open() 读写文件
open() 是python中内置的函数,类似print可以直接调用。open可以将数据写到文件中,也把文件中的内容转换为python的数据类型。
open()写入文件
可以将数据写到一个txt文件中。
# mode = w 写入权限with open(file="data.txt",mode="w",encoding="utf8") as f:# 写入内容f.write("helloworld")f.write("中国")
- with open() as f: 固定的用法, f就相当于是一个变量名,可以改为别的名字
- file=“data.txt” 文件名
- mode=“w” 写入权限
- mode=“a” 追加
- encoding=“utf8” 指定字符集编码
- f.write() 写入数据。
执行完成之后,可以看到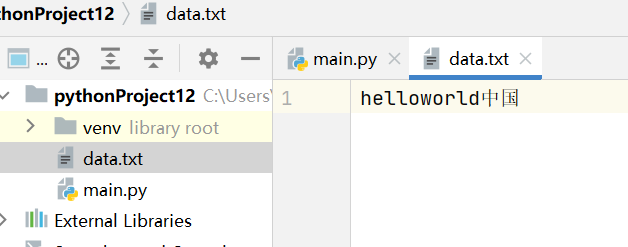
默认写入的数据 不会换行。
可以通过字符串\n 进行换行
with open(file="data.txt",mode='w',encoding="utf8") as f:for i in range(100):f.write(f"test{i}\n") # \n 换行符
循环写入100行数据。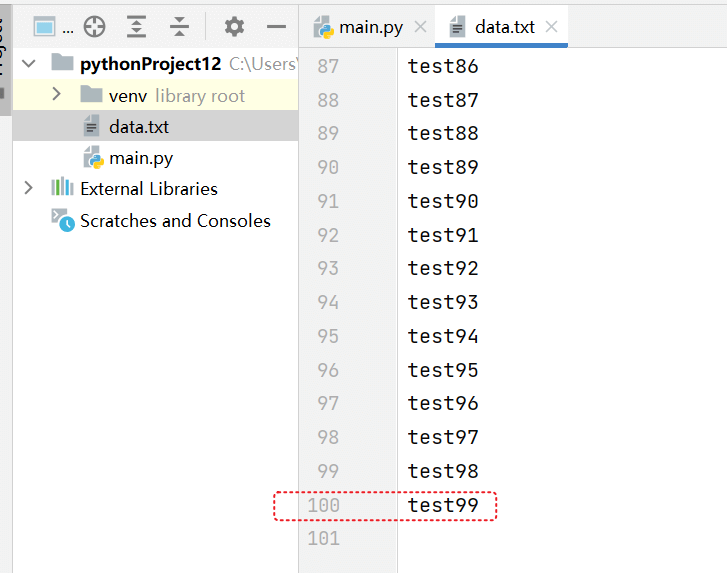
生成测试数据🎈
usernames = ["zhangsan","","***&&&"]passwords = ["12345","123456","12345678901234567",""]
将用户名和密码的的排列组合,生成 放到一个文件中。
usernames = ["zhangsan","","***&&&"]
passwords = ["12345","123456","12345678901234567",""]
with open(file="testdata.txt",mode='w',encoding="utf8") as f:
# 写入表头
f.write("用户名,密码\n")
for name in usernames:
for passwd in passwords:
# 将用户名和密码写入到文件中
f.write(f"{name},{passwd}\n")
执行完成之后,可以看到效果。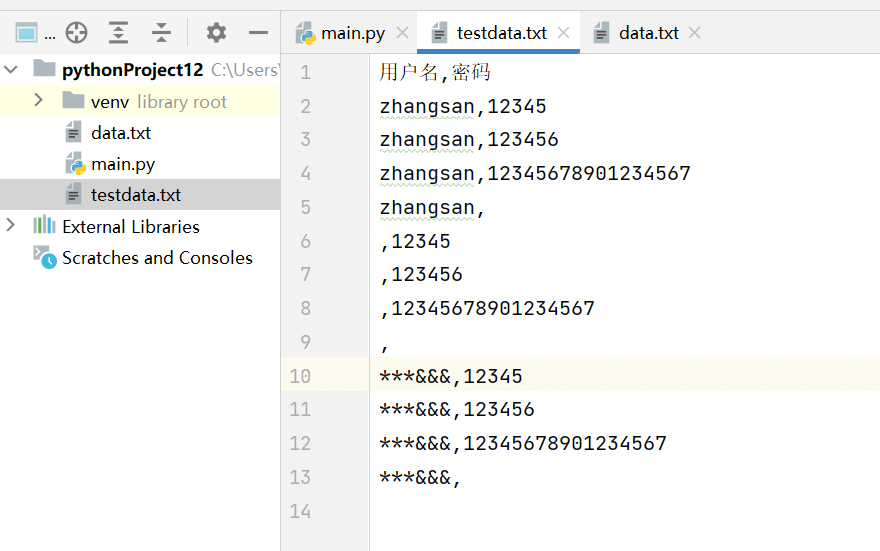
open() 读取文件内容
上面的操作可以往文件中写入数据。也可以从文件中读取数据。读取数据的方式只需要。
只需要将 mode=”r” 设置为读取方式。
with open(file="./data.txt",mode="r",encoding="utf8") as f:
# 将文件内容打印出来
print(f.read())
- mode=”r” 读取
- f.read() 读取到文件的内容。


