
这时ICCV 2019的一篇关于视频显著性,实际上就是无监督视频目标分割的一篇文章。
主要工作
- 文章主要解决的是如何在视频显著性目标检测中考虑运动(motion)信息。
- 现有的视频显著性目标检测方法要么没有显式模拟和收集运动线索(motion cues),要么忽略了光流图像内的空间上下文信息。
- 早期基于图的方法,虽然基于时空一致性,组合了外观信息和运动信息,但是受限于使用手工提取的低级特征,并且缺少训练数据挖掘(这一点或许是指手工提取特征表征能力有限),很难收集准确的运动模式特征,和复杂场景中目标的语义特征。
- 基于全卷积网络的方法,通过简单地将之前的帧图像或者之前的预测的显著性图,与当前帧拼接来形成CNN的输入。这些基于CNN的方法并没有利用运动估计,例如光流信息,并且容易被来自视频外观中分散(distractive)和杂乱(cluttered)的背景所干扰。
- 最近的一些方法使用循环神经网络来利用长距离的时空特征。这样的一些方法利用了flow warping来将之前帧的特征与当前帧的对齐,但却忽视了光流图像中的空间一致性(spatial coherence)和运动对比(motion contrast)信息。
- 本文中构建了两个子任务:静态显著性预测和运动显著性预测。针对子任务,各自构建了一个编解码模型。运动显著性网络使用中间特征和最终解码器预测来分别对静态显著性预测网络的外观特征进行引导和增强。从而充分利用运动信息与视频的外观信息。
- 现有的视频显著性目标检测方法要么没有显式模拟和收集运动线索(motion cues),要么忽略了光流图像内的空间上下文信息。
-
整体结构
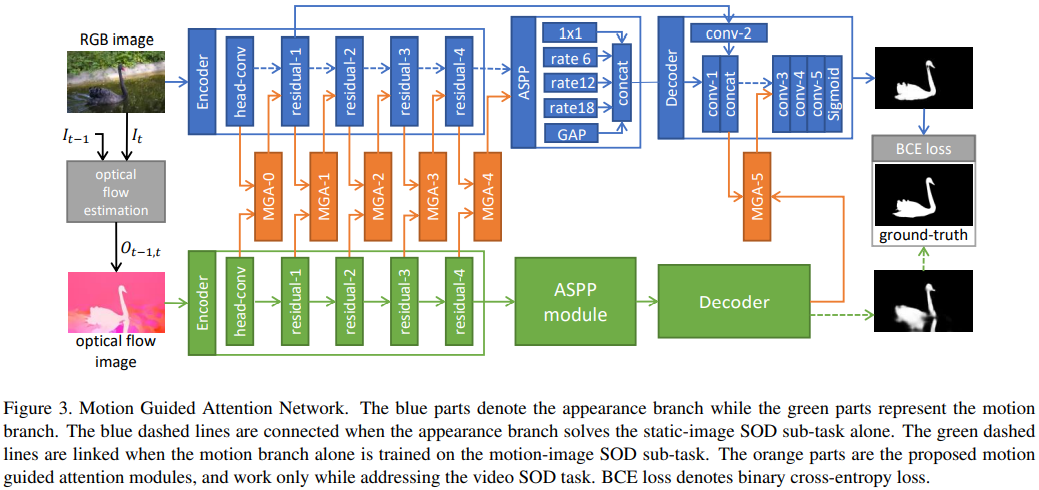
两路分支,分别输入单帧图像和对应的前向光流(foward flow)。
- 编码器:外观分支使用的是ResNet101,而运动分支使用的是ResNet34.
