第一章:集合概述
- 集合是 Java 提供的一种容器,可以用来存储多个数据。
- 集合的本质是用来
存储对象(有时,你会看到直接向集合中插入基本类型数据,会很疑惑,不是只能存储对象吗?其实不然,因为 JDK5 的新特性自动装箱和拆箱,所以在存储基本类型的数据的时候,会转换为对应的包装类型对象)。 - 集合和数组既然都是容器,它们有啥区别?
- ① 数组的长度是固定的,集合的长度是可变的。
- ② 数组中可以存储基本类型数据,也可以存储对象;但是,集合中只能存储对象。
- 集合主要分为两大类型:
- ① Collection(单列集合):表示一组对象。
- ② Map(双列集合):表示一组映射关系或键值对。

第二章:Collection 接口
2.1 概述
- Collection 接口是 List、Set 接口的父接口,该接口中定义的方法既可以用于操作 List 集合,也可以用于操作 Set 集合。
- JDK 不提供此接口的任何直接实现,而是提供更具体的子接口(如:List 、Set 等)实现。
- 在JDK 5 之前,Java 集合会丢失容器中所有的对象的数据类型,将所有对象都当成Object类型来处理;但是,从JDK 5 增加了
泛型以后,Java 集合就可以记住容器中对象的数据类型。
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E> {...}
2.2 常用方法
2.2.1 添加元素
- 添加元素对象到当前集合中:
boolean add(E e);
- 添加另一个集合中的所有元素到当前集合中:
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);
- 示例:
package com.github.demo1;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collection;/*** @author 许大仙* @version 1.0* @since 2021-09-27 14:41*/public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {Collection<String> collection = new ArrayList<>();collection.add("hello");collection.add("world");System.out.println("collection = " + collection); // collection = [hello, world]}}
- 示例:
package com.github.demo2;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collection;/*** @author 许大仙* @version 1.0* @since 2021-09-27 16:10*/public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {Collection<String> c1 = new ArrayList<>();c1.add("aa");c1.add("bb");c1.add("cc");Collection<String> c2 = new ArrayList<>();c2.add("ee");c2.add("ff");// 将c2中的所有元素添加到c1中c1.addAll(c2);System.out.println("c1 = " + c1); // c1 = [aa, bb, cc, ee, ff]}}
- 示例:
package com.github.demo3;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collection;/*** @author 许大仙* @version 1.0* @since 2021-09-27 16:13*/public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {Collection<Object> c1 = new ArrayList<>();c1.add("aa");c1.add("bb");c1.add("cc");Collection<Object> c2 = new ArrayList<>();c2.add("ee");c2.add("ff");c1.add(c2);System.out.println("c1 = " + c1); // c1 = [aa, bb, cc, [ee, ff]]}}
2.2.2 删除元素
- 从当前集合中删除第一个找到的与 obj 对象 equals 返回 true 的元素:
boolean remove(Object o);
- 从当前集合中删除所有与 coll 集合中相同的元素:
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c)
- 清空集合:
void clear();
- 示例:
package com.github.demo4;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collection;/*** @author 许大仙* @version 1.0* @since 2021-09-27 16:35*/public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {Collection<String> c1 = new ArrayList<>();c1.add("aa");c1.add("bb");c1.add("cc");System.out.println("c1 = " + c1); // c1 = [aa, bb, cc]c1.remove("aa");System.out.println("c1 = " + c1); // c1 = [bb, cc]}}
- 示例:
package com.github.demo5;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-27 16:38
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<Object> c1 = new ArrayList<>();
c1.add("aa");
c1.add("bb");
c1.add("cc");
Collection<Object> c2 = new ArrayList<>();
c2.add("ee");
c2.add("ff");
c1.add(c2);
System.out.println("c1 = " + c1); // c1 = [aa, bb, cc]
c1.remove(c2);
System.out.println("c1 = " + c1); // c1 = [aa, bb, cc]
}
}
- 示例:
package com.github.demo6;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-27 16:41
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> c1 = new ArrayList<>();
c1.add("aa");
c1.add("bb");
c1.add("cc");
Collection<String> c2 = new ArrayList<>();
c2.add("ee");
c2.add("ff");
c1.addAll(c2);
System.out.println("c1 = " + c1); // c1 = [aa, bb, cc, ee, ff]
c1.removeAll(c2);
System.out.println("c1 = " + c1); // c1 = [aa, bb, cc]
}
}
2.2.3 判断
- 判断当前集合是否为空集合:
boolean isEmpty();
- 判断当前集合中是否存在一个与 obj 对象 equals 返回 true 的元素:
boolean contains(Object o);
- 判断 c 集合中的元素是否在当前集合中都存在,即 c 集合是否为当前集合的子集:
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c)
- 示例:
package com.github.demo7;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-27 16:43
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> c1 = new ArrayList<>();
c1.add("aa");
c1.add("bb");
c1.add("cc");
c1.add("dd");
System.out.println("c1 = " + c1.isEmpty()); // c1 = false
c1.clear();
System.out.println("c1 = " + c1.isEmpty()); // c1 = true
}
}
- 示例:
package com.github.demo8;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-27 16:46
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> c1 = new ArrayList<>();
c1.add("aa");
c1.add("bb");
c1.add("cc");
c1.add("dd");
System.out.println("c1 = " + c1.contains("aa")); // c1 = true
System.out.println("c1 = " + c1.contains("aaa")); // c1 = false
}
}
- 示例:
package com.github.demo9;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-27 16:47
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> c1 = new ArrayList<>();
c1.add("aa");
c1.add("bb");
c1.add("cc");
c1.add("dd");
Collection<String> c2 = new ArrayList<>();
c2.add("aa");
c2.add("bb");
c2.add("ee");
System.out.println("c1.containsAll(c2) = " + c1.containsAll(c2)); // c1.containsAll(c2) = false
Collection<String> c3 = new ArrayList<>();
c2.add("aa");
c2.add("bb");
System.out.println("c1.containsAll(c3) = " + c1.containsAll(c3)); // c1.containsAll(c3) = true
}
}
2.2.4 获取集合中元素的个数
- 获取当前集合中实际存储的元素个数:
int size();
- 示例:
package com.github.demo10;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-27 16:50
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> c1 = new ArrayList<>();
c1.add("aa");
c1.add("bb");
c1.add("cc");
c1.add("dd");
System.out.println("c1.size() = " + c1.size()); // c1.size() = 4
c1.clear();
System.out.println("c1.size() = " + c1.size()); // c1.size() = 0
}
}
2.2.5 交集
- 当前集合仅保留与 c 集合中的元素相同的元素,即当前集合中仅保留两个集合的交集:
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c);
- 示例:
package com.github.demo11;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-27 16:53
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> c1 = new ArrayList<>();
c1.add("aa");
c1.add("bb");
c1.add("cc");
c1.add("dd");
Collection<String> c2 = new ArrayList<>();
c2.add("bb");
c1.retainAll(c2);
System.out.println("c1 = " + c1); // c1 = [bb]
}
}
2.2.6 转数组
- 返回包含当前集合中所有元素的数组:
Object[] toArray();
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);
- 示例:
