作业
登录Linux服务器1. 进入 /tmp 目录2. 创建 fanmao目录3. 进入fanmao目录4. 创建文件 helloworld.txt 并输入内容“你好,Mysql”5. 将fanmao目录压缩为 fanmao.tar.gz6. fanmao.tar.gz 下载到Windows本地7. 创建远程仓库 fanmao05288. 将 fanmao.tar.gz 文件上传到fanmao0528 远程仓库9. 浏览器打开远程仓库地址 截图发群:要求 截图中能够显示出 远程仓库的地址 并且有仓库中的问题
25 2021-05-29 10:09:39 cd /tmp/
26 2021-05-29 10:09:45 mkdir fanmao
27 2021-05-29 10:09:47 cd fanmao/
28 2021-05-29 10:09:56 vi helloworld.txt
29 2021-05-29 10:10:18 cd ..
30 2021-05-29 10:10:20 ls
31 2021-05-29 10:10:46 tar -zcvf fanmao.tar.gz fanmao/
32 2021-05-29 10:10:48 ls
33 2021-05-29 10:13:49 sz fanmao.tar.gz
git 操作
2 cd Desktop/
3 pwd
4 git clone https://gitee.com/imzack/hellofanmao.git
5 ls
6 mv fanmao.tar.gz hellofanmao/
7 ls
8 cd hellofanmao/
9 ls
10 git add .
11 git commit -m "add fanmao"
12 git push
13 history
查询条件
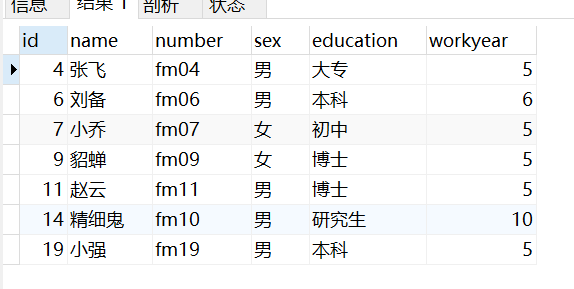
where between… and… 区间
-- 5-10 工作经验的学员信息
select * from taofei54
where workyear BETWEEN 5 AND 10;
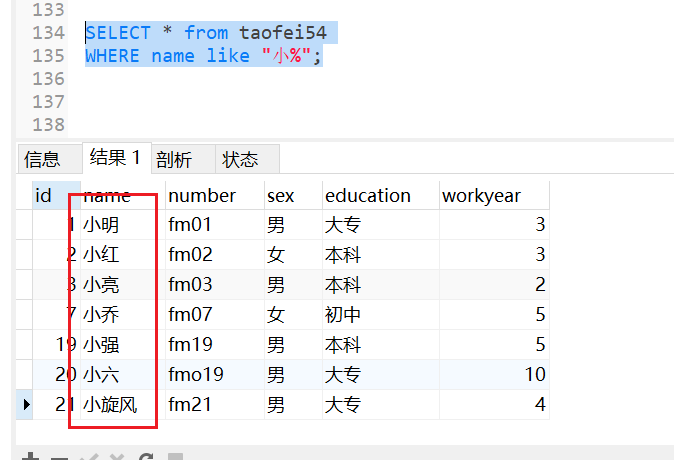
where like… 模糊查询
查询姓名以小 开头的学员;
