本文所使用的文件在这里 附件.zip。
第一章:存储相关概念
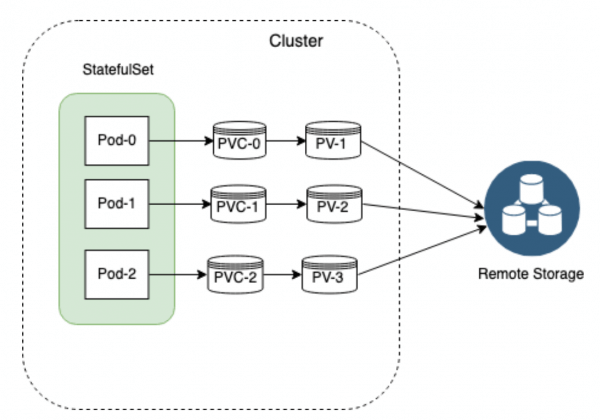
- 在容器世界中,无状态是一个核心原则,然而我们始终需要保存数据,并提供给他人进行访问,所以就需要一个方案用于保持数据,以备重启之需。
- 在 Kubernetes 中,PVC 是管理有状态应用的一个推荐方案。有了 PVC 的帮助,Pod 可以申请并连接到存储卷,这些存储卷在 Pod 生命周期结束之后,还能独立存在。
- PVC 在存储方面让开发和运维的职责得以分离。运维人员负责供应存储,而开发人员则可以在不知后端细节的情况下,申请使用这些存储卷。
- PVC 由一系列组件构成:
- PVC:是 Pod 对存储的请求。PVC 会被 Pod 动态加载成为一个存储卷。
- PV,可以由运维手工分配,也可以使用
StorageClass动态分配。PV 受 Kubernetes 管理,但并不与特定的 Pod 直接绑定。 - StorageClass:由管理员创建,可以用来动态的创建存储卷和 PV。
- 物理存储:实际连接和加载的存储卷。
- 分布式存储系统是一个有效的解决有状态工作负载高可用问题的方案。Ceph 就是一个分布式存储系统,近年来其影响主键扩大。Rook 是一个编排器,能够支持包括 Ceph 在内的多种存储方案。Rook 简化了 Ceph 在 Kubernetes 集群中的部署过程。
- 在生产环境中使用 Rook + Ceph 组合的用户正在日益增加,尤其是自建数据中心的用户,CENGNopen in new window、Gini、GPR 等很多组织都在进行评估。
第二章 Ceph
- Ceph 可以有如下的功能:
- Ceph 对象存储:键值存储,其接口就是简单的 GET,PUT,DEL 等。如七牛,阿里云 oss 等。
- Ceph 块设备:AWS 的 EBS ,青云的云硬盘和阿里云的盘古系统,还有Ceph的RBD(RBD 是 Ceph 面向块存储的接口)
- Ceph 文件系统:它比块存储具有更丰富的接口,需要考虑目录、文件属性等支持,实现一个支持并行化的文件存储应该是最困难的。
- 一个 Ceph 存储集群需要
- 至少一个 Ceph 监视器、Ceph 管理器、Ceph OSD(对象存储守护程序)
- 需要运行 Ceph 文件系统客户端,则需要部署 Ceph Metadata Server。
- Monitors: Ceph Monitor (
ceph-mon) 监视器:维护集群状态信息- 维护集群状态的映射,包括监视器映射,管理器映射,OSD 映射,MDS 映射和 CRUSH 映射。
- 这些映射是 Ceph 守护程序相互协调所必需的关键群集状态。
- 监视器还负责管理守护程序和客户端之间的身份验证。
- 通常至少需要三个监视器(这也是为什么需要三个 Node 节点的原因所在)才能实现冗余和高可用性。
- Managers: Ceph Manager 守护进程(
ceph-mgr) : 负责跟踪运行时指标和 Ceph 集群的当前状态- Ceph Manager 守护进程(ceph-mgr)负责跟踪运行时指标和 Ceph 集群的当前状态
- 包括存储利用率,当前性能指标和系统负载。
- Ceph Manager 守护程序还托管基于 python 的模块,以管理和公开 Ceph 集群信息,包括基于 Web 的 Ceph Dashboard 和REST API 。
- 通常,至少需要两个管理器才能实现高可用性。
- Ceph OSDs: Ceph OSD (对象存储守护进程,
ceph-osd) 【存储数据】- 通过检查其他 Ceph OSD 守护程序的心跳来存储数据,处理数据复制,恢复,重新平衡,并向 Ceph 监视器和管理器提供一些监视信息。
- 通常至少需要 3 个 Ceph OSD 才能实现冗余和高可用性。
- MDSs: Ceph Metadata Server (MDS,
ceph-mdsceph 元数据服务器)- 存储能代表 Ceph File System 的元数据(如:Ceph 块设备和 Ceph 对象存储不使用 MDS)。
- Ceph 元数据服务器允许 POSIX 文件系统用户执行基本命令(如 ls,find 等),而不会给 Ceph 存储集群带来巨大负担。
第三章 Rook
3.1 基本概念
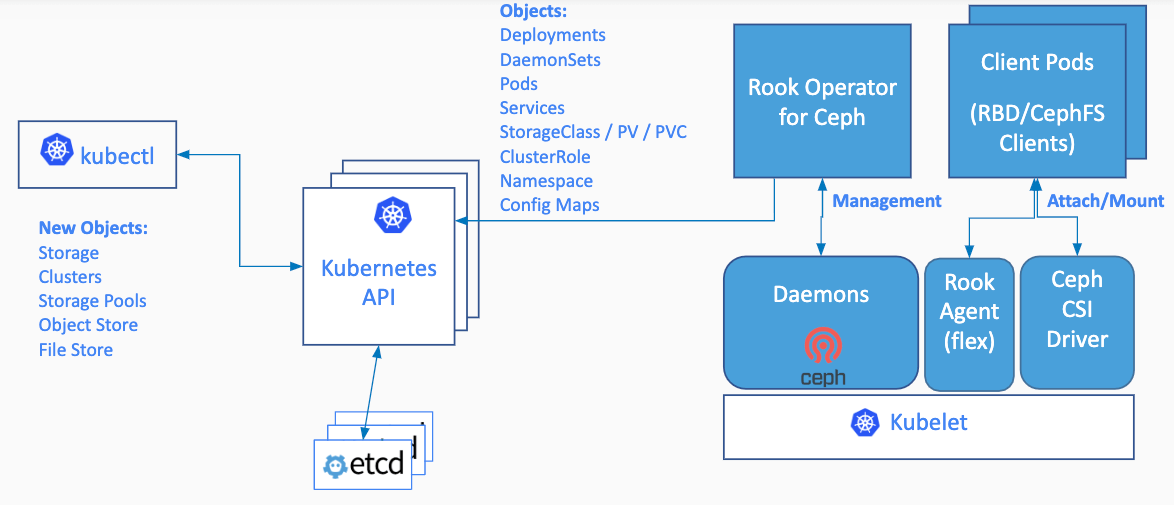
- Rook 是云原生平台的存储编排工具。
- Rook 工作原理如下:
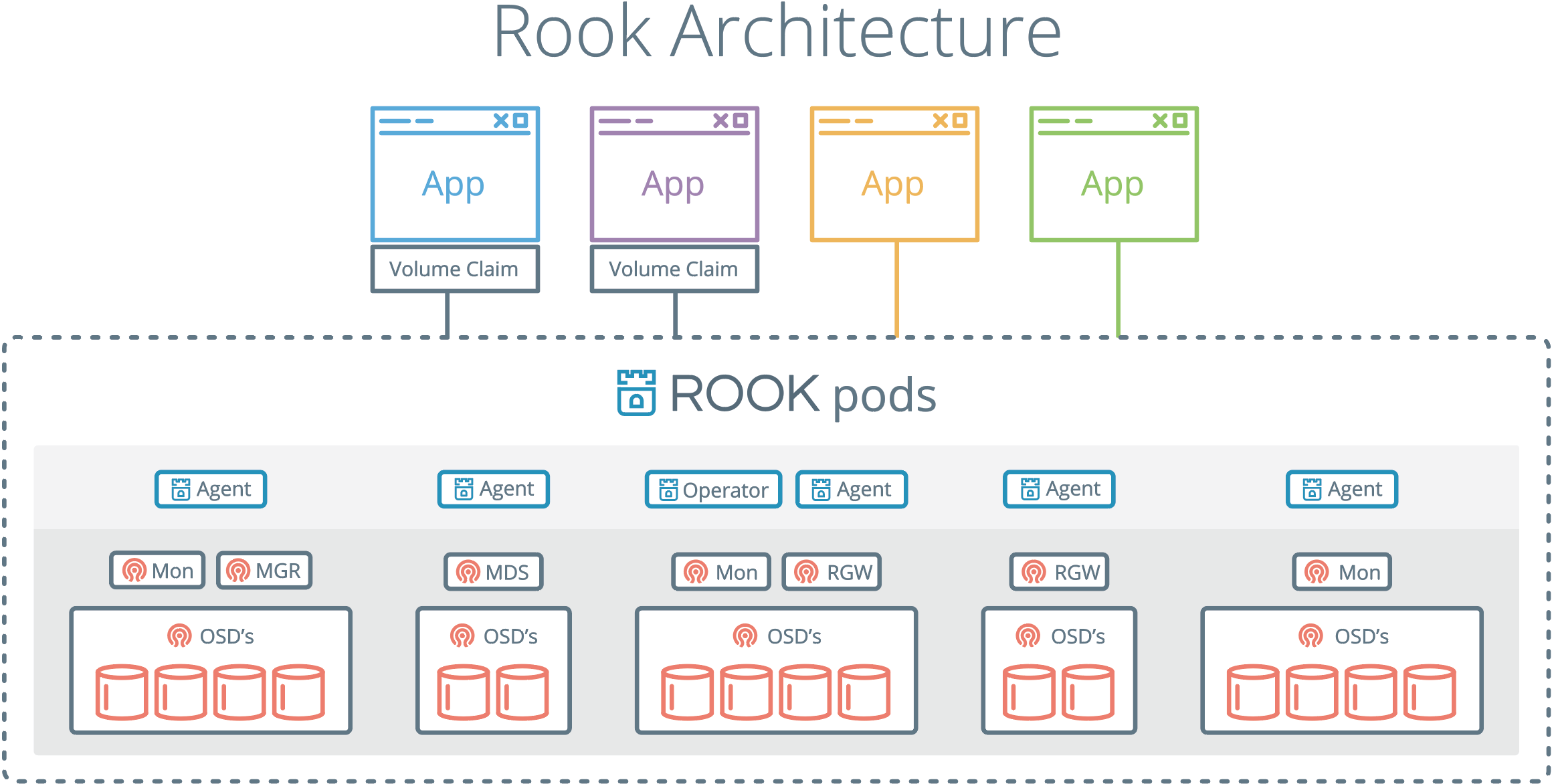
- Rook 的架构图如下:
