原文: https://howtodoinjava.com/junit/how-to-write-parameterized-testcases-with-junit-4/
在本 JUnit 教程中,学习创建和执行 junit 参数化测试。 参数化测试是正常测试,它使用不同的测试参数反复执行。 它可以帮助开发人员在使用不同输入类型执行相同测试以测试函数健壮性,以及可能的函数边界上面节省时间。
1. JUnit Maven 依赖项
下面是 maven 依赖项,我们应该在测试示例代码之前添加到您的 maven 项目中。
<!-- Junit --><dependency><groupId>junit</groupId><artifactId>junit</artifactId><version>4.11</version><scope>test</scope></dependency><dependency><groupId>junit</groupId><artifactId>junit-dep</artifactId><version>4.11</version><scope>test</scope></dependency>
2. 具有构造器参数的 JUnit 参数化测试
参数化测试使用@RunWith注解以及@Parameters注解来馈送输入。
2.1 要测试的类
下面是测试类,我们将为其编写测试用例。
package corejava.test.junit;public final class MathUtils{//Return square of a functionpublic static int square(final int number) {return number * number;}}
2.2 参数化测试
让我们为上述数学工具类编写参数化测试。
package corejava.test.junit;import java.util.Arrays;import org.junit.Assert;import org.junit.Test;import org.junit.runner.RunWith;import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters;@RunWith(Parameterized.class)public class JunitTestsWithParameters {// @Parameters annotation marks this method as parameters provider@Parameters(name = "Run #Square of : {0}^2={1}")public static Iterable<Object []> data(){return Arrays.asList(new Object[][] { { 1, 1 },{ 2, 4 },{ 3, 19 },{ 4, 16 },{ 5, 25 } });}// Our two parametersprivate final int input;private final int resultExpected;// Constructor is initialized with one set of parameters every timepublic JunitTestsWithParameters(final int input, final int result){this.input = input;this.resultExpected = result;}@Testpublic void testUserMapping() {// You can use here assert alsoAssert.assertEquals(resultExpected, MathUtils.square(input));}}
请注意:
- 我们必须按照给定的方式声明参数。
- 参数传递给类的构造器以设置变量,因此可以在测试用例中使用。
- 参数类的返回类型为“
List[]”,要使用的数据类型已限于字符串或原始值
现在检查程序输出。
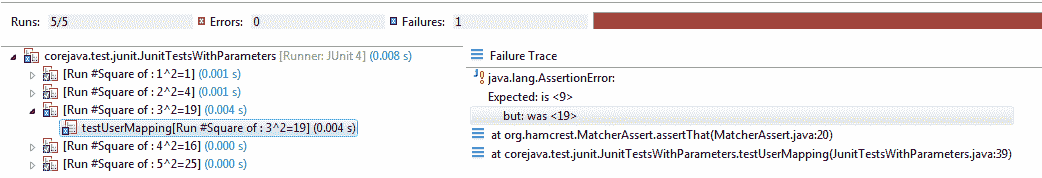
测试执行结果
3. 带有字段注入的 JUnit 参数化测试
为了传递参数进行测试,我们可以通过字段注入传递参数,而不是通过构造器传递参数。 在这种方法中,我们声明确切的字段数作为输入参数。 每个字段一个参数。
让我们通过场注入重新测试我们的MathUtils类。 请注意,我们如何用@Parameter注解的字段替换构造器。
import org.junit.Assert;import org.junit.Test;import org.junit.runner.RunWith;import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameter;import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters;@RunWith(Parameterized.class)public class JunitTestsWithFieldInjection {@Parameters(name = "Run #Square of : {0}^2={1}")public static Iterable<Object[]> data() {return Arrays.asList(new Object[][] { { 1, 1 }, { 2, 4 }, { 3, 9 }, { 4, 16 }, { 5, 25 } });}@Parameter(value = 0)public int input;@Parameter(value = 1)public int resultExpected;@Testpublic void testSquare(){Assert.assertEquals(resultExpected, MathUtils.square(input));}}
3.1 单个字段注入
如果仅要注入一个字段,则无需在@Parameter注解中放置value属性。 默认值始终为“value = 0”。
import org.junit.Assert;import org.junit.Test;import org.junit.runner.RunWith;import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameter;import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters;@RunWith(Parameterized.class)public class JunitTestsWithParameters {@Parameters(name = "Argument number {0} is positive")public static Iterable<Object[]> data() {return Arrays.asList(new Object[][] { { 0 }, { 1 }, { 2 }, { 3 }, { 4 } });}@Parameterpublic int input;@Testpublic void testPositiveNumber(){Assert.assertEquals(true, input >= 0);}}
在本文中,我们学习了如何创建参数化测试,并使用不同的参数集运行测试的多次迭代。 它有助于测试带有参数的方法。
学习愉快!