SELECT * from taofei54
WHERE name like "小%";
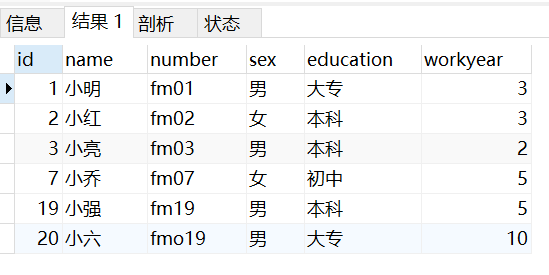
like 中支持两种通配符
- % 匹配多个字符串
- _ 匹配一个字符串
-- 匹配 1个字符串
SELECT * from taofei54
WHERE name like "小_";
where … is Null 空值
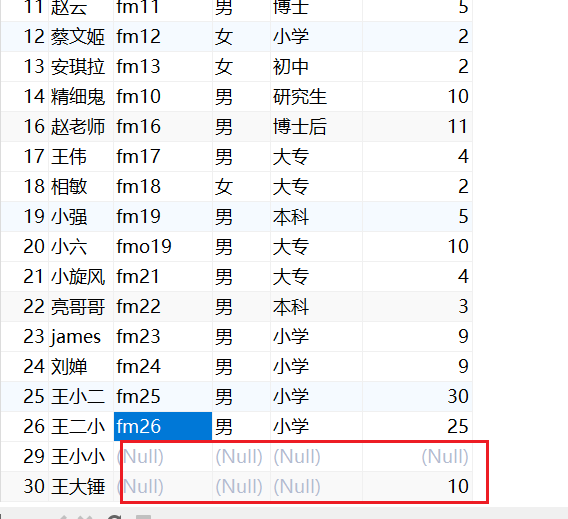
数据表中有 Null 空值。查询的时候使用语法
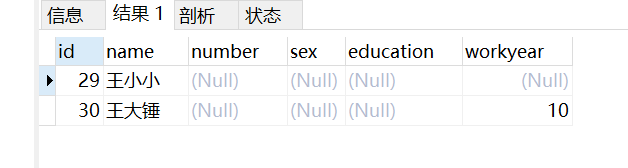
-- 查询学号为空的信息
SELECT * from taofei54
WHERE number is null;
not 表示相反
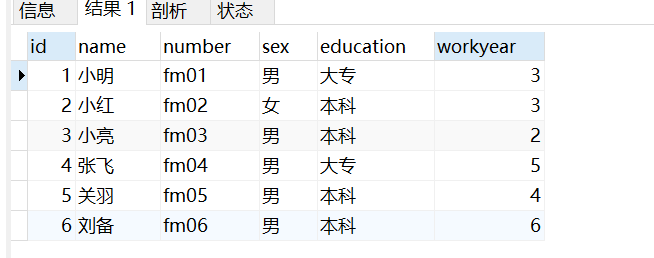
-- 查询学号不为空
select * from taofei54
where number is not null;
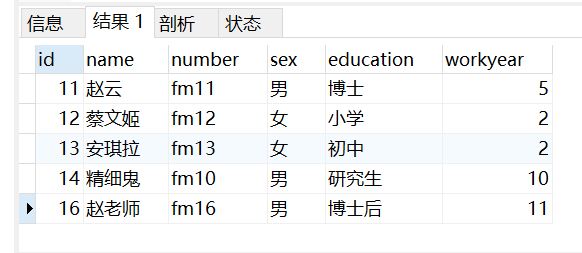
-- 查询 姓名中不含有 "小" 的学员信息
select * from taofei54
where name not like "%小%"
SELECT * from taofei54
WHERE education not in ("本科","大专")
排序 order by
默认排序是按照升序进行排序的。
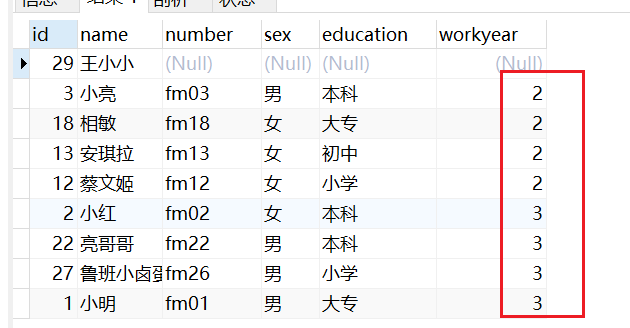
-- 默认按照升序进行排序 workyear 进行排序
select * from taofei54
ORDER BY workyear;
多个字段排序, order by 后面跟多个字段;
-- 根据两个字段排序,workyear 值一样的情况下,number 排序
SELECT * from taofei54
ORDER BY workyear,number;
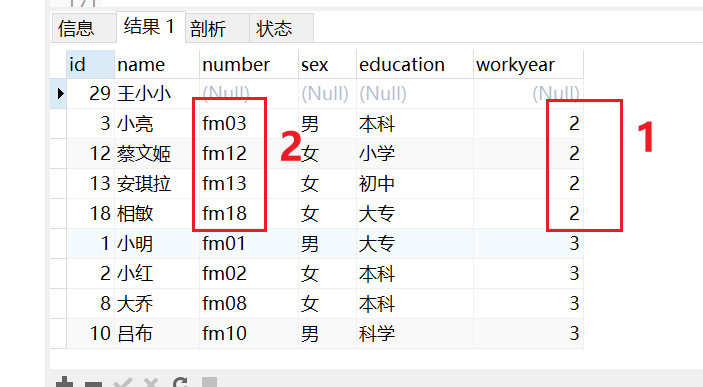
-- 查询 学历为本科,研究生的学员,以工作年限进行排序(升序)
SELECT * from taofei54
WHERE education in ("本科","研究生") # 1. 查询