3.2 Operator 是什么?
- k8s 中 Operator + CRD(CustomResourceDefinitions【k8s自定义资源类型】),可以快速帮我们部署一些有状态应用集群,如redis,mysql,Zookeeper 等。
- Rook 的 Operator 是 k8s 集群和存储集群之间进行交互的解析器。
很多时候,我们在进行 k8s 的二次开发的时候就需要使用到 CRD + Operator 。
第四章 部署
4.1 前提条件
- Kubernetes 的版本必须是 v1.17 以上版本。
- Kubernetes 集群各个节点主机需要安装 lvm2 :
yum -y install lvm2
- Kubernetes 集群各节点主机内核版本不低于 4.17 。
- Kubernetes 集群至少有 3 个工作节点,为了配置 Ceph 存储集群,至少需要以下本地存储选项之一:
- 原始设备(无分区或格式化文件系统)。
- 原始分区(无格式化文件系统)。
block模式下存储类中可用的 PV 。
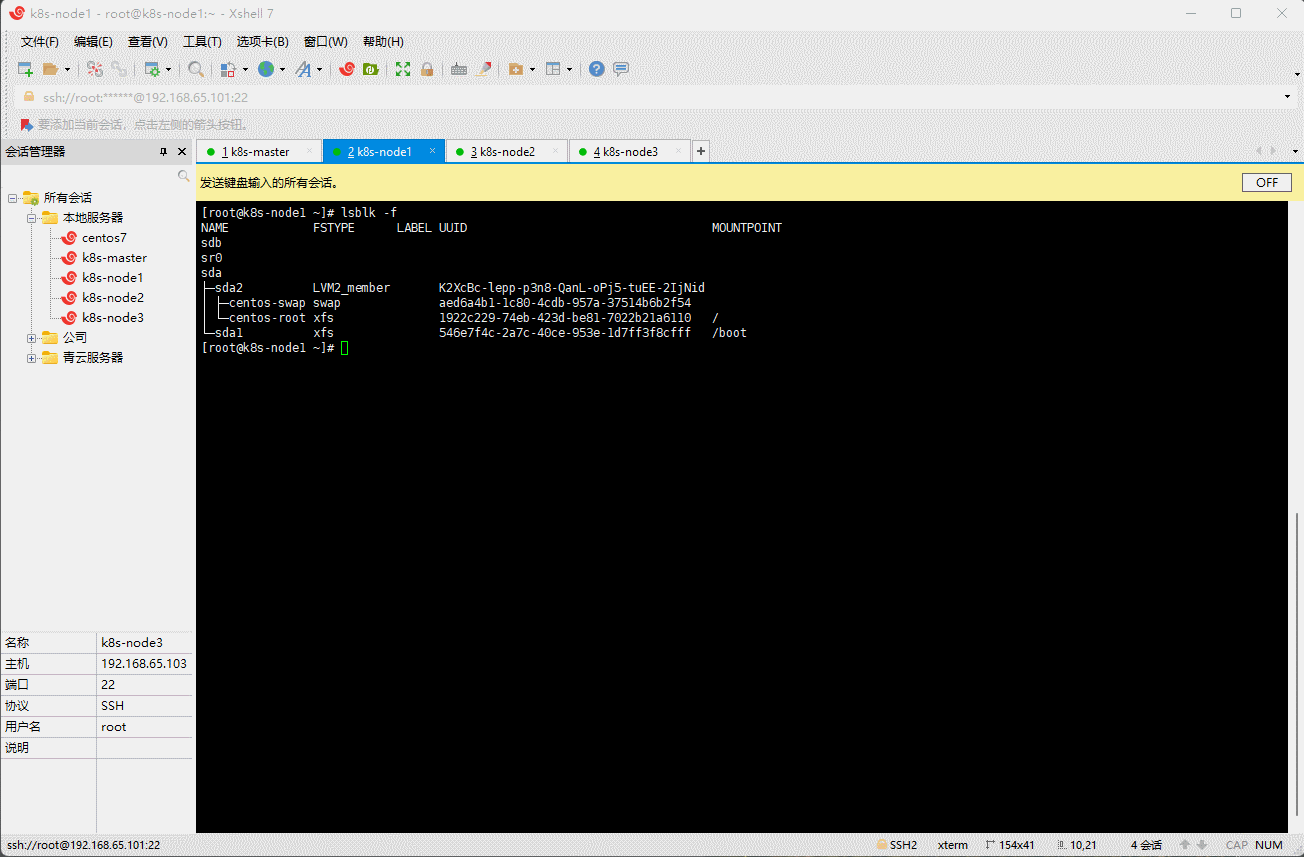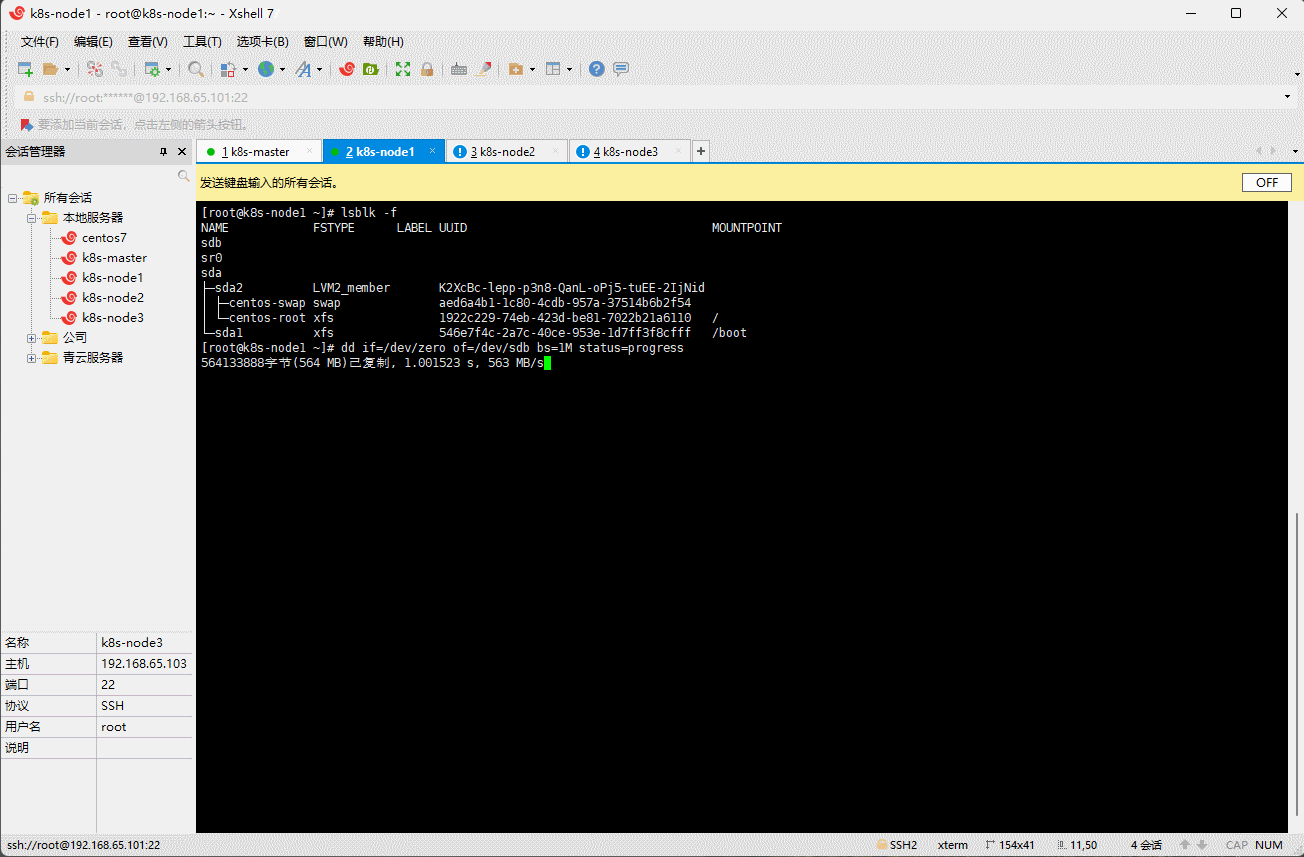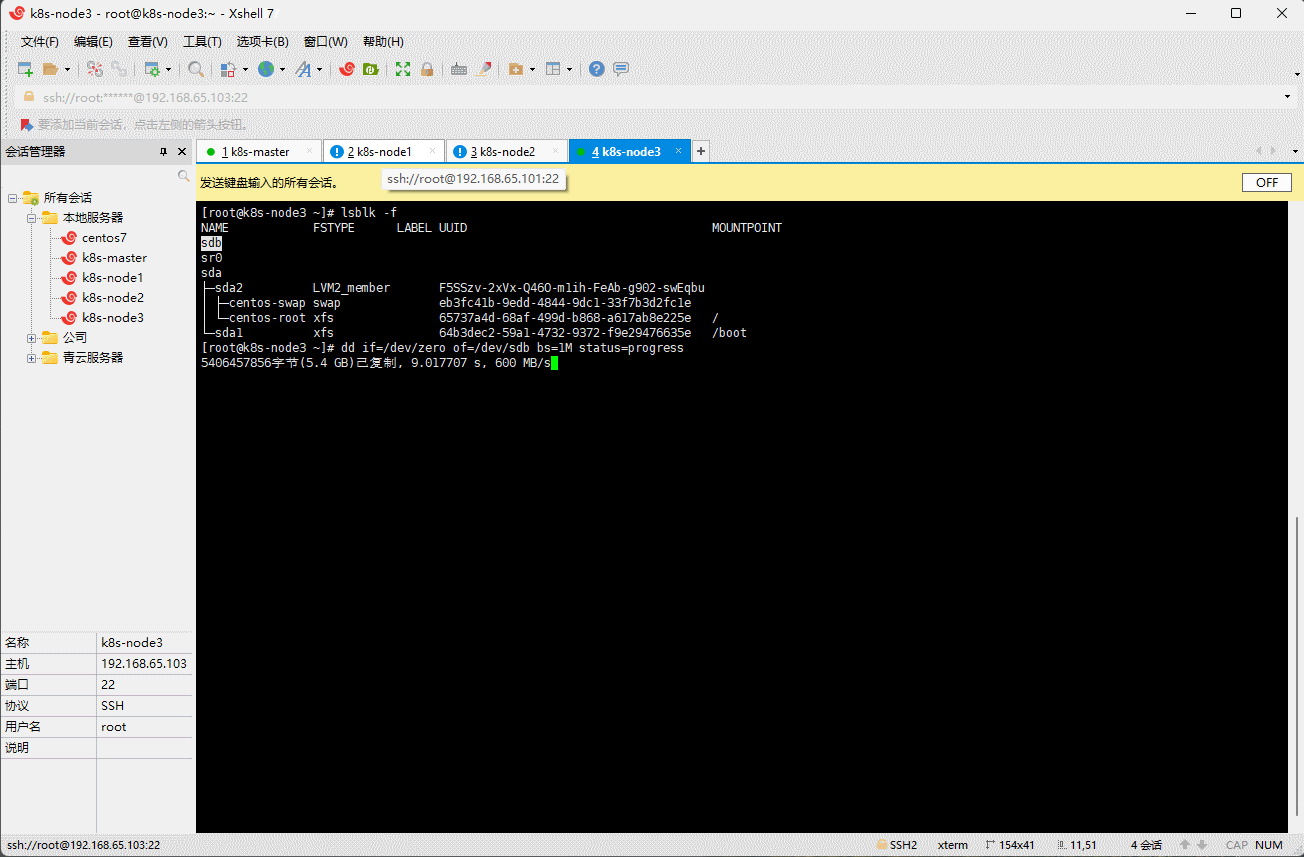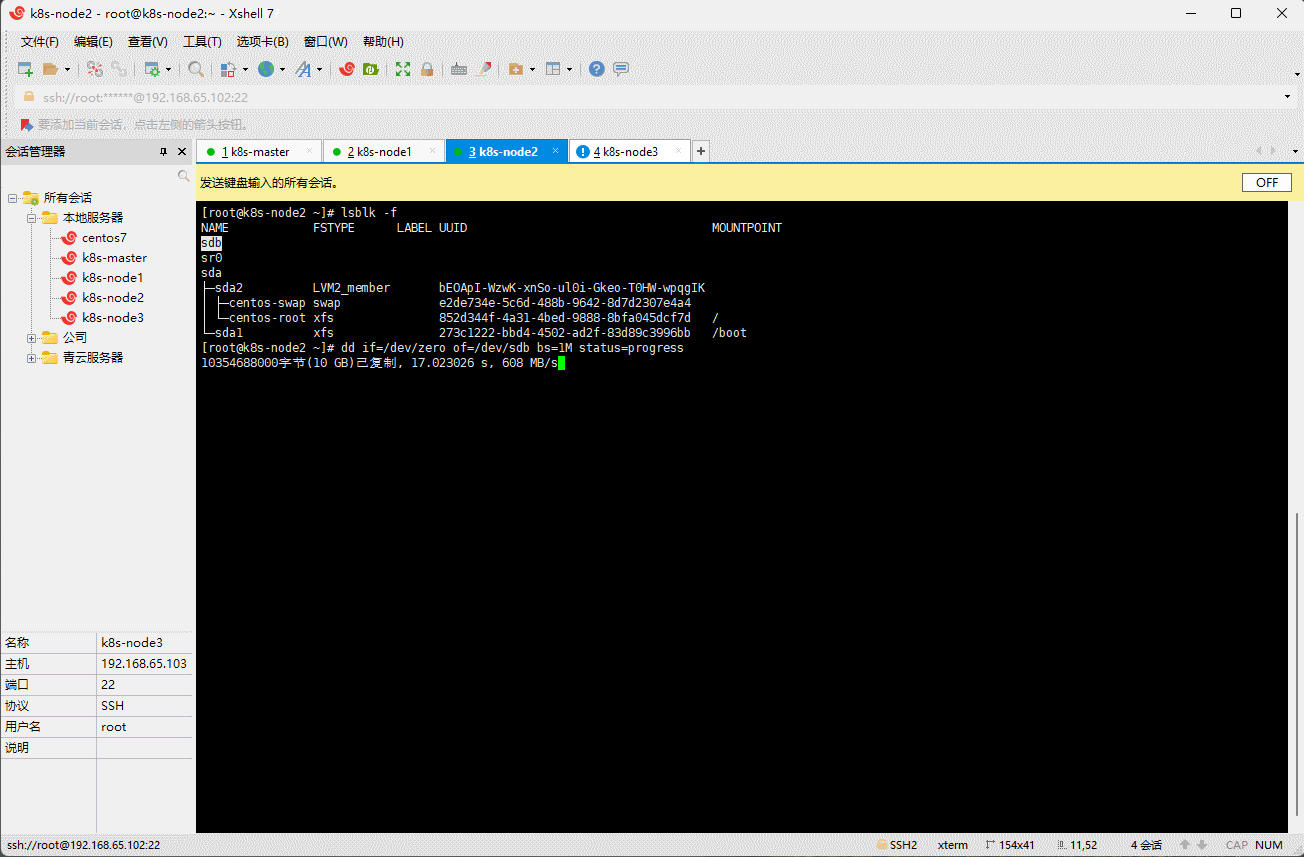
- 我们可以使用以下命令确认我们的分区或设备是否为格式化文件系统:
lsblk -f
NAME FSTYPE LABEL UUID MOUNTPOINTvda└─vda1 LVM2_member >eSO50t-GkUV-YKTH-WsGq-hNJY-eKNf-3i07IB├─ubuntu--vg-root ext4 c2366f76-6e21-4f10-a8f3-6776212e2fe4 /└─ubuntu--vg-swap_1 swap 9492a3dc-ad75-47cd-9596-678e8cf17ff9 [SWAP]vdb
- 如果该
FSTYPE字段不为空,则在相应设备的顶部有一个文件系统。在这种情况下,您可以将 vdb 用于 Ceph,而不能使用 vda 及其分区。
注意:云厂商需要磁盘清零,假设
lsblk -f命令查询的结果是 vdc ,那么就需要执行dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/vdc bs=1M status=progress命令。
- 在 VMware 中的 k8s-node1 和 k8s-node2 以及 K8s-node3 节点添加硬盘,本次只以 k8s-node1 为例,其余节点依次类推即可:
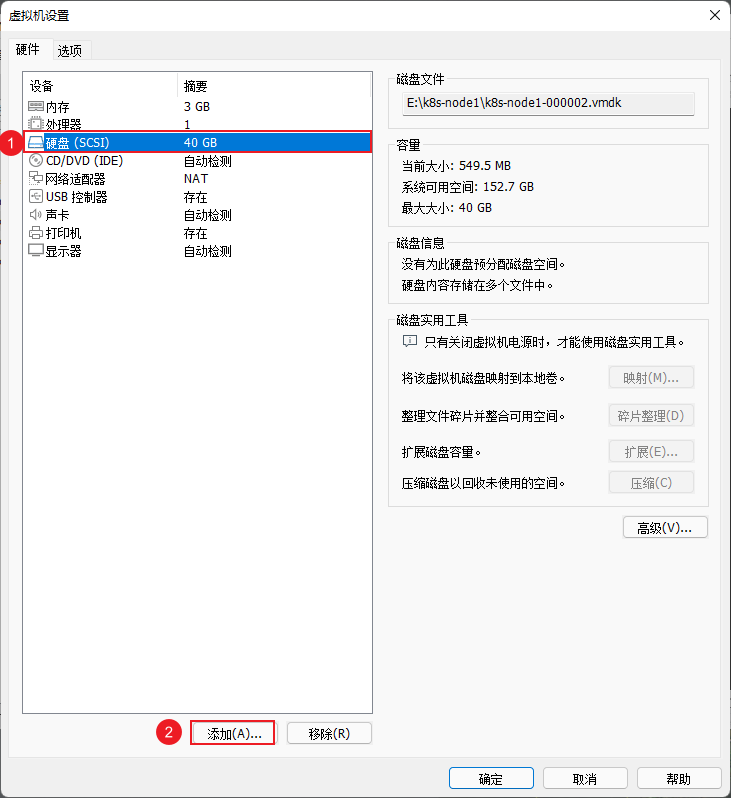
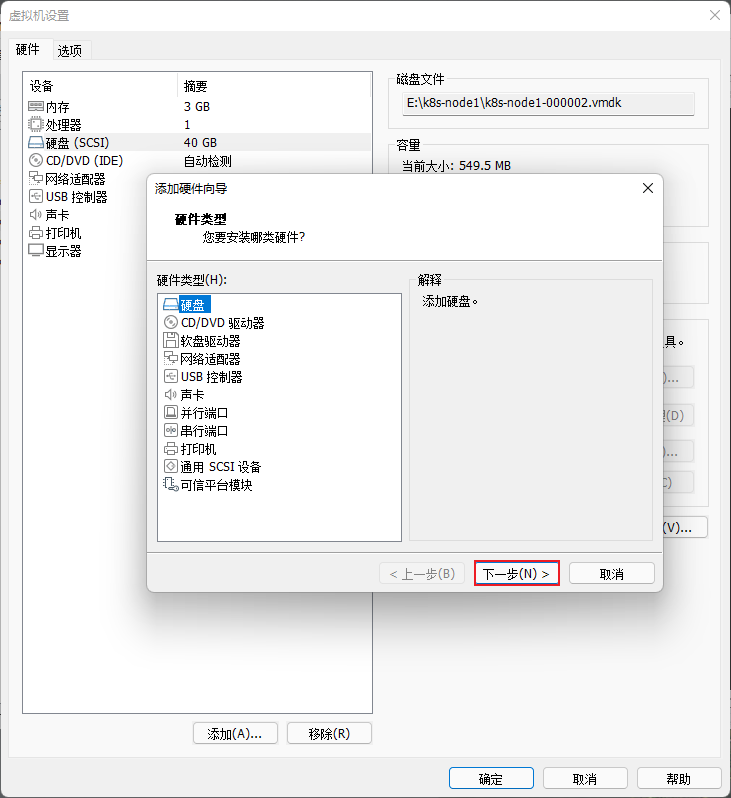
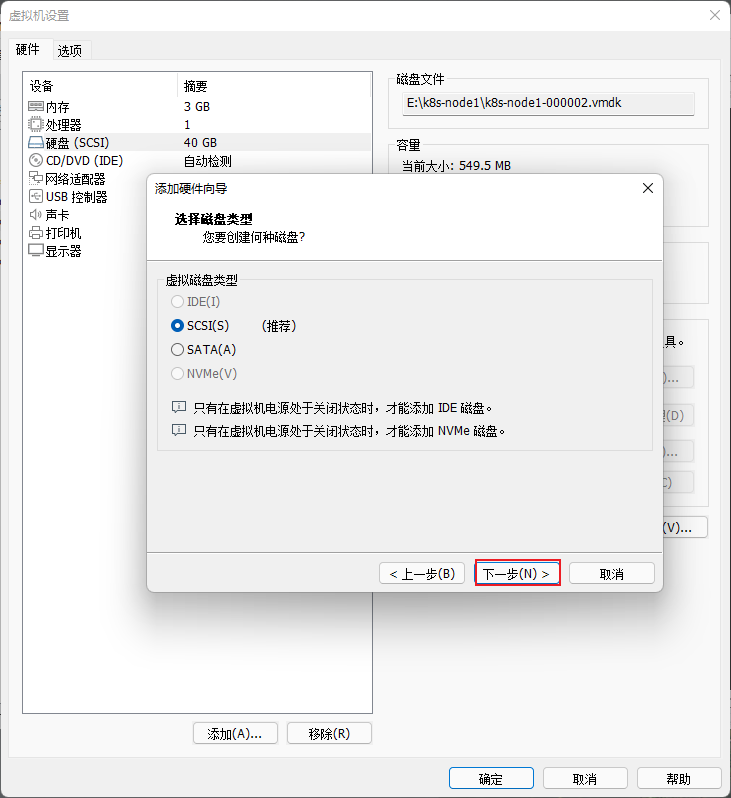
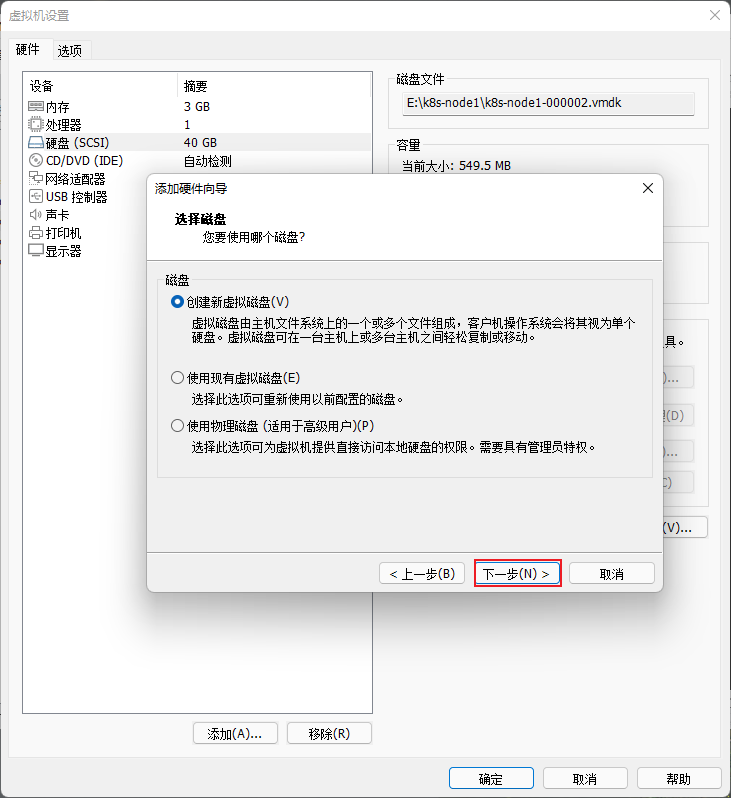
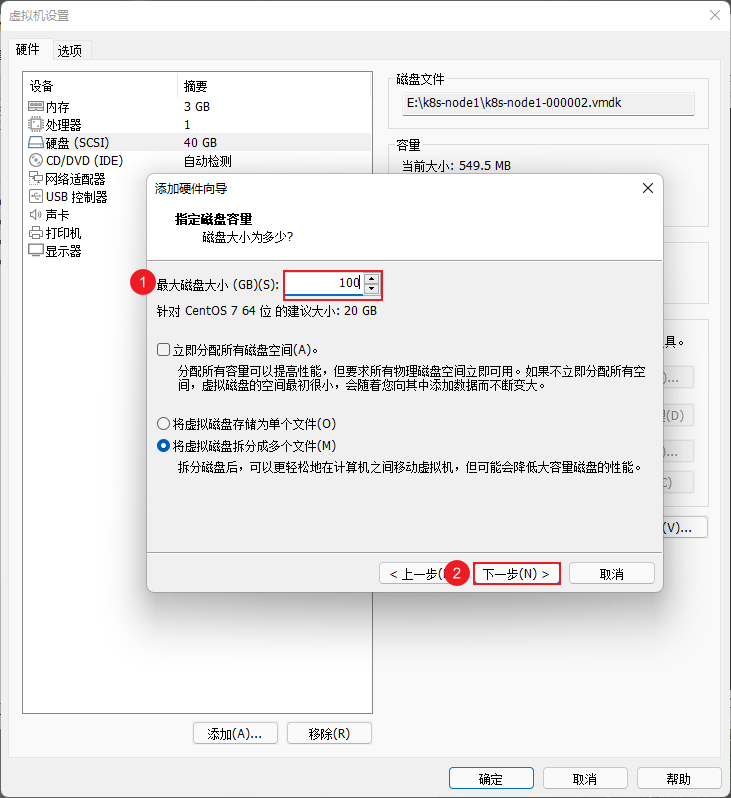
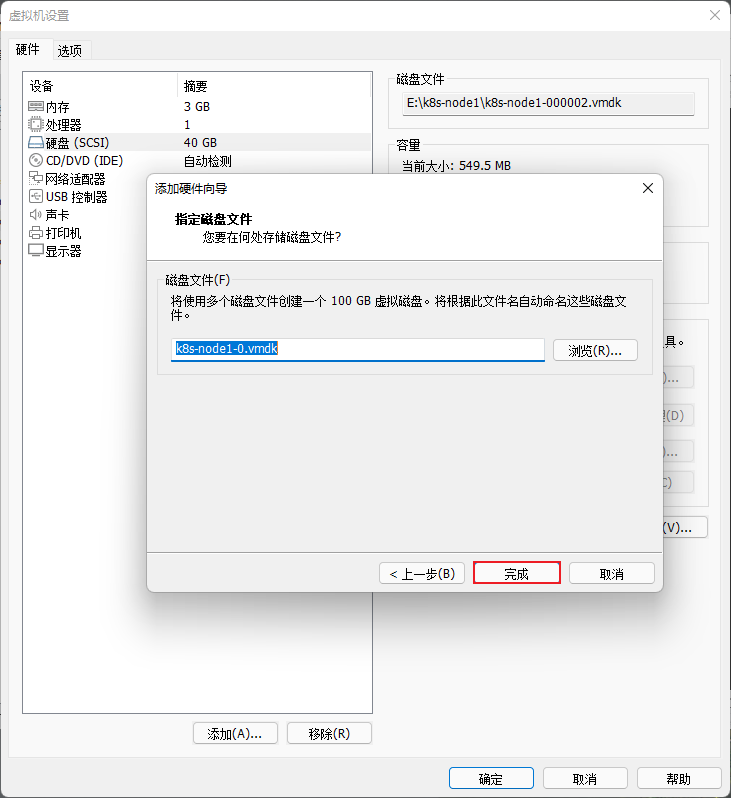
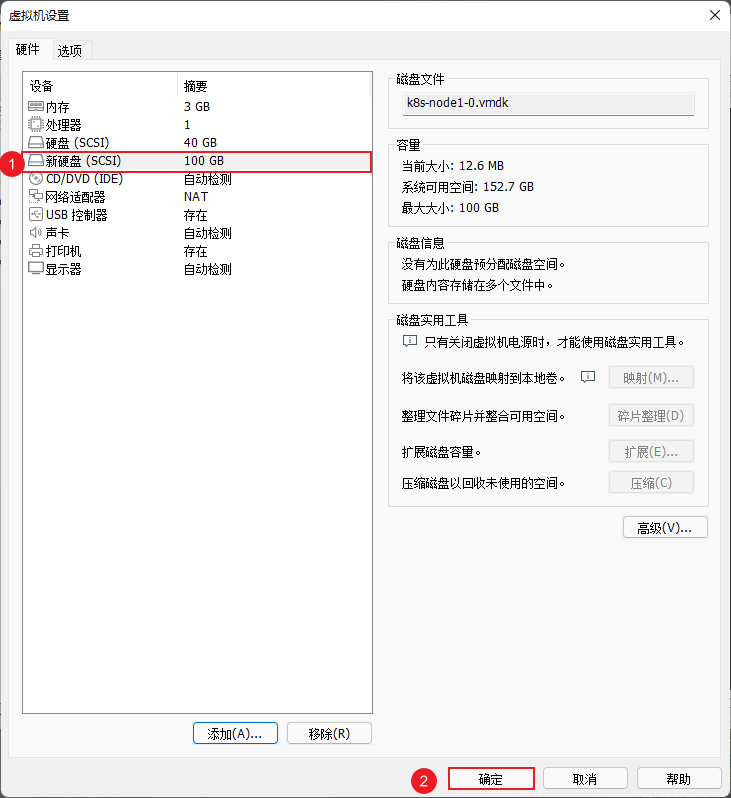
注意:将 k8s-node1 、k8s-node2 以及 k8s-node3 节点重启一下。
- 查看 k8s-node1 、k8s-node2 和 k8s-node3 节点的分区或设备是否为格式化文件系统:
lsblk -f
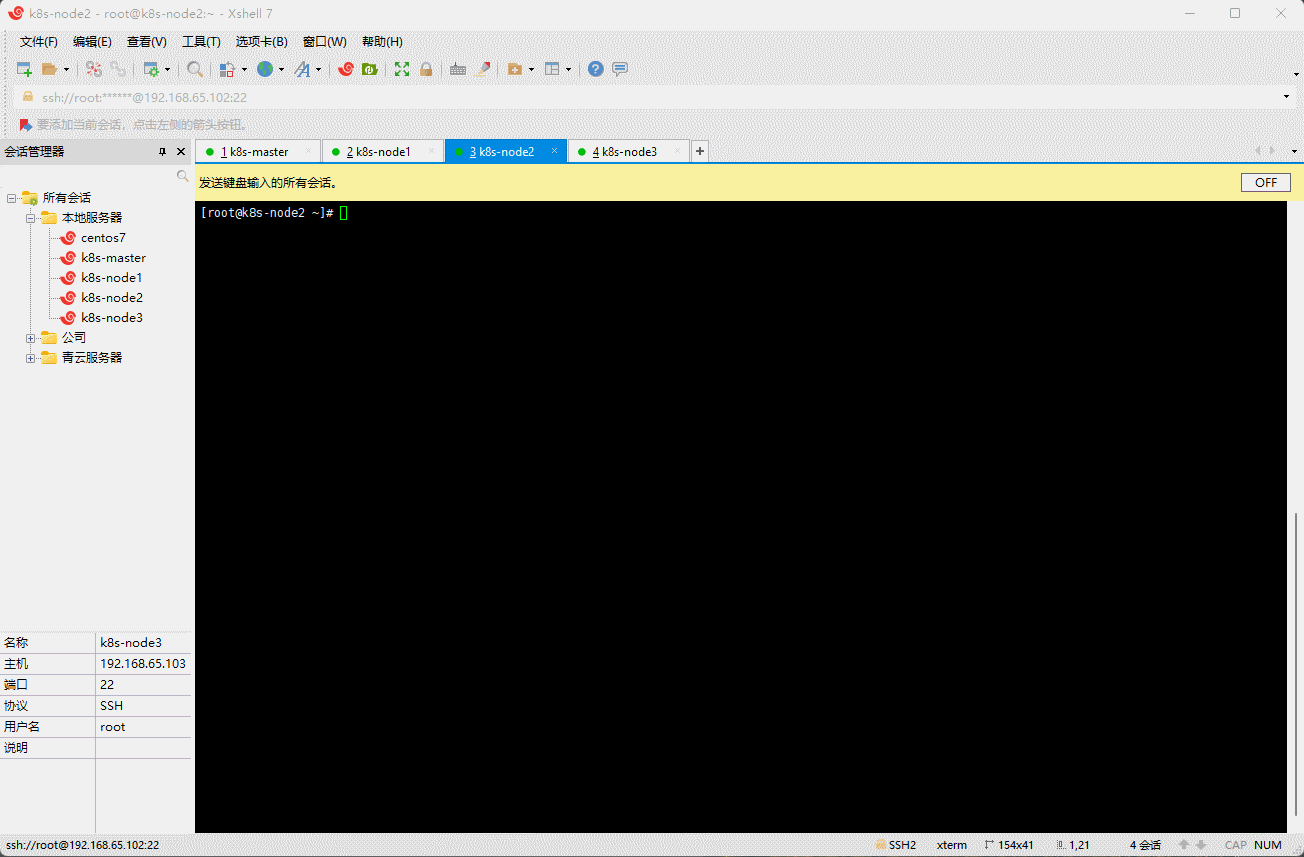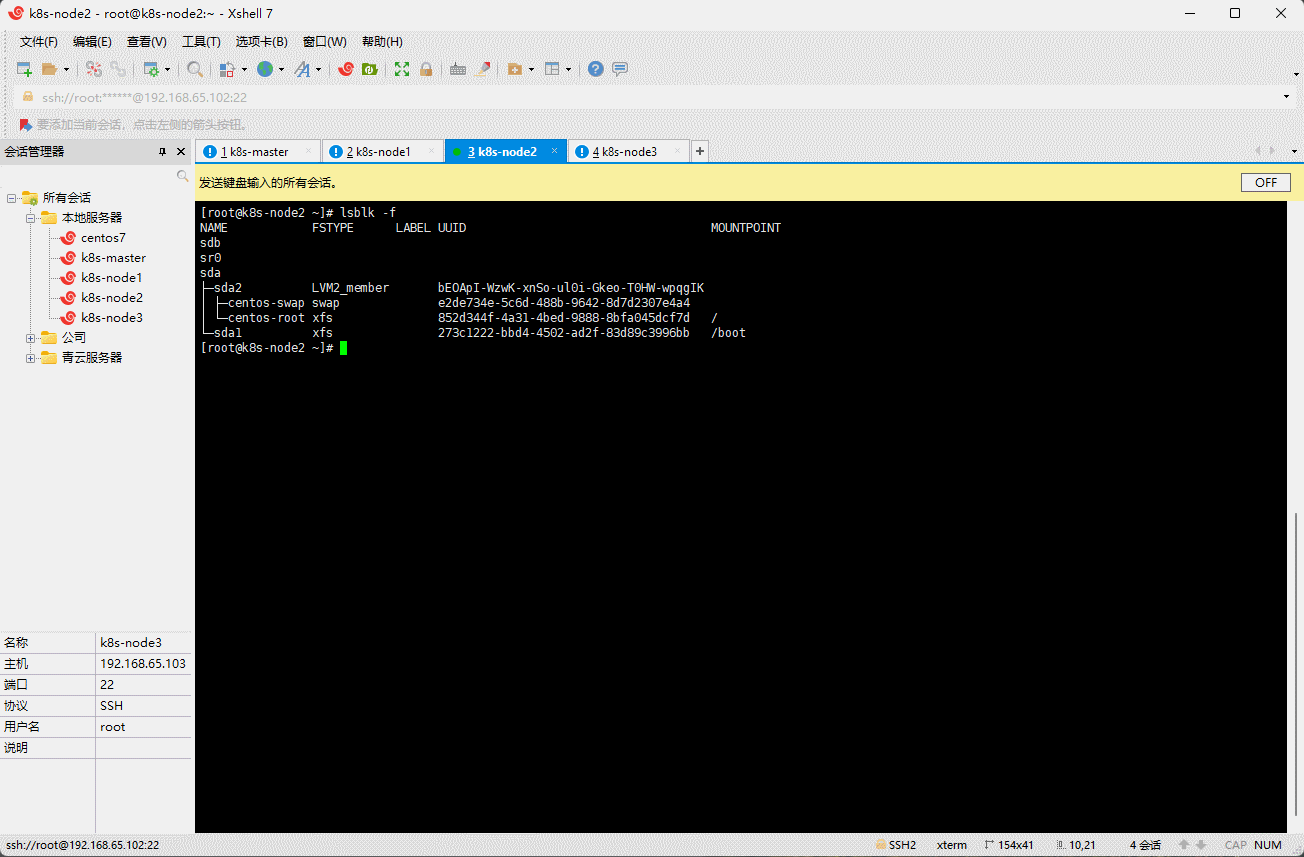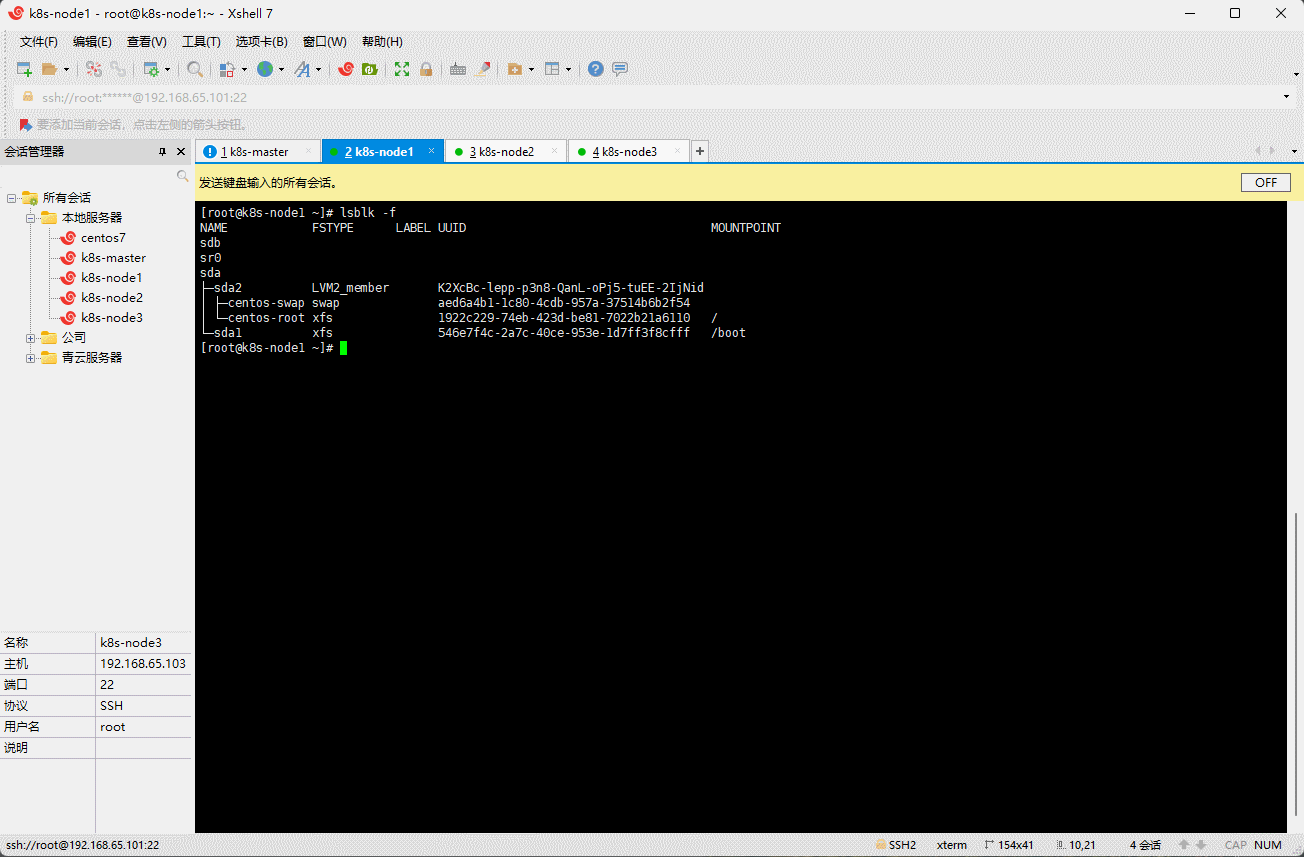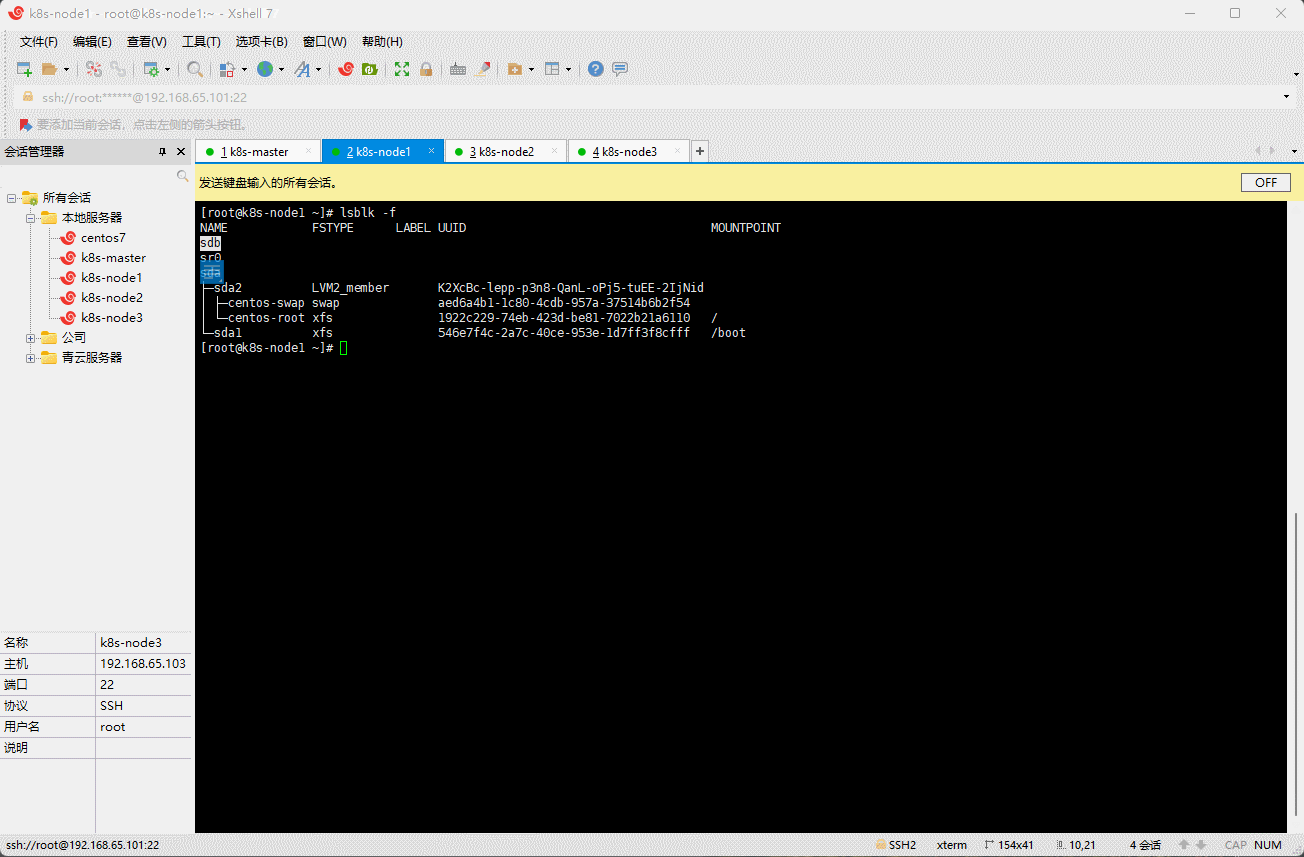
- 对 k8s-node1 、k8s-node2 和 k8s-node3 节点的无格式化系统进行清零:
dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdb bs=1M status=progress
4.2 部署 & 修改 Operator
- 下载 rook 的源码:
wget https://github.com/rook/rook/archive/refs/tags/v1.9.2.zip
- 解压:
unzip v1.9.2.zip
- 进入 examples 目录:
cd rook-1.9.2/deploy/examples

- 修改 operator.yaml 文件(修改好的文件在这里 operator.yaml):
vi operator.yaml
kind: ConfigMapapiVersion: v1metadata:name: rook-ceph-operator-confignamespace: rook-cephdata:ROOK_LOG_LEVEL: "INFO"ROOK_CSI_ENABLE_CEPHFS: "true"ROOK_CSI_ENABLE_RBD: "true"ROOK_CSI_ENABLE_NFS: "false"ROOK_CSI_ENABLE_GRPC_METRICS: "false"CSI_ENABLE_ENCRYPTION: "false"CSI_PROVISIONER_REPLICAS: "2"CSI_ENABLE_CEPHFS_SNAPSHOTTER: "true"CSI_ENABLE_RBD_SNAPSHOTTER: "true"CSI_FORCE_CEPHFS_KERNEL_CLIENT: "true"CSI_RBD_FSGROUPPOLICY: "ReadWriteOnceWithFSType"CSI_CEPHFS_FSGROUPPOLICY: "ReadWriteOnceWithFSType"CSI_NFS_FSGROUPPOLICY: "ReadWriteOnceWithFSType"ROOK_CSI_ALLOW_UNSUPPORTED_VERSION: "false"CSI_PLUGIN_ENABLE_SELINUX_HOST_MOUNT: "false"# 原来# these images to the desired release of the CSI driver.