第一章:基础认知
1.1 CSS 介绍
- CSS:层叠样式表(Cascading style sheets)。
- CSS 的作用:给页面中的 HTML 标签设置样式。

1.2 CSS 的语法规则
CSS 写在 style 标签中,而 style 标签一般写在 head 标签里面,title 标签下面。
示例:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>CSS 的语法规则</title><style>/* 选择器 p{} */p {/* CSS 属性的格式是 属性名: 属性值; */color: red;}</style></head><body><p>你好,世界</p></body></html>
1.3 CSS 初体验
- 常见属性: | CSS 常见属性 | 作用 | | —- | —- | | color | 文字颜色 | | font-size | 文字大小 | | background-color | 背景颜色 | | width | 宽度 | | height | 高度 |
注意:
- CSS 标点符号都是
英文状态的。- 每一个样式键值对写完之后,需要以分号结尾。
- 示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p {
/* 文字颜色 */
color: red;
/* 文字大小 */
font-size: 30px;
/* 背景颜色 */
background-color: pink;
/* 宽度 */
width: 300px;
/* 高度 */
height: 300px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>你好,世界</p>
</body>
</html>
1.4 CSS 引入方式
- 内嵌式:CSS 写在 style 标签中。
注意:style 标签虽然可以写在页面的任何位置,但是通常约定写在 head 标签中。
约定大于配置。
- 外联式:CSS 写在一个单独的
.css文件中。
注意:需要通过 link 标签在网页中引入。
- 行内式:CSS 写在标签的 style 属性中。
注意:这里不推荐,但是之后会配合 js 使用。
- 示例:外联式
p {
/* 文字颜色 */
color: red;
/* 文字大小 */
font-size: 30px;
/* 背景颜色 */
background-color: pink;
/* 宽度 */
width: 300px;
/* 高度 */
height: 300px;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<!-- 样式表 -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/style.css">
</head>
<body>
<p>你好,世界</p>
</body>
</html>
- 示例:行内式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>行内式</title>
</head>
<body>
<p style="color: red;background-color: pink;font-size: 30px;width: 300px;height: 300px;">你好,世界</p>
</body>
</html>
第二章:基础选择器
2.1 选择器的作用
- 选择器的作用:选中页面中对应的标签,方便后续设置样式。
2.2 标签选择器
- 结构:
标签名 {css属性名: css属性值; }。 - 作用:通过标签名,找到页面中所有的这类标签,设置样式。
注意:
- 标签选择器选择的是一类标签,而不是单独的某一个。
- 标签选择器无论嵌套关系有多深,都能找到对应的标签。
- 示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/* 选择器 {} */
/* 标签选择器就是以标签名命名的选择器 */
/* 标签选择器会选中所有的标签,都生效 css */
p {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Lorem, ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Vitae minima totam non consequatur officiis quo
voluptatibus, ea ipsa nulla, cumque magni. Minus maiores temporibus cupiditate illo quaerat modi expedita
facilis?</p>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Libero minima dolorum velit, labore incidunt aut architecto ducimus molestias omnis? Aliquid asperiores eveniet quibusdam impedit, facilis dolor id voluptatem! Numquam, maiores!</p>
<div>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur, adipisicing elit. Fuga, nisi adipisci. Esse ea inventore dolorem voluptas pariatur, suscipit, quam repellat animi eaque aperiam at alias nesciunt! Facere qui ut possimus?</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
2.3 类选择器
- 结构:
.类名{css属性名: css属性值;}。 - 作用:通过类名,找到页面中所有带这个类名的标签,设置样式。
注意:
- ① 所有标签上都有 class 属性,class 属性的属性值称为
类名(类似于名字)。- ② 类名可以由数字、字母、下划线、中划线组成,但是不能以数字或中划线开头。
- ③ 一个标签可以同时有多个类名,类名之间以空格隔开。
- ④ 类名可以重复,一个类选择器可以同时选中多个标签。