- 另外这里调整了扩张率,最终下采样为输入的1/8。
- 这里认为运动分支使用的是光流图像,其中并没有包含向RGB图像那样丰富的高层语义信息和细致的边界信息。所以使用一个轻量结构足矣。而外观分支使用的是单独的帧。
- 使用了ASPP来进一步捕获长距离对比关系。文章提到的中间的3x3卷积的扩张率为12,24,36。
- 解码器:外观分支和图中一致,但是运动分支的解码器仅包括三层类似于图中conv-{3-5}的结构,之后就直接预测运动显著性图。
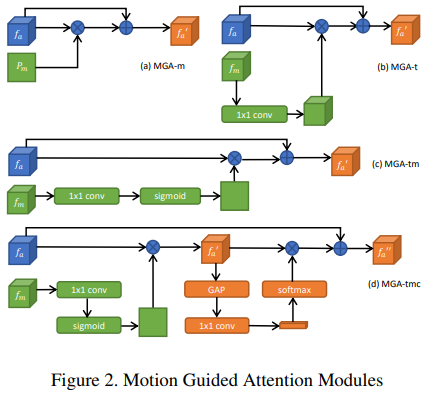
- 连接两个子网络:文章设计了几种MGA模块,图中比较直观。实际上就是“空间/通道注意力“与”残差连接”的组合。要注意,这里的‘-m’结构,对于运动分支输入的是预测的map,而‘-t’系列,则输入的是特征tensor。至于‘-c’则是进一步引入了通道注意力。
- 这里使用残差结构主要是为了放指外观特征完全被运动特征给抑制掉(涉及到了乘法),所以将空间注意力的形式设定成了对于特征中关键区域的增强。
- 包含‘-m‘的模块对应输出为map的分支的1x1卷积输出通道数为1。
- 这里的GAP表述全剧平均池化。
- 在’MGA-tmc‘中的f’的处理中,实际使用的操作不完全与图中一致。实际这里的softmax表示的是。这里C是一个标量,本身是等于f’被池化以及1x1卷积处理后的特征的通道数。只是这里被乘在了Softmax上,这样可以让得到的通道权重矢量由和为1变为均值为1。(不太理解这样的好处)
- 注意:MGA-5使用MGA-m模块,而MGA-{0-4}可以从MGA-{t,tm,tmc}中选择。消融实验有效果对比。
- 编码器:外观分支使用的是ResNet101,而运动分支使用的是ResNet34.
多任务训练策略:注意图中展示的虚线部分,这里提到了这篇文章另一个有意思的地方,就是分阶段训练的设定。先分别训练两个单独的子网络,这时图中的虚线部分是有连接的。之后在整体进行微调,此时虚线断开。
- First, we initialize the appearance sub-network using a ResNet-101 pretrained on ImageNet, and then fine-tune the appearance branch on a static-image salient object detection dataset.
- Second, we implement the ‘optical flow estimation’ [Flownet 2.0: Evolution of optical flow estimation with deep networks], and employ it to render optical flow images according to [A naturalistic open source movie for optical flow evaluation] on our training set of video salient object detection. The optical flow images are computed as a forward flow from the previous frame to the current frame.
- Third, the motion sub-network is initialized using an ImageNet-pretrained ResNet-34 model, and then is trained on these synthesized optical flow images and their corresponding saliency maps in the video salient object detection dataset.
- Lastly, the proposed MGA modules integrate the two branches to form our proposed network, which is tuned with a mixture of static-image and video salient object detection datasets.
- Since training samples of a static image or the first frame
in an video have no corresponding motion images, we assume that their previous frame are as the same as themselves. That is to say, objects in these samples are not in
motion and no salient motions exist. For such cases, we
simply fill zeros in the motion inputs of the MGA modules.
实验细节
In this paper, we choose the train set of DUTS, DAVIS and FBMS as our training set. We evaluate video salient object detection methods on DAVIS, FBMS and ViSal benchmark.
- DUTS is a commonly used static-image salient object detection dataset.
- ViSal dataset can be used to rate the generalization of video salient object detection models, since all video SOD algorithms are not trained with any subsets of ViSal.
- SGD algorithm is used to train the proposed network with an initial learning rate of 10−8 , a weight decay of 0.0005 and an momentum of 0.9.
- The proposed method costs about 0.07 seconds for a single frame, regardless of flow estimation.
