⭐表示重要。
第一章:Lombok 是什么?
- 官网。
- 官网介绍:
- Project Lombok is a java library that automatically plugs into your editor and build tools, spicing up your java.
- Never write another getter or equals method again, with one annotation your class has a fully featured builder, Automate your logging variables, and much more.
- 翻译:
- Project Lombok 是一个 java 库,可以自动插入编辑器和构建工具,从而增强 java 的功能。
- 永远不要再写额外的 getter 或 equals 方法,用一个注解注释你的类让其有一个功能齐全的构建者模式,自动化你的日志记录变量,等等。
- 白话:Lombok 是一个 Java 实用工具,可以用来帮助开发人员消除 Java 中的冗长代码,尤其是对于简单的 Java 对象(POJO),它通过
注解实现这一目的。 - 对比:
- 没有使用 Lombok : ```java package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
- @author 许大仙
- @version 1.0
@since 2021-11-21 08:16 */ public class UserOld {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
public UserOld() { }
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
@Override public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {return true;}if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {return false;}UserOld userOld = (UserOld) o;return Objects.equals(id, userOld.id) && Objects.equals(userName, userOld.userName) && Objects.equals(password, userOld.password) && Objects.equals(phone, userOld.phone) && Objects.equals(email, userOld.email);
}
@Override public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id, userName, password, phone, email);
}
@Override public String toString() {
return "UserOld{" +"id=" + id +", userName='" + userName + '\'' +", password='" + password + '\'' +", phone='" + phone + '\'' +", email='" + email + '\'' +'}';
} } ```
- 使用了 Lombok : ```java package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import lombok.Data;
/**
- @author 许大仙
- @version 1.0
@since 2021-11-21 08:19 */ @Data public class User { private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email; } ```
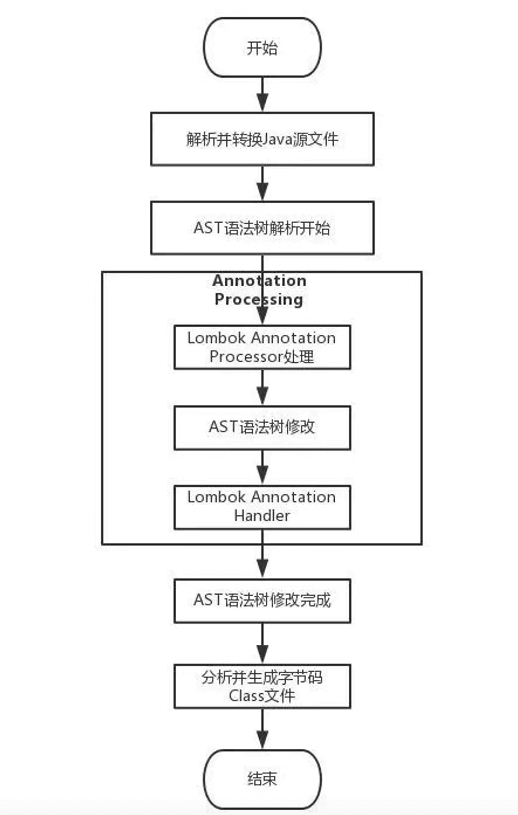
第二章:Lombok 的原理
- JSR 269:插件化注解处理 API(Pluggable Annotation Processing API)。
- 在 JSR 269 之前可以使用注解,但必须借助反射机制,而反射的方法局限性较大,由于必须定义 @Retention 为 RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME ,只能在
运行期通过反射来获取注解值,使得运行时代码效率降低。 - 其次,如果想在编译阶段利用注解来进行一些检查,对用户的某些不合理代码给出错误报告,反射的使用方法就无能为力了。
- 而 JSR 269 之后我们可以在 javac 的
编译期利用注解做这些事情。
第三章:Lombok的安装
- IDEA 2021+ 中已经集成了 Lombok 插件了,无需安装。
- Maven 的 pom.xml
<dependency><groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId><artifactId>lombok</artifactId><version>1.18.22</version></dependency>
第四章:Lombok的特性(⭐)
4.1 @Getter 和 @Setter
- @Getter 或 @Setter 标注成员变量,以使 Lombok 自动生成默认的 getter 和 setter。
@Getter 和 @Setter 可以作用于类或属性。
示例:
- User.java
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import lombok.AccessLevel;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-11-21 08:19
*/
public class User {
@Getter
@Setter
private Integer id;
@Getter(AccessLevel.PRIVATE)
@Setter(AccessLevel.PACKAGE)
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
}
- 生成的代码:
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
public User() {
}
public Integer getId() {
return this.id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
private String getUserName() {
return this.userName;
}
void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
}
- 示例:
- User.java
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-11-21 08:19
*/
@Setter
@Getter
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
}
- 生成的代码:
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
public User() {
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public Integer getId() {
return this.id;
}
public String getUserName() {
return this.userName;
}
public String getPassword() {
return this.password;
}
public String getPhone() {
return this.phone;
}
public String getEmail() {
return this.email;
}
}
4.2 @ToString
- @ToString 生成 toString() 方法。
@ToString 作用于类上。
示例:
- User.java
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import lombok.ToString;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-11-21 08:19
*/
@ToString
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
}
- 生成的代码:
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
public User() {
}
public String toString() {
return "User(id=" + this.id + ", userName=" + this.userName + ", password=" + this.password + ", phone=" + this.phone + ", email=" + this.email + ")";
}
}
4.3 @EqualsAndHashCode
- @EqualsAndHashCode 生成 equals() 和 hashCode() 方法。
@EqualsAndHashCode 作用于类上。
示例:
- User.java
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-11-21 08:19
*/
@EqualsAndHashCode(exclude = {"phone", "email", "password"})