package com.github.demo12;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-27 16:55
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<>();
c.add("aa");
c.add("bb");
c.add("cc");
c.add("dd");
Object[] objects = c.toArray();
System.out.println("objects = " + Arrays.toString(objects)); // objects = [aa, bb, cc, dd]
String[] strings = c.toArray(new String[c.size()]);
System.out.println("strings = " + Arrays.toString(strings)); // strings = [aa, bb, cc, dd]
}
}
第三章:Iterator 迭代器
3.1 Iterator 接口
- 在程序开发中,经常需要遍历集合中的所有元素。针对这种需求,JDK 专门提供了一个接口
java.util.Iterator。 - Iterator 接口也是 Java 集合中的医院,但是它和 Collection 、Map 接口有所不同,Collection 接口和 Map 接口主要用来存储元素,而 Iterator 接口主要用于迭代访问(即遍历)Collection 中的元素,因此 Iterator 对象也称为迭代器。
- 获取迭代器的方法(Collection 接口中提供的方法):
Iterator<E> iterator();
Iterator 接口中的常用方法:
① 判断是否有元素可以迭代,如果有,返回 true ;否则,返回 false :
boolean hasNext();② 返回迭代的下一个元素:
E next();
注意:在使用迭代器进行遍历集合的时候,如果集合中已经没有元素了,还使用迭代器的 next 方法,将会抛出 java.util.NoSuchElementException 异常。
- 示例:
package com.github.collection1.demo1;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-28 08:18
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> collection = new ArrayList<>();
collection.add("aa");
collection.add("bb");
collection.add("cc");
collection.add("dd");
// 获取迭代器
Iterator<String> iterator = collection.iterator();
// 判断集合中是否有元素
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// 取出集合中的元素
String next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
}
}
- 示例:
package com.github.collection1.demo2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-28 08:31
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> collection = new ArrayList<>();
collection.add("aa");
collection.add("bb");
collection.add("cc");
collection.add("dd");
for (Iterator<String> iterator = collection.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
String next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
}
}
3.2 迭代器实现原理
- 每个集合容器的内部结构都是不同的,但是迭代器都可以进行统一的遍历是实现,是怎么做到的?
- Collection 接口提供了获取 Iterator 的方法:
Iterator<E> iterator();
- 那么,Collection 接口的每个子类都必须重写这个方法。
- 以 ArrayList 为例:
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{
// 重写了iterator方法
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
...
}
...
}
3.3 使用 Iterator 迭代器删除元素
- Iterator 接口中有一个删除的方法:
default void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("remove");
}
- 既然,Collection 接口中已经有了 remove(xxx) 的方法,为什么 Iterator 迭代器中还要提供 remove() 方法?
- 因为Collection 接口的 remove(xxx) 方法无法根据指定条件删除。
注意:不要在使用 Iterator 迭代器迭代元素的时候,调用 Collection 的 remove(xxx) 方法,否则会报 java.util.ConcurrentModificationException 异常或出现其他不确定的行为。
- 示例:删除集合中的偶数元素
package com.github.collection1.demo3;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-28 09:35
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<Integer> collection = new ArrayList<>();
collection.add(1);
collection.add(2);
collection.add(3);
collection.add(4);
System.out.println("原来集合中的元素 = " + collection); // 原来集合中的元素 = [1, 2, 3, 4]
for (Iterator<Integer> iterator = collection.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
Integer ele = iterator.next();
if (ele % 2 == 0) {
iterator.remove();
}
}
System.out.println("后来集合中的元素 = " + collection); // 后来集合中的元素 = [1, 3]
}
}
3.4 并发修改异常( ConcurrentModificationException )
异常的产生原因:在迭代器遍历集合的过程中,调用集合自身的功能(例如:调用集合的 add 和 remove 方法),改变集合的长度。
示例:并发修改异常
package com.github.collection1.demo4;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-28 09:50
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> collection = new ArrayList<>();
collection.add("aa");
collection.add("bb");
collection.add("cc");
collection.add("dd");
for (Iterator<String> iterator = collection.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
String ele = iterator.next();
System.out.println("ele = " + ele);
collection.add("ee");
}
}
}

- 如果在 Iterator、ListIterator 迭代器创建后的任意时间从结构上修改了集合(通过迭代器自身的remove或add方法之外的任何其他方式),则迭代器会抛出 ConcurrentModificationException 异常。因此,面对并发的修改,迭代器很快会失败,而不是冒着在将来不确定的时间发生不确定行为的风险。
- 这样设计时因此,迭代器代表集合中的某个元素的位置,内部会存储某些能够代表该位置的信息。当集合发生改变的时候,该信息的含义可能会发生变化,这个时候操作迭代器就有可能造成不可预料的后果。因此,果断抛出异常阻止,是最好的方法,者就是 Iterator 迭代器的快速失败机制。
- 需要注意的是,迭代器的快速失败机制行文不能得到保证,一般来说,存在不同步的并发修改时,不可能做出任何坚决的保证。快速失败机制尽最大努力抛出 ConcurrentModificationException 。因此,
迭代器的快速失败行文应该仅仅用于检测bug。 - 快速失败机制的实现原理:
- ① 在 ArrayList 等集合类中都有一个 modCount 变量,它用来记录集合的结构被修改的次数。
- ② 当我们给集合添加或删除元素的时候,会导致 modCount++ 。
- ③ 当我们使用 Iterator 迭代器遍历集合的时候,会使用一个变量记录当前集合的 modCount 。例如:
int expectedModCount = modCount;,并且,在迭代器每次 next() 迭代元素的时候,都要检查expectedModCount != modCount,如果不相等,则说明调用了 Iterator 迭代器以外的 Collection 的 add 、remove 等方法,修改了集合的结构,使得 modCount++ ,值变了,就会抛出 ConcurrentModificationException 。
3.5 集合存储自定义对象并迭代
- 示例:
package com.github.collection1.demo5;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-28 10:07
*/
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Person(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" + "name='" + this.name + '\'' + ", age=" + this.age + '}';
}
}
package com.github.collection1.demo5;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-28 10:07
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<Person> collection = new ArrayList<>();
collection.add(new Person("张三", 11));
collection.add(new Person("李四", 59));
collection.add(new Person("王五", 19));
collection.add(new Person("赵六", 42));
collection.add(new Person("田七", 8));
collection.add(new Person("王八", 2));
for (Iterator<Person> iterator = collection.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
Person next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
}
}
3.6 增强 for 循环
- 增强 for 循环(也称为 for each 循环)是 JDK 5 之后出来的一个高级的 for 循环,专门用来遍历数组和集合。
- 语法:
for(元素的数据类型 变量: 数组 或 Collection集合){
// 写代码
}
- 示例:遍历数组(不要在遍历数组的时候对数组的元素进行修改)
package com.github.collection1.demo6;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-28 10:41
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建数组
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// 遍历数组
for (int i : arr) {
System.out.println("i = " + i);
}
}
}
- 示例:遍历集合(不要在遍历集合的时候对集合中的元素进行增加、删除、替换等操作)
package com.github.collection1.demo7;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-28 10:45
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合