# ROOK_CSI_CEPH_IMAGE: "quay.io/cephcsi/cephcsi:v3.6.1"# ROOK_CSI_REGISTRAR_IMAGE: "k8s.gcr.io/sig-storage/csi-node-driver-registrar:v2.5.0"# ROOK_CSI_RESIZER_IMAGE: "k8s.gcr.io/sig-storage/csi-resizer:v1.4.0"# ROOK_CSI_PROVISIONER_IMAGE: "k8s.gcr.io/sig-storage/csi-provisioner:v3.1.0"# ROOK_CSI_SNAPSHOTTER_IMAGE: "k8s.gcr.io/sig-storage/csi-snapshotter:v5.0.1"# ROOK_CSI_ATTACHER_IMAGE: "k8s.gcr.io/sig-storage/csi-attacher:v3.4.0"# ROOK_CSI_NFS_IMAGE: "k8s.gcr.io/sig-storage/nfsplugin:v3.1.0"# 打开注释,进行修改# ------------ 修改 -------------ROOK_CSI_CEPH_IMAGE: "ccr.ccs.tencentyun.com/cephcsi/cephcsi:v3.6.1"ROOK_CSI_REGISTRAR_IMAGE: "ccr.ccs.tencentyun.com/sig-storage/csi-node-driver-registrar:v2.5.0"ROOK_CSI_RESIZER_IMAGE: "ccr.ccs.tencentyun.com/sig-storage/csi-resizer:v1.4.0"ROOK_CSI_PROVISIONER_IMAGE: "ccr.ccs.tencentyun.com/sig-storage/csi-provisioner:v3.1.0"ROOK_CSI_SNAPSHOTTER_IMAGE: "ccr.ccs.tencentyun.com/sig-storage/csi-snapshotter:v5.0.1"ROOK_CSI_ATTACHER_IMAGE: "ccr.ccs.tencentyun.com/sig-storage/csi-attacher:v3.4.0"ROOK_CSI_NFS_IMAGE: "ccr.ccs.tencentyun.com/sig-storage/nfsplugin:v3.1.0"# ------------ 修改 ----------------apiVersion: apps/v1kind: Deploymentmetadata:name: rook-ceph-operatornamespace: rook-cephlabels:operator: rookstorage-backend: cephapp.kubernetes.io/name: rook-cephapp.kubernetes.io/instance: rook-cephapp.kubernetes.io/component: rook-ceph-operatorapp.kubernetes.io/part-of: rook-ceph-operatorspec:selector:matchLabels:app: rook-ceph-operatorreplicas: 1template:metadata:labels:app: rook-ceph-operatorspec:serviceAccountName: rook-ceph-systemcontainers:- name: rook-ceph-operator# ------------ 修改 -------------image: ccr.ccs.tencentyun.com/k8s-rook/ceph:v1.9.2 # 原来 rook/ceph:v1.9.2# ------------ 修改 -------------args: ["ceph", "operator"]securityContext:runAsNonRoot: truerunAsUser: 2016runAsGroup: 2016

- 安装:
kubectl create -f crds.yaml -f common.yaml -f operator.yaml

4.3 部署集群
- 修改
cluster.yaml使用我们指定的磁盘当做存储节点即可(修改好的文件在这里cluster.yaml):
vi cluster.yaml
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1kind: CephClustermetadata:name: rook-cephnamespace: rook-cephspec:cephVersion:# ------------ 修改 -------------image: ccr.ccs.tencentyun.com/k8s-ceph/ceph:v16.2.7 # 原来是 quay.io/ceph/ceph:v16.2.7# ------------ 修改 -------------allowUnsupported: falsedataDirHostPath: /var/lib/rookskipUpgradeChecks: falsecontinueUpgradeAfterChecksEvenIfNotHealthy: falsewaitTimeoutForHealthyOSDInMinutes: 10mon:count: 3allowMultiplePerNode: falsemgr:count: 2allowMultiplePerNode: falsemodules:- name: pg_autoscalerenabled: truedashboard:enabled: truessl: truemonitoring:enabled: falsenetwork:connections:encryption:enabled: falsecompression:enabled: falsecrashCollector:disable: falsecleanupPolicy:confirmation: ""sanitizeDisks:method: quickdataSource: zeroiteration: 1allowUninstallWithVolumes: falseannotations:labels:resources:removeOSDsIfOutAndSafeToRemove: falsepriorityClassNames:mon: system-node-criticalosd: system-node-criticalmgr: system-cluster-criticalstorage: # cluster level storage configuration and selection# ------------ 修改 -------------useAllNodes: falseuseAllDevices: falseconfig:osdsPerDevice: '3' # 每个设备的 osd 数量nodes:- name: "k8s-node1" # 必须符合 kubernetes.io/hostname ,通过 kubectl get nodes --show-labels 查看devices:- name: "sdb"- name: "k8s-node2"devices:- name: "sdb"- name: "k8s-node3"devices:- name: "sdb"# ------------ 修改 -------------onlyApplyOSDPlacement: false

- 安装:
kubectl create -f cluster.yaml
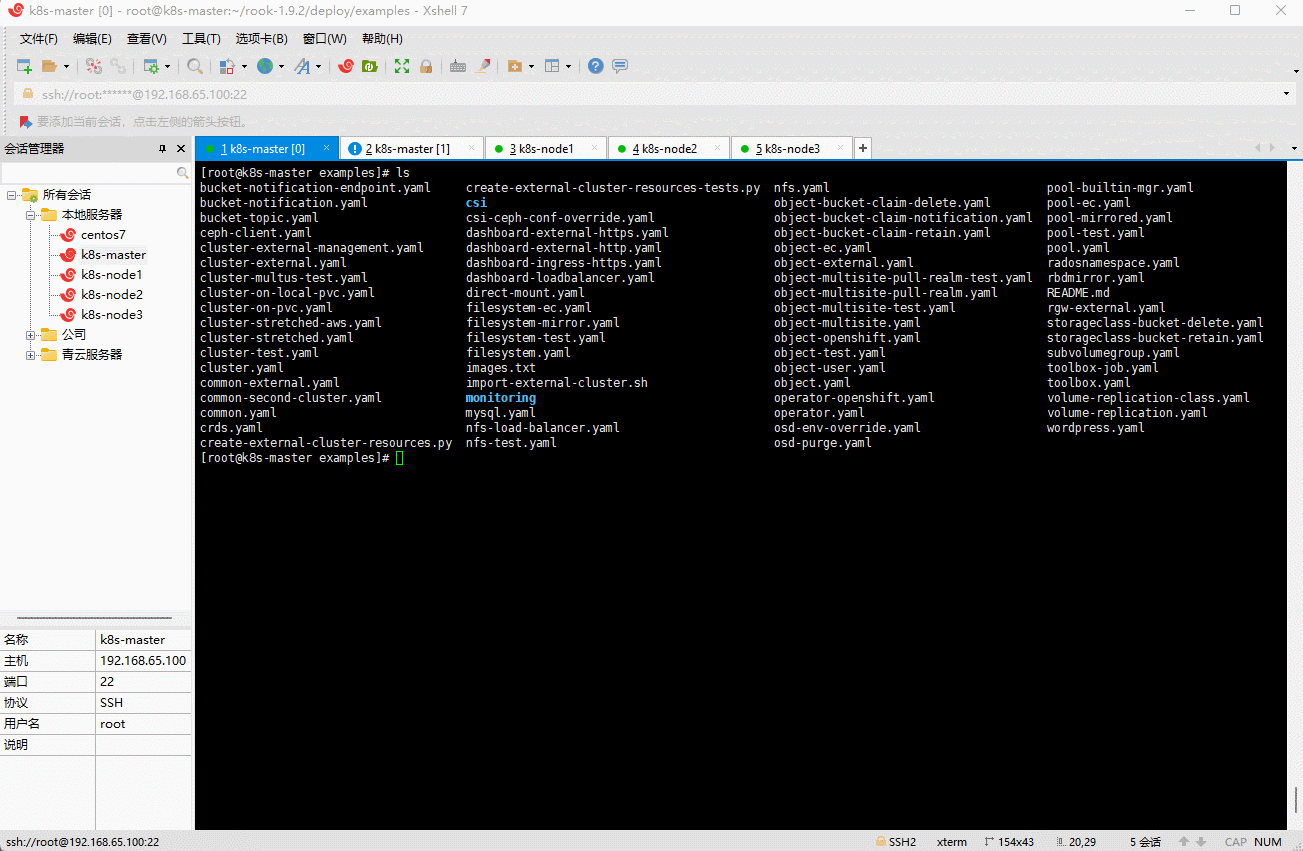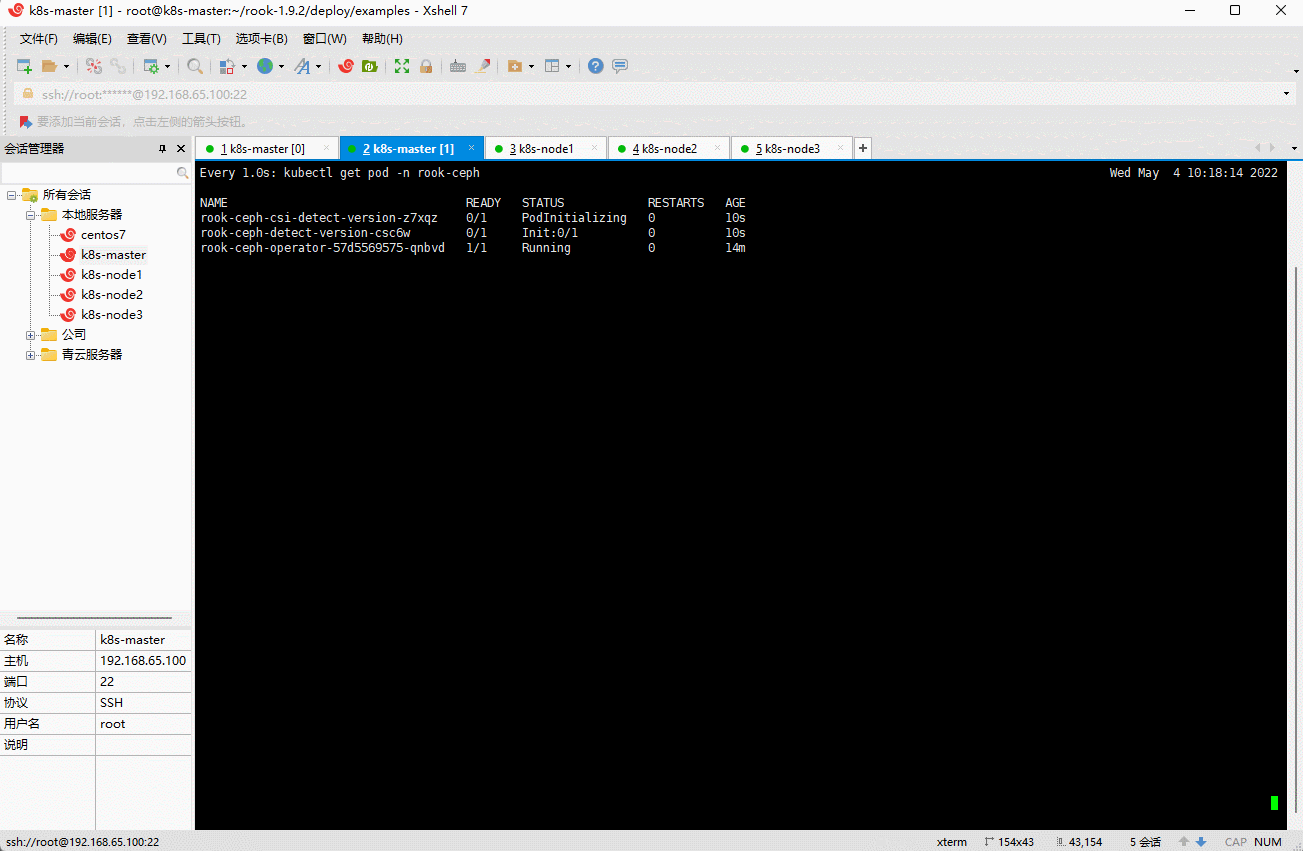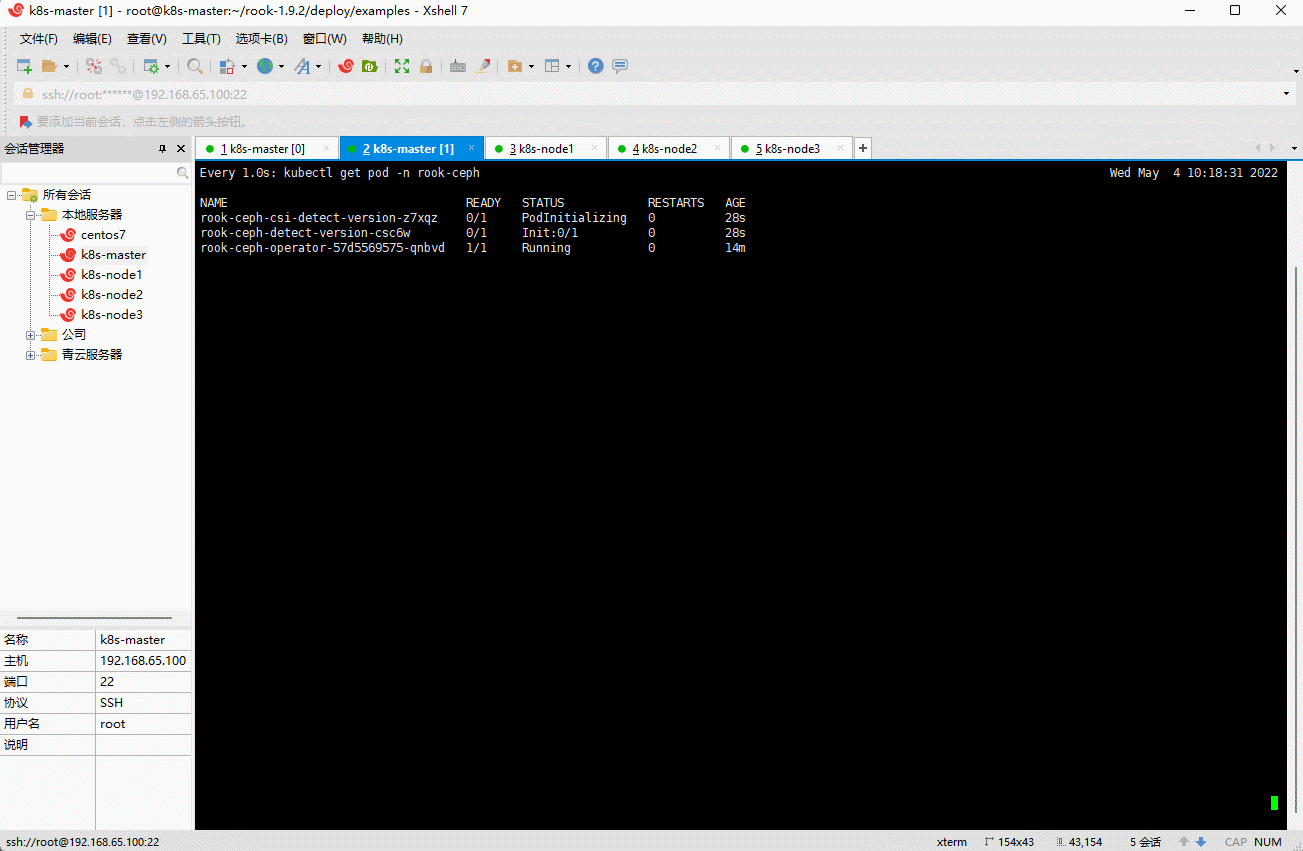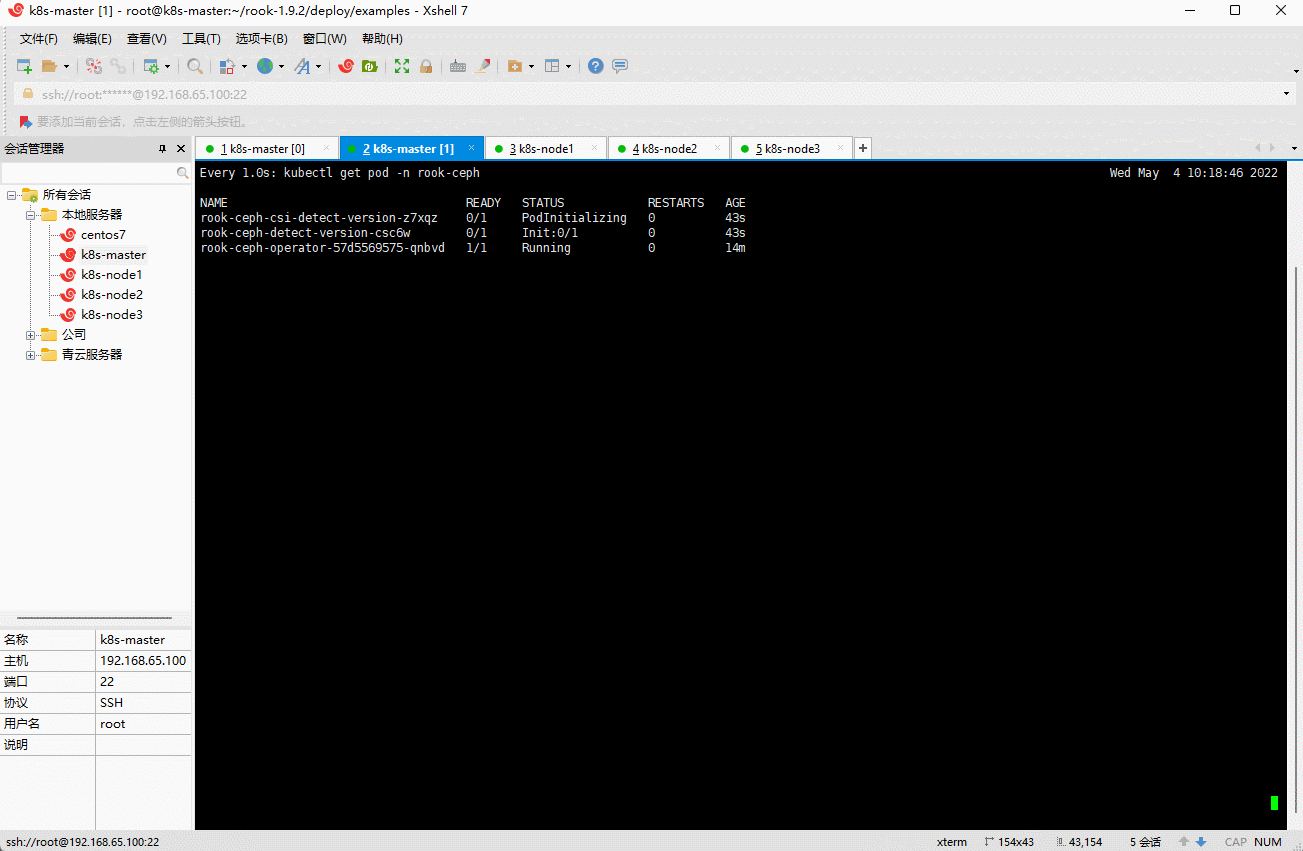
- 出现如下结果,就说明已经安装完毕:

4.4 部署 dashboard
- 默认情况下,其实已经安装了 dashboard 。
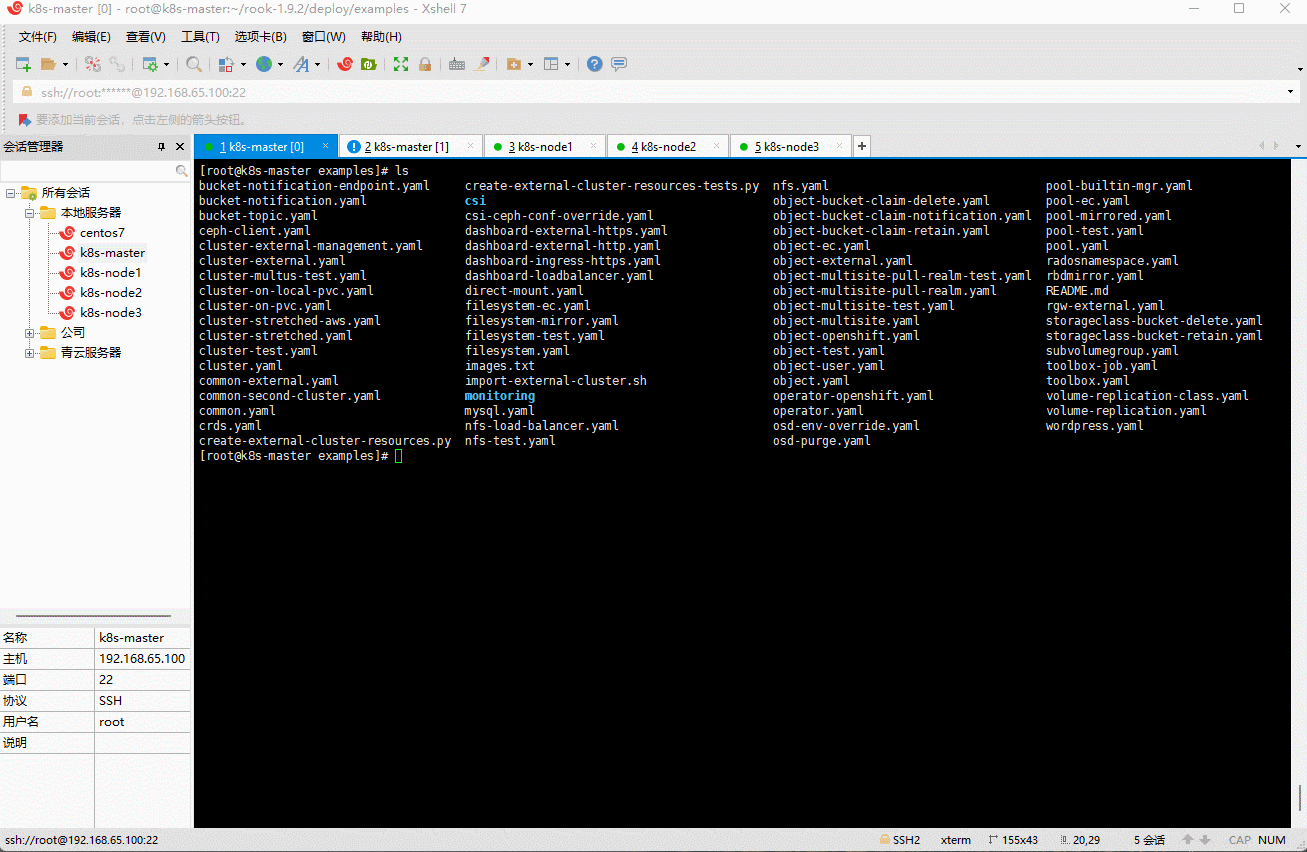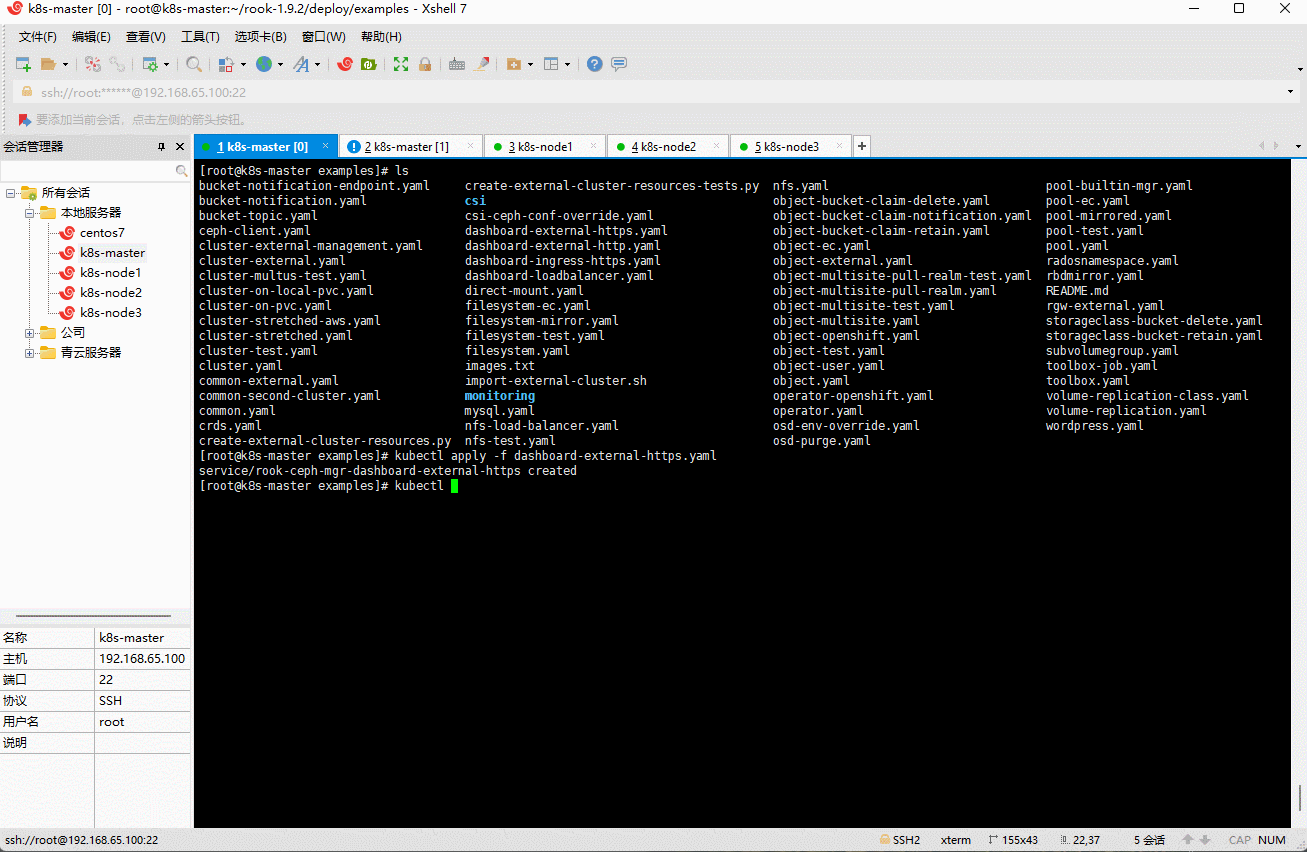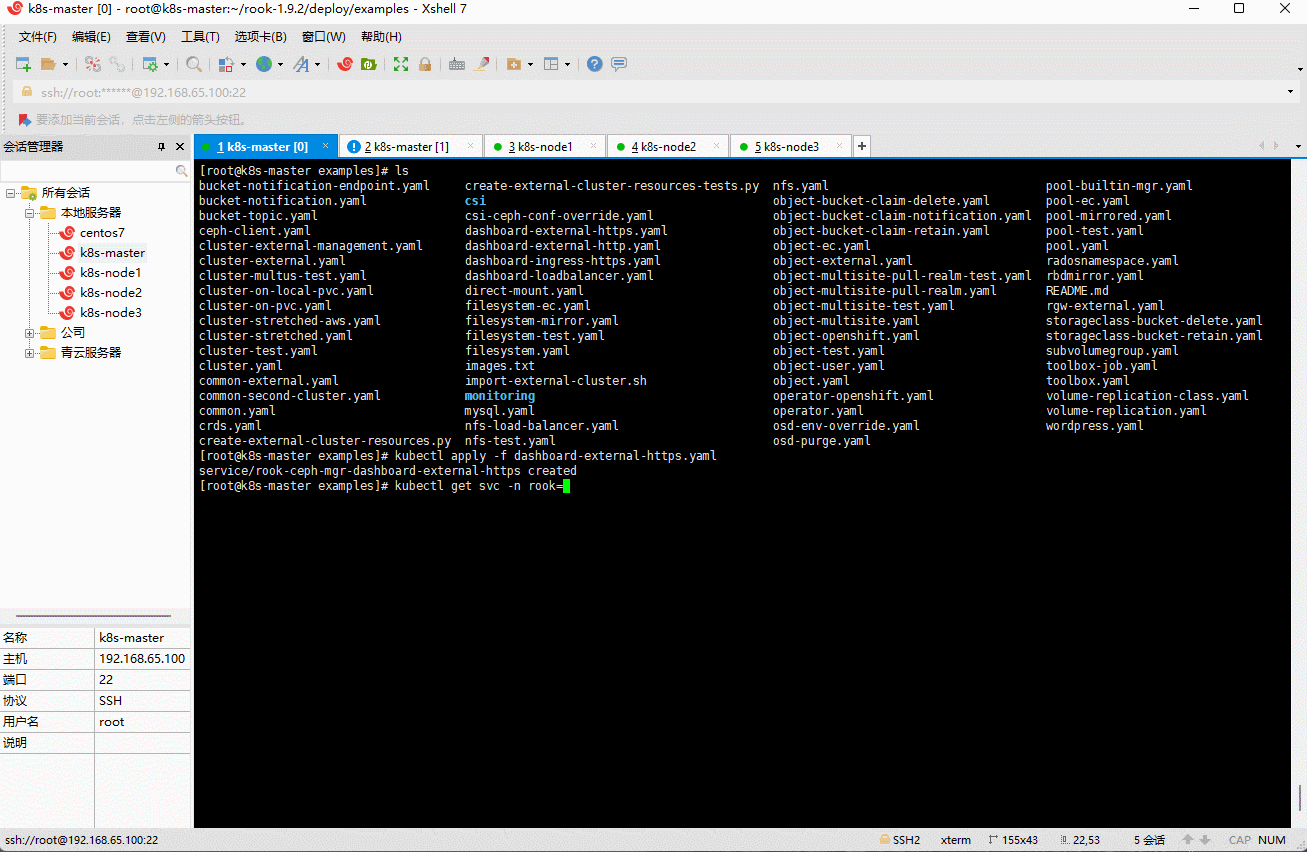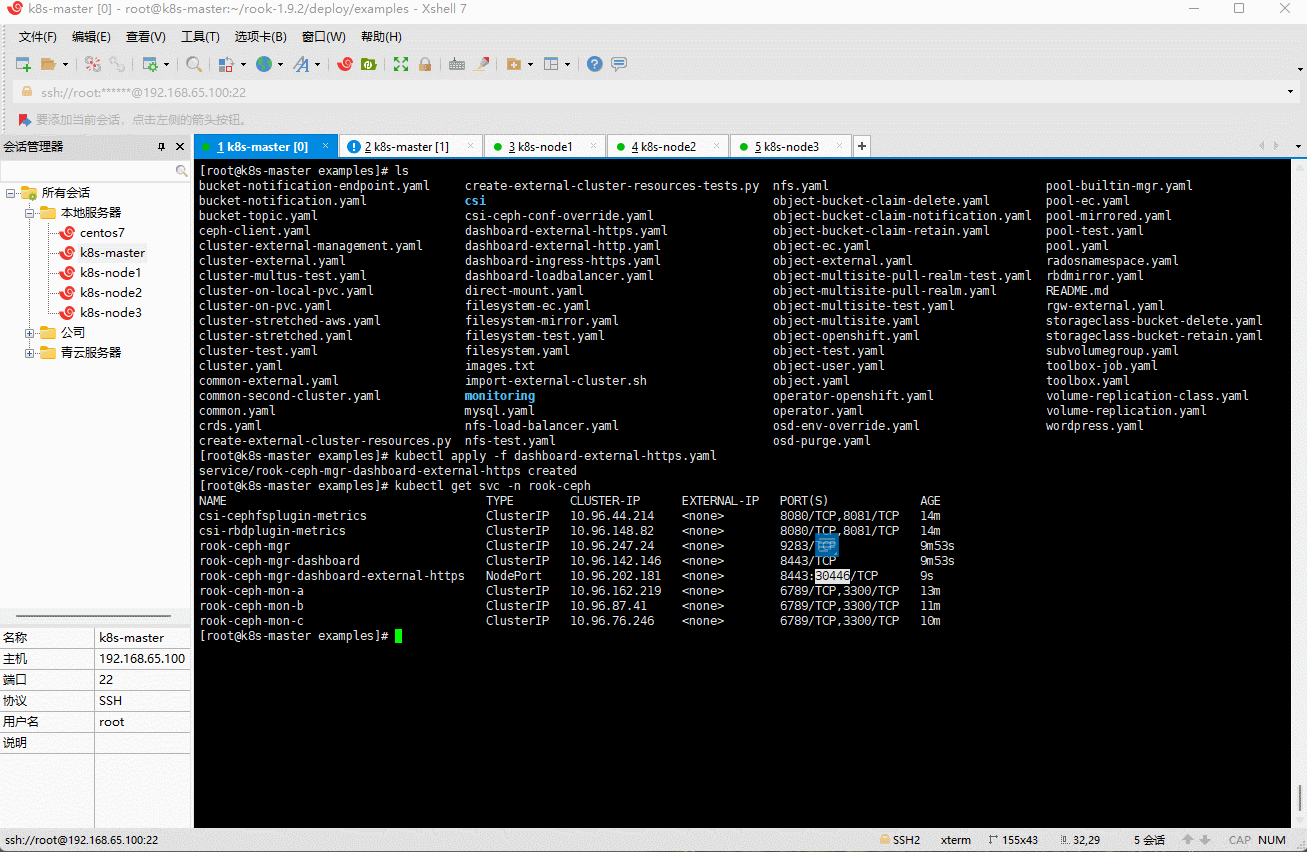
- 当然,我们也可以选择 NodePort 的形式:
kubectl apply -f dashboard-external-https.yaml
- 获取的 dashboard 的密码:
# 用户名是 admin 密码是 1/L!SSnCgwj1=P#/iB@xkubectl -n rook-ceph get secret rook-ceph-dashboard-password -o jsonpath="{['data']['password']}" | base64 -d

- 浏览器访问:
https://192.168.65.100:30446

第五章:实战
5.1 块存储和共享存储
- Ceph 分为块存储(RBD)和共享存储(CephFS)两类。
- Ceph 中的块存储(RBD)一般用于单节点读写(RWO,ReadWriteOnce),适用于有状态应用。
- Ceph 中的共享存储(CephFs)一般用于多节点读写(RWX,ReadWriteMany),适用于无状态应用。
- Rook 可以帮准我们创建好 StorageClass,我们只需要在 PVC 中指定存储类,Rook 就会调用 StorageClass 里面的 Provisioner供应商,接下来对 Ceph 集群操作。
5.2 配置块存储(RBD)
官网。
块存储,RWO 模式 ,STS 删除,PVC 不会删除,需要自己手动维护。
安装块存储的 StorageClass:
# 此文件就在 rook-1.9.2/deploy/examples/csi/rbd/storageclass.yamlvi rook-ceph-block.yaml
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1kind: CephBlockPoolmetadata:name: replicapoolnamespace: rook-ceph # namespace:clusterspec:failureDomain: hostreplicated:size: 3# Disallow setting pool with replica 1, this could lead to data loss without recovery.# Make sure you're *ABSOLUTELY CERTAIN* that is what you wantrequireSafeReplicaSize: true# gives a hint (%) to Ceph in terms of expected consumption of the total cluster capacity of a given pool# for more info: https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/rados/operations/placement-groups/#specifying-expected-pool-size#targetSizeRatio: .5---apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1kind: StorageClassmetadata:name: rook-ceph-block# Change "rook-ceph" provisioner prefix to match the operator namespace if neededprovisioner: rook-ceph.rbd.csi.ceph.comparameters:# clusterID is the namespace where the rook cluster is running# If you change this namespace, also change the namespace below where the secret namespaces are definedclusterID: rook-ceph # namespace:cluster# If you want to use erasure coded pool with RBD, you need to create# two pools. one erasure coded and one replicated.