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
}
- 生成的代码:
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
public User() {
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
} else if (!(o instanceof User)) {
return false;
} else {
User other = (User)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
} else {
Object this$id = this.id;
Object other$id = other.id;
if (this$id == null) {
if (other$id != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$id.equals(other$id)) {
return false;
}
Object this$userName = this.userName;
Object other$userName = other.userName;
if (this$userName == null) {
if (other$userName != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$userName.equals(other$userName)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
}
protected boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return other instanceof User;
}
public int hashCode() {
int PRIME = true;
int result = 1;
Object $id = this.id;
int result = result * 59 + ($id == null ? 43 : $id.hashCode());
Object $userName = this.userName;
result = result * 59 + ($userName == null ? 43 : $userName.hashCode());
return result;
}
}
4.4 @NoArgsConstructor
- @NoArgsConstructor 自动生成无参构造方法。
@NoArgsConstructor 作用于类上。
示例:
- User.java
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-11-21 08:19
*/
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
}
- 生成的代码:
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
public User() {
}
}
4.5 @RequiredArgsConstructor
- @RequiredArgsConstructor 生成一个包含常量(final)和标识了 @NotNull 变量的构造方法。
- @RequiredArgsConstructor 作用于类上。
应用场景:Spring 推荐使用构造器注入,那么只需要将需要注入的属性设置为 private final 的,然后在 handler 、serivce 等上面使用此注解即可完成自动装配。
示例:
- User.java
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import lombok.NonNull;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-11-21 08:19
*/
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class User {
private Integer id;
@NonNull
private String userName;
private final String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
}
- 生成的代码:
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import lombok.NonNull;
public class User {
private Integer id;
@NonNull
private String userName;
private final String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
public User(@NonNull String userName, String password) {
if (userName == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("userName is marked non-null but is null");
} else {
this.userName = userName;
this.password = password;
}
}
}
4.6 @AllArgsConstructor
- @AllArgsConstructor 自动生成全参数的构造函数。
@AllArgsConstructor 作用于类上。
示例:
- User.java
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.NonNull;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-11-21 08:19
*/
@AllArgsConstructor
public class User {
private Integer id;
@NonNull
private String userName;
private final String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
}
- 生成的代码:
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import lombok.NonNull;
public class User {
private Integer id;
@NonNull
private String userName;
private final String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
public User(Integer id, @NonNull String userName, String password, String phone, String email) {
if (userName == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("userName is marked non-null but is null");
} else {
this.id = id;
this.userName = userName;
this.password = password;
this.phone = phone;
this.email = email;
}
}
}
4.7 @NonNull
- @NonNull 会判断是否为 null ,如果为 null ,则会抛出 java.lang.NullPointerException。
@NonNull 作用于属性、方法、参数、局部变量、任意语句中。
示例:
- User.java
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import lombok.NonNull;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-11-21 08:19
*/
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
public void test(@NonNull String s){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
- 生成的代码:
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import lombok.NonNull;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
public User() {
}
public void test(@NonNull String s) {
if (s == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("s is marked non-null but is null");
} else {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
4.8 @Data
@Data = @Setter + @Getter+@RequiredArgsConstructor + @ToString + @EqualsAndHashCode 。
示例:
- User.java
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NonNull;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-11-21 08:19