Collection<Integer> collection = new ArrayList<>();
// 向集合中添加元素
collection.add(1);
collection.add(2);
collection.add(3);
collection.add(4);
// 遍历集合
for (Integer i : collection) {
System.out.println("i = " + i);
}
}
}
3.7 java.lang.Iterable 接口
java.lang.Iterable接口,实现这个接口,允许对象称为"for each"语句的目标。- JDK 5 的时候,Collection 接口继承了
java.lang.Iterable接口,因此 Collection 系列的集合就可以直接使用 foreach 循环。 java.lang.Iterable接口的抽象方法:
// 获取对应的迭代器,用来遍历数组或集合中的元素的。
Iterator<T> iterator();
- foreach 循环遍历集合的本质就是使用 Iterator 迭代器进行遍历的。
注意:不要在使用 foreach 循环遍历集合的时候,使用 Collection 的 remove() 等方法。否则,要么报 java.util.ConcurrentModificationException 异常,要么行为不确定。
第四章:List 接口
4.1 概述
- 鉴于 Java 中数组用来存储数据的局限性,我们通常使用 List 来代替数组。
- List 集合类中
元素有序(元素存储和取出的顺序一致)、且可重复,集合中的每个元素都有其对应的顺序索引。 - List 容器中的元素都对应一个整数类型的序号记载其在容器中的位置,根据根据序号存取容器中的元素。
- List 接口的常用类:
- ArrayList 。
- LinkedList 。
- Vector(已过时)。
4.2 常用方法
4.2.1 添加元素
- 在指定的索引位置上添加元素:
void add(int index, E element);
- 在指定的索引位置上添加另一个集合中的所有元素:
boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c);
- 示例:
package com.github.list.demo1;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-28 13:18
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 向集合的尾部添加
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
System.out.println("list = " + list); // list = [1, 2, 3, 4]
// 在指定的索引上添加元素
list.add(1, 10);
System.out.println("list = " + list); // list = [1, 10, 2, 3, 4]
}
}
- 示例:
package com.github.list.demo2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-28 13:25
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aa");
list.add("bb");
list.add("cc");
list.add("dd");
System.out.println("list = " + list); // list = [aa, bb, cc, dd]
List<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
list2.add("ee");
list2.add("ff");
list.addAll(1, list2);
System.out.println("list = " + list); // list = [aa, ee, ff, bb, cc, dd]
}
}
4.2.2 获取元素
- 根据索引获取元素:
E get(int index);
- 根据开始索引和结束索引获取子 List 集合:
List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex);
- 示例:
package com.github.list.demo3;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-28 13:28
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aa");
list.add("bb");
list.add("cc");
list.add("dd");
String s = list.get(1);
System.out.println("s = " + s); // s = bb
}
}
- 示例:
package com.github.list.demo4;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-28 13:31
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aa");
list.add("bb");
list.add("cc");
list.add("dd");
System.out.println("list = " + list); // list = [aa, bb, cc, dd]
List<String> list1 = list.subList(1, 3);
System.out.println("list1 = " + list1); // list1 = [bb, cc]
}
}
- 示例:
package com.github.list.demo5;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-28 13:33
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aa");
list.add("bb");
list.add("cc");
list.add("dd");
// 遍历List集合
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
}
}
4.2.3 获取元素索引
- 从前往后根据元素查找其索引,如果找到,返回该元素的索引;否则,返回 -1 :
int indexOf(Object o);
- 从后往前根据元素查找其索引,如果找到,返回该元素的索引;否则,返回 -1 :
int lastIndexOf(Object o);
- 示例:
package com.github.list.demo6;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-28 13:35
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aa");
list.add("bb");
list.add("cc");
list.add("dd");
list.add("aa");
int index = list.indexOf("aa");
System.out.println("index = " + index); // index = 0
int index1 = list.indexOf("ee");
System.out.println("index1 = " + index1); // index1 = -1
}
}
- 示例:
package com.github.list.demo7;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-28 13:38
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aa");
list.add("bb");
list.add("cc");
list.add("dd");
list.add("aa");
int index = list.lastIndexOf("aa");
System.out.println("index = " + index); // index = 4
int index1 = list.lastIndexOf("ff");
System.out.println("index1 = " + index1); // index1 = -1
}
}
4.2.4 删除元素
- 根据索引删除元素,返回删除的元素:
E remove(int index);
- 示例:
package com.github.list.demo8;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-28 13:40
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aa");
list.add("bb");
list.add("cc");
list.add("dd");
list.add("aa");
System.out.println("list = " + list); // list = [aa, bb, cc, dd, aa]
String remove = list.remove(2);
System.out.println("remove = " + remove); // remove = cc
System.out.println("list = " + list); // list = [aa, bb, dd, aa]
}
}
4.2.5 替换元素
- 替换指定索引上的元素:
E set(int index, E element);
- 示例:
package com.github.list.demo9;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-28 13:43
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aa");
list.add("bb");
list.add("cc");
list.add("dd");
list.add("aa");
System.out.println("list = " + list); // list = [aa, bb, cc, dd, aa]
list.set(4, "java");
System.out.println("list = " + list); // list = [aa, bb, cc, dd, java]
}
}
4.3 List 特有的迭代器 ListIterator(了解)
- List 接口提供了获取 ListIterator 的方法,该方法返回一个 ListIterator 对象:
ListIterator<E> listIterator();
// 如果从后向前遍历,index就是最后一个元素的索引,即list的size()
ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index);
ListIterator 接口继承了 Iterator 接口,提供了专门操作 List 的方法:
是否有下一个元素:
boolean hasNext();返回下一个元素:
E next();返回后一个元素的索引:
int nextIndex();返回前一个元素的索引:
int previousIndex();逆向遍历集合,向前是否还有元素:
boolean hasPrevious();获取前一个元素:
E previous();通过迭代器添加元素到集合中:
void add(E e);通过迭代器替换元素:
void set(E e);
示例:
package com.github.list.demo10;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ListIterator;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-28 13:59
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aa");
list.add("bb");
list.add("cc");
list.add("dd");
list.add("aa");
for (ListIterator<String> iterator = list.listIterator(list.size()); iterator.hasPrevious();) {
String previous = iterator.previous();
System.out.println(previous);
}
}
}
4.4 List接口的实现类之一:ArrayList
4.4.1 概述
- ArrayList 具备了List接口的特性(有序、重复、索引)。
- ArrayList 集合底层的实现原理是数组,大小可变。
- ArrayList 的特点:查询速度快、增删慢。
- ArrayList 在 JDK8 前后的实现区别:
- JDK7 :ArrayList 像饿汉式,直接创建了一个初始容量为 10 的数组,每次扩容是原来长度的 1.5 倍。
- JDK8 :ArrayList 像懒汉式,一开始创建一个长度为 0 的数组,当添加第一个元素的时候再创建一个容器为 10 的数组,每次扩容是原来长度的 1.5 倍。
