world!abc[root@localhost ~]# sed 's/l/a/2' hello.txthelao world!helao world!helao world!helao world!helao world!helao world!abc[root@localhost ~]# sed 's/l/a/3' hello.txthello worad!hello worad!hello worad!hello worad!hello worad!hello worad!abc[root@localhost ~]# sed 's/l/a/g' hello.txtheaao worad!heaao worad!heaao worad!heaao worad!heaao worad!heaao worad!abc[root@localhost ~]# sed 's/l/a/' hello.txthealo world!healo world!healo world!healo world!healo world!healo world!abc
替换hello.txt 文件中每1行中的前2个 l 为 a。
我们现在的替换操作都是会匹配文件中的所有行,如果我们只想替换指定行中的内容怎么办呢?只需要增加address 参数即可。
- 2s/l/a/g 2s 只替换第2行的内容。
- 2,5s/l/a/g 2,5s 从第2行开始 到第5行结束。
[root@localhost ~]# sed '2s/l/a/g' hello.txthello world!heaao worad!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!abc[root@VM-0-14-centos tmp]# sed '2,5s/l/a/g' hello.txthello world!heaao worad!heaao worad!heaao worad!heaao worad!hello world!abc
这就是替换操作的常见应用场景
注意了,咱们前面所讲的sed命令的所有操作,在执行之后都不会修改源文件中的内容,这样只能作为测试,如果需要修改源文件的话,其实也很简单,只需要增加一个 -i 参数即可,我们来演示一下
-i 修改源文件
[root@localhost ~]# sed -i '2s/l/a/g' hello.txt[root@localhost ~]# cat hello.txthello world!heaao worad!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!abc
ok,针对sed命令我们就讲到这。
Linux三剑客之awk
最后我们来看一下第三个剑客 awk,awk是一个强大的文本分析工具,相对于grep的查找,sed的编辑,awk在其对数据分析并生成报告时,显得尤为强大,简单来说awk就是把文件逐行的读入,以空白字符为默认分隔符将每行内容切片,切开的部分再进行各种分析处理。
awk的基本格式:awk [option] programe file这里的option是一个可选项,一般在这里来指定文件中数据的字段分隔符programe 是具体的处理逻辑file表示我们要操作的文件
在具体使用awk之前我们还需要掌握awk的一个特性,就是awk在处理文本数据的时候,它会自动给每行中的每个字段分配一个变量变量从1开始,$1表示是文本中的第1个数据字段$2表示是文本中的第2个数据字段以此类推。还有一个特殊的 $0 它代表整个文本行的内容
那下面我们来操作一下hello.txt这个文件这个文件的字段中间默认是空格
[root@localhost ~]# cat hello.txthello world!heaao worad!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!abc[root@localhost ~]# awk '{print $1}' hello.txthelloheaaohellohellohellohelloabc[root@localhost ~]# awk '{print $2}' hello.txtworld!worad!world!world!world!world![root@localhost ~]# awk '{print $0}' hello.txthello world!heaao worad!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!abc
将 acccess.log 文件上传到 /tmp 目录下。
access.log
输出 /tmp/access.log 文件中的 所有ip地址。 ip地址位于每一行的第一列。
awk '{print $1}' /tmp/access.log

统计文件中的ip 地址,去重后统计有多少个ip地址。
awk '{print $1}' /tmp/access.log | sort | uniq | wc

linux中还有一个文件 /etc/passwd 里面存储的是用户信息但是这个文件中的字段之间是使用:分割的,这个时候想要操作某列字段的话就需要我们手工指定字段分隔符了。
咱们前面说了,可以在option里面指定字段分隔符,通过-F 参数awk -F: ‘{print $1}’ /etc/passwd
-F 指定分割符
[root@localhost ~]# awk -F: '{print $1}' /etc/passwdrootbindaemonadmlpsyncshutdownhaltoperatorgamesftpnobodysystemd-networkdbuspolkitdsshdpostfix
处理指定包含内容
我们在处理数据的时候还可以对数据进行一些过滤操作,只获取满足条件的数据在programe中可以使用正则表达式进行过滤,awk ‘/world/ {print $1}’ hello.txt 这种写法表示对每次读取到的那一行数据进行匹配
[root@localhost ~]# cat hello.txthello world!heaao worad!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!abc[root@localhost ~]# awk '/world/ {print $0}' hello.txthello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world![root@localhost ~]# awk '/abc/ {print $0}' hello.txtabc
使用awk 命令 查看 /etc/man_db.conf 文件中 包含 man的行中的内容。
awk '/man/ {print $0}' /etc/man_db.conf
指定行
如果我们只想对某一列数据进行匹配呢?awk ‘($1 ~ /world/) {print $1}’ hello.txt 在这里面可以通过$来指定具体是哪一列,需要把具体的对比逻辑放到小括号里面
- ($1 ~ /world/) 指定第一列,从第一列中搜索 world
- ($2 ~ /world/) 指定第二列,从第二列中搜索 world
[root@localhost ~]# awk '($1 ~ /world/) {print $0}' hello.txt[root@localhost ~]# awk '($2 ~ /world/) {print $0}' hello.txthello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world![root@localhost ~]# awk '($2 ~ /wor[a-z]d/) {print $0}' hello.txthello world!heaao worad!hello world!hello world!hello world!hello world!