*/
@Data
public class User {
private Integer id;
@NonNull
private String userName;
private final String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
}
- 生成的代码:
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import lombok.NonNull;
public class User {
private Integer id;
@NonNull
private String userName;
private final String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
public User(@NonNull String userName, String password) {
if (userName == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("userName is marked non-null but is null");
} else {
this.userName = userName;
this.password = password;
}
}
public Integer getId() {
return this.id;
}
@NonNull
public String getUserName() {
return this.userName;
}
public String getPassword() {
return this.password;
}
public String getPhone() {
return this.phone;
}
public String getEmail() {
return this.email;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setUserName(@NonNull String userName) {
if (userName == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("userName is marked non-null but is null");
} else {
this.userName = userName;
}
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
} else if (!(o instanceof User)) {
return false;
} else {
User other = (User)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
} else {
label71: {
Object this$id = this.getId();
Object other$id = other.getId();
if (this$id == null) {
if (other$id == null) {
break label71;
}
} else if (this$id.equals(other$id)) {
break label71;
}
return false;
}
Object this$userName = this.getUserName();
Object other$userName = other.getUserName();
if (this$userName == null) {
if (other$userName != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$userName.equals(other$userName)) {
return false;
}
label57: {
Object this$password = this.getPassword();
Object other$password = other.getPassword();
if (this$password == null) {
if (other$password == null) {
break label57;
}
} else if (this$password.equals(other$password)) {
break label57;
}
return false;
}
Object this$phone = this.getPhone();
Object other$phone = other.getPhone();
if (this$phone == null) {
if (other$phone != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$phone.equals(other$phone)) {
return false;
}
Object this$email = this.getEmail();
Object other$email = other.getEmail();
if (this$email == null) {
if (other$email == null) {
return true;
}
} else if (this$email.equals(other$email)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
}
protected boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return other instanceof User;
}
public int hashCode() {
int PRIME = true;
int result = 1;
Object $id = this.getId();
int result = result * 59 + ($id == null ? 43 : $id.hashCode());
Object $userName = this.getUserName();
result = result * 59 + ($userName == null ? 43 : $userName.hashCode());
Object $password = this.getPassword();
result = result * 59 + ($password == null ? 43 : $password.hashCode());
Object $phone = this.getPhone();
result = result * 59 + ($phone == null ? 43 : $phone.hashCode());
Object $email = this.getEmail();
result = result * 59 + ($email == null ? 43 : $email.hashCode());
return result;
}
public String toString() {
Integer var10000 = this.getId();
return "User(id=" + var10000 + ", userName=" + this.getUserName() + ", password=" + this.getPassword() + ", phone=" + this.getPhone() + ", email=" + this.getEmail() + ")";
}
}
4.9 @Builder
- @Builder 使用构造者模式生成对象。
- @Builder 作用于类、方法和构造器上。
- 示例:
- User.java
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import lombok.Builder;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-11-21 08:19
*/
@Builder
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
}
- 生成的代码:
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
User(Integer id, String userName, String password, String phone, String email) {
this.id = id;
this.userName = userName;
this.password = password;
this.phone = phone;
this.email = email;
}
public static User.UserBuilder builder() {
return new User.UserBuilder();
}
public static class UserBuilder {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
UserBuilder() {
}
public User.UserBuilder id(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
return this;
}
public User.UserBuilder userName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
return this;
}
public User.UserBuilder password(String password) {
this.password = password;