- ArrayList 是线程不安全的集合,运行速度快。
4.4.2 ArrayList的类成员变量
- 默认容量:
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
- 空数组:
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
- 默认容量的空数组:
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
- ArrayList 集合中的核心数组:
transient Object[] elementData;
- 记录数组中存储个数:
private int size;
- 数组扩容的最大值:
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
4.4.3 ArrayList 类的构造方法
- 无参构造方法:
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
- 传入指定容量的构造方法:
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
4.4.4 ArrayList 类的 add 方法
public boolean add(E e) {
// 检查容量 size初始化的时候是0,那么size+1就是1
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
// 将元素添加到数组中,size计数器++
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
// minCapacity此时是1
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
// 如果存储元素的数据 == 默认的空的数组,无参构造器中赋值
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
// 返回DEFAULT_CAPACITY=10和minCapacity=1的最大值,即10
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
// 扩容
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
// 10- 数组的长度0 > 0
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
// 传入10
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
// 数组的原来长度 0
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 新容量 = 数组原来的长度 + 数组原来的长度 / 2
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); // 0
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) // 0 -10 < 0
newCapacity = minCapacity; // 新容量 = 10
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) // 判断是否超过最大容量
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); // 数组的复制
}
4.4.5 ArrayList 类的 get 方法
public E get(int index) {
// 检查索引
rangeCheck(index);
// 返回数组中指定索引处的元素
return elementData(index);
}
4.4.6 ArrayList 类的 set 方法
public E set(int index, E element) {
// 检查索引
rangeCheck(index);
// 获取旧的元素
E oldValue = elementData(index);
// 将新的元素设置到指定的索引处
elementData[index] = element;
// 返回旧的元素
return oldValue;
}
4.4.7 ArrayList 类的 remove 方法
public E remove(int index) {
// 检查索引
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
// 获取旧的元素
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
// 将index后面的元素依次复制到前面
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
// 最后一个元素设置为null
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
// 返回旧的元素
return oldValue;
}
4.5 List 接口的实现类之二:LinkedList
4.5.1 概述
- LinkedList 具备了 List 接口的特性(有序、重复、索引)。
- LinkedList 地城实现原理是双向链表。
- LinkedList 的增删速度快、查询慢。
- LinkedList 是线程不安全的集合,运行速度快。
4.5.2 LinkedList 集合特有方法
- 元素插入到链表开头:
public void addFirst(E e) {}
- 元素插入到列表结尾:
public void addLast(E e) {}
- 获取链表开头的元素:
public E getFirst() {}
- 获取链表结尾的元素:
public E getLast() {}
- 移除链表开头的元素:
public E removeFirst() {}
- 移除链表结尾的元素:
public E removeLast() {}
- 示例:
package com.github.linkedlist.demo1;
import java.util.LinkedList;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-28 14:22
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
linkedList.add("aa");
linkedList.add("bb");
linkedList.add("cc");
linkedList.add("dd");
System.out.println("linkedList = " + linkedList); // linkedList = [aa, bb, cc, dd]
linkedList.addFirst("你好啊");
System.out.println("linkedList = " + linkedList); // linkedList = [你好啊, aa, bb, cc, dd]
linkedList.addLast("你好呢");
System.out.println("linkedList = " + linkedList); // linkedList = [你好啊, aa, bb, cc, dd, 你好呢]
System.out.println(linkedList.getFirst()); // 你好啊
System.out.println(linkedList.getLast()); // 你好呢
linkedList.removeFirst();
System.out.println("linkedList = " + linkedList); // linkedList = [aa, bb, cc, dd, 你好呢]
linkedList.removeLast();
System.out.println("linkedList = " + linkedList); // linkedList = [aa, bb, cc, dd]
}
}
4.5.3 LinkedList 的类成员变量
- 集合中存储元素个数的计数器:
transient int size = 0;
- 第一个元素:
transient Node<E> first;
- 最后一个元素:
transient Node<E> last;
4.5.4 LinkedList 的成员内部类 Node
// 节点
private static class Node<E> {
E item; // 存储的元素
Node<E> next; // 下一个节点对象
Node<E> prev; // 上一个节点对象
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
4.5.5 LinkedList 类的 add 方法
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
// 声明新的节点对象 = last
final Node<E> l = last; // l = null
// 创建新的节点对象
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
// 新的节点赋值给最后一个节点
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
// 将新的节点赋值给first
first = newNode;
else
// 将新的节点赋值给最后一个节点的最后
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
4.5.6 LinkedList 类的 get 方法
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
// 索引是否小于长度的一半,二分查找
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
第五章:Set 接口
5.1 概述
- Set 接口是 Collection 接口的子接口,Set 接口没有提供额外的方法。
- Set 集合不允许包含相同的元素,如果试着将两个相同的元素加入同一个 Set 集合中,则会添加失败(不会抛出异常)。
- Set 判断两个对象是否相同不是使用
==运算符,而是根据equals方法。 - Set 集合支持的遍历方式和 Collection 集合一样:foreach 和 Iterator。
Set 的常用实现类:HashSet 、TreeSet 、LinkedHashSet 。
示例:
package com.github.set.demo1;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-29 08:29
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add("aa");
set.add("bb");
set.add("cc");
set.add("aa");
System.out.println("set = " + set); // set = [aa, bb, cc]
System.out.println("----------------");
// foreach
for (String s : set) {
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("----------------");
// iterator
for (Iterator<String> iterator = set.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
String next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
}
}
5.2 Set 的实现类之一:HashSet
- HashSet 是 Set 接口的典型实现,大多数时候使用 Set 集合的时候都使用这个实现类。
- HashSet 按照 Hash 算法来存储集合中的元素,因此具有很好的存取、查找、删除性能。
- HashSet 的底层实现原理是哈希表,在内部使用的是 HashMap 来实现的。
- HashSet 具有以下的特点:
- ① 不能保证元素的顺序(元素存储顺序和取出顺序不一定相同)。
- ② HashSet 不是线程安全的。
- ③ 集合元素可以为
null。
HashSet集合判断两个元素相等的标准:两个对象的 hashCode() 方法比较相等,并且两个对象的 equals() 方法返回值也相等。示例:
package com.github.set.demo2;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-29 08:58
*/
public class Person {
/**
* 姓名
*/
private String name;
/**
* 年龄
*/
private Integer age;
public Person() {}
public Person(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || this.getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
Person person = (Person)o;
