1 前言
- 根据前面的知识,微服务架构已经初具雏形。但是还有一些问题:不同的微服务一般会有不同的网络地址,客户端在访问这些微服务的时候需要记住几十甚至几百个地址,这对于客户端来说,是非常复杂而且难以维护的。
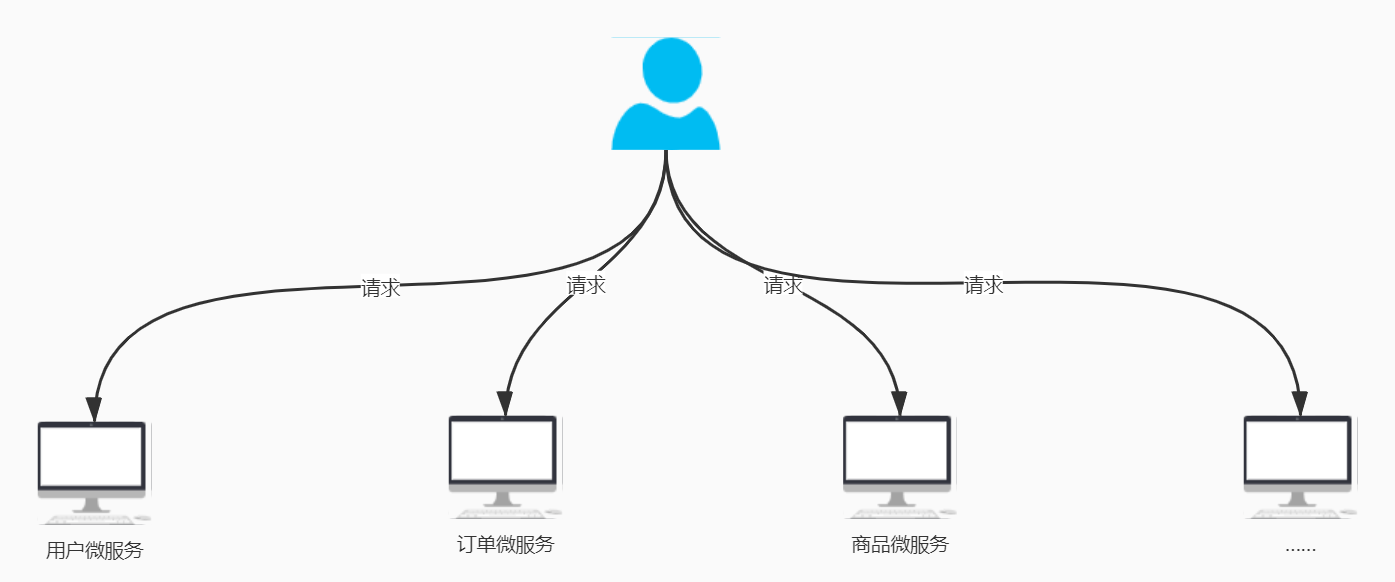
- 如果让客户端直接和各个微服务通信,可能会有很多问题:
 客户端会请求多个不同的服务,需要维护不同的请求地址,增加了开发难度。
客户端会请求多个不同的服务,需要维护不同的请求地址,增加了开发难度。 在某些场景下存在跨域请求的问题。
在某些场景下存在跨域请求的问题。 加大身份认证的难度,每个微服务需要独立认证。
加大身份认证的难度,每个微服务需要独立认证。- 因此,我们需要一个微服务网关,介于客户端和服务器之间的中间层,所有的外部请求都会先经过微服务网关。客户端只需要和网关交互,只需要知道一个网关地址即可,这样简化了开发,并且还有以下好处:
 易于监控。
易于监控。 易于认证。
易于认证。 减少了客户端和各个微服务之间的交互次数。
减少了客户端和各个微服务之间的交互次数。

2 微服务网关的概念
2.1 什么是微服务网关
- API网关是一个服务器,是系统对外的唯一入口。API网关封装了系统内部架构,为每个客户端提供一个定制的API。API网关方式的核心要点是:所有的客户端和消费端都通过统一的网关接入微服务,在网关层处理所有的非业务功能。
- 通常,网关也提供REST/HTTP的访问API。服务端通过API网关注册和管理服务。
2.2 微服务网关的作用和应用场景
- 网关的具体的职责有:身份认证、监控、负载均衡、缓存、请求分片和管理、静态响应处理。当然,最主要的职责还是和
外界联系。
3 常见的API网关实现方式
3.1 Kong
- 基于Nginx+Lua开发,性能高,稳定,有多个可用的插件(限流、鉴权等等)可用开箱即用。
- 问题:
 只支持HTTP协议。
只支持HTTP协议。 二次开发、自由扩展困难。
二次开发、自由扩展困难。 提供管理API,缺乏更医用的管理和配置方式。
提供管理API,缺乏更医用的管理和配置方式。
3.2 Zuul
- Netflix开源,功能丰富,使用Java开发,易于二次开发,需要运行在Web容器中,如Tomcat。
- 问题:
 缺乏管控,无法动态配置。
缺乏管控,无法动态配置。 依赖组件较多。
依赖组件较多。 处理HTTP请求依赖的是Web容器,性能不如Nginx。
处理HTTP请求依赖的是Web容器,性能不如Nginx。
3.3 Traefik
