原文: https://howtodoinjava.com/spring-boot/actuator-endpoints-example/
在此 Spring Boot 执行器教程中,了解可用于任何运行应用程序的内置 HTTP 端点,以用于不同的监视和管理目的。 在 spring 框架之前,如果我们必须在应用程序中引入这种类型的监视功能,则必须手动开发所有这些组件,并且这些组件也非常符合我们的需求。 但是通过 Spring Boot,我们有了Actuator模块,这非常容易。
我们只需要配置几件事就可以完成 – 所有管理和监视相关信息都可以轻松获得。 让我们学习配置 Spring Boot 执行器端点。
1. SpringBoot 执行器模块
使用 Spring Boot 的模块Actuator,您可以监视和管理生产环境中的应用程序使用情况,而无需对其进行编码和配置。 这些监视和管理信息通过 REST(如端点 URL)公开。
1.1. 执行器 Maven 依赖
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId></dependency>
1.2. 重要的执行器端点
一些重要且广泛使用的执行器端点如下:
| 端点 | 用法 |
|---|---|
/env |
返回当前环境中的属性列表 |
/health |
返响应用程序运行状况信息。 |
/auditevents |
返回所有自动配置的候选对象以及应用它们“被”或“未被”的原因。 |
/beans |
返响应用程序中所有 Spring Bean 的完整列表。 |
/trace |
返回跟踪日志(默认情况下,最近的 100 个 HTTP 请求)。 |
/dump |
它执行线程转储。 |
/metrics |
它显示了一些有用的指标信息,例如 JVM 内存使用情况,系统 CPU 使用情况,打开的文件等等。 |
1.3. 与安全性相关的属性
默认情况下,所有执行器端点均启用 SpringSecurity。它是内置的基于表单的身份验证,其中的用户 ID 为用户,并随机生成一个密码。 然后需要以下条目才能为您的敏感端点自定义基本认证安全性。
management.security.enabled = truemanagement.security.roles = ADMINsecurity.basic.enabled = truesecurity.user.name = adminsecurity.user.password = admin
请注意,默认情况下,要访问执行器受限的端点,您必须具有ACTUATOR角色。 您需要通过management.security.roles属性覆盖此配置。
1.4. 使用WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的执行器安全性
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;@Configurationpublic class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {@Autowiredpublic void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("admin").password("admin").roles("ADMIN");}}
1.5. CORS 支持
CORS 支持默认为禁用,并且仅在设置了endpoints.cors.allowed-origins属性后才启用。
endpoints.cors.allowed-origins = http://example.comendpoints.cors.allowed-methods = GET,POST
2. Spring Boot 执行器端点示例
在此示例中,我们将创建一个简单的字符串启动应用程序,并访问执行器端点以进一步了解它们。
2.1. 开发环境
- JDK 1.8,Eclipse,Maven – 开发环境
- SpringBoot – 基础应用程序框架
- SpringBoot 执行器 – 管理端点
2.2. 创建 Maven 项目