ORDER BY workyear # 2. 排序
desc 降序
-- 查询性别为男,学历本科,工作年限5-10
-- 年限排序(降序排序)
SELECT * from taofei54
WHERE sex="男" and education="本科" AND workyear BETWEEN 5 and 10
ORDER BY workyear DESC;

limit 限制
-- 查询出成绩最高的学员信息
SELECT * from student
ORDER BY score DEsc
LIMIT 1;
SELECT * from student
ORDER BY score desc
limit 2, 3; # 2 表示从 第(2+1)条记录开始,3表示显示3条记录。


-- 查询最近的5个订单
SELECT * from orders
ORDER BY ordertime desc
limit 5
-- 查询最近的第5-10个订单
select * from orders
ORDER BY ordertime desc
limit 4,6
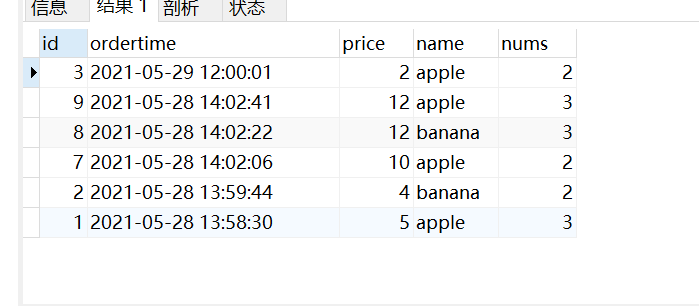
列中添加新字段
查询的时候再列中查询新的字段
-- 按照总价进行排序;
select *, price*nums from orders
order by price*nums desc;
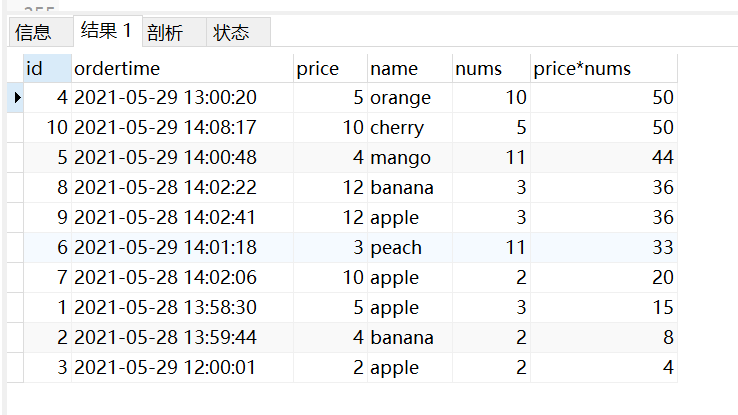
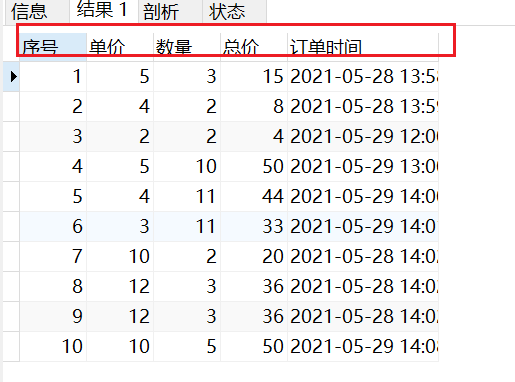
字段名设置别名
SELECT id as 序号, price as 单价, nums as 数量, price*nums as 总价, ordertime as 订单时间 from orders;
distinct字段去重
查询 订单表中 所有的name
-- 查询订单表中 name
select name from orders;

去除重复数据
--去除重复
select distinct(name) from orders;
max 最大值
-- 最大
select max(nums) from orders;
min 最小值

sum 求和
-- 今天总共卖出多少件 水果?