# You need to specify the replicated pool here in the `pool` parameter, it is# used for the metadata of the images.# The erasure coded pool must be set as the `dataPool` parameter below.#dataPool: ec-data-poolpool: replicapool# (optional) mapOptions is a comma-separated list of map options.# For krbd options refer# https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/man/8/rbd/#kernel-rbd-krbd-options# For nbd options refer# https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/man/8/rbd-nbd/#options# mapOptions: lock_on_read,queue_depth=1024# (optional) unmapOptions is a comma-separated list of unmap options.# For krbd options refer# https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/man/8/rbd/#kernel-rbd-krbd-options# For nbd options refer# https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/man/8/rbd-nbd/#options# unmapOptions: force# (optional) Set it to true to encrypt each volume with encryption keys# from a key management system (KMS)# encrypted: "true"# (optional) Use external key management system (KMS) for encryption key by# specifying a unique ID matching a KMS ConfigMap. The ID is only used for# correlation to configmap entry.# encryptionKMSID: <kms-config-id># RBD image format. Defaults to "2".imageFormat: "2"# RBD image features. Available for imageFormat: "2". CSI RBD currently supports only `layering` feature.imageFeatures: layering# The secrets contain Ceph admin credentials. These are generated automatically by the operator# in the same namespace as the cluster.csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-name: rook-csi-rbd-provisionercsi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-namespace: rook-ceph # namespace:clustercsi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-name: rook-csi-rbd-provisionercsi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-namespace: rook-ceph # namespace:clustercsi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-name: rook-csi-rbd-nodecsi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-namespace: rook-ceph # namespace:cluster# Specify the filesystem type of the volume. If not specified, csi-provisioner# will set default as `ext4`. Note that `xfs` is not recommended due to potential deadlock# in hyperconverged settings where the volume is mounted on the same node as the osds.csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: ext4# uncomment the following to use rbd-nbd as mounter on supported nodes# **IMPORTANT**: CephCSI v3.4.0 onwards a volume healer functionality is added to reattach# the PVC to application pod if nodeplugin pod restart.# Its still in Alpha support. Therefore, this option is not recommended for production use.#mounter: rbd-nbdallowVolumeExpansion: truereclaimPolicy: Delete