- 示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/* 类选择器 */
/* .类名 {} */
.two {
color: red;
}
.size {
font-size: 30px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>11111</p>
<!-- 类:定义 和 使用 才能生效 -->
<!-- 一个标签可以使用多个类名,需要空格隔开 -->
<p class="two size">22222</p>
<p>33333</p>
</body>
</html>
2.4 id 选择器
- 结构:
#id属性值{css属性名: 属性值;}。 - 作用:通过 id 属性值,找到页面中所有带这个 id 属性值的标签,设置样式。
注意:
- ① 所有标签上都有 id 属性。
- ② id 属性值类似于身份证号码,在一个页面中是唯一的,不可重复的。
- ③ 一个标签上只能有一个 id 属性值。
- ④ 一个 id 选择器只能选中一个标签。
- 示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/* id 选择器 */
/* #id属性值 {} */
#two {
color: red;
font-size: 12px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>11111</p>
<p id="two">22222</p>
<p>33333</p>
</body>
</html>
2.5 通配符选择器
- 结构:
*{css属性名: 属性值;}。 - 作用:找到页面中所有的标签,设置样式。
注意:
- 开发中使用极少,只会在极其特殊的情况下才会使用。
- 后续会用来去除标签默认的 margin 和 padding 。
- 示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>div</div>
<p>p</p>
<h1>h1</h1>
<span>span</span>
</body>
</html>
第三章:字体和文本样式
3.1 字体样式
3.1.1 字体大小
- 属性名:
font-size。 - 取值:
数字 + px。
注意:
- Chrome 浏览器默认文字大小是 16px 。
- 单位需要设置,否则无效。
- 示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p {
/* 字体大小 */
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 默认的字体大小是 16px -->
<p>你好,世界</p>
</body>
</html>
3.1.2 字体粗细
- 属性名:
font-weight。 取值:
关键字。 | 关键字 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | normal | 正常 | | bold | 加粗 |
纯数字:100 ~ 900 的整百数。 | 数值 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | 400 | 正常 | | 700 | 加粗 |
注意:
- 不是所有的字体都提供 9 种粗细,因此部分取值页面中可能没有变化。
- 实际开发中以
正常和加粗两种取值使用最多。
- 示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p {
/* 文字正常 */
font-weight: normal;
}
div {
/* 文字加粗 */
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>我是正常文字</p>
<div>我是加粗文字</div>
</body>
</html>
3.1.3 字体样式(是否倾斜)
- 属性名:
font-style。 取值:
- 正常(默认值):normal 。
- 倾斜:italic 。
示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
/* 文字正常 */
font-style: normal;
}
p {
/* 文字倾斜 */
font-style: italic;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>我是正常文字</div>
<p>我是倾斜文字</p>
</body>
</html>
3.1.4 常见字体系列(了解)
- 无衬线字体(sans-serif):
- ① 特点:文字笔画粗细均匀,并且首尾无装饰。
- ② 场景:
网页中大多采用无衬线字体。 - ③ 常见该系列字体:黑体、Arial。
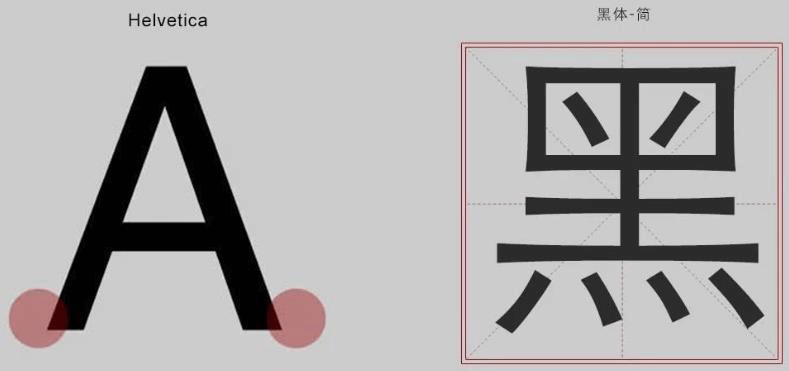
- 衬线字体(serif):
- ① 特点:文字笔画粗细不均,并且首尾有笔锋装饰。
- ② 场景:报刊书籍中应用广泛。
- ③ 常见该系列字体:宋体、Times New Roman。
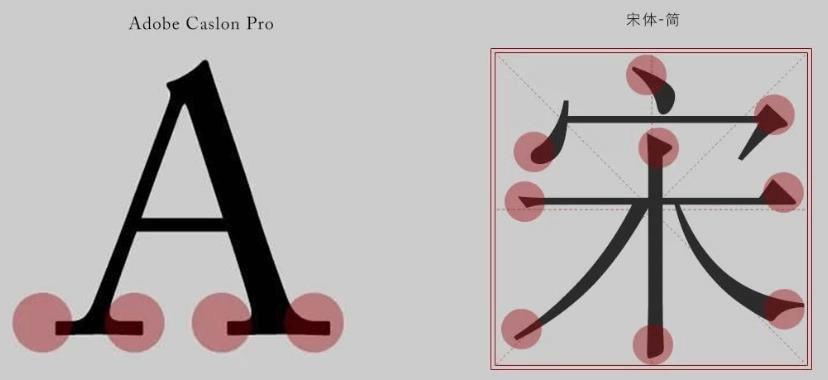
- 等宽字体(monospace):
- ① 特点:每个字母或文字的宽度相等。
- ② 场景:一般用于程序代码编写,有利于代码的阅读和编写。
- ③ 常见该系列字体:Consolas、fira code。
3.1.5 字体系列
- 属性名:
font-family。 - 常见取值:
具体字体1,具体字体2,具体字体3,具体字体4,...,字体系列。- 具体字体:”Microsoft YaHei”、微软雅黑、黑体、宋体、楷体等……
- 字体系列:sans-serif、serif、monospace 等……
- 渲染规则:
- ① 从左往右按照顺序查找,如果电脑中未安装该字体,则显示下一个字体。
- ② 如果都不支持,此时会根据操作系统,显示最后字体系列的默认字体。
注意:
- ① 如果字体名称中存在多个单词,推荐使用引号包裹。
- ② 最后一项字体系列不需要引号包裹。
- ③ 网页开发时,尽量使用系统常见自带字体,保证不同用户浏览网页都可以正确显示。
- 示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
