原文: https://howtodoinjava.com/resteasy/resteasy-containerrequestfilter-example/
了解如何使用 RESTEasy ContainerRequestFilter创建安全筛选器,该筛选器能够对基于 RESTEasy 的 Web 应用执行认证和授权。
1. RESTEasy ContainerRequestFilter和ContainerReponseFilter
最近发布了新的 RESTEasy 版本 3.0.2.Final,并使其与 JAX-RS 2.0 兼容。 如果您还记得以前的 JAX-RS 版本没有关于实现过滤器和拦截器的规范。 这就是所有 JAX-RS 实现都有自己独特风格的原因。 RESTEasy 的PreProcessorInterceptor和PostProcessorInterceptor现在已弃用。
现在,JAX-RS 在过滤器和拦截器方面有了自己的规范。 您可以阅读 Bill Burke 的帖子中的详细讨论。
在 resteasy 中,过滤器在调用resource方法之前和之后运行。 这些过滤器实质上是ContainerRequestFilter和ContainerReponseFilter。 ContainerRequestFilter在调用 JAX-RS 资源方法之前运行。 ContainerResponseFilter在调用 JAX-RS 资源方法之后运行。 需要注意的是,ContainerRequestFilter有两种风格:匹配前和匹配后。 预先匹配的ContainerRequestFilter用@PreMatching注解指定,并且将在 JAX-RS 资源方法与传入的 HTTP 请求匹配之前执行。 在匹配 Java 资源方法之后,执行匹配后的ContainerRequestFilters。
过滤器修改请求或响应头时,拦截器处理消息正文。 它们可用于实现特定的内容编码。 它们可用于生成数字签名,或在编组 Java 对象模型之前或之后发布或预处理 Java 对象模型。
2. RESTEasy ContainerRequestFilter示例
在本文中,我将修改 resteasy 认证和授权教程,该教程最初是使用PreProcessorInterceptor在 RESTEasy 2.3.1.GA 中编写的。 我已将其更新为基于 JAX-RS 2.0 规范的 RESTEasy 版本 3.0.2.Final。
2.1 更新 Maven 依赖项
在使用 Maven 时,我已经更新了pom.xml文件,如下所示。 如果您使用的是 ant 或 jar 文件,请相应地更新所需的 jar。
<dependencies><!-- core library --><dependency><groupId>org.jboss.resteasy</groupId><artifactId>resteasy-jaxrs</artifactId><version>3.0.2.Final</version></dependency><!-- JAXB support --><dependency><groupId>org.jboss.resteasy</groupId><artifactId>resteasy-jaxb-provider</artifactId><version>3.0.2.Final</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.jboss.resteasy</groupId><artifactId>jaxrs-api</artifactId><version>3.0.2.Final</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>net.sf.scannotation</groupId><artifactId>scannotation</artifactId><version>1.0.3</version></dependency></dependencies>
2.2 RESTEasy 安全拦截器
由于 JAX-RS 2.0 具有用于处理前后请求的过滤器,因此我们将使用ContainerRequestFilter接口。 记住PreProcessorInterceptor现在已弃用。
@Providerpublic class SecurityInterceptor implements javax.ws.rs.container.ContainerRequestFilter{@Overridepublic void filter(ContainerRequestContext requestContext){//More code...}}
现在,首先我们必须访问资源方法以检查安全性约束及其定义的属性。
ResourceMethodInvoker methodInvoker = (ResourceMethodInvoker)requestContext.getProperty("org.jboss.resteasy.core.ResourceMethodInvoker");Method method = methodInvoker.getMethod();
现在我们可以访问资源方法了。 现在,一切将与我们之前所做的相同。 即
- 检查
PermitAll注解(如果存在),则无需进一步检查任何内容 - 检查
DenyAll注解(如果存在),然后返回拒绝访问 - 检查