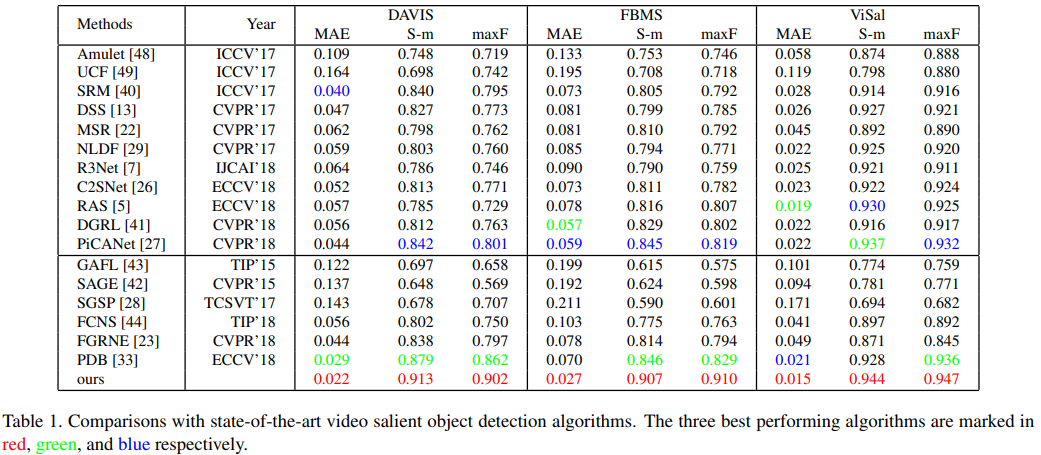
Our proposed method is implemented by adopting MGA-tmc module at the positions of MGA-{0-4}, and MGA-m module at the position of MGA-5. The results of our method in Table 1 are obtained without any post-processing.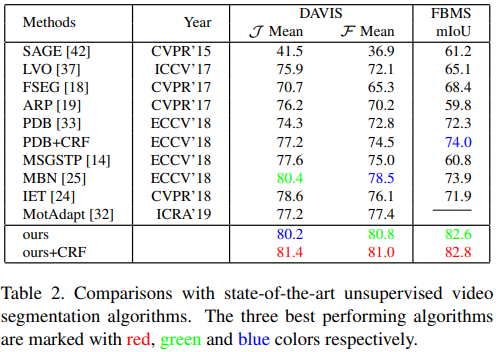
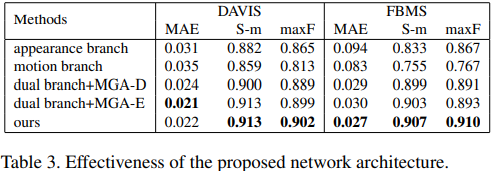
这里的MGA-D表示仅保留解码器里的MGA。而MGA-E表示仅保留编码器里的MGA。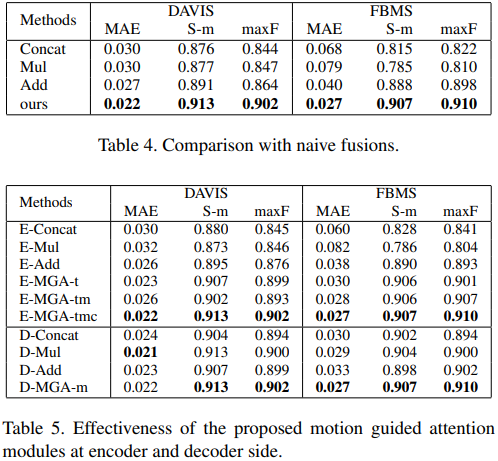
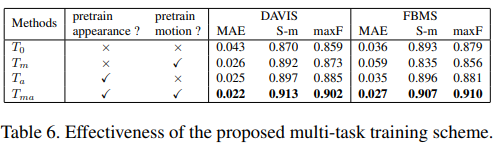
这里针对多任务训练策略进行了消融比较。
- T0表示不对两个子网络进行单独的训练。直接初始化后便整体进行训练。
- Ta和Tm都分别会预先对外观网络和运动网络进行训练。
Tma就是提出的多任务训练策略。即在端到端整体训练之前,先针对各自的子任务进行微调。
一些摘录
The most important difference between static images and videos is that objects in videos have motion, which is also a key factor that causes visual attention. That is, the motion of certain objects may make the object more prominent than others.
How to effectively take object motion into consideration during video salient object detection is a critical issue for the following reasons.
- First, object saliency in a video is not only determined by object appearance (including color, texture and semantics), but also affected by object motion between consecutive frames.
- Itti et al. [A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis] suggest that differences between consecutive frames resulting from object motion are more attractive to human attention.
- Second, object motion provides an essential hint on spatial coherence. Neighboring image patches with similar displacements very possibly belong to the same foreground object, or the background region.
- Third, exploiting motion cues makes the segmentation of salient objects in a video easier, and hence, produces saliency maps of higher quality.
- For example, in RGB frames, the background may contain diverse contents with different colors and texture, and the foreground object may be composed of parts with sharp edges and different appearances.
- It is challenging to locate and segment complete salient objects in such video frames without motion
cues.
参考链接
- First, object saliency in a video is not only determined by object appearance (including color, texture and semantics), but also affected by object motion between consecutive frames.
- 代码:https://github.com/lhaof/Motion-Guided-Attention