/* 如果用户电脑没有安装 Arial,就按 Microsoft YaHei 字体显示文字,依次类推 */
font-family: "Arial", "Microsoft YaHei", "黑体", "宋体", sans-serif;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>这是一个 div 标签</div>
</body>
</html>
3.1.6 样式的层叠问题
- 问题:给同一个标签设置了相同的样式,此时浏览器会如何渲染呢?
- 结果:如果给同一个标签设置了相同的样式,此时样式会层叠(覆盖),写在最下面的会生效。
注意:CSS(层叠样式表)中的层叠就是叠加的意思,即样式可以一层一层的层叠覆盖。
- 示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>样式的层叠问题</title>
<style>
p {
/* 层叠性:后面的会覆盖前面的 */
color: blue;
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>我是一个 p 标签</p>
</body>
</html>
3.1.7 font 复合属性
- 属性名:
font. - 取值:
font: style weight size family。 - 省略要求:只能省略前两个,如果省略了相当于设置了默认值。
注意:如果需要同时设置
单独和连写的形式,要么将单独的样式写在连写的下面,要么将单独的样式写在连写的里面。
- 示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
/* font: style weight size family */
font: normal bold 20px "Arial", "Microsoft YaHei", "黑体", "宋体", sans-serif;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>我是一个 div 标签</div>
</body>
</html>
3.2 文本样式
3.2.1 文本缩进
- 属性名:
text-indent。 取值:
- 数字 + px 。
- 数字 + em (推荐,1em = 当前标签的 font-size 的大小)。
示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p {
/* 文本缩进 2个字符 */
text-indent: 2em;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>黑洞(英文:Black Hole)是现代广义相对论中,存在于宇宙空间中的一种天体。黑洞的引力极其强大,使得视界内的逃逸速度大于光速。故而,“黑洞是时空曲率大到光都无法从其事件视界逃脱的天体”。</p>
<p>1916年,德国天文学家卡尔·史瓦西通过计算得到了爱因斯坦场方程的一个真空解,这个解表明,如果一个静态球对称星体实际半径小于一个定值,其周围会产生奇异的现象,即存在一个界面——“视界”,一旦进入这个界面,即使光也无法逃脱。这个定值称作史瓦西半径,这种“不可思议的天体”被美国物理学家约翰·阿奇博尔德·惠勒命名为“黑洞”。</p>
</body>
</html>
3.2.2 文本水平对齐方式
- 属性名:
text-align。 - 取值: | 属性值 | 效果 | | —- | —- | | left | 左对齐 | | center | 居中对齐 | | right | 右对齐 |
注意:
- 如果需要让文本水平居中,text-align 属性是给
文本所在的标签(文本的父元素)设置的。text-align: center;能让文本、span 标签、a 标签、input 标签、img 标签水平居中。
- 示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
h1 {
background-color: pink;
}
.left {
text-align: left;
}
.center {
text-align: center;
}
.right {
text-align: right;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="left">左对齐</h1>
<h1 class="center">居中对齐</h1>
<h1 class="right">右对齐</h1>
</body>
</html>
3.2.3 文本修饰
- 属性名:
text-decoration。 - 取值: | 属性值 | 效果 | | —- | —- | | underline | 下划线(常用) | | line-through | 删除线(不常用) | | overline | 上划线(几乎不用) | | none | 无装饰线(常用) |
注意:开发中会使用
text-decoration:none;清除 a 标签默认的下划线。
- 示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p {
text-decoration: underline;
}
div {
text-decoration: line-through;
}
h2 {
text-decoration: overline;
}
a {
text-decoration: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Vel delectus eveniet earum quis optio, commodi, esse
perferendis tempora veritatis in molestiae nostrum ducimus est sed laborum facilis recusandae. Unde, eius.</p>
<div>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Labore consequuntur commodi possimus earum deleniti
quibusdam aliquam iusto ab porro. Corporis maxime itaque dolores aliquam dicta, praesentium enim in velit porro!