RolesAllowed注解,然后从注解中获取所需的角色。 从请求中获取授权信息,并根据应用逻辑进行匹配。 如果授权成功,则授予访问权限,否则返回拒绝访问权限。
2.3 RESTEasy SecurityInterceptor源代码
SecurityInterceptor的完整代码如下。
package com.howtodoinjava.demo.rest.security;import java.io.IOException;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.util.Arrays;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.List;import java.util.Set;import java.util.StringTokenizer;import javax.annotation.security.DenyAll;import javax.annotation.security.PermitAll;import javax.annotation.security.RolesAllowed;import javax.ws.rs.container.ContainerRequestContext;import javax.ws.rs.core.MultivaluedMap;import javax.ws.rs.ext.Provider;import org.jboss.resteasy.core.Headers;import org.jboss.resteasy.core.ResourceMethodInvoker;import org.jboss.resteasy.core.ServerResponse;import org.jboss.resteasy.util.Base64;/*** This interceptor verify the access permissions for a user* based on username and passowrd provided in request* */@Providerpublic class SecurityInterceptor implements javax.ws.rs.container.ContainerRequestFilter{private static final String AUTHORIZATION_PROPERTY = "Authorization";private static final String AUTHENTICATION_SCHEME = "Basic";private static final ServerResponse ACCESS_DENIED = new ServerResponse("Access denied for this resource", 401, new Headers<Object>());;private static final ServerResponse ACCESS_FORBIDDEN = new ServerResponse("Nobody can access this resource", 403, new Headers<Object>());;private static final ServerResponse SERVER_ERROR = new ServerResponse("INTERNAL SERVER ERROR", 500, new Headers<Object>());;@Overridepublic void filter(ContainerRequestContext requestContext){ResourceMethodInvoker methodInvoker = (ResourceMethodInvoker) requestContext.getProperty("org.jboss.resteasy.core.ResourceMethodInvoker");Method method = methodInvoker.getMethod();//Access allowed for allif( ! method.isAnnotationPresent(PermitAll.class)){//Access denied for allif(method.isAnnotationPresent(DenyAll.class)){requestContext.abortWith(ACCESS_FORBIDDEN);return;}//Get request headersfinal MultivaluedMap<String, String> headers = requestContext.getHeaders();//Fetch authorization headerfinal List<String> authorization = headers.get(AUTHORIZATION_PROPERTY);//If no authorization information present; block accessif(authorization == null || authorization.isEmpty()){requestContext.abortWith(ACCESS_DENIED);return;}//Get