首先从 Spring 初始化器站点创建一个具有Web,Rest Repositories和Actuator依赖项的 spring boot 项目。 以压缩格式下载项目。 解压缩,然后将 eclipse 中的项目导入为 maven 项目。
Spring boot 执行器项目
2.3. 添加简单的 Rest 端点
现在,向应用程序添加一个简单的 Rest 端点/example。
package com.example.springbootmanagementexample;import java.util.Date;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestControllerpublic class SimpleRestController {@GetMapping("/example")public String example() {return "Hello User !! " + new Date();}}
3. Spring Boot 执行器端点演示
我在application.properties文件中添加了management.security.enabled = false条目以禁用执行器安全性。 在这里,我对执行器端点响应更感兴趣。
使用mvn clean install进行 maven 构建,然后使用java -jar target\spring-boot-management-example-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar命令启动应用程序。 这将在默认端口8080中启动一台 tomcat 服务器,并将在其中部署应用程序。
在浏览器中访问/example API,以在服务器上生成少量监视信息。
http://localhost:8080/env
这将提供有关服务器的所有环境配置。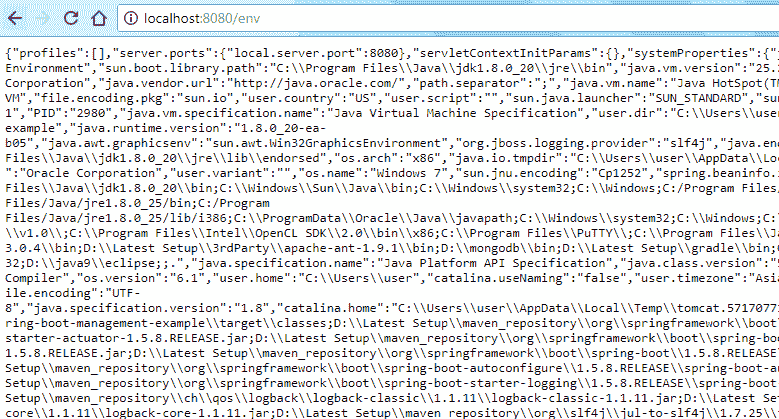
env端点输出http://localhost:8080/beans
这将在上下文中加载所有 SpringBean。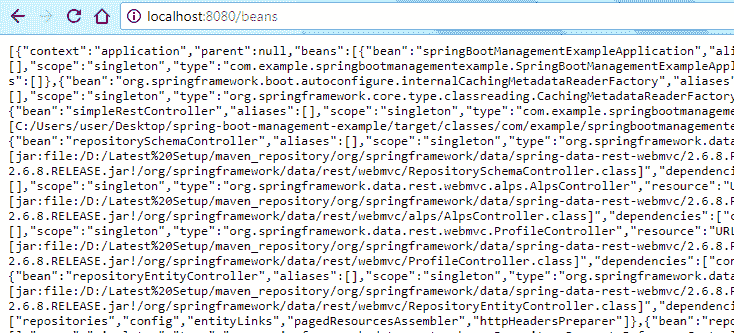
beans端点输出http://localhost:8080/dump
这将给出当前服务器线程转储。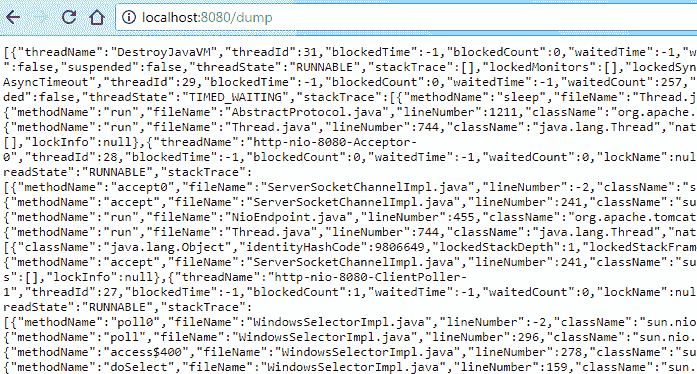
dump端点输出http://localhost:8080/health
这将提供应用程序和服务器的一般运行状况。
health端点输出http://localhost:8080/metrics/metrics端点列出了所有可用于跟踪的指标。{"mem": 316656,"mem.free": 169495,"processors": 4,"instance.uptime": 1449726,"uptime": 1463662,"systemload.average": -1.0,"heap.committed": 263168,"heap.init": 131072,"heap.used": 93672,"heap": 1846272,"nonheap.committed": 54400,........}
这些端点将在浏览器中提供标准信息。 这些是我们通常引用的基本重要端点,但是如链接所述,Spring Boot 提供了更多端点。
4. 执行器高级配置选项
4.1. 更改管理端点上下文路径
默认情况下,所有端点都位于应用程序的默认上下文路径中。 仍然,如果我们需要将这些端点公开在不同的端点中,则需要在application.properties中指定它们。
management.context-path=/manage
现在,您将可以在新 URL 下访问所有执行器端点。 例如
/manage/health/manage/dump/manage/env/manage/bean
4.2. 定制管理服务器端口
要自定义管理端点端口,我们需要将此条目添加到application.properties文件中。
management.port=8081
5. 总结
在此 SpringBoot 执行器示例中,我们学习了使用很少的简单配置即可配置管理和监视端点。 因此,下次,您需要添加应用程序运行状况检查或添加监视支持,则应考虑添加 Spring 执行器项目并使用这些端点。
随时在评论部分中提出您的问题。
学习愉快!

