前后端分离时代,后台模板引擎已经开始退出历史舞台了,不过,貌似目前后台模板引擎主要用来生成后台代码,做代码生成器。
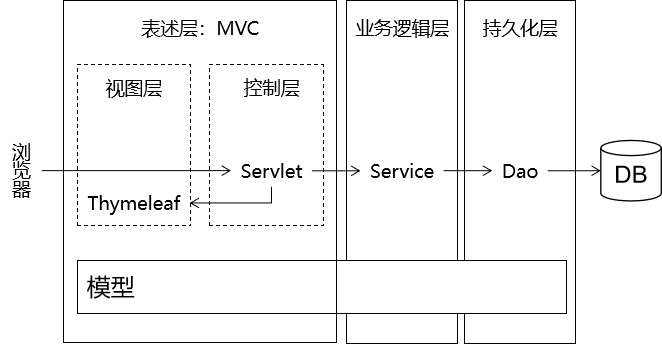
第一章:MVC
1.1 概念
- M(Model):模型、V(View):视图、C(Controller):控制器。
- MVC是在表现层开发中运用的一种设计理念,主张将封装
数据的模型、显示用户界面的视图以及协调调度的控制器分开。 - MVC的好处:
- ① 进一步是实现各个组件之间的解耦。
- ② 让各个组件可以单独维护。
- ③ 将视图分离出来以后,后端工程师和前端工程师对接更为方便。
1.2 MVC和三层架构之间的关系
第二章:Thymeleaf简介
2.1 Thymeleaf的概念
- Thymeleaf是一款用于渲染XML/XHTML/HTML5内容的模板引擎,类似于JSP、Velocity、FreeMarker等,它可以轻易的和SpringMVC等web框架进行集成并作为web应用的模板引擎,它的主要作用是在静态页面上渲染动态数据。
2.2 Thymeleaf的优势
- Thymeleaf是SpringBoot官方推荐的视图模板技术,和SpringBoot完美整合。
Thymeleaf不经过服务器运算依然可以查看原始值,对前端工程师更为友好。
示例:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title></head><body><p th:text="${username}">你好啊</p></body></html>
2.3 物理视图和逻辑视图
2.3.1 物理视图
- 在Servlet中,将请求转发到一个HTMNL页面的时候,使用
完整的转发路径就是物理视图,如:/pages/login.html。
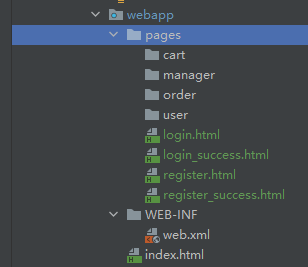
- 如果我们将所有的HTML页面都放在某个统一的目录下,那么转发地址就会呈现明显的规律:
- /pages/cart/xxx.html。
- /pages/register.html。
- /pages/register_success.html。
- ……
- 路径的开头都是
/pages/。 - 路径的结尾都是
.html。 - 那么,路径的开头部分我们称为
视图前缀,路径的结尾部分我们称为视图后缀。
2.3.2 逻辑视图
物理视图 = 视图前缀 + 逻辑视图 + 视图后缀。
示例: | 物理视图 | 视图前缀 | 逻辑视图 | 视图后缀 | | —- | —- | —- | —- | | /pages/register.html | /pages/ | register | .html | | /pages/login.html | /pages/ | login | .html |
第三章:Thymeleaf的入门
- 导入jar包:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf</artifactId>
<version>3.0.12.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
- 在web.xml中配置上下文参数:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<!-- 在上下文参数中配置视图前缀和视图后缀 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>view-prefix</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/view/</param-value>
</context-param>
<context-param>
<param-name>view-suffix</param-name>
<param-value>.html</param-value>
</context-param>
</web-app>
解释:为什么要放在WEB-INF目录下?