- Go语言开发,轻量易用,提供大多数功能如服务路由,负载均衡等等,提供Web UI界面。
- 问题:
 二进制文件部署,二次开发难度大。
二进制文件部署,二次开发难度大。 UI更多的是监控,缺乏配置、管理能力。
UI更多的是监控,缺乏配置、管理能力。
3.4 Spring Cloud Gateway
3.5 Nginx+Lua实现
- 使用Nginx的反向代理和负载均衡可实现对API服务器的负载均衡和高可用。
- 问题:
 自注册的问题。
自注册的问题。 网关本身的扩展性。
网关本身的扩展性。
4 基于Nginx的网关实现
4.1 Nginx介绍
- Nginx是一个自由的、开源的、高性能的HTTP服务器和反向代理服务器,同时也是一个IMAP、POP3、SMTP代理服务器。
- Nginx可以作为一个HTTP服务器进行网关的发布,同时Nginx也可以作为反向代理服务器实现负载均衡。
4.2 正向代理和反向代理
4.2.1 正向代理
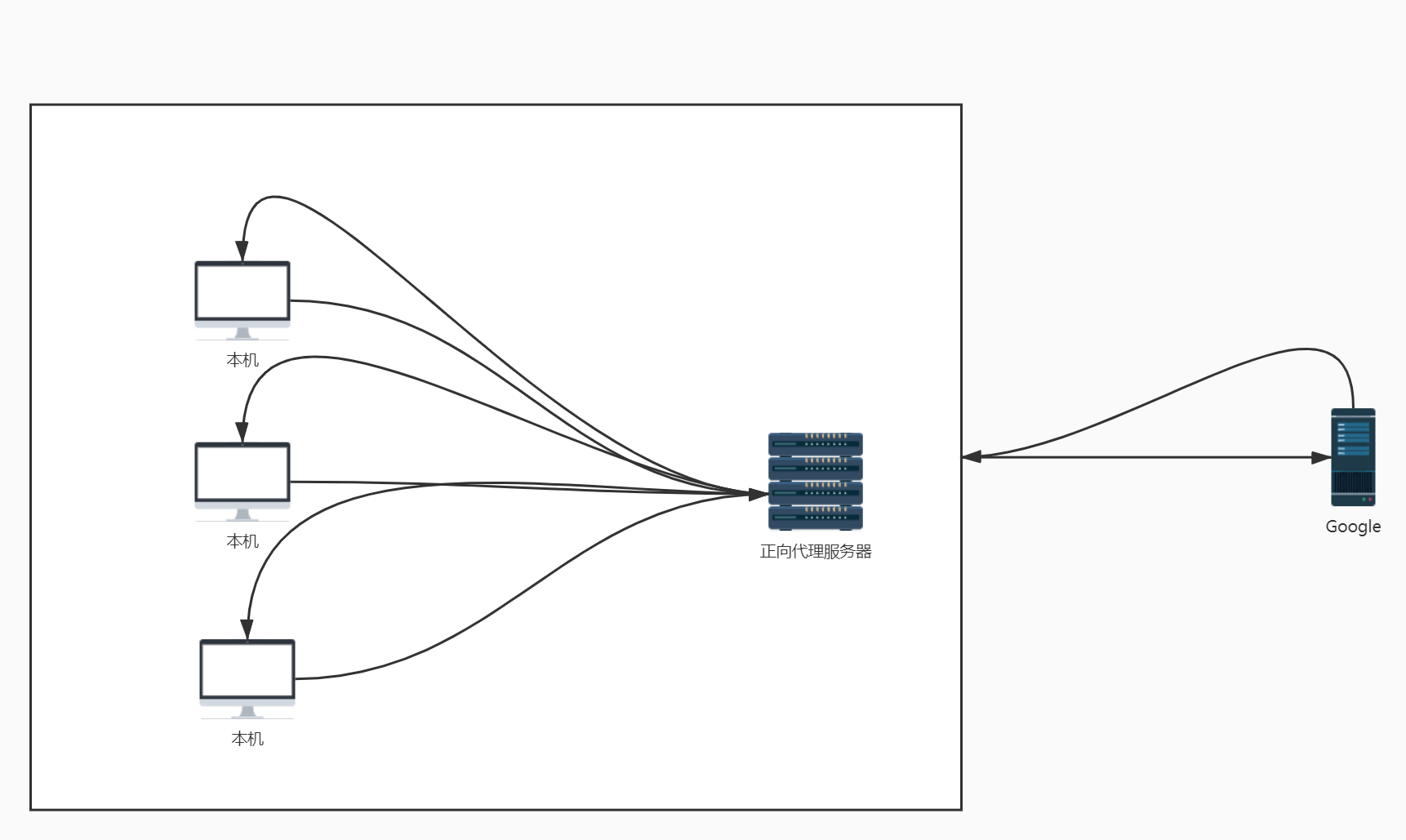
- 正向代理:代理服务器代理客户端发出请求。
- 正向代理服务器是一个位于客户端和远程服务器之间的服务器,为了从远程服务器获取内容,客户端向代理服务器发送一个请求并且指定远程服务器,然后代理服务器向远程服务器转交请求并将获取的内容返回给客户端。
- 客户端必须要进行一些特别的设置才能使用正向代理(比如你需要自己搭建VPN服务器,或者买一些第三方的服务)。
4.2.2 反向代理
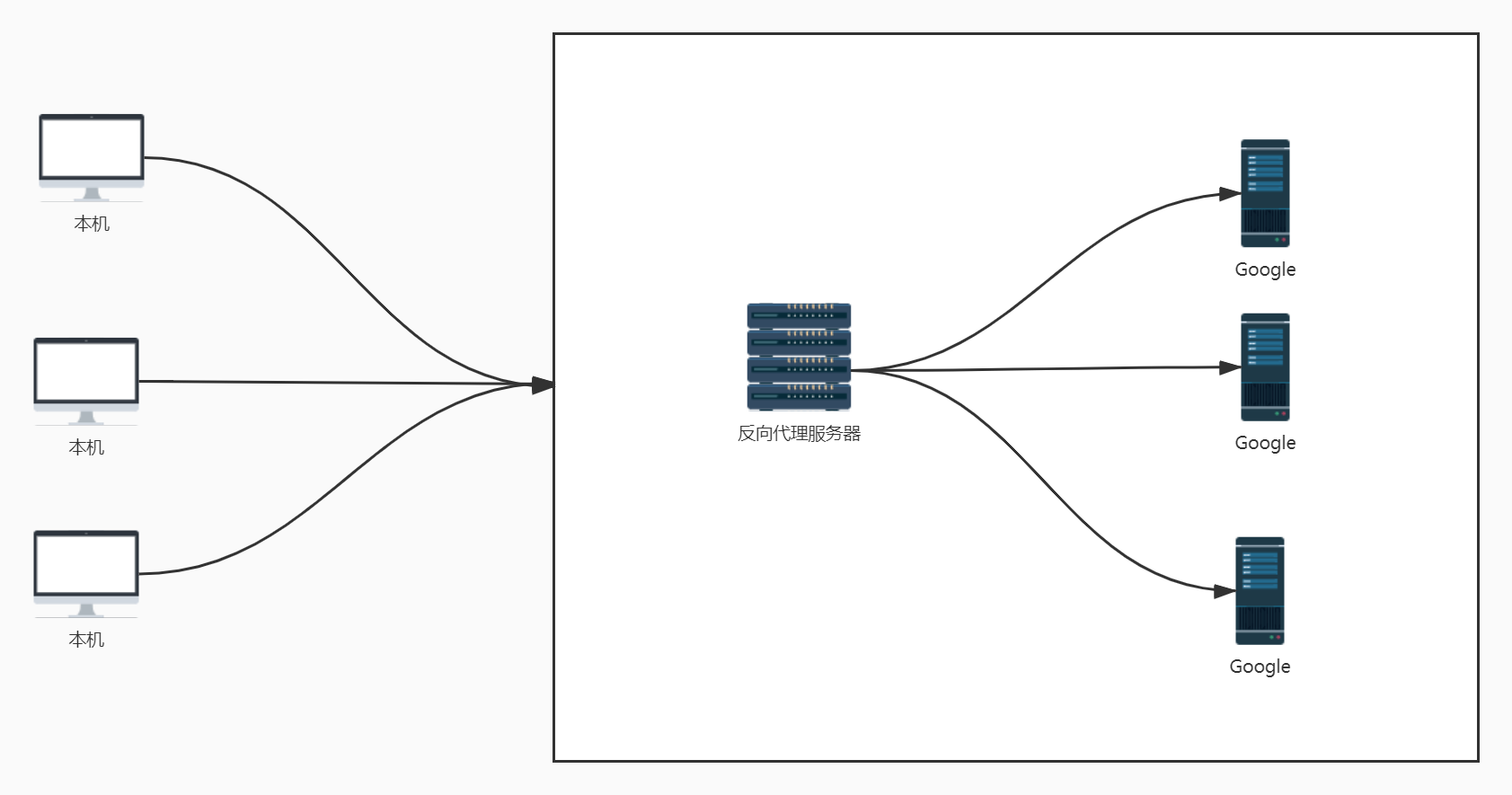
- 多个客户端给服务器发送请求,Nginx服务器收到请求之后,按照一定的规则分发给了后端的业务处理服务器进行处理。此时,请求的来源对于客户端是明确的,但是请求具体由那台服务器处理的并不明确,Nginx扮演的就是一个反向代理角色。客户端是无法感知代理的存在的,反向代理对外是透明的,访问者并不知道自己访问的是一个代理。因为客户端不需要任何配置就可以访问。
- 反向代理:代理的是服务端接收请求,主要用于服务器集群分布式部署的情况,反向代理隐藏了服务器的信息。
- 如果只是单纯的需要一个最基础的具备转发功能的网关,那么使用Nginx是一个不错的选择。
4.3 准备工作
4.4 配置Nginx的请求转发
location /api-product{ proxy_pass http://localhost:9004/;}location /api-order{ proxy_pass http://localhost:8003/;}