return Objects.equals(this.name, person.name) && Objects.equals(this.age, person.age);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(this.name, this.age);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" + "name='" + this.name + '\'' + ", age=" + this.age + '}';
}
}
package com.github.set.demo2;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-29 08:59
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Person> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(new Person("张三", 18));
set.add(new Person("张三", 18));
set.add(new Person("张三", 21));
set.add(new Person("李四", 20));
set.add(new Person("李四", 18));
System.out.println("set = " + set); // set = [Person{name='张三', age=21}, Person{name='张三', age=18}, Person{name='李四', age=20}, Person{name='李四', age=18}]
}
}
5.2 Set 的实现类之二:LinkedHashSet
- LinkedHashSe t是 HashSet 的子类。
- LinkedHashSet 根据元素的 hashCode 值来决定元素的存储位置,但是它同时使用双向链表维护元素的次序,这使得元素看起来是以插入顺序保存的。
- LinkedHashSet 的插入性能略低于 HashSet ,但是在迭代访问Set里面的全部元素的时候有很好的性能。
LinkedHashSet 不允许集合元素重复。
示例:
package com.github.set.demo3;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-29 10:06
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> set = new LinkedHashSet<>();
set.add("aa");
set.add("cc");
set.add("bb");
set.add("aa");
System.out.println("set = " + set); // [aa, cc, bb]
}
}
5.3 Set 的实现类之三:TreeSet
5.3.1 概述
- TreeSet 是 SortedSet 接口的实现类,TreeSet 可以确保集合元素处于排序状态。
- TreeSet 底层使用红黑树结构存储数据,在内部使用的是 TreeMap 来实现的。

- TreeSet 有两种排序方法:自然排序和定制排序。默认情况下,TreeSet 采用自然排序。
5.3.2 自然排序
- 自然排序:TreeSet 会调用集合元素的 compareTo(Object obj) 方法来比较元素之间的大小关系,然后将集合元素按升序(默认情况)排列。
- 如果视图将一个对象添加到 TreeSet 中,则该对象所属的类必须实现 Comparable 接口。
Comparable 的实现:
- BigDecimal 、BigInteger 以及所有的数值型对应的包装类:按照它们对应的数值大小进行比较。
- Character :按照字符的 Unicode 值进行比较。
- Boolean :true 对应的包装类实例大于 false 对应的包装类实例。
- String :按照字符串中字符的 Unicode 值进行比较。
- Date 、Time :后面的时间、日期比前面的时间、日期大。
示例:
package com.github.set.demo4;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-29 14:19
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add("g");
set.add("b");
set.add("d");
set.add("c");
set.add("f");
System.out.println("set = " + set); // set = [b, c, d, f, g]
}
}
- 示例:
package com.github.set.demo5;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-29 14:30
*/
public class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person() {}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
return Integer.compare(this.getAge(), o.getAge());
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" + "name='" + this.name + '\'' + ", age='" + this.age + '\'' + '}';
}
}
package com.github.set.demo5;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-29 14:30
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Person> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add(new Person("张三", 15));
set.add(new Person("李四", 99));
set.add(new Person("王五", 58));
set.add(new Person("赵六", 9));
set.add(new Person("田七", 1));
set.add(new Person("王八", 44));
// set = [Person{name='田七', age='1'}, Person{name='赵六', age='9'}, Person{name='张三', age='15'}, Person{name='王八',
// age='44'}, Person{name='王五', age='58'}, Person{name='李四', age='99'}]
System.out.println("set = " + set);
}
}
5.3.3 定制排序
- 定制排序,通过 Comparator 接口来实现。需要重写 compare(T o1,T o2) 方法。
- 利用 int compare(T o1,T o2) 方法,比较 o1 和 o2 的大小:如果方法返回正整数,则表示 o1 大于 o2 ;如果返回 0 ,表示相等;返回负整数,表示 o1 小于 o2 。
- 要实现定制排序,需要将实现 Comparator 接口的实例作为形参传递给 TreeSet 的构造器。
- 使用定制排序判断两个元素相等的标准是:通过 Comparator 比较两个元素返回了 0 。
- 示例:
package com.github.set.demo6;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-29 14:30
*/
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person() {}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" + "name='" + this.name + '\'' + ", age='" + this.age + '\'' + '}';
}
}
package com.github.set.demo6;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-29 14:38
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Person> set = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Person>() {
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
return Integer.compare(o2.getAge(), o1.getAge());
}
});
set.add(new Person("张三", 15));
set.add(new Person("李四", 99));
set.add(new Person("王五", 58));
set.add(new Person("赵六", 9));
set.add(new Person("田七", 1));
set.add(new Person("王八", 44));
// set = [Person{name='李四', age='99'}, Person{name='王五', age='58'}, Person{name='王八', age='44'}, Person{name='张三', age='15'}, Person{name='赵六', age='9'}, Person{name='田七', age='1'}]
System.out.println("set = " + set);
}
}
第六章:Collections 工具类
6.1 概述
- Collections 是一个操作 Set 、List 和 Map 等集合的工具类。
- Collections 中提供了一系列的静态的方法对集合元素进行排序、查询和修改等操作,还提供了对集合对象设置不可变、对集合对象实现同步控制等方法。
6.2 常用方法
- 反转 List 中元素的顺序:
public static void reverse(List<?> list) {}
- 对 List 集合中的元素进行随机排序:
public static void shuffle(List<?> list) {}
- 根据元素的自然顺序对 List 集合中的元素进行排序:
public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void sort(List<T> list) {}
- 根据指定的 Comparator 对 List 集合元素进行排序:
public static <T> void sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c) {}
- 根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素:
public static <T extends Object & Comparable<? super T>> T max(Collection<? extends T> coll) {}
- 根据指定的 Comparator,返回给定集合中的最大元素:
public static <T> T max(Collection<? extends T> coll, Comparator<? super T> comp) {}
- 根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最小元素:
public static <T extends Object & Comparable<? super T>> T min(Collection<? extends T> coll) {}
- 根据指定的 Comparator,返回给定集合中的最小元素:
public static <T> T min(Collection<? extends T> coll, Comparator<? super T> comp) {}
- 返回指定集合中指定元素出现的次数:
public static int frequency(Collection<?> c, Object o) {}
- 集合元素的复制:
public static <T> void copy(List<? super T> dest, List<? extends T> src) {}
- 使用新值替换 List 集合中的所有旧值:
public static <T> boolean replaceAll(List<T> list, T oldVal, T newVal) {}
- 示例:
package com.github.collections.demo1;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-29 15:24
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aa");
list.add("dd");
list.add("hh");
list.add("bb");
System.out.println("list = " + list); // list = [aa, dd, hh, bb]
Collections.reverse(list);