- ① WEB-INF目录不允许浏览器直接访问,所以我们的视图模板文件放在这个目录下,是一种保护。以免外界可以随意访问视图模板文件。
- ② 访问WEB-INF目录下的页面,都必须通过Servlet转发过来,简单说就是:不经过Servlet访问不了,就方便我们在Servlet中检查当前用户是否有权限访问。
- ③ 放在WEB-INF目录下之后,重定向进不去怎么办?重定向到Servlet,再通过Servlet转发到WEB-INF下。
- 创建Servlet的基类:ViewBaseServlet,以及这个会被框架代替
package com.example.javaweb2;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.thymeleaf.TemplateEngine;
import org.thymeleaf.context.WebContext;
import org.thymeleaf.templatemode.TemplateMode;
import org.thymeleaf.templateresolver.ServletContextTemplateResolver;
public class ViewBaseServlet extends HttpServlet {
private TemplateEngine templateEngine;
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
// 获取ServletContext对象
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
// 创建Thymeleaf解析器对象
ServletContextTemplateResolver templateResolver = new ServletContextTemplateResolver(servletContext);
// 给解析器设置参数
// ①HTML是默认模式,明确设置是为了代码更容易理解
templateResolver.setTemplateMode(TemplateMode.HTML);
// ②设置前缀
templateResolver.setPrefix(servletContext.getInitParameter("view-prefix"));
// ③设置后缀
templateResolver.setSuffix(servletContext.getInitParameter("view-suffix"));
// ④设置缓存过期时间(毫秒)
templateResolver.setCacheTTLMs(60000L);
// ⑤设置是否缓存
templateResolver.setCacheable(true);
// ⑥设置服务器端编码方式
templateResolver.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
// 创建模板引擎
this.templateEngine = new TemplateEngine();
// 给模板引擎设置模板解析器
this.templateEngine.setTemplateResolver(templateResolver);
}
protected void processTemplate(String templateName, HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws IOException {
// 1.设置响应体内容类型和字符集
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
// 2.创建WebContext对象
WebContext webContext = new WebContext(req, resp, this.getServletContext());
// 3.处理模板数据
this.templateEngine.process(templateName, webContext, resp.getWriter());
}
}
- 在/WEB-INF/目录下新建demo.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 th:text="${test}">这里要显示一个动态的数据</h1>
</body>
</html>
- 创建Servlet:
package com.example.javaweb2;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-10-22 10:31
*/
@WebServlet(value = "/test")
public class TestThymeleafServlet extends ViewBaseServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(request, response);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setAttribute("test", "123456");
this.processTemplate("demo", request, response);
}
}
第四章:Thymeleaf的基本语法
4.1 th名称空间
th名称空间:让我们能够使用thymeleaf的语法。
示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 th:text="${test}">这里要显示一个动态的数据</h1>
</body>
</html>
4.2 表达式语法
4.2.1 th:text
- th:text:用于修改标签的文本值。
th:text的作用:
- ① 不经过服务器解析,直接用浏览器打开HTML文件,看到的是
标签体原始值。 - ② 经过服务器解析,Thymeleaf引擎会根据
th:text属性指定的标签体新值取替换标签体原始值。
- ① 不经过服务器解析,直接用浏览器打开HTML文件,看到的是
示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 th:text="${test}">这里要显示一个动态的数据</h1>
</body>
</html>
4.2.2 th:xxx
th:xxx:用于修改标签的属性值。xxx表示任意属性,如:value、name等。
示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- th:xxx将会改变HTML标签原有的属性值 -->
<input type="text" th:value="文本框新值" value="文本框旧值"><br>
</body>
</html>
4.2.3 @{}
- @{}:在字符串前附加上下文路径。
- 语法:
<a href="" th:href="@{/index.html(a=${xxx},b='abc')}">首页</a>
@{}的作用:实际开发过程中,项目在不同环境部署时,Web应用的名字有可能发生变化,所以上下文路径不能写死;而通过@{}动态获取上下文路径后,不管怎么变都不怕!
示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="" th:href="@{/index.html}">首页</a>
</body>
</html>
4.3 域对象在Thymeleaf中的应用
- 域对象是在服务器中有一定作用范围的对象,在这个范围内的所有动态资源都能够共享对象中保存的数据。
- 域对象的分类:
- 请求域:只在一次请求范围中有效。
- 会话域:在一次会话范围内有效。
- 全局域(应用域):在整个项目范围内有效。
- Thymeleaf读取请求域中的信息:
<h1 th:text="${test}">这里要显示一个动态的数据</h1>
- Thymeleaf读取会话域中的信息:
<h1 th:text="${session.test}">这里要显示一个动态的数据</h1>
- Thymeleaf读取应用域中的信息:
<h1 th:text="${application.test}">这里要显示一个动态的数据</h1>
- 示例:
- index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" >
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="/app/test">test</a>
</body>
</html>
- TestThymeleafServlet.java
package com.example.javaweb2;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-10-22 10:31
*/
@WebServlet(value = "/test")
public class TestThymeleafServlet extends ViewBaseServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(request, response);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 向请求域中设置数据
request.setAttribute("test", "request123456");
// 向会话域中设置数据
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
session.setAttribute("test", "session123456");
// 向应用域中设置数据
ServletContext servletContext = request.getServletContext();
servletContext.setAttribute("test", "application123456");
this.processTemplate("demo", request, response);
}
}
- demo.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p th:text="${test}">请求域中的值</p>