</div>
<h2>Lorem ipsum dolor sit, amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Veritatis voluptatem non eveniet odio! Beatae dolorem
odit officia, quo voluptates saepe pariatur, laboriosam quam distinctio nobis reprehenderit non, ex hic quas.
</h2>
<a href="#">我是超链接</a>
</body>
</html>
3.3 行高
- 属性名:
line-height。
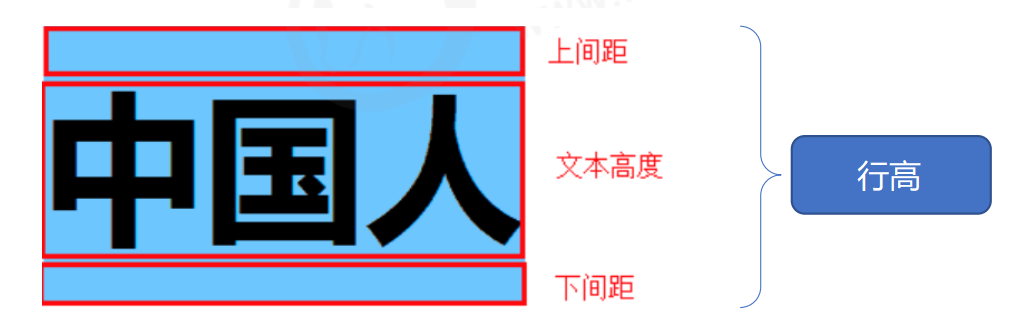
- 作用:控制一行的上下行间距。
- 取值:
- 数字 + px 。
- 倍数(当前标签 font-size 的倍数)。
- 应用:
- ① 让
单行文本垂直居中可以设置line-height: 文字父元素高度。 - ② 网页精准布局的时候,会设置
line-height:1取消上下间距。
- ① 让
行高和 font 连写:
font: style weight size/line-height family ;。示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p {
line-height: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>黑洞的中间的奇点蕴含着无限的物质,就连光也无法逃逸。黑洞产生的引力能把周围的一切物质:时空、星球、光等等所有一切都吸进质量无穷大的奇点之中。</p>
<p>我相信,人类对于黑洞、白洞都存在浓厚的兴趣,太神奇了,能将所有的物质都浓缩到一个奇点上面,这个技术如果能掌握,一定能让科技进步一大截!</p>
</body>
</html>
- 示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color:pink;
text-align: center;
/* 文字是单行的 */
/* 垂直居中技巧:设置行高属性值 = 自身高度属性值 */
line-height: 200px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>文字</div>
</body>
</html>
第四章:其他
4.1 颜色常见取值(了解)
- 属性名:
- 如:文字颜色
color。 - 如:背景颜色
background-color。
- 如:文字颜色
- 属性值: | 颜色表示方式 | 表示含义 | 属性值 | | —- | —- | —- | | 关键词 | 预定义的颜色名 | red、green、blue、yellow..… | | rgb表示法 | 红绿蓝三原色。每项取值范围∶0~255 | rgb(0,0,0)、rgb(255,255,255)、rgb(255,0,0)…… | | rgba表示法 | 红绿蓝三原色+a表示透明度,取值范围是∶0~1 | rgba(255,255,255,0.5)、rgba(255,0,0,0.3)…… | | 十六进制表示法 | #开头,将数字转换成十六进制表示 | #000000、#ff0000、#e92322,简写∶#000、#f00 |
4.2 标签水平居中
- 如果需要让 div 、p 、h 标签水平居中,可以通过
margin:0 auto;实现。
注意:
- ① 如果需要让 div 、p 、h 标签水平居中,直接给
当前元素本身设置即可。- ②
margin:0 auto;一般针对于固定宽度的盒子,如果大盒子没有设置宽度,此时会默认占满父元素的宽度。
- 示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
background-color: pink;
}
.inner {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
/* div 、p 、h 标签水平居中 */
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="inner"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