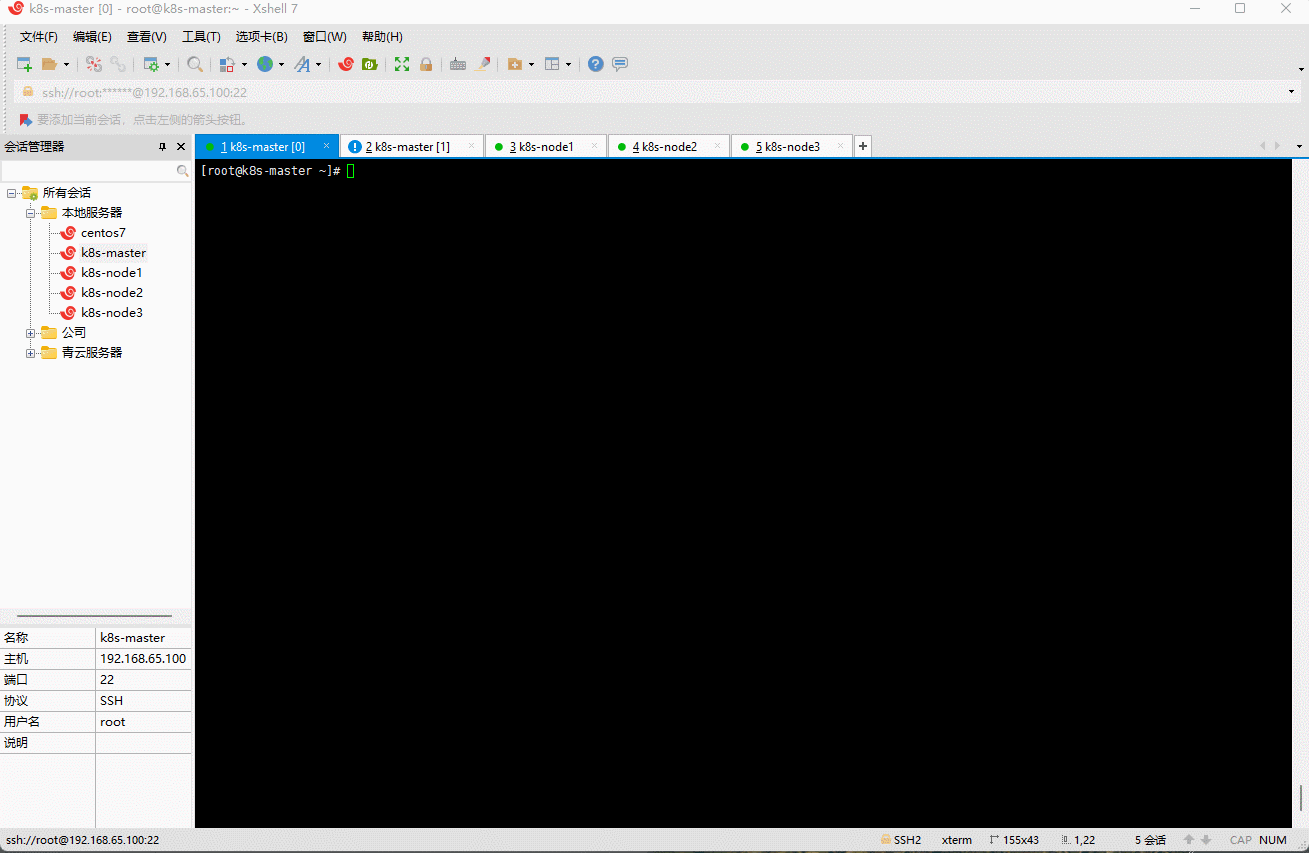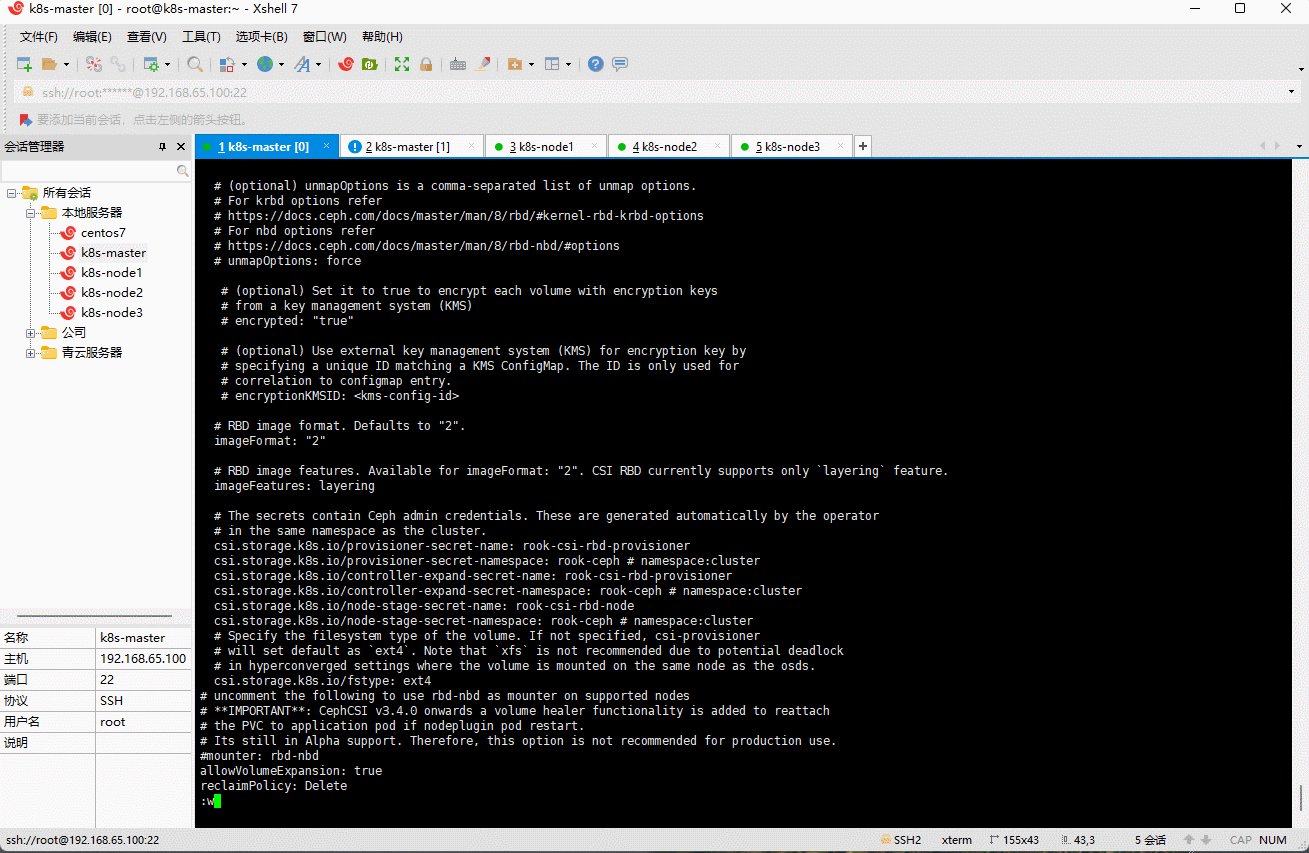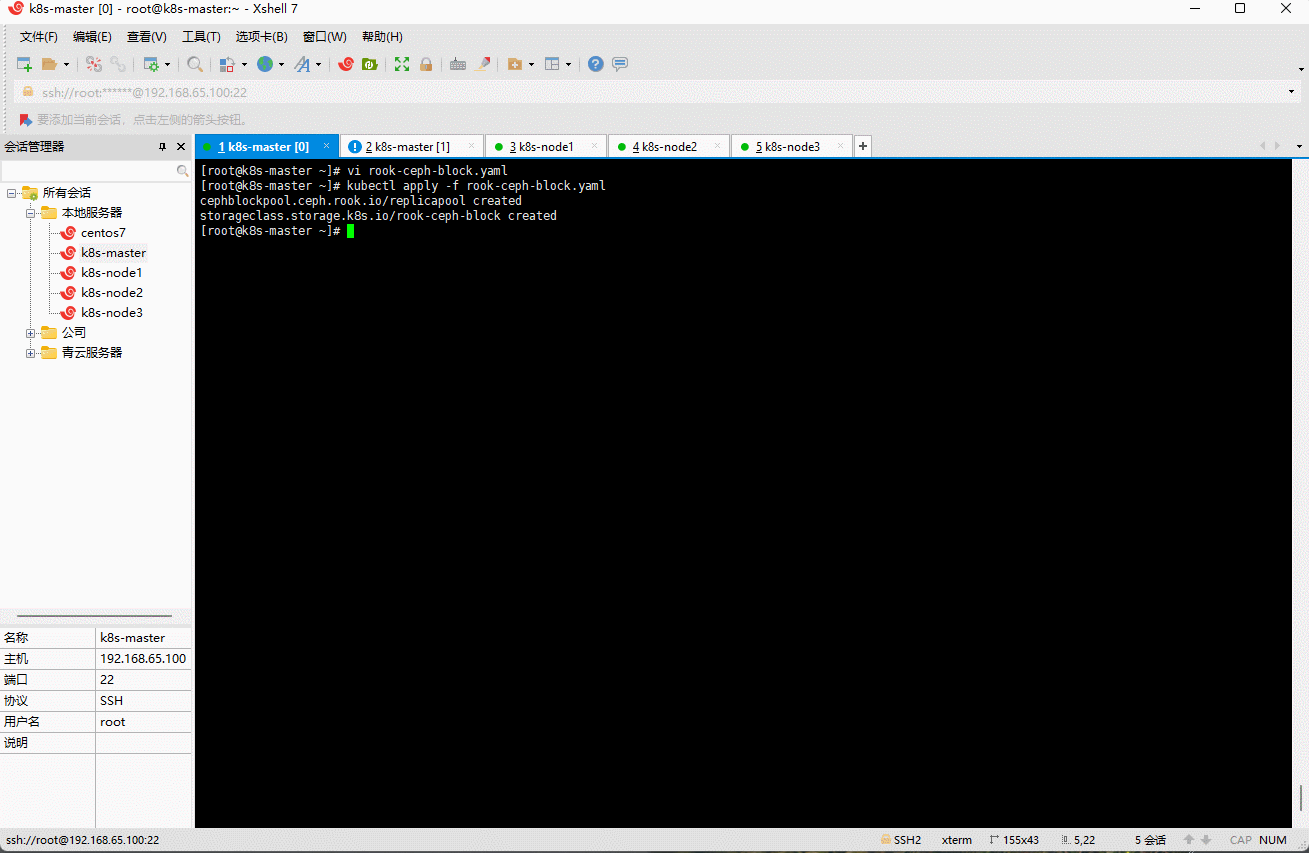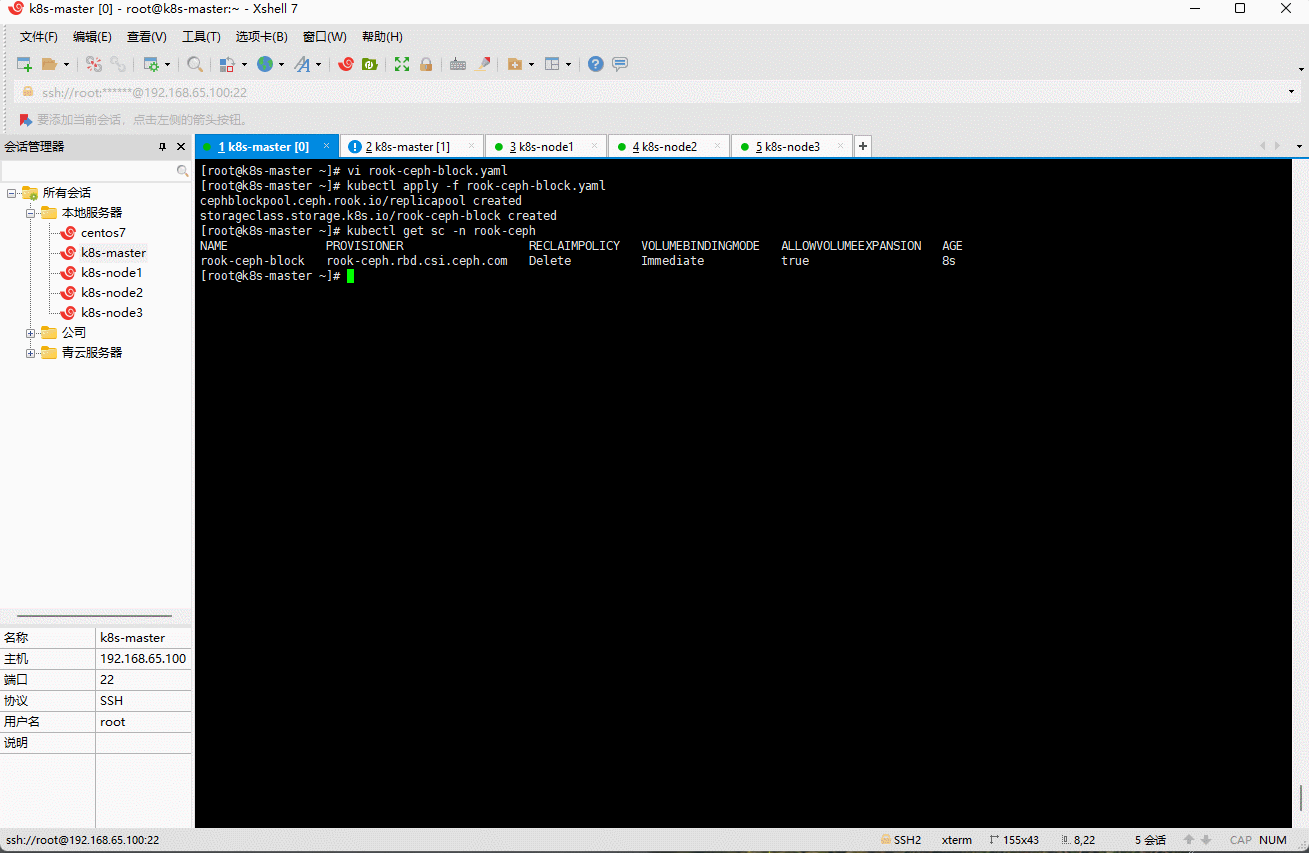
kubectl apply -f rook-ceph-block.yaml
- 测试:
apiVersion: apps/v1kind: StatefulSetmetadata:name: sts-nginxnamespace: defaultspec:selector:matchLabels:app: sts-nginx # has to match .spec.template.metadata.labelsserviceName: "sts-nginx"replicas: 3 # by default is 1template:metadata:labels:app: sts-nginx # has to match .spec.selector.matchLabelsspec:terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 10containers:- name: sts-nginximage: nginxports:- containerPort: 80name: webvolumeMounts:- name: wwwmountPath: /usr/share/nginx/htmlvolumeClaimTemplates:- metadata:name: wwwspec:accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ]storageClassName: "rook-ceph-block"resources:requests:storage: 20Mi---apiVersion: v1kind: Servicemetadata:name: sts-nginxnamespace: defaultspec:selector:app: sts-nginxtype: ClusterIPports:- name: sts-nginxport: 80targetPort: 80protocol: TCP
5.3 配置文件存储(CephFS)
官网。
文件存储(CephFS),RWX 模式,多个 Pod 共同操作一个地方。
安装:
vi rook-cephfs.yaml
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1kind: CephFilesystemmetadata:name: myfsnamespace: rook-ceph # namespace:clusterspec:# The metadata pool spec. Must use replication.metadataPool:replicated:size: 3requireSafeReplicaSize: trueparameters:# Inline compression mode for the data pool# Further reference: https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/rados/configuration/bluestore-config-ref/#inline-compressioncompression_mode:none# gives a hint (%) to Ceph in terms of expected consumption of the total cluster capacity of a given pool# for more info: https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/rados/operations/placement-groups/#specifying-expected-pool-size#target_size_ratio: ".5"# The list of data pool specs. Can use replication or erasure coding.dataPools:- name: replicatedfailureDomain: hostreplicated:size: 3# Disallow setting pool with replica 1, this could lead to data loss without recovery.