System.out.println("list = " + list); // list = [bb, hh, dd, aa]
String max = Collections.max(list);
System.out.println("max = " + max); // max = hh
int gg = Collections.binarySearch(list, "gg");
System.out.println("gg = " + gg); // gg = -2
}
}
6.3 Collections 的同步控制方法
- Collections 类提供了多个 synchronizedXxx() 方法,该方法可以将指定集合包装成线程安全的集合,从而可以解决多线程并发访问集合时的线程安全问题。
- 将 Collection 集合转换为线程安全的集合:
public static <T> Collection<T> synchronizedCollection(Collection<T> c) {}
- 将 Set 集合转换为线程安全的集合:
public static <T> Set<T> synchronizedSet(Set<T> s) {}
- 将 List 集合转换为线程安全的集合:
public static <T> List<T> synchronizedList(List<T> list) {}
- 将 Map 集合转换为线程安全的集合:
public static <K,V> Map<K,V> synchronizedMap(Map<K,V> m) {}
- 示例:
package com.github.collections.demo2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-29 15:34
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
list.add("aa");
list.add("bb");
list.add("cc");
list.add("dd");
list.add("ee");
System.out.println("list = " + list);
}
}
第七章:Map 接口
7.1 概述
- Map 和 Collection 并列存在。用于保存具有映射关系的数据:key - value 。
- Map 中的 key 和 value 可以是任何引用类型的数据。
- Map 中的 key不允许重复,即同一个 Map 对象所对应的类,必须重写 equals() 和 hashCode() 方法。
- 通常情况下,使用 String 作为 Map 的 key 。
- Map 中的 key 和 value 之间存在单向一对一的关系,即通过指定的 key 能找到唯一的、确定的 value 。
- Map 接口的常用实现类:HashMap 、TreeMap 、LinkedHashMap 和 Properties 。其中,HashMap 是 Map 接口使用频率最高的实现类。

7.2 Map 接口常用的方法
- 将指定的 key - value 添加(修改)当前 Map 对象中:
V put(K key, V value);
- 将 m 中所有的 key - value 存放到当前的 Map 对象中:
void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m);
- 根据指定的 key 从当前 Map 对象中移除 key - value,并返回 value :
V remove(Object key);
- 清空当前 Map 对象中的所有 key - value :
void clear();
- 根据指定的 key 获取对应的 value :
V get(Object key);
- 是否包含指定的 key :
boolean containsKey(Object key);
- 是否包含指定的 value :
boolean containsValue(Object value);
- 返回 Map 对象中的 key - value 的个数:
int size();
- 判断当前 Map 是否为空(没有元素):
boolean isEmpty();
- 判断当前 Map 和参数对象 obj 是否相等:
boolean equals(Object o);
- 返回所有 key 构成的 Set 集合:
Set<K> keySet();
- 返回所有 value 构成的 Collection 集合:
Collection<V> values();
- 返回所有 key - value 构成的 Set 集合:
Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet();
- 示例:
package com.github.map.demo1;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-29 17:07
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("张三", 18);
map.put("李四", 28);
map.put("王五", 45);
System.out.println("map = " + map); // map = {李四=28, 张三=18, 王五=45}
Map<String, Integer> map2 = new HashMap<>();
map2.put("赵六", 9);
map2.put("田七", 30);
System.out.println("map2 = " + map2); // map2 = {赵六=9, 田七=30}
map.putAll(map2);
System.out.println("map = " + map); // map = {李四=28, 张三=18, 王五=45, 赵六=9, 田七=30}
Integer age = map.get("张三");
System.out.println("age = " + age); // age = 18
age = map.get("王八");
System.out.println("age = " + age); // age = null
System.out.println("map.isEmpty() = " + map.isEmpty()); // map.isEmpty() = false
int size = map.size();
System.out.println("size = " + size); // size = 5
System.out.println("map.equals(map2) = " + map.equals(map2)); // map.equals(map2) = false
age = map.remove("张三");
System.out.println("age = " + age); // age = 18
Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
System.out.println("keySet = " + keySet); // keySet = [李四, 王五, 赵六, 田七]
Collection<Integer> values = map.values();
System.out.println("values = " + values); // values = [28, 45, 9, 30]
}
}
- 示例:
package com.github.map.demo2;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Map的遍历
*
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-29 17:14
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("张三", 18);
map.put("李四", 28);
map.put("王五", 45);
for (Iterator<String> iterator = map.keySet().iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
String key = iterator.next();
Integer value = map.get(key);
System.out.println("key:" + key + ",value:" + value);
}
}
}
- 示例:
package com.github.map.demo3;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-29 17:16
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("张三", 18);
map.put("李四", 28);
map.put("王五", 45);
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
Integer value = map.get(key);
System.out.println("key:" + key + ",value:" + value);
}
}
}
- 示例:
package com.github.map.demo4;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-29 17:17
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("张三", 18);
map.put("李四", 28);
map.put("王五", 45);
for (Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> iterator = map.entrySet().iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry = iterator.next();
String key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("key:" + key + ",value:" + value);
}
}
}
- 示例:
package com.github.map.demo5;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-29 17:19
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("张三", 18);
map.put("李四", 28);
map.put("王五", 45);
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {
String key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("key:" + key + ",value:" + value);
}
}
}
7.2 Map 的实现类之一:HashMap
7.2.1 概述
- HashMap 是 Map 接口使用频率较高的实现类。
- 允许使用 null 键和 null 值,和 HashSet 一样,不能保证映射的顺序。
- 所有的 key 构成的集合是 Set:不重复的。所以,key 所在的类需要重写 equals() 和 hashCode() 方法。
- 所有的 value 构成的集合是 Collection:可以重复的。所以,value 所在的类需要重写 equals() 方法。
- 一个 key - value 构成一个 entry 。
- HashMap 判断两个 key 相等的标准:两个 key 的 hashCode() 和 equals() 分别都相等。
- HashMap 判断两个 value 相等的标准:两个 value 的 equals() 相等。
72.2 HashMap 的成员变量
- 哈希表数组的初始化容量:
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
- 哈希表数组的最大容量:
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
- 默认的加载因子:
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
- 阈值(转红黑树):
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
- 阈值(解除红黑树):
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
- 阈值(转红黑树):
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
7.2.3 HashMap 的内部类Node
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable {
// Node节点
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash; // 对象的hash值
final K key; // 存储对象
V value; // 使用Set的时候,是Object的对象
Node<K,V> next; // 链表的下一个节点
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
...