<p th:text="${session.test}">会话域中的值</p>
<p th:text="${application.test}">应用域中的值</p>
</body>
</html>
4.4 获取请求参数
- 语法:
${param.参数名}
- 示例:
- index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" >
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="/app/test?name=zhangsan&age=25">test</a>
</body>
</html>
- TestThymeleafServlet.java
package com.example.javaweb2;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-10-22 10:31
*/
@WebServlet(value = "/test")
public class TestThymeleafServlet extends ViewBaseServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(request, response);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
this.processTemplate("demo", request, response);
}
}
- demo.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
姓名:<p th:text="${param.name}">李四</p>
年龄:<p th:text="${param.age}">18</p>
</body>
</html>
4.5 内置对象
- 内置对象:就是在Thymeleaf的表达式中可以直接使用的对象。
- 基本内置对象(不常用):
- 公共内置对象:

4.6 OGNL
- OGNL(Object-Graph Navigation Language):对象图导航语言,从根对象出发,通过特定的语法,逐层访问对象的各种属性。
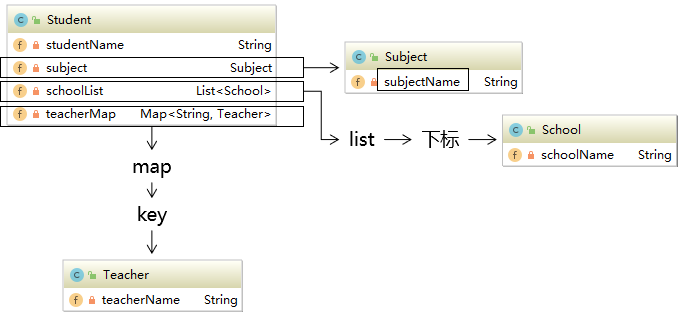
语法:
- ① 起点,在Thymeleaf环境下,
${}中的表达式可以从下列元素开始:- 访问属性域的起点:
- 请求域属性名。
- session。
- application。
- param。
- 内置对象:
- request。
- session。
- lists。
- strings。
- 访问属性域的起点:
- ② 属性访问语法:
- 访问对象属性(使用getXxx()、setXxx()方法定义的属性):对象.属性名。
- 访问List集合或数组:集合或数组[下标]。
- 访问Map集合:Map集合.key 或 Map集合[‘key’]。
- ① 起点,在Thymeleaf环境下,
示例:
- index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" >
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="/app/test">test</a>
</body>
</html>
- School.java
package com.example.domain;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-10-22 14:55
*/
public class School {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
- Subject.java
package com.example.domain;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-10-22 14:55
*/
public class Subject {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
- Teacher.java
package com.example.domain;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-10-22 14:54
*/
public class Teacher {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
- Student.java
package com.example.domain;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-10-22 14:55
*/
public class Student {
private String name;
private List<Subject> subjectList;
private School school;
private Map<String,Teacher> teacherMap;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public List<Subject> getSubjectList() {
return subjectList;
}
public void setSubjectList(List<Subject> subjectList) {
this.subjectList = subjectList;
}
public School getSchool() {
return school;
}
public void setSchool(School school) {
this.school = school;
}
public Map<String, Teacher> getTeacherMap() {
return teacherMap;
}
public void setTeacherMap(Map<String, Teacher> teacherMap) {
this.teacherMap = teacherMap;
}
}
- TestThymeleafServlet.java
package com.example.javaweb2;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import com.example.domain.School;
import com.example.domain.Student;
import com.example.domain.Subject;
import com.example.domain.Teacher;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-10-22 10:31
*/
@WebServlet(value = "/test")
public class TestThymeleafServlet extends ViewBaseServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(request, response);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
teacher.setName("小美老师");
School school = new School();
school.setName("好好学习小学");
Subject subject = new Subject();
subject.setName("语文");
Subject subject2 = new Subject();
subject.setName("语文");
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("张三童鞋");
student.setSubjectList(List.of(subject,subject2));
student.setSchool(school);
student.setTeacherMap(Map.of("xiaomei",teacher));
request.setAttribute("student", student);
this.processTemplate("demo", request, response);
}
}
- demo.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p th:text="${student.name}"></p>
<p th:text="${student.subjectList[0].name}"></p>
<p th:text="${student.school.name}"></p>
<p th:text="${student.teacherMap['xiaomei'].name}"></p>
</body>
</html>
4.7 分支和循环
4.7.1 th:if和th:unless
th:if和th:unless相当于Java中的if-else结构。
示例:
- index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" >
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="/app/test">test</a>
</body>
</html>
- Employee.java
package com.example.domain;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-10-22 15:34
*/
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private double salary;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(Integer id, String name, double salary) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}