select * from orders;
select sum(nums) from orders
where ordertime like ("%05-29%")
avg 平均值
SELECT avg(score) from student
WHERE sname = "张三"

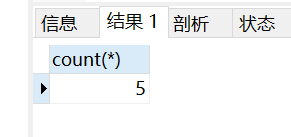
count 出现次数
-- 统计结果中有多少条记录
select count(*) from orders
where ordertime like "2021-05-29%"
子查询
- 查询最高工资的人员 ```sql — 工资最高的人是谁?
— 1.查询最高的工资 select max(salary) from employees;
— 2. 查询工资为 60000的人员信息 SELECT * from employees where salary = 60000;
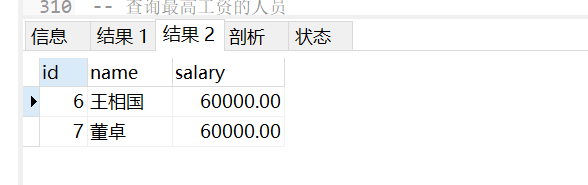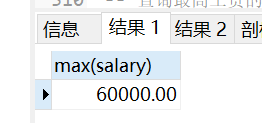<br />可以使用 子查询的方式将 两个sql语句整合在一起
```sql
-- 查询最高工资的人员
SELECT * from employees
where salary = (
SELECT max(salary) from employees
);
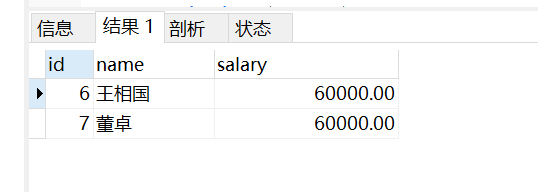
- 查询第二高的工资的人员信息
思路:
- 工资去重再排序,找到第二高工资是多少
select distinct(salary) from employees
order by salary desc
limit 1,1
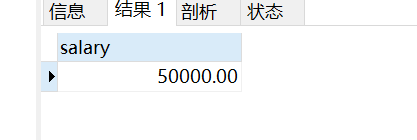
- 知道了第二高的工资是 50000,再查询工资为50000的人员信息
select * from employees where salary = 50000
两条sql语句合并在一起
select * from employees
where salary = (
select distinct(salary) from employees
order by salary desc
limit 1,1
);

子查询 就是将1条sql的结果作为另外一条sql的条件。
练习
-- 1 班级名称去重后显示
select distinct(classname) from fanmaostu;
-- 2. 统计总共有多少个班级
select count(DISTINCT(classname)) from fanmaostu;
-- 3. fanmao53 班级中学员平均年龄
select avg(age) from fanmaostu
WHERE classname = "fanmao53";
-- 4. 找出年纪最大的人
select * from fanmaostu
where age = (
select max(age) from fanmaostu
);
-- 5. 找出年纪第二大的人
select * from fanmaostu
WHERE age = (
SELECT distinct(age) from fanmaostu
order by age desc
limit 1,1
);