# Make sure you're *ABSOLUTELY CERTAIN* that is what you wantrequireSafeReplicaSize: trueparameters:# Inline compression mode for the data pool# Further reference: https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/rados/configuration/bluestore-config-ref/#inline-compressioncompression_mode:none# gives a hint (%) to Ceph in terms of expected consumption of the total cluster capacity of a given pool# for more info: https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/rados/operations/placement-groups/#specifying-expected-pool-size#target_size_ratio: ".5"# Whether to preserve filesystem after CephFilesystem CRD deletionpreserveFilesystemOnDelete: true# The metadata service (mds) configurationmetadataServer:# The number of active MDS instancesactiveCount: 1# Whether each active MDS instance will have an active standby with a warm metadata cache for faster failover.# If false, standbys will be available, but will not have a warm cache.activeStandby: true# The affinity rules to apply to the mds deploymentplacement:# nodeAffinity:# requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:# nodeSelectorTerms:# - matchExpressions:# - key: role# operator: In# values:# - mds-node# topologySpreadConstraints:# tolerations:# - key: mds-node# operator: Exists# podAffinity:podAntiAffinity:requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:- labelSelector:matchExpressions:- key: appoperator: Invalues:- rook-ceph-mds# topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname will place MDS across different hoststopologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostnamepreferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:- weight: 100podAffinityTerm:labelSelector:matchExpressions:- key: appoperator: Invalues:- rook-ceph-mds# topologyKey: */zone can be used to spread MDS across different AZ# Use <topologyKey: failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/zone> in k8s cluster if your cluster is v1.16 or lower# Use <topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone> in k8s cluster is v1.17 or uppertopologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone# A key/value list of annotations# annotations:# key: value# A key/value list of labels# labels:# key: value# resources:# The requests and limits set here, allow the filesystem MDS Pod(s) to use half of one CPU core and 1 gigabyte of memory# limits:# cpu: "500m"# memory: "1024Mi"# requests:# cpu: "500m"# memory: "1024Mi"priorityClassName: system-cluster-criticallivenessProbe:disabled: falsestartupProbe:disabled: false# Filesystem mirroring settings# mirroring:# enabled: true# list of Kubernetes Secrets containing the peer token# for more details see: https://docs.ceph.com/en/latest/dev/cephfs-mirroring/#bootstrap-peers# peers:#secretNames:#- secondary-cluster-peer# specify the schedule(s) on which snapshots should be taken# see the official syntax here https://docs.ceph.com/en/latest/cephfs/snap-schedule/#add-and-remove-schedules# snapshotSchedules:# - path: /# interval: 24h # daily snapshots# startTime: 11:55# manage retention policies# see syntax duration here