- TestThymeleafServlet.java
package com.example.javaweb2;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import com.example.domain.Employee;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-10-22 10:31
*/
@WebServlet(value = "/test")
public class TestThymeleafServlet extends ViewBaseServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(request, response);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
List<Employee> employeeList = new ArrayList<>();
employeeList.add(new Employee(1,"张三",5000));
employeeList.add(new Employee(2,"李四",4000));
employeeList.add(new Employee(3,"王五",6000));
request.setAttribute("employeeList", employeeList);
this.processTemplate("demo", request, response);
}
}
- demo.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<table>
<tr>
<th>员工编号</th>
<th>员工姓名</th>
<th>员工工资</th>
</tr>
<tr th:if="${#lists.isEmpty(employeeList)}">
<td colspan="3">抱歉!没有查询到你搜索的数据!</td>
</tr>
<tr th:if="${not #lists.isEmpty(employeeList)}">
<td colspan="3">有数据!</td>
</tr>
<tr th:unless="${#lists.isEmpty(employeeList)}">
<td colspan="3">有数据!</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
4.7.2 th:switch和th:case
th:switch和th:case相当于Java中的switch和case。
示例:
- index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" >
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="/app/test">test</a>
</body>
</html>
- TestThymeleafServlet.java
package com.example.javaweb2;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-10-22 10:31
*/
@WebServlet(value = "/test")
public class TestThymeleafServlet extends ViewBaseServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(request, response);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setAttribute("num", 1);
this.processTemplate("demo", request, response);
}
}
- demo.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:switch="${num}">
<p th:case="1">1</p>
<p th:case="2">2</p>
<p th:case="3">3</p>
<p th:case="4">4</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
4.7.3 th:each
th:each相当于Java中的forEach语法。
示例:
- index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" >
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="/app/test">test</a>
</body>
</html>
- Employee.java
package com.example.domain;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-10-22 15:34
*/
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private double salary;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(Integer id, String name, double salary) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}
- TestThymeleafServlet.java
package com.example.javaweb2;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import com.example.domain.Employee;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-10-22 10:31
*/
@WebServlet(value = "/test")
public class TestThymeleafServlet extends ViewBaseServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(request, response);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
List<Employee> employeeList = new ArrayList<>();
employeeList.add(new Employee(1,"张三",5000));
employeeList.add(new Employee(2,"李四",4000));
employeeList.add(new Employee(3,"王五",6000));
request.setAttribute("employeeList", employeeList);
this.processTemplate("demo", request, response);
}
}
- demo.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<table>
<tr>
<th>员工编号</th>
<th>员工姓名</th>
<th>员工工资</th>
</tr>
<!--
使用th:each遍历
用法:
1. th:each写在什么标签上? 每次遍历出来一条数据就要添加一个什么标签,那么th:each就写在这个标签上
2. th:each的语法 th:each="遍历出来的数据,数据的状态 : 要遍历的数据"
3. status表示遍历的状态,它包含如下属性:
3.1 index 遍历出来的每一个元素的下标
3.2 count 遍历出来的每一个元素的计数
3.3 size 遍历的集合的长度
3.4 current 遍历出来的当前元素
3.5 even/odd 表示遍历出来的元素是否是奇数或者是否是偶数
3.6 first 表示遍历出来的元素是否是第一个
3.7 last 表示遍历出来的元素是否是最后一个
-->
<tr th:if="${not #lists.isEmpty(employeeList)}" th:each="emp,status : ${employeeList}">
<td th:text="${status.count}">这里显示编号</td>
<td th:text="${emp.id}">主键</td>
<td th:text="${emp.name}">姓名</td>
<td th:text="${emp.salary}">薪水</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
4.8 Thymeleaf包含其他模板文件
- 应用场景:抽取各个页面的公共部分
步骤:
① 创建页面的公共代码片段,使用th:fragment来给这个片段命名
<div th:fragment="header"> <p>被抽取出来的头部内容</p> </div>② 在需要的页面进行包含 | 语法 | 效果 | 特点 | | —- | —- | —- | | th:insert | 把目标的代码片段整个插入到当前标签内部 | 它会保留页面自身的标签 | | th:replace | 用目标的代码替换当前标签 | 它不会保留页面自身的标签 | | th:include | 把目标的代码片段去除最外层标签,然后再插入到当前标签内部 | 它会去掉片段外层标记,同时保留页面自身标记 |
示例:
<!-- 代码片段所在页面的逻辑视图 :: 代码片段的名称 -->
<div id="badBoy" th:insert="segment :: header">
div标签的原始内容
</div>
<div id="worseBoy" th:replace="segment :: header">
div标签的原始内容
</div>
<div id="worstBoy" th:include="segment :: header">
div标签的原始内容
</div>