#user nobody;worker_processes 1;#error_log logs/error.log;#error_log logs/error.log notice;#error_log logs/error.log info;#pid logs/nginx.pid;events { worker_connections 1024;}http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; #log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' # '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' # '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; #access_log logs/access.log main; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; #gzip on; server { listen 80; server_name localhost; #charset koi8-r; #access_log logs/host.access.log main; location / { root html; index index.html index.htm; } location /api-product{ proxy_pass http://localhost:9004/; } location /api-order{ proxy_pass http://localhost:8003/; } #error_page 404 /404.html; # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html # error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } # proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80 # #location ~ \.php$ { # proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1; #} # pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000 # #location ~ \.php$ { # root html; # fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; # fastcgi_index index.php; # fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; # include fastcgi_params; #} # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root # concurs with nginx's one # #location ~ /\.ht { # deny all; #} } # another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration # #server { # listen 8000; # listen somename:8080; # server_name somename alias another.alias; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} # HTTPS server # #server { # listen 443 ssl; # server_name localhost; # ssl_certificate cert.pem; # ssl_certificate_key cert.key; # ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; # ssl_session_timeout 5m; # ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; # ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #}}

客户端会请求多个不同的服务,需要维护不同的请求地址,增加了开发难度。
在某些场景下存在跨域请求的问题。
加大身份认证的难度,每个微服务需要独立认证。
易于监控。
易于认证。
减少了客户端和各个微服务之间的交互次数。

只支持HTTP协议。
二次开发、自由扩展困难。
提供管理API,缺乏更医用的管理和配置方式。
缺乏管控,无法动态配置。
依赖组件较多。
处理HTTP请求依赖的是Web容器,性能不如Nginx。
二进制文件部署,二次开发难度大。
UI更多的是监控,缺乏配置、管理能力。
自注册的问题。
网关本身的扩展性。