https://docs.ceph.com/en/latest/cephfs/snap-schedule/#add-and-remove-retention-policies# snapshotRetention:# - path: /# duration: "h 24"---apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1kind: StorageClassmetadata:name: rook-cephfsannotations:storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true"# Change "rook-ceph" provisioner prefix to match the operator namespace if neededprovisioner: rook-ceph.cephfs.csi.ceph.com # driver:namespace:operatorparameters:# clusterID is the namespace where the rook cluster is running# If you change this namespace, also change the namespace below where the secret namespaces are definedclusterID: rook-ceph # namespace:cluster# CephFS filesystem name into which the volume shall be createdfsName: myfs# Ceph pool into which the volume shall be created# Required for provisionVolume: "true"pool: myfs-replicated# The secrets contain Ceph admin credentials. These are generated automatically by the operator# in the same namespace as the cluster.csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-name: rook-csi-cephfs-provisionercsi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-namespace: rook-ceph # namespace:clustercsi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-name: rook-csi-cephfs-provisionercsi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-namespace: rook-ceph # namespace:clustercsi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-name: rook-csi-cephfs-nodecsi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-namespace: rook-ceph # namespace:cluster# (optional) The driver can use either ceph-fuse (fuse) or ceph kernel client (kernel)# If omitted, default volume mounter will be used - this is determined by probing for ceph-fuse# or by setting the default mounter explicitly via --volumemounter command-line argument.# mounter: kernelreclaimPolicy: DeleteallowVolumeExpansion: truemountOptions:# uncomment the following line for debugging#- debug
kubectl apply -f rook-cephfs.yaml

- 测试:
apiVersion: apps/v1kind: Deploymentmetadata:name: nginx-deploynamespace: defaultlabels:app: nginx-deployspec:selector:matchLabels:app: nginx-deployreplicas: 3strategy:rollingUpdate:maxSurge: 25%maxUnavailable: 25%type: RollingUpdatetemplate:metadata:labels:app: nginx-deployspec:containers:- name: nginx-deployimage: nginxvolumeMounts:- name: localtimemountPath: /etc/localtime- name: nginx-html-storagemountPath: /usr/share/nginx/htmlvolumes:- name: localtimehostPath:path: /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai- name: nginx-html-storagepersistentVolumeClaim:claimName: nginx-pv-claim---apiVersion: v1kind: PersistentVolumeClaimmetadata:name: nginx-pv-claimlabels:app: nginx-deployspec:storageClassName: rook-cephfsaccessModes:- ReadWriteMany ##如果是ReadWriteOnce将会是什么效果resources:requests:storage: 10Mi