return this;
}
public User.UserBuilder phone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
return this;
}
public User.UserBuilder email(String email) {
this.email = email;
return this;
}
public User build() {
return new User(this.id, this.userName, this.password, this.phone, this.email);
}
public String toString() {
return "User.UserBuilder(id=" + this.id + ", userName=" + this.userName + ", password=" + this.password + ", phone=" + this.phone + ", email=" + this.email + ")";
}
}
}
4.10 @Value
@Value 类似于 @Data ,但是生成的属性是 final 类型的。
示例:
- User.java
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import lombok.Value;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-11-21 08:19
*/
@Value
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
}
- 生成的代码:
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
public final class User {
private final Integer id;
private final String userName;
private final String password;
private final String phone;
private final String email;
public User(Integer id, String userName, String password, String phone, String email) {
this.id = id;
this.userName = userName;
this.password = password;
this.phone = phone;
this.email = email;
}
public Integer getId() {
return this.id;
}
public String getUserName() {
return this.userName;
}
public String getPassword() {
return this.password;
}
public String getPhone() {
return this.phone;
}
public String getEmail() {
return this.email;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
} else if (!(o instanceof User)) {
return false;
} else {
User other = (User)o;
Object this$id = this.getId();
Object other$id = other.getId();
if (this$id == null) {
if (other$id != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$id.equals(other$id)) {
return false;
}
label61: {
Object this$userName = this.getUserName();
Object other$userName = other.getUserName();
if (this$userName == null) {
if (other$userName == null) {
break label61;
}
} else if (this$userName.equals(other$userName)) {
break label61;
}
return false;
}
label54: {
Object this$password = this.getPassword();
Object other$password = other.getPassword();
if (this$password == null) {
if (other$password == null) {
break label54;
}
} else if (this$password.equals(other$password)) {
break label54;
}
return false;
}
Object this$phone = this.getPhone();
Object other$phone = other.getPhone();
if (this$phone == null) {
if (other$phone != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$phone.equals(other$phone)) {
return false;
}
Object this$email = this.getEmail();
Object other$email = other.getEmail();
if (this$email == null) {
if (other$email != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$email.equals(other$email)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
public int hashCode() {
int PRIME = true;
int result = 1;
Object $id = this.getId();
int result = result * 59 + ($id == null ? 43 : $id.hashCode());
Object $userName = this.getUserName();
result = result * 59 + ($userName == null ? 43 : $userName.hashCode());
Object $password = this.getPassword();
result = result * 59 + ($password == null ? 43 : $password.hashCode());
Object $phone = this.getPhone();
result = result * 59 + ($phone == null ? 43 : $phone.hashCode());
Object $email = this.getEmail();
result = result * 59 + ($email == null ? 43 : $email.hashCode());
return result;
}
public String toString() {
Integer var10000 = this.getId();
return "User(id=" + var10000 + ", userName=" + this.getUserName() + ", password=" + this.getPassword() + ", phone=" + this.getPhone() + ", email=" + this.getEmail() + ")";
}
}
4.11 @Synchronized
@Synchronized 作用在方法上,自动添加到同步机制,生成的代码并不是直接锁方法而是锁代码块。
示例:
- User.java
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import lombok.Synchronized;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-11-21 08:19
*/
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
@Synchronized
public void sellTickets(){
}
}
- 生成的代码:
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
public class User {
private final Object $lock = new Object[0];
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
public User() {
}
public void sellTickets() {
synchronized(this.$lock) {
;
}
}
}
4.12 @Cleanup
@Cleanup 作用于局部变量,用于确保已分配的资源被释放,自动帮我们调用 close() 方法。比如 IO 的连接关闭。
示例:
- User.java
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import lombok.Cleanup;
import java.io.*;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-11-21 08:19
*/