}
7.2.4 HashMap 的 put 方法
// HashMap存储对象的方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
// 存储值 参数:传递新计算的hash值,要存储的元素
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
/**
* 存储值
* @param hash 重新计算的hash值
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
// Node类型的数组;Node类型的节点;n,i
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
// tab = Node[] = null
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
// n = (tab数组 = resize()扩容后返回的数组)的长度,默认为16
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// (n - 1) & hash:数组的长度-1 & hash,确定存储的位置
// 判断数组的索引上是不是null,并赋值给p
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
// 数组的索引 = 赋值新的节点对象
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else { // 数组的索引不为null,说明,要存储的对象已经有了
Node<K,V> e; K k;
// 判断已经存在的对象和要存储对象的hash值、equals方法
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else { // 遍历该索引下的链表,和每个元素比较hashCode和equals,替换
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
// 将存储的对象,再次计算哈希值
// 尽量降低哈希值的碰撞
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
// 数组的扩容
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
7.2.5 JDK 7 和 JDK 8 的 HashMap 的区别
- JDK7 及以前版本:HashMap 是 数组+链表结构。
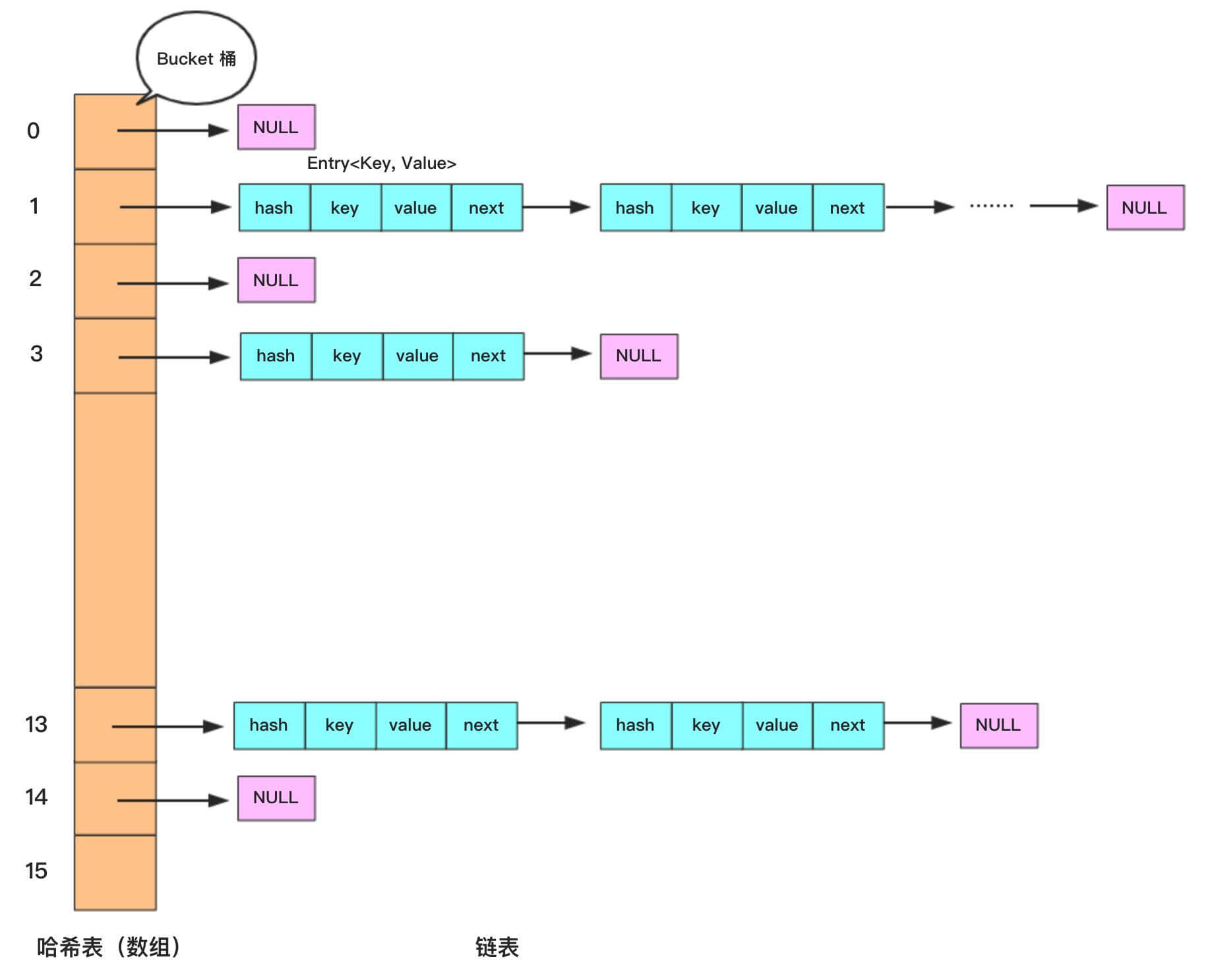
- JDK8 :HashMap 是 数组+链表+红黑树。
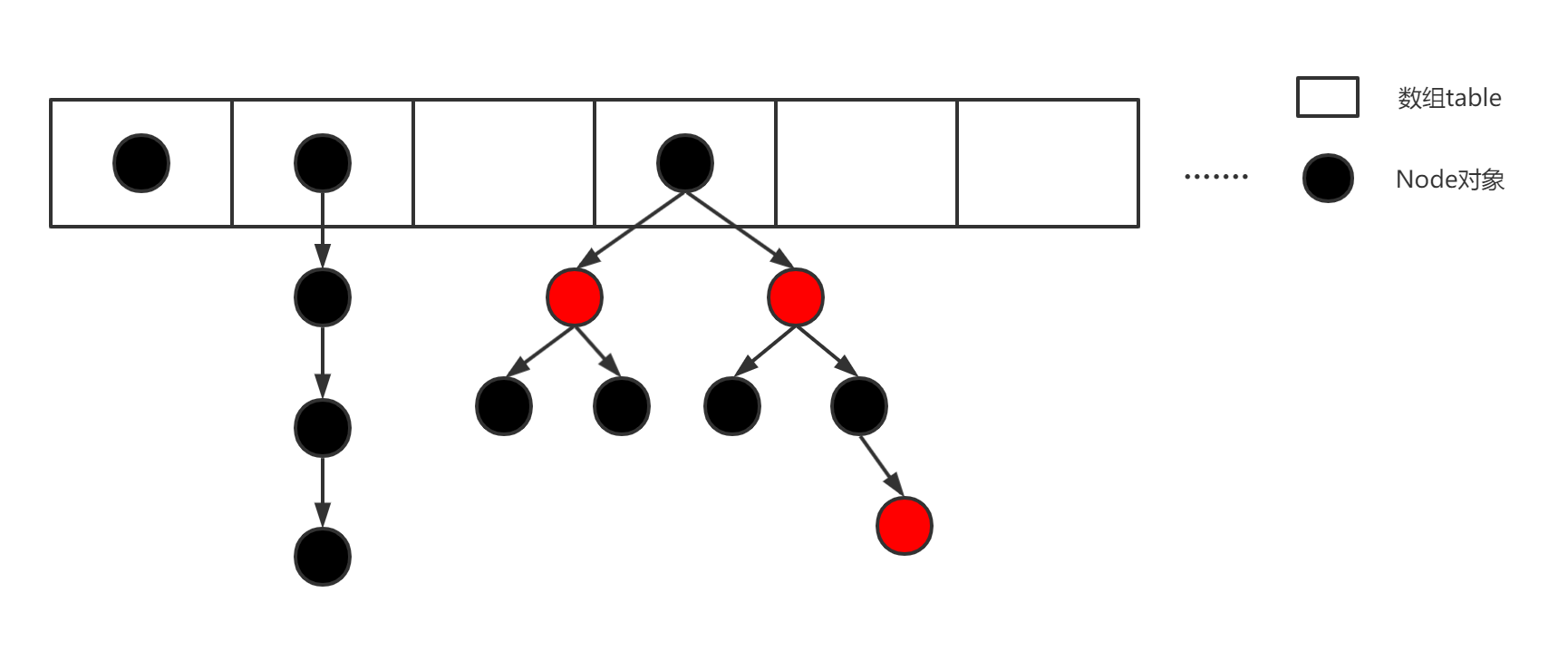
链表转红黑树的条件:
- ① 链表长度 > 8 。
- ② 数组长度 > 64 。
红黑树转链表的条件:链表的长度 < 6 。
7.3 Map 的实现类之二:LinkedHashMap
- LinkedHashMap 是 HashMap 的子类。
- 在 HashMap 存储结构的基础上,使用了一对双向链表来记录添加元素的顺序。
和 LinkedHashSet 类似,LinkedHashMap 可以维护 Map 的迭代顺序:迭代顺序和 key - value 对的插入顺序一致。
示例:
package com.github.map.demo6;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-30 08:35
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
map.put("张三", 18);
map.put("李四", 19);
map.put("王五", 20);
map.put("赵六", 21);
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {
String key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("key:" + key + ",value:" + value);
}
}
}
7.4 Map 的实现类之三:Hashtable
- Hashtable 是个古老的 Map 实现类,JDK1.0 就提供了。不同于 HashMap ,Hashtable 是线程安全的。
- Hashtable 的实现原理和 HashMap 相同,功能相同。底层都是使用哈希表结构,查询速度快,很多情况下可以互用。
- 和 HashMap 不同的是,Hashtable 不允许使用 null 作为 key 和 value 。
- 和 HashMap 相同的是,Hashtable 不能保证 key - value 对的顺序。