注意:这里如果是不匹配的意思的话需要使用 !~
学习任务
针对apache中的access访问日志进行分析
access.log
查看所有的ip 地址,
awk '{print $1}' /tmp/access.log
所有的ip地址 去重 并排序
[root@VM-0-14-centos logs]# awk '{print $1}' access.log | sort | uniq106.53.123.231106.75.211.240106.75.251.234112.64.119.204112.65.61.166114.132.240.211114.85.158.77115.205.144.130116.235.32.47116.235.32.50117.136.120.250117.136.8.206119.90.42.91119.90.52.38122.234.89.243125.25.17.235128.14.209.162138.68.19.237140.207.23.108140.207.23.255143.198.136.88143.244.183.157147.182.226.61147.182.226.83157.55.39.73164.92.246.22165.232.161.227165.232.173.178165.232.175.155165.232.175.77175.107.1.64177.143.255.152180.163.220.4180.163.220.5180.163.220.66180.163.220.67
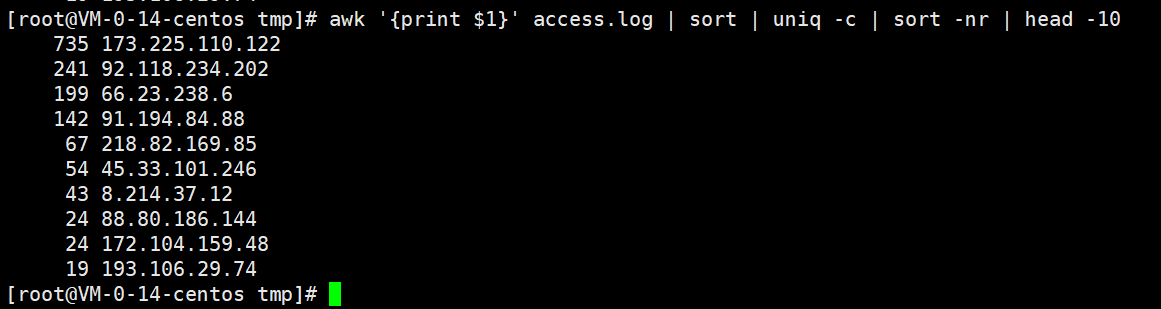
- 统计每个ip地址出现的次数。 比如 180.163.220.4 出现2次。 控制台输出
2 180.163.220.4
awk '{print $1}' access.log | sort | uniq -c | sort -nr | head -10
tail -f 实时追踪日志
启动禅道服务
/opt/zbox/zbox start
实时查看禅道的访问日志 ```bash tail -f /opt/zbox/logs/apache_access.log
---<a name="wN1Ln"></a># 作业1. 服务器上启动 禅道服务1. 使用netstat 命令查看已经启动的端口。需要找到 80端口 3306端口 说明禅道启动成功1. 使用 kill 命令结束 80端口对应的进程 kill pid1. 使用 killall 命令结束 3306 端口对应的进程 需要进程名1. 使用 ps 命令检查 zbox 相关的进程信息1. 查看cpu,内存信息1. 单独查看内存信息1. 查看磁盘相关信息1. 在/root 目录下创建 fanmao/85/01/ 文件夹, fanmao/85/02/文件夹1. 在 /root/fanmao/85/01/ 目录下创建 fanmao.1G 文件,文件的大小为1G1. 在/root/fanmao/85/02/ 目录下创建 fanmao.2G 文件, 文件的大小为2G1. 在 /root 目录下 找到 文件大小在 1G - 2G 之间(包含1G, 2G)的文件---1. 重启启动 禅道服务1. 浏览器上 登录禅道, 编写一条测试用例, 测试用例为 【外卖下订单流程】,要求至少包含用户操作,商家操作,骑手操作。(至少10个操作步骤)1. 查找文件路径 文件名中包含 access 并且文件名的后缀名为 .log```bashfind / -name '*access*.log'
locate access | grep '.log$'
统计 /opt/zbox/logs/apache_access.log 文件中的所有ip 并按照ip出现的次数 从大到小 输出出来。
awk '{print $1}' /opt/zbox/logs/apache_access.log | sort | uniq -c | sort -rn
将 /opt/zbox/logs/apache_access.log 文件中 ip地址是 以 116 开头(比如 116.227.31.240)的 这一行内容找到 并 重定向到 /tmp/ip.txt 文件中。
grep '^116' /opt/zbox/logs/apache_access.log > /tmp/ip.txt
awk '($1 ~ /^116/) {print $0}' /opt/zbox/logs/apache_access.log > /tmp/ip.txt
怎么查看昨天的日志 加分
date 命令可以查看日期
access.log
找出 系统中最大的 5个文件。