encoded username and passwordfinal String encodedUserPassword = authorization.get(0).replaceFirst(AUTHENTICATION_SCHEME + " ", "");//Decode username and passwordString usernameAndPassword = null;try {usernameAndPassword = new String(Base64.decode(encodedUserPassword));} catch (IOException e) {requestContext.abortWith(SERVER_ERROR);return;}//Split username and password tokensfinal StringTokenizer tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(usernameAndPassword, ":");final String username = tokenizer.nextToken();final String password = tokenizer.nextToken();//Verifying Username and passwordSystem.out.println(username);System.out.println(password);//Verify user accessif(method.isAnnotationPresent(RolesAllowed.class)){RolesAllowed rolesAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(RolesAllowed.class);Set<String> rolesSet = new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList(rolesAnnotation.value()));//Is user valid?if( ! isUserAllowed(username, password, rolesSet)){requestContext.abortWith(ACCESS_DENIED);return;}}}}private boolean isUserAllowed(final String username, final String password, final Set<String> rolesSet){boolean isAllowed = false;//Step 1\. Fetch password from database and match with password in argument//If both match then get the defined role for user from database and continue; else return isAllowed [false]//Access the database and do this part yourself//String userRole = userMgr.getUserRole(username);String userRole = "ADMIN";//Step 2\. Verify user roleif(rolesSet.contains(userRole)){isAllowed = true;}return isAllowed;}}
2.4 RESTEasy 安全过滤器演示
要测试安全代码,请将 Web 应用部署在任何应用服务器(例如 Tomcat)中。 现在,发送以下请求:
不带用户名和密码的 HTTP GET
http://localhost:8080/RESTEasyEtagDemo/user-service/users/1
用户能够成功访问 API。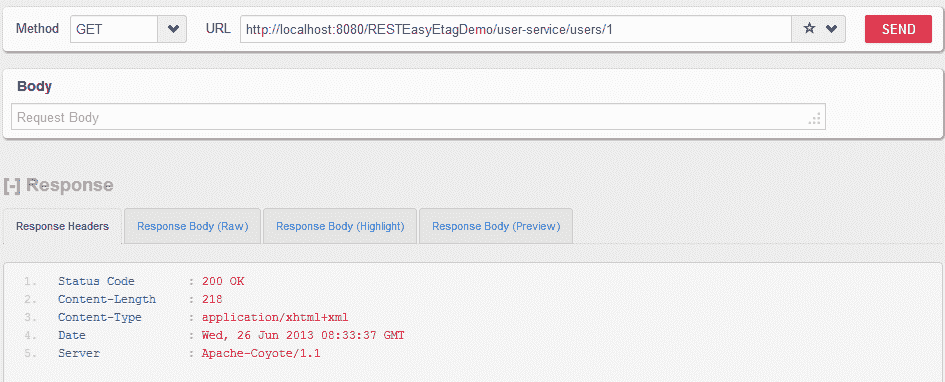
不带用户名和密码的 HTTP PUT
http://localhost:8080/RESTEasyEtagDemo/user-service/users/1
用户无法访问 API。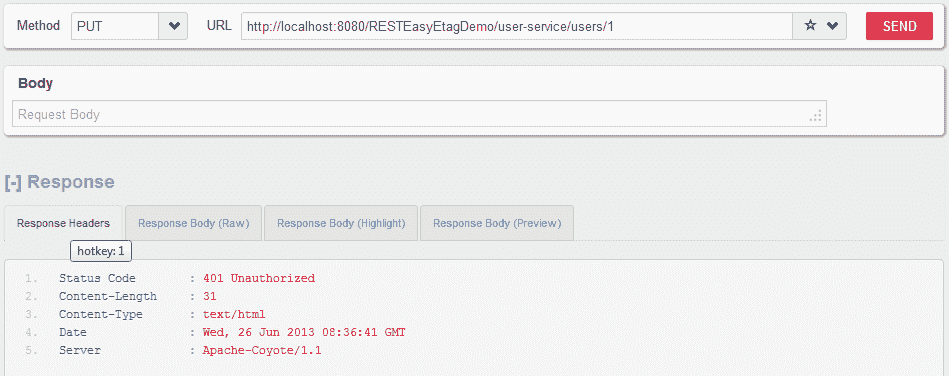
添加基本授权凭据
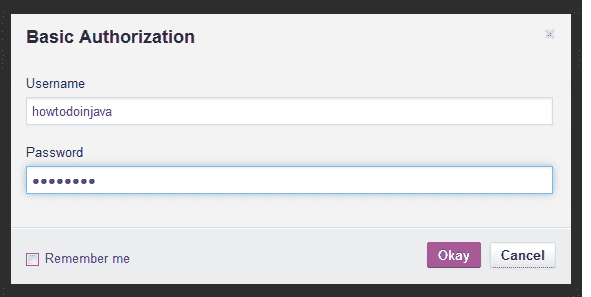
带有用户名和密码的 HTTP PUT
http://localhost:8080/RESTEasyEtagDemo/user-service/users/1
用户能够访问受保护的 API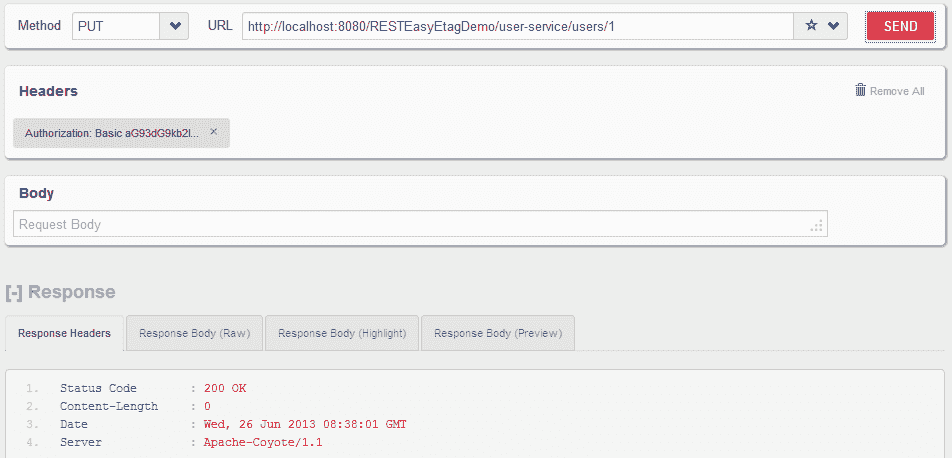
以上就是 resteasy 安全拦截器示例。 如果您有任何疑问或建议,请给我评论。
更新:以下是在 tomcat 7 中运行此项目的步骤。
今天,我再次致力于在 tomcat 7 上运行的该项目。要成功运行,我执行了以下步骤:
在 eclipse 中导入项目
在项目根文件夹中运行提示符
> mvn eclipse:eclipse -Dwtpversion=2.0(参考)更新方法上的
@Produces和@Consumes注解启动 tomcat 服务器并测试应用。 您将获得理想的结果。
学习愉快!