- Hashtable 判断两个 key 相等、两个 value 相等的标准,与 HashMap 一致。
7.5 Map 的实现类之四:TreeMap
- TreeMap 存储 Key - Value 对时,需要根据 key - value 对进行排序。
- TreeMap 可以保证所有的 key - value 对处于有序状态。
- TreeMap 底层使用红黑树结构存储数据。
- TreeMap 的 key 的排序:
- 自然排序:TreeMap 的所有的 key 必须实现 Comparable 接口,而且所有的 key 应该是同一个类的对象,否则将会抛出 ClasssCastException 。
- 定制排序:创建 TreeMap 时,传入一个Comparator 对象,该对象负责对TreeMap中的所有key进行排序。此时不需要 Map 的 key 实现 Comparable 接口。
TreeMap 判断两个 key 相等的标准:两个 key 通过 compareTo() 方法或者 compare() 方法返回 0 。
示例:
package com.github.map.demo7;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-30 09:04
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("c", 25);
map.put("h", 18);
map.put("a", 21);
map.put("b", 98);
System.out.println("map = " + map);
}
}
- 示例:
package com.github.map.demo8;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-30 09:06
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Person, String> map = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<Person>() {
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();
}
});
map.put(new Person("张三", 18), "大一");
map.put(new Person("李四", 20), "大一");
map.put(new Person("王五", 19), "大二");
map.put(new Person("赵六", 23), "大四");
map.put(new Person("田七", 17), "大一");
System.out.println("map = " + map);
}
}
7.6 Map 的实现类之五:Properties
- Properties 类是 Hashtable 的子类,该对象是用来处理属性文件的。
- 由于属性文件的 key 和 value 都是字符串类型,所以 Properties 里的 key 和 value 都是字符串类型。
存取数据的时候,建议使用 setPropert y和 getProperty 方法。
示例:
package com.github.map.demo9;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-09-30 09:16
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("hello", "你好");
properties.setProperty("world", "世界");
String hello = properties.getProperty("hello");
System.out.println("hello = " + hello);
String world = properties.getProperty("world");
System.out.println("world = " + world);
Enumeration<?> enumeration = properties.propertyNames();
while (enumeration.hasMoreElements()) {
Object key = enumeration.nextElement();
Object value = properties.get(key);
System.out.println("key = " + key + ",value = " + value);
}
for (String name : properties.stringPropertyNames()) {
String property = properties.getProperty(name);
System.out.println("key = " + name + ",value = " + property);
}
}
}