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
/** 复制文件
* @param sources
* @param aim
* @throws IOException
*/
public void copyFile(File sources, File aim) throws IOException {
@Cleanup FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(sources);
@Cleanup FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(aim);
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(buf)) != -1) {
fos.write(buf, 0, len);
}
}
}
- 生成的代码:
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Collections;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
public User() {
}
public void copyFile(File sources, File aim) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(sources);
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(aim);
try {
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(buf)) != -1) {
fos.write(buf, 0, len);
}
} finally {
if (Collections.singletonList(fos).get(0) != null) {
fos.close();
}
}
} finally {
if (Collections.singletonList(fis).get(0) != null) {
fis.close();
}
}
}
}
4.13 @SneakyThrows
@SneakyThrows 作用于方法和构造器,用于抛出指定的异常,而不需要手动捕获异常,然后抛出。
示例:
- User.java
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import lombok.Cleanup;
import lombok.SneakyThrows;
import java.io.*;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-11-21 08:19
*/
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
/** 复制文件
* @param sources
* @param aim
*/
@SneakyThrows
public void copyFile(File sources, File aim) {
@Cleanup FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(sources);
@Cleanup FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(aim);
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(buf)) != -1) {
fos.write(buf, 0, len);
}
}
}
- 生成的代码:
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.util.Collections;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
public User() {
}
public void copyFile(File sources, File aim) {
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(sources);
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(aim);
try {
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(buf)) != -1) {
fos.write(buf, 0, len);
}
} finally {
if (Collections.singletonList(fos).get(0) != null) {
fos.close();
}
}
} finally {
if (Collections.singletonList(fis).get(0) != null) {
fis.close();
}
}
} catch (Throwable var17) {
throw var17;
}
}
}
4.14 @Log
- @Log 、@Slf4j 、@Log4j 、@Log4j2 作用于类上,用于生成日志。
实际开发中,需要导入相关的依赖库。
示例:
- User.java
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import lombok.Cleanup;
import lombok.SneakyThrows;
import lombok.extern.java.Log;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-11-21 08:19
*/
@Log
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
/** 复制文件
* @param sources
* @param aim
*/
@SneakyThrows
public void copyFile(File sources, File aim) {
log.info("文件开始复制");
@Cleanup FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(sources);
@Cleanup FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(aim);
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(buf)) != -1) {
fos.write(buf, 0, len);
}
log.info("文件结束复制");
}
}
- 生成的代码:
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class User {
private static final Logger log = Logger.getLogger(User.class.getName());
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
public User() {
}
public void copyFile(File sources, File aim) {
try {
log.info("文件开始复制");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(sources);
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(aim);
try {
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(buf)) != -1) {
fos.write(buf, 0, len);
}
log.info("文件结束复制");
} finally {
if (Collections.singletonList(fos).get(0) != null) {
fos.close();
}
}
} finally {
if (Collections.singletonList(fis).get(0) != null) {
fis.close();
}
}
} catch (Throwable var17) {
throw var17;
}
}
}
4.15 var
var 表示局部变量的类型推断,其实,在 JDK 9 中已经集成了该语法。
示例:
- User.java
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* @author 许大仙
* @version 1.0
* @since 2021-11-21 08:19
*/
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
public void test() {
var list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("aa");
list.add("bb");
System.out.println("list = " + list);
}
}
- 生成的代码:
package com.github.fairy.era.bean;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String email;
public User() {
}
public void test() {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList();
list.add("aa");
list.add("bb");
System.out.println("list = " + list);